What is Demand Forecasting?
Demand forecasting predicts future customer demand for products or services based on historical data, market trends, and other influencing factors. Accurate demand forecasting helps businesses anticipate sales, manage inventory levels, plan production schedules, and make informed purchasing and resource allocation decisions.
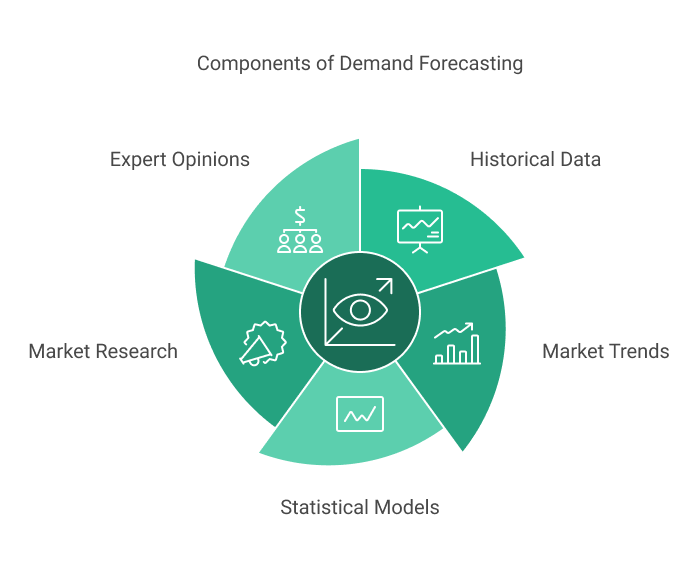
The process uses quantitative methods, such as statistical models and data analysis, as well as qualitative inputs, like market research and expert opinions, to create demand estimates. Effective demand forecasting helps prevent stockouts, reduce overstocking, and ensure businesses can efficiently meet customer needs without carrying excessive inventory.
Source: WorkTrek
Demand forecasting is vital for optimizing supply chain operations, minimizing costs, and improving customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability. It is used across industries, from retail to manufacturing, to balance supply with demand, maintain profitability, and manage the complexities of production and distribution. By understanding and predicting customer behavior, businesses can improve planning, reduce waste, and make proactive, data-driven decisions.
What is the importance of demand forecasting for businesses?
Demand forecasting is critical for businesses across various industries. It enables them to predict future customer demand for their products or services. By accurately anticipating demand, companies can make informed decisions about production, inventory management, staffing, and financial planning. This blog post will explore why demand forecasting is so important for businesses.
- Optimizing Inventory Levels One of the primary benefits of demand forecasting is that it allows businesses to optimize their inventory levels. By predicting future demand, companies can ensure they have enough stock to meet customer needs without overstocking and tying up excessive capital in inventory. This is particularly important for businesses dealing with perishable goods or products with short life cycles, as overstocking can lead to waste and financial losses.
Accurate demand forecasting enables businesses to implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory management strategies, where stock arrives as it is needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence. This approach also frees up capital that can be invested in other business areas, such as marketing or research and development.
- Improving Production Planning Demand forecasting is also critical for effective production planning. By anticipating future demand, manufacturers can optimize their production schedules, ensuring they have the right products available at the right time. This helps to minimize production bottlenecks, reduce lead times, and improve overall operational efficiency.
With accurate demand forecasts, businesses can also make informed decisions about capacity planning, such as investing in additional machinery or hiring more staff to meet projected demand. This proactive approach can help companies avoid the costs and disruptions of last-minute production changes or emergency hiring.
- Enhancing Customer Service Another key benefit of demand forecasting is improving businesses’ customer service levels. By anticipating customer needs and ensuring that the right products are available when and where needed, companies can reduce stockouts and backorders, which can frustrate customers and lead to lost sales.
Accurate demand forecasting also enables businesses to provide better information to customers about product availability and delivery times. This transparency can help to build trust and loyalty, as customers appreciate knowing when they can expect to receive their orders.
- Supporting Financial Planning Demand forecasting is also essential for effective financial planning. By predicting future sales volumes, businesses can develop more accurate revenue and cash flow projections, which inform decisions about budgeting, investment, and growth strategies.
Accurate demand forecasts can also help businesses to manage their costs more effectively. By anticipating future demand, companies can negotiate better terms with suppliers, optimize their transportation and logistics networks, and reduce the costs associated with excess inventory or emergency production runs.

- Enabling Agile Decision-Making Finally, demand forecasting gives businesses the insights they need to make agile decisions in response to changing market conditions. By continuously monitoring and updating their demand forecasts, companies can quickly identify shifts in customer preferences, competitive pressures, or economic conditions and adapt their strategies accordingly.
This agility is particularly important in today’s fast-paced, constantly evolving business environment. By staying ahead of the curve and making data-driven decisions based on accurate demand forecasts, businesses can maintain their competitive edge and drive long-term growth and profitability.
In conclusion, demand forecasting is a vital process for businesses of all sizes and across all industries. By enabling companies to optimize their inventory levels, improve production planning, enhance customer service, support financial planning, and make agile decisions, demand forecasting provides a foundation for operational excellence and business success. As such, investing in robust demand forecasting capabilities should be a top priority for any organization looking to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
What are the factors that effect demand forecasting
Demand forecasting is a complex process involving analyzing various factors that can influence future customer demand. These factors can vary depending on the industry, product, and market, but some common ones include:
- Economic Conditions: Economic indicators such as GDP, inflation, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence can all impact demand for products and services. During economic downturns, for example, consumers may reduce their spending, leading to lower demand for non-essential items.
- Market Trends: Shifts in market trends, such as changes in consumer preferences, the emergence of new technologies, or competitors’ introduction of new products, can all affect demand. Companies need to stay attuned to these trends and adjust their forecasts accordingly.
- Seasonality: Many products and services experience seasonal fluctuations in demand. Retailers, for example, typically see higher demand during the holiday season, while demand for outdoor products may spike during the summer months. Incorporating seasonality into demand forecasts is critical for accurate planning.
- Promotions and Marketing: Promotional activities, such as discounts, advertising campaigns, and product launches, can significantly impact short-term demand. Companies need to factor these activities into their forecasts to ensure they have sufficient stock to meet the anticipated spike in demand.
- Historical Sales Data: Historical sales data is one of the most important inputs for demand forecasting. Companies can identify patterns and use them to predict future demand by analyzing past sales trends. However, relying solely on historical data can be problematic if there have been significant changes in the market or the company’s products.
- External Events: External events, such as natural disasters, political instability, or global pandemics, can disrupt supply chains and unpredictably affect demand. Companies must be prepared for these events and have contingency plans to adjust their forecasts and operations.
- Product Life Cycle: Products typically go through different stages in their life cycle, from introduction to growth, maturity, and decline. Demand forecasting needs to consider these stages, as demand patterns can vary significantly depending on where a product is in its life cycle.
- Customer Segments: Different customer segments can have different demand patterns and preferences. By segmenting their customer base and analyzing each segment’s unique characteristics and behaviors, companies can develop more accurate demand forecasts tailored to each group.
- Lead Time: The lead time required to produce and deliver a product can impact demand forecasting. Long lead times can make responding to sudden changes in demand more difficult, while short lead times may require more frequent forecast updates.
- Technological Advancements: Advancements in technology, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, enable companies to analyze vast amounts of data and generate more accurate demand forecasts. By leveraging these tools, companies can identify complex patterns and relationships that may not be apparent through traditional forecasting methods.
To create accurate demand forecasts, companies need to consider all of these factors and how they may interact with each other. This requires a comprehensive approach that involves gathering data from multiple sources, analyzing it using advanced statistical techniques, and continuously updating and refining the forecasts based on new information.
Effective demand forecasting also requires close collaboration between different organizational functions, including sales, marketing, finance, and supply chain management. By sharing information and insights, these teams can develop a more holistic view of the factors that impact demand and make more informed decisions.
Ultimately, the key to successful demand forecasting is to balance historical data, market insights, and forward-looking analysis. By combining these elements in a structured and systematic way, companies can develop robust demand forecasts that enable them to optimize their operations, improve their financial performance, and deliver superior value to their customers.
Different types of Demand Forecasting
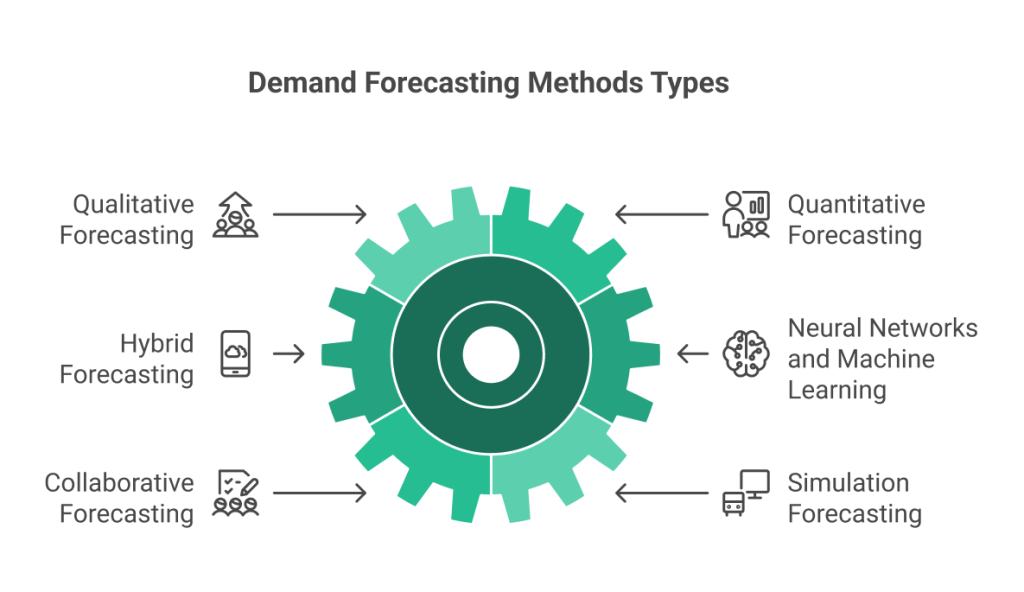
Businesses can use several types of demand forecasting methods, depending on their specific needs, data availability, and the nature of their products or services. Some of the most common types of demand forecasting include:
- Qualitative Forecasting:
- Jury of Executive Opinion: A group of experts, usually company executives, share their opinions and collectively develop a demand forecast.
- Delphi Method: A panel of experts iteratively answer questionnaires, provide feedback, and revise their predictions until a consensus is reached.
- Sales Force Composite: Salespeople provide individual forecasts for their respective territories, which they aggregate to create an overall forecast.
- Market Research: Surveys, focus groups, and other primary research methods are used to gather customer preferences and intentions data.
- Quantitative Forecasting: A Time-series Model:
- Naive Approach: Assumes that future demand will be equal to the most recent period’s actual demand.
- Moving Average: Takes the average of a fixed number of past periods to smooth out short-term fluctuations and predict future demand.
- Weighted Moving Average: Similar to moving average, but assigns greater weight to more recent periods.
- Exponential Smoothing: Assigns exponentially decreasing weights to older data points, giving more importance to recent observations.
- Trend Projection: Uses linear or nonlinear regression to fit a trend line to historical data and project future demand.
- Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA): A sophisticated model that accounts for trends, seasonality, and other patterns in historical data.
- Hybrid Forecasting:
- Combines qualitative and quantitative methods to leverage the strengths of both approaches.
- Example: Using market research to adjust the results of a time-series model based on anticipated changes in customer behavior.
- Neural Networks and Machine Learning:
- Uses artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze large amounts of data and identify complex patterns and relationships that may not be apparent through traditional methods.
- Can continually learn and adapt as new data becomes available, improving forecast accuracy over time.
- Collaborative Forecasting:
- Involves the sharing of information and insights between a company and its customers or suppliers to develop a more accurate and comprehensive demand forecast.
- Can be facilitated through tools such as vendor-managed inventory (VMI) systems or collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment (CPFR) processes.
- Simulation Forecasting:
- Uses computer models to simulate various scenarios and assess their potential impact on demand.
- Can be useful for evaluating the effects of different pricing strategies, promotional activities, or distribution channel changes.
Data and Illustration: WorkTrek
The choice of demand forecasting method will depend on various factors, including the availability and quality of historical data, the complexity of the market and the product, the level of accuracy required, and the resources and expertise available within the organization.
In practice, many companies use a combination of different forecasting methods to develop a more robust and comprehensive view of future demand. By regularly monitoring and adjusting these forecasts based on actual sales data and market feedback, businesses can continually improve their accuracy and make more informed decisions about production, inventory management, and resource allocation.
Use CMMS to optimize demand forecasting
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can be a valuable tool for supporting demand forecasting in several ways. While a CMMS is primarily designed for managing maintenance operations, the data it collects can provide valuable insights into equipment performance, maintenance requirements, and spare parts consumption, all of which can influence demand forecasting. Here are some ways a CMMS can help with demand forecasting:
- Historical Maintenance Data: A CMMS stores historical data on equipment maintenance, including the frequency and types of maintenance tasks performed, the duration of each task, and the resources required. This data can identify patterns and trends in maintenance requirements, informing demand forecasting for spare parts, consumables, and other maintenance-related items.
- Predictive Maintenance Insights: Many modern CMMS solutions include predictive maintenance capabilities. These capabilities use advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze equipment data and predict when maintenance will be required. These insights can be used to forecast demand for spare parts and other maintenance supplies, helping to ensure that the right items are available when needed.
- Equipment Performance Data: A CMMS tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) for each piece of equipment, such as uptime, downtime, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). This data can provide valuable insights into the reliability and performance of each asset, which can be used to forecast maintenance requirements and the associated demand for parts and supplies.
- Inventory Management: A CMMS can help organizations to manage their inventory of spare parts and maintenance supplies more effectively. By tracking inventory levels, usage rates, and reorder points, a CMMS can provide visibility into current and future inventory requirements, which can inform demand forecasting and help to optimize stock levels.
- Maintenance Budgeting and Planning: A CMMS can develop maintenance budgets and plans based on historical data, equipment criticality, and other factors. These plans can provide a foundation for forecasting maintenance-related demand, including labor, parts, and supplies.
- Integration with Other Systems: Many CMMS solutions can integrate with other business systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) or supply chain management (SCM) platforms. This integration can enable sharing of data and insights between different functions, such as maintenance, procurement, and logistics, which can support more accurate and comprehensive demand forecasting.
To leverage a CMMS for demand forecasting, organizations should:
- Ensure the CMMS accurately captures all relevant maintenance data, including work orders, equipment history, and inventory transactions.
- Use the CMMS to develop a comprehensive view of maintenance requirements, including both planned and unplanned activities.
- Analyze CMMS data to identify patterns and trends in maintenance demand and use this information to develop forecasts for spare parts, consumables, and other supplies.
- Integrate the CMMS with other business systems to enable the sharing of data and insights across different functions.
- Continuously monitor and adjust demand forecasts based on actual maintenance data and changing business requirements.
By leveraging a CMMS in this way, organizations can develop more accurate and reliable demand forecasts for maintenance-related items, helping to optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve overall maintenance efficiency.
However, it’s important to note that a CMMS is just one piece of the puzzle regarding demand forecasting and should be used in conjunction with other tools and techniques, such as statistical analysis, market research, and collaborative planning with suppliers and customers.
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



