Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIf you are running a maintenance organization, you are likely dealing with breakdown maintenance.
Preventive maintenance can be resource-intensive but is ideally suited for critical equipment.
Based on our experience working with customers, most organizations prefer a breakdown maintenance approach to non-critical equipment.
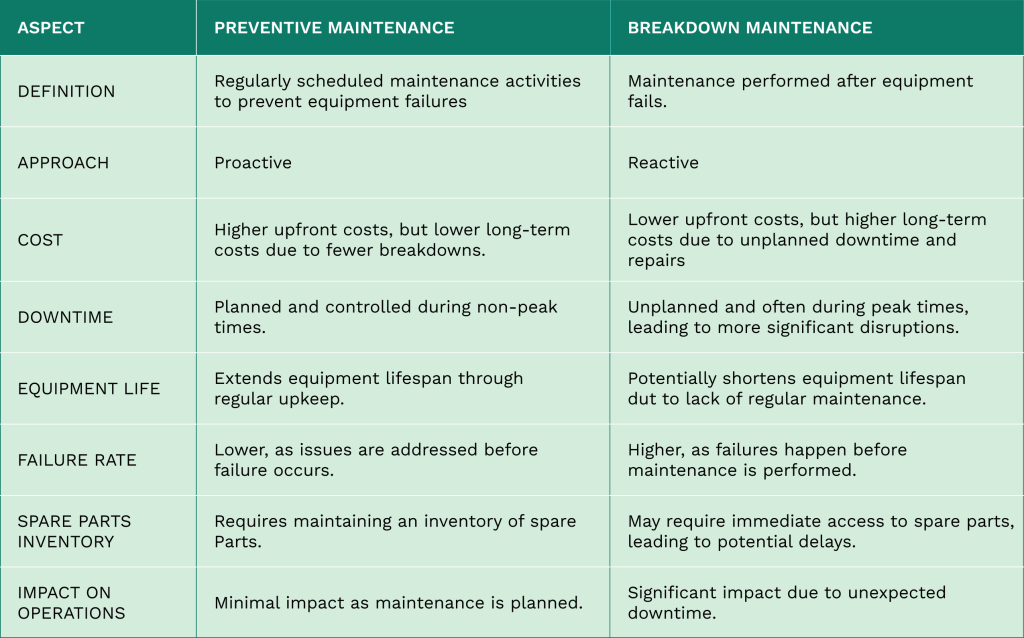
Source: WorkTrek
This article provides several practical tips for improving your approach to breakdown maintenance.
If you are looking for a more detailed guide on breakdown maintenance, refer to our comprehensive guide on the topic.
Defining Breakdown Maintenance
Breakdown maintenance is a type of corrective maintenance. It happens when machines fail.
This also means that teams only take action after equipment stops working.
This method, also called reactive maintenance, is used for parts that are easy to replace or cannot be fixed. Some companies choose it for non-critical gear.
Breakdown maintenance can be quick and doesn’t require much planning. However, it can lead to extended downtimes and higher costs if not managed well.
Having defined maintenance procedures can help mitigate unexpected equipment failures.
Tips for Breakdown Maintenance
Below are a few practical tips for improving breakdown maintenance. We’ve learned these tips working with clients across a variety of industries.
Identify Critical Equipment and Areas
The first step in the process is to identify critical equipment. This involves assessing which machines or systems are vital to operations.
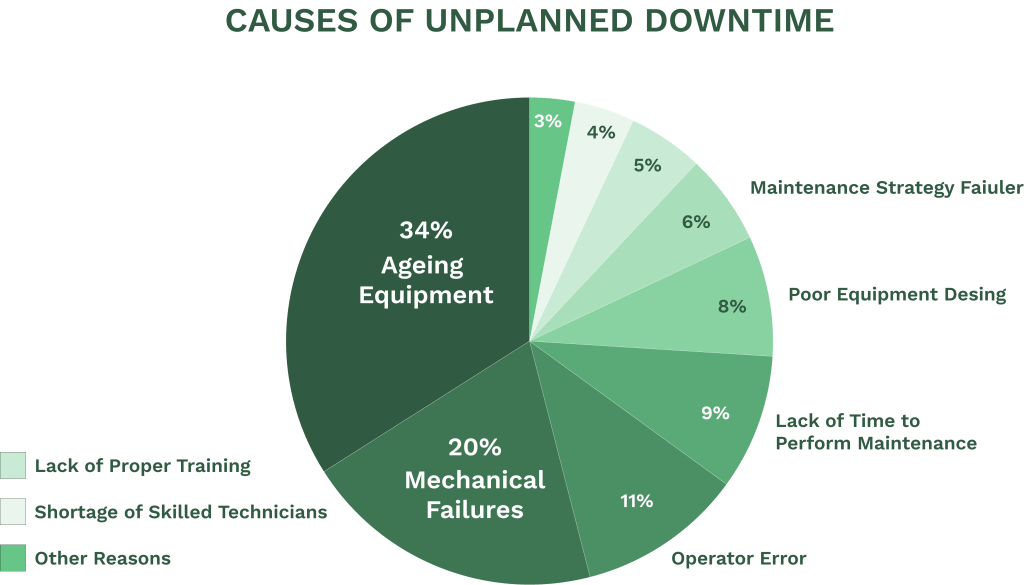
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: PlanetEngineering
List all equipment and rank them based on importance. Use factors like production impact, repair costs, and safety risks to determine criticality.iiIt’s helpful to make a map of critical areas in the facility. This allows quick response when breakdowns occur. Teams should also gather technical information for each piece of equipment, including manuals and repair histories.
Safety Protocols and Risk Management
Regardless of the type of maintenance you are performing, safety is paramount. Teams must develop clear safety protocols for different types of equipment and situations.
Perform risk assessments for each critical piece of machinery. This helps identify potential hazards and necessary precautions.
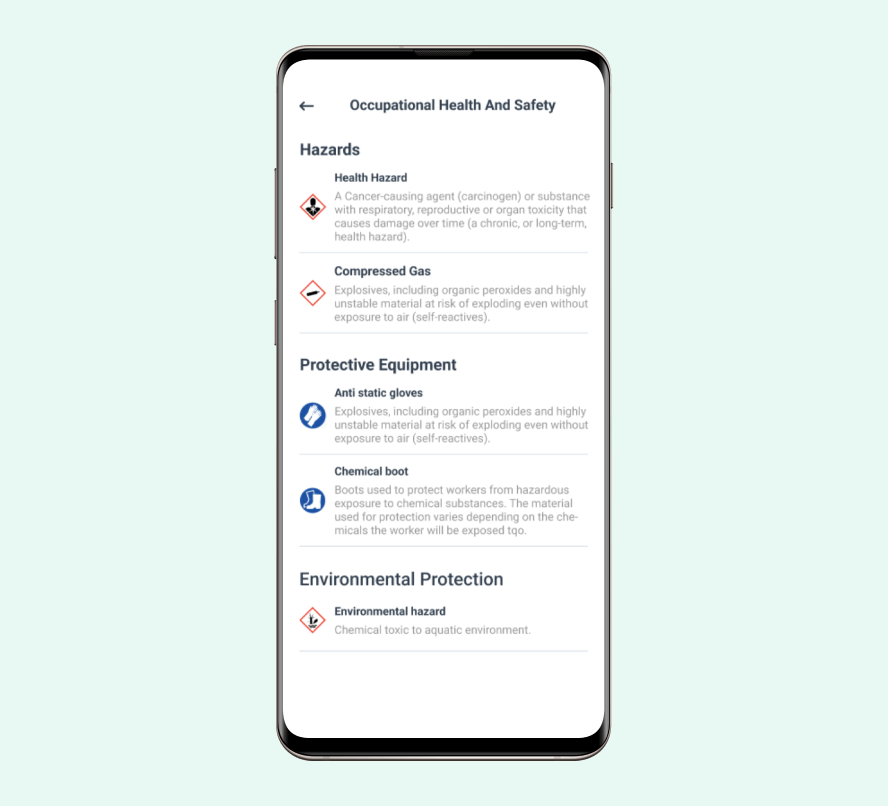
Safety gear requirements should be clearly defined for each maintenance task. If you use Lock Out Tag Out (LOTO) products, ensure your staff is fully trained.
Training
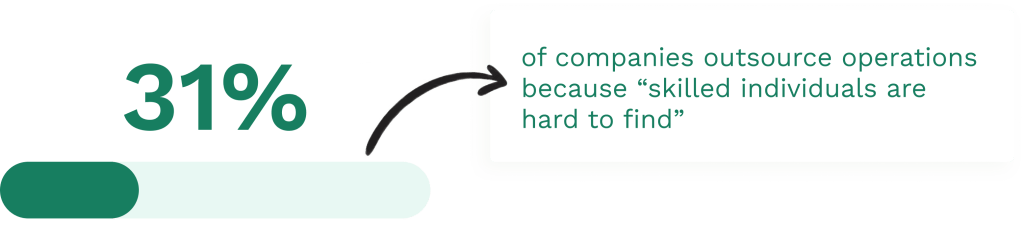
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Infraspeak Blog
Proper safety procedure training is critical. This improves efficiency, improves safety, and saves the company resources.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Linkedin Learning
An effective training strategy can also help with employee retention. According to a LinkedIn study,94% of workers will stay long with an employer if offered learning opportunities.
Parts Inventory
Good inventory management and low-quantity alerts are key to effective breakdown maintenance. It ensures teams have the right parts and tools when needed.
Maintenance departments should keep a detailed spare parts inventory in their maintenance report. This list should be updated regularly and include part numbers, quantities, and storage locations.
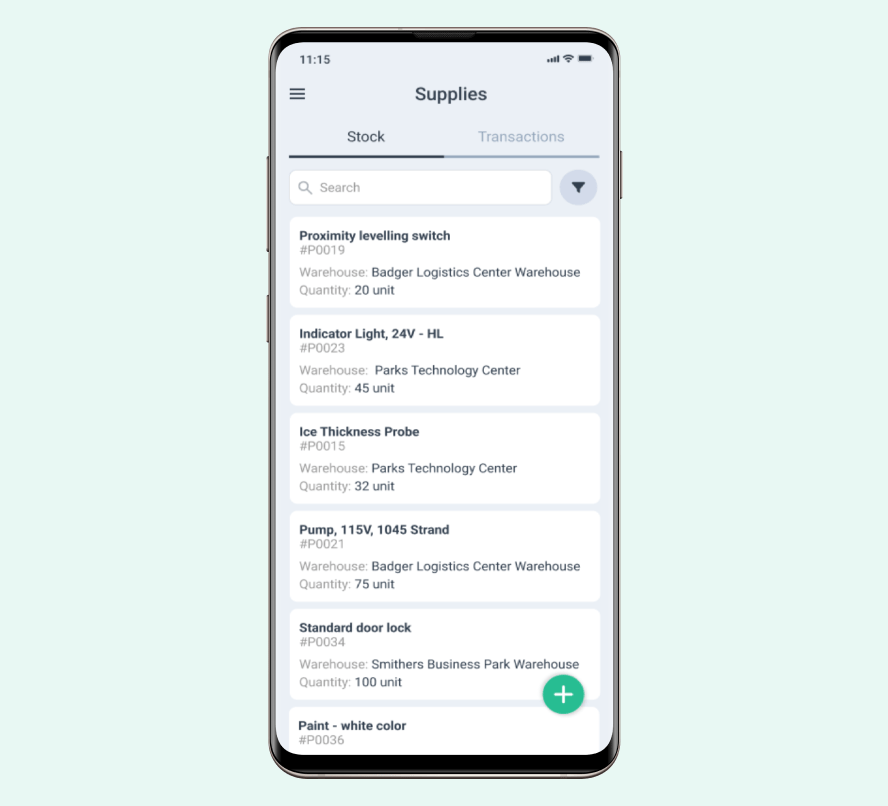
It’s wise to keep essential spare parts on hand for critical equipment. This reduces downtime during breakdowns. Teams should set up a system to track part usage and reorder when stocks are low.

Tools and supplies needed for common repairs should also be readily available. This includes safety equipment, cleaning materials, and diagnostic tools. Regular inventory checks help ensure everything is in good condition and ready for use.
Communication and Reporting Procedures
Better communication can benefit all teams. This can include setting up daily standups, using chat software, or using group chat capabilities.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Simon&Simone
Keep it simple. This could be an app or a phone hotline. Make it easy for workers to flag issues quickly.
Create detailed breakdown reports. Include what broke, why, and how it was fixed. Share these with all teams. This helps everyone learn from each event.
Hold brief meetings after major repairs to discuss what went well and what didn’t. Use these talks to improve your handling of breakdowns.
Implementing Continuous Improvement
Always look for ways to improve. Review each breakdown afterward. Ask what went wrong and how to prevent it next time.
Track key stats like repair times and costs. Set goals to improve these numbers over time.
Get feedback from machine operators. They often notice small changes that can signal future problems.
Stay up to date on new maintenance tech. Tools like vibration sensors can catch issues early.
Share success stories and lessons learned across teams. This spreads good practices and builds a culture of improvement.
Implement CMMS Software
CMMS software is a vital tool for managing breakdown maintenance. It helps track equipment, schedule repairs, and manage work orders.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: GoodFirms
CMMS systems store each asset’s information, including repair history and part details, and will reduce manual paper records.
This makes diagnosing issues easier and ordering parts quickly when breakdowns happen.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Pumps&Systems
Teams can use CMMS to set up alerts for routine checks. This helps prevent minor problems from turning into big breakdowns. The software also tracks costs, assisting managers in seeing where money is spent on repairs.
The Role of Maintenance Data and Analytics
Data is crucial for smart breakdown maintenance planning. Good data helps teams spot trends and make better choices.
Maintenance software collects repair times, part usage, and equipment downtime. This data shows which machines break down most often and why.f
Analytics tools and SMART maintenance can predict when gear might fail. This lets teams fix things before they break. Managers can use data to decide if it’s cheaper to keep fixing old equipment or buy new.
Charts and reports make it easy to see how well the maintenance team is doing. This helps improve processes over time.
Documentation and Knowledge Transfer
Good documentation is vital for sharing know-how. Teams should write down all repair steps and note any tricks they learn.
Creating a database of maintenance history is smart. This helps spot trends and prevent future issues. The database should include:
- Problem details
- Fix steps
- Parts used
Time taken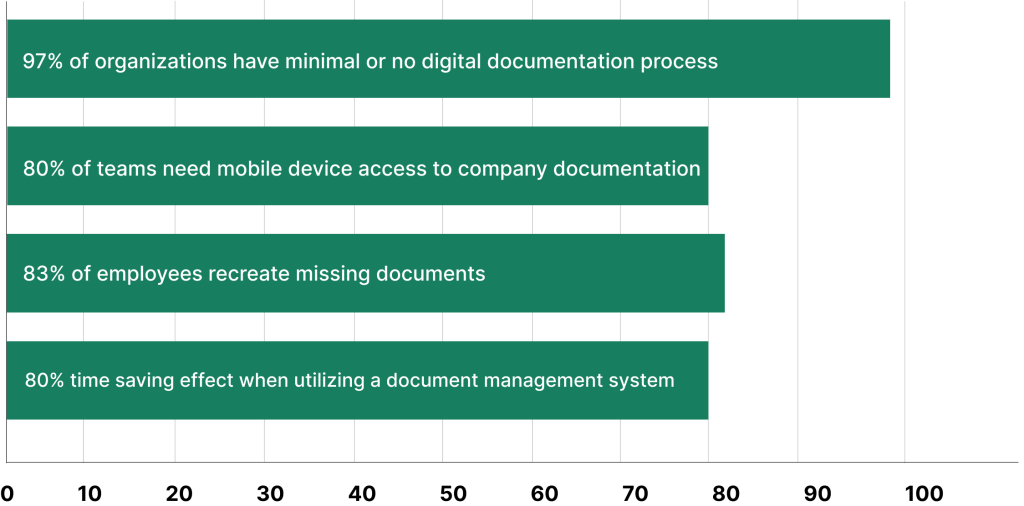
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: The Growth Blueprint
Older workers should teach newer ones. This passes on years of wisdom. Setting up mentor programs can help with this.
Regular team meetings help spread best practices. Workers can share what they’ve learned from recent jobs.

Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Tools
Condition monitoring tools watch equipment while it runs. They can spot signs of wear before a breakdown happens.
Sensors check things like temperature, vibration, and oil quality. When something’s wrong, they send alerts, giving teams time to plan repairs before a complete breakdown.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: icon
Diagnostic tools help find the exact cause of a problem. They can test electrical systems, check fluid levels, and analyze error codes.
Some tools use AI to learn what “normal” looks like for each machine. This makes it easier to spot when something’s off. Mobile apps let workers check equipment status from anywhere.
Effective Utilization of Tools and Equipment
Proper tool use is vital in breakdown maintenance. Keep tools clean and ready for use. Store them in a set spot so workers can find them fast. Check tools often to make sure they work well.
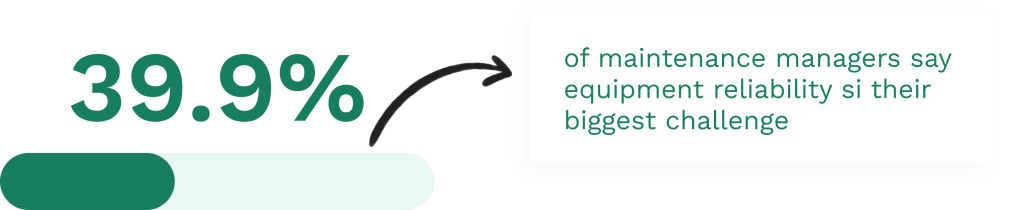
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: dynaway
Train staff on how to use tools correctly. This helps avoid equipment damage and keeps workers safe. Have a system to track who has which tools. This prevents tools from getting lost.
Keep spare parts for tools on hand. If a tool breaks, you can fix it fast. For non-critical gear, have backup options ready.
Materials and Replacement Parts Planning
Good parts planning helps fix breakdowns fast. Keep a stock of common parts like light bulbs, batteries, and fuses. Know which parts break most often and have extras.
Make a list of key suppliers for quick orders. Set up deals with them for fast delivery. The track part used to know when to order more.
For rare or costly parts, think about sharing with other sites. This can save money. Use software to track part levels and order history.
Plan for disposal of old parts. Some may need special handling. Set up a system to recycle when possible.
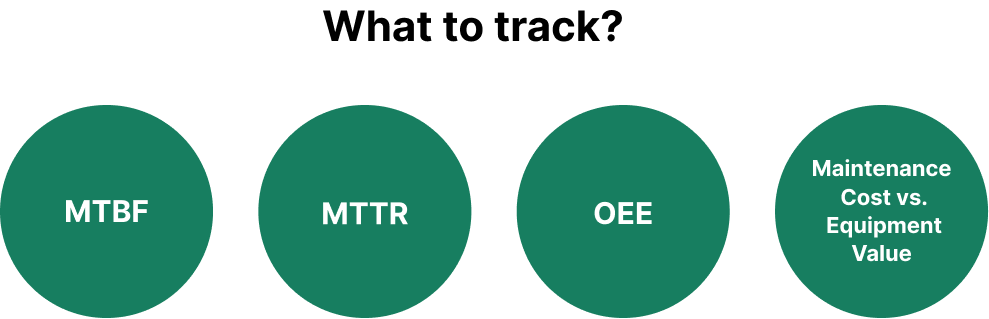
Performance Metrics and KPIs
Breakdown Maintenance planning relies on solid data. Teams should track:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
- Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
- Maintenance Costs vs. Equipment Value
Source: WorkTrek
These numbers show how well the maintenance plan works. Low MTBF or high MTTR may mean equipment needs more care.
Tracking these KPIs can help you better predict future breakdowns and help the team set clear goals for improvement.
Maintenance and Spare Parts Correlation
Match spare parts to your maintenance plan. Know which parts each machine needs. Keep those on hand.
Study equipment failure modes. Stock parts that often break or wear out. This helps prevent long downtimes.
Use maintenance data to spot trends. If a part fails often, keep more in stock. If it rarely breaks, stock less.
Link spare parts to work orders. This shows which parts are used most, helping plan future orders and stock levels.
Conclusion
Breakdown maintenance is an effective way to maintain non-critical equipment. Establish protocols for maintenance procedures, well-organized inventory, clear safety protocols, and effective communication.
These can help significantly improve your approach to breakdown maintenance.










