Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKey Takeaways:
- Regular preventive maintenance can reduce CNC machine downtime by up to 30% and extend equipment lifespan by 20%
- Unplanned CNC machine breakdowns cost approximately 5 times more than implementing a structured preventive maintenance plan
- Precision manufacturing demands that CNC machines maintain accuracy within 0.0001 inches, making proper maintenance critical for consistent quality
When your CNC machines go down unexpectedly, production stops, deadlines get missed, and costs spiral out of control. But here’s the thing: most CNC machine breakdowns are entirely preventable with the right maintenance approach.
CNC machines are the workhorses of modern manufacturing, capable of incredible precision and operating for thousands of hours. Yet despite being rugged machines built to withstand harsh environments, they still need regular attention to maintain accuracy and prevent costly repairs.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about CNC maintenance, from daily tasks to annual inspections, and show you how the right computerized maintenance management system can transform your preventive maintenance program.
Why CNC Machine Maintenance Matters
Before diving into specific maintenance tasks, let’s discuss why proper CNC machine maintenance is critical to your operations.
Modern CNC machines, whether they’re lathes, mills, or CNC routers, represent a significant capital investment.
According to a 2024 study by Grand View Research, the global CNC machine market is expected to reach $128.4 billion by 2030, reflecting the critical role these machines play in manufacturing.
But here’s where it gets interesting: that same investment can quickly turn into a liability without proper maintenance.
The Real Cost of CNC Machine Breakdown
When a CNC machine operates without regular maintenance intervention, several things happen. As machine operations become less precise, the cooling system may fail, the hydraulic oil may degrade, and, eventually, the machine will break down.
Research from Plant Engineering magazine reveals that unplanned downtime in manufacturing can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $250,000 per hour, depending on the industry and production requirements.
For most CNC machines in a machine shop, even a few hours of unexpected downtime represent thousands in lost revenue.
But like everything in life, there’s more to it than just the immediate costs.
When maintenance teams ignore proper maintenance schedules, several compounding problems occur:
- Precision drifts beyond acceptable tolerances, leading to scrap parts and rework
- Energy consumption increases as components work harder to overcome friction and wear
- The likelihood of catastrophic failure rises exponentially
- Tool holders and cutting tools wear unevenly, requiring premature replacement
- The machine bed develops inaccuracies that are expensive to correct
The Preventive Maintenance Advantage
The good news? A solid preventive maintenance plan changes everything.
According to research by Deloitte, manufacturers who implement preventive maintenance programs typically see:
- 25-30% reduction in maintenance costs
- 70-75% decrease in equipment breakdowns
- 35-45% reduction in downtime
- 20-25% increase in production capacity
These aren’t just random numbers; they represent real improvements that directly impact your bottom line.
When you schedule maintenance properly and follow a comprehensive maintenance checklist, you’re not spending money on upkeep; you’re investing in consistent quality, minimal downtime, and machine longevity.
Think about it this way: would you rather spend 15 minutes every morning on daily maintenance tasks, or deal with a multi-day shutdown and emergency machine replacement?
Understanding Your CNC Maintenance Needs
Not all CNC machines are created equal. You should focus your maintenance approach on the specific demands of your equipment and production environment.
Factors That Influence Maintenance Requirements
What are the factors that influence your maintenance strategy of CNC machines?
Machine Usage Intensity
A CNC lathe running three shifts per day, five days a week, needs more frequent attention than one operating eight hours daily.
The Manufacturing Technology Insights report suggests that high-utilization machines may need certain checks performed twice as often as standard schedules recommend.
Operating Environment
Machines in dirty, humid, or temperature-varying environments require more aggressive maintenance schedules. Dust collection systems, for example, need more frequent filter replacement in environments with high particulate matter.
Material Being Machined
Cutting exotic alloys, abrasive materials, or producing fine powders all accelerate wear on various components. Your preventive maintenance checklist should account for these material-specific demands.
Machine Age and Design
Modern CNC machines often feature automated sensors that monitor conditions in real-time, while older machines may require more hands-on inspection.
However, age doesn’t necessarily mean higher maintenance. Sometimes older, simpler designs are easier to maintain than complex multi-axis systems with fancy electronics.
The Role of Your Valued Maintenance Professional’s Knowledge
Here’s something that often gets overlooked: the expertise of your maintenance teams is just as important as any checklist.
A seasoned technician who knows how a CNC machine operates when it’s functioning correctly can detect subtle changes before they become serious problems. They notice when the cooling unit sounds slightly different, recognize when hydraulic pressure fluctuates beyond normal ranges, and can tell when a machine inspection reveals early warning signs invisible to the untrained eye.
This is why documentation matters so much. Every maintenance intervention, every observation, every minor repair should be logged. Over time, this data reveals patterns that help predict future maintenance needs and inform machine replacement decisions.
Daily CNC Maintenance Checklist
Let’s get practical. Your daily maintenance routine forms the foundation of optimal machine performance. These tasks typically take 10-15 minutes per machine and should be completed before production begins each day.
Visual Inspection and Cleaning
Start every day with a thorough visual inspection. This isn’t just about cleanliness, though that matters; it’s about catching problems before they escalate.
Machine Bed and Surfaces
The machine bed should be free of chips, coolant residue, and debris. Metal chips left overnight can cause scoring on precision surfaces or jam moving components. Use a brush or shop vacuum to remove chips. Try to avoid using compressed air, which can force debris into places it shouldn’t go.
Chuck and Spindle Area
Inspect the chuck or spindle for any buildup. Most CNC machines require that this area remain clean to maintain proper toolholder grip and prevent runout. Any contamination here directly affects part accuracy.
Way Covers and Bellows
These protective covers prevent chips and coolant from reaching sensitive slideways. Check that they’re intact, properly positioned, and moving freely. A torn bellows can lead to the rapid deterioration of precision surfaces underneath.
Fluid Level Checks
Proper fluid management is critical for machine operations. Your daily tasks should include:
Coolant Tank Inspection
Check coolant levels and top off as needed. But don’t just add coolant mindlessly, look at the concentration. According to Machining Cloud’s maintenance research, maintaining proper 4r5 helps prevent bacterial growth while ensuring effective cooling and lubrication.
Look at the coolant quality too. Does it smell bad? Is there visible contamination? These signs indicate the coolant systems need more than just a top-up.
Hydraulic Fluid Levels
Inspect the hydraulic tank and check hydraulic fluid levels against the sight glass. The hydraulic system is what generates the clamping force for chucks and powers many machine functions. Low hydraulic oil can lead to weak clamping, potentially causing parts to shift during machining. This can be dangerous and lead to an expensive problem.
Lubrication Unit Status
Modern CNC machines typically have automatic lubrication systems, but you still need to verify they’re functioning correctly. Check that the lubrication levels are adequate and that the system is actually delivering oil to the slideways. Some machines have indicator lights or counters showing the last lubrication cycle.
Pressure and System Checks
Hydraulic Pressure
Use the machine’s pressure gauge to verify that hydraulic pressure is within the specified range (typically around 4.5 MPa for most systems, though always consult your machine manual). Low pressure indicates a leak or pump problem that needs immediate attention.
Air Filters and Pneumatic System
Check the pneumatic air pressure at the regulator. Most CNC machines require clean, dry air at 80-100 PSI for proper operation. Inspect air filters for contamination and drain any moisture from the air tank or filter/regulator assembly. Moisture in the pneumatic system can cause erratic operation and damage precision components.
Safety and Operational Verification
Emergency Push Buttons
Test all emergency push buttons to ensure they immediately stop machine operations. This isn’t just a safety formality since malfunctioning emergency stops can lead to serious accidents.
Limit Switches
Verify that limit switches are triggering properly. These prevent the machine from over-traveling and potentially crashing.
Electrical Connections
Look for any loose wires, frayed cables, or signs of overheating around electrical enclosures. Check that the cooling fans for the control cabinet are running.
Temperature Sensors
If your machine has accessible temperature sensors, verify they’re reading within normal ranges. Overheating is a leading cause of electronic failures in CNC controls.

Tool and Fixture Inspection
Tool Holders
Inspect tool holders for any damage, excessive wear, or contamination in the taper. Clean the tool holder tapers and the spindle taper before installing tools. Even a small chip or contamination can cause runout problems.
Chuck or Fixture Condition
Check that chucks are securely mounted and that jaws move smoothly. For machines with quick-change fixtures, verify that locating pins and surfaces are clean and undamaged.
Chip and Coolant Management
Chip Conveyor Operation
If your machine has a chip conveyor, verify that it moves freely and removes chips from the coolant tank effectively. Chips that settle in the coolant tank can damage the pump and contaminate the coolant.
Chip Accumulation
Clear any chips from around the machine base, doors, and access panels. Chips can prevent doors from closing properly or damage precision surfaces if they get trapped in moving joints.
Weekly CNC Maintenance Tasks
While daily tasks keep your machines running, weekly maintenance digs a bit deeper to catch issues before they can impact production.
Thorough Cleaning and Inspection
Complete Machine Wipedown
Use this opportunity to clean all surfaces more thoroughly than the daily wipedown. Clean the machine enclosure windows, control panel screen, and any sight glasses. Being able to see clearly inside the machine makes it easier to spot problems.

Slideway and Linear Guide Inspection
Carefully inspect all slideways and linear guides for any signs of scoring, unusual wear, or insufficient lubrication. These precision surfaces are critical to maintain accuracy. Look for any dry spots where lubrication isn’t reaching.
Coolant Nozzle Cleaning
Coolant nozzles can become clogged with chips or buildup, reducing cooling effectiveness. Remove and clean all coolant nozzles, ensuring they’re directing coolant exactly where it’s needed.

Mechanical System Checks
Belt Inspection
Many CNC machines use belts for spindle drive or axis motion. Inspect belts for proper tension, alignment, and any signs of wear, cracking, or glazing. A failing belt can cause positioning errors or variations in spindle speed.
Coupling Inspection
Check all flexible couplings between motors and leadscrews or ballscrews for any signs of wear or looseness. A worn coupling can introduce backlash, which can harm positioning accuracy.
Tool Changer Mechanism
If your machine has an automatic tool changer, lubricate the tool changer mechanism according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Check that tools lock securely in the spindle and that the magazine rotates smoothly.
Electrical System Verification
Control Cabinet Cleanliness
Open the electrical cabinet and inspect for dust accumulation, loose connections, or any signs of overheating (discoloration of components or wiring). Use filtered compressed air or a vacuum to gently remove dust from circuit boards and components.
Cooling Fan Performance
Verify that all cooling fans are running smoothly and producing no unusual noise. Check that the cooling fans for the spindle motor, servo drives, and control cabinet are all operational.
Cable Condition
Inspect cables in cable chains or trays for any damage, excessive bending, or wear. Cable failures can cause intermittent problems that are hard to diagnose.
Hydraulic System Maintenance
Hydraulic Filter Check
Inspect the hydraulic filter indicator. Many systems have a visual indicator that changes color when the filter needs replacement. Even if not indicated, note the filter condition in your maintenance log.
Leak Detection
Carefully inspect all hydraulic connections, hoses, and the hydraulic tank for any signs of leakage. Even small leaks can lead to contamination and pressure loss.
Hydraulic Oil Condition
While you’re checking levels daily, take time weekly to assess oil quality. Look for any signs of contamination, milky appearance (indicating water intrusion), or unusual smell.
Monthly Maintenance Requirements
Monthly maintenance tasks are more involved and may require taking the machine out of production for several hours. Schedule these during slow periods or planned downtime to minimize impact.
Coolant System Overhaul
Coolant Concentration Testing
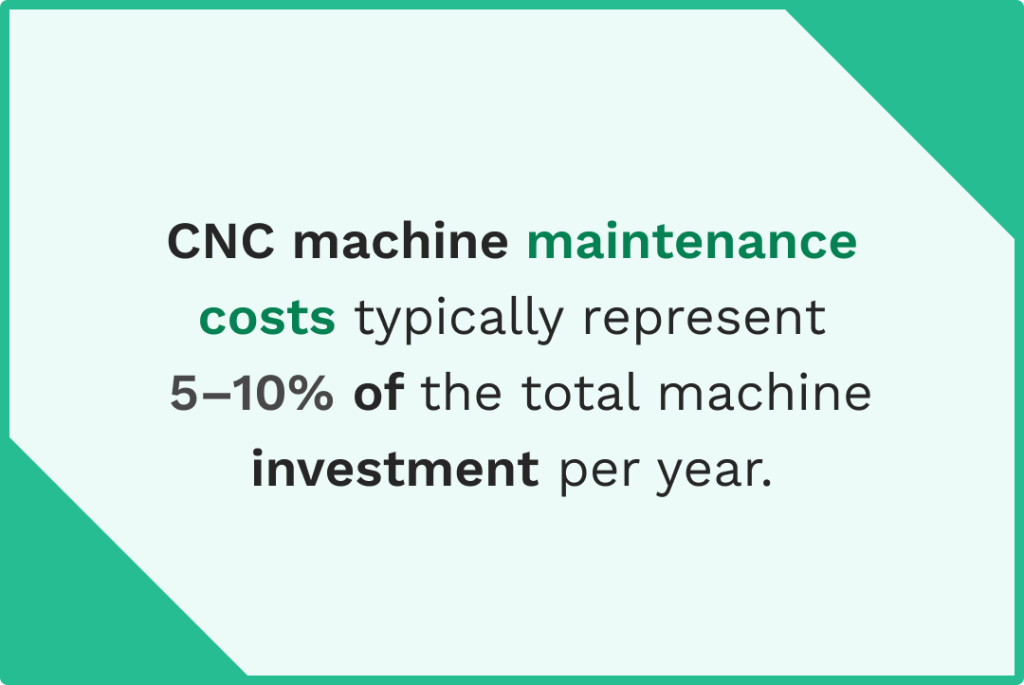
Use a refractometer to measure coolant concentration accurately. Maintaining proper concentration is crucial for preventing bacterial growth, ensuring adequate lubrication, and providing effective cooling. Most machining operations require 5-10% concentration, but check your coolant manufacturer’s recommendations.
Coolant pH Testing
Coolant pH should typically be between 8.5 and 9.5. pH outside this range can indicate bacterial contamination or coolant breakdown. Low pH can cause corrosion, while high pH may indicate bacterial growth.
Tramp Oil Removal
Floating oil on the coolant surface should be skimmed off. This “tramp oil” comes from hydraulic system leaks, way lubrication, or machine oil and promotes bacterial growth if left in the coolant.
Filter Replacement and Cleaning
Air Filter Replacement
Replace air filters for the pneumatic system and machine enclosure. Clean or replace filters according to usage intensity—high-dust environments may require more frequent changes.
Hydraulic Oil Filter
Depending on machine usage and manufacturer recommendations, the hydraulic oil filter may need replacement monthly or quarterly. Don’t wait for the indicator to show it’s clogged. That can mean that contaminants have already been circulating.
Coolant Filter Cleaning
If your machine has coolant filters (bag filters, magnetic filters, or paper filters), clean or replace them according to the manufacturer’s schedule. A clogged filter reduces coolant flow, affecting both cooling performance and chip washing.
Lubrication System Maintenance
Lubricant Level and Quality
Check not just the level but also the condition of the lubricant. If the lubricant appears contaminated or has an unusual consistency, it may need replacement rather than just a top-up.
Lubrication Line Inspection
Verify that lubrication is actually reaching all points. Sometimes, lubrication lines can become kinked, clogged, or disconnected, leaving equipment problems without proper lubrication even though the reservoir is full.
Precision and Calibration Checks
Inspect Belts and Adjust Tension
Thoroughly inspect all drive belts and adjust tension to manufacturer specifications. Belts that are too loose slip, causing positioning errors. Belts that are too tight put unnecessary stress on bearings.
Backlash Testing
Use the machine’s diagnostic software or MDI (Manual Data Input) to test for backlash in each axis. Rapid reverse movements should be crisp without any “lost motion.” Increasing backlash indicates wear in the ballscrew assembly or couplings.
Spindle Runout Check
Use a dial indicator to check spindle runout. Excessive runout (typically more than 0.0002″ for precision work) indicates bearing wear or contamination in the spindle taper and requires immediate attention.
Semi-Annual and Annual Maintenance Plans
Some maintenance tasks are too involved for monthly schedules but are critical for long-term machine longevity and maintaining precise operations.
Semi-Annual Maintenance
Deep Coolant Tank Cleaning
Every six months, completely drain the coolant tank, remove all settled chips and sludge, and clean the tank thoroughly. This is also the time to inspect the coolant tank for any bacterial growth or biofilm formation that needs to be addressed.
According to Blaser Swisslube’s coolant management guide, bacterial growth in coolant systems is one of the most common causes of coolant degradation. It can lead to offensive odors, skin irritation for operators, and reduced cooling performance.
Replace Hydraulic Oil Filters
Even if the indicator hasn’t shown its time, semi-annual filter replacement is good practice for hydraulic systems. At this time, also sample and test the hydraulic oil for contamination.
Battery Backup Inspection
Many CNC controls have battery backups that maintain settings and programs during power outages. These batteries typically need replacement every 2-3 years. Check battery voltage and replace it if it’s declining.
Annual Maintenance Plan
Your annual maintenance plan should be comprehensive, addressing items that don’t require frequent attention but are critical to avoiding machine replacement and maintaining optimal machine performance.
Complete Hydraulic Oil Change
Drain the entire hydraulic system, clean the hydraulic tank, and refill with fresh hydraulic oil. This is also the time to inspect the hydraulic pump for any wear or damage.
Spindle Bearing Inspection
Have a qualified technician inspect spindle bearings for wear, excess play, or any indications of impending failure. Spindle failure is one of the most expensive repairs on a CNC machine, so early detection is crucial.
Ballscrew and Linear Guide Inspection
Inspect ballscrews and linear guides for wear, pitting, or any signs of inadequate lubrication. Measure backlash and compare it to baseline measurements. Increasing backlash indicates wear that will eventually require ballscrew replacement.
Complete Machine Calibration
Perform a complete machine calibration, including:
- Axis travel accuracy verification
- Spindle alignment check
- Tool changer repeatability
- Backlash compensation adjustment
Many machine shops use a laser interferometer or ballbar system for this annual calibration to ensure the machine still meets its original accuracy specifications.
Software and Control System Backup
Back up all machine parameters, programs, and control settings. Software corruption or control failures are rare, but when they happen, having a complete backup can mean the difference between hours of downtime versus days.
Professional Service Consideration
For annual maintenance, many machine shops bring in the machine manufacturer’s service technician. This professional has specialized knowledge, diagnostic tools, and access to detailed service manuals specific to your machine model.
A manufacturer’s technician can perform tasks that require specialized equipment:
- Precision alignment of ballscrews and slideways
- Spindle bearing preload adjustment
- Servo motor alignment
- Control system firmware updates
- Comprehensive diagnostic testing
While this service has a cost, it’s typically far less expensive than the potential downtime and repairs from an undiagnosed problem that develops into a major failure.
How CMMS Software Powers Successful Preventive Maintenance
Now here’s where things get really interesting. Everything we’ve discussed so far, which includes all those daily tasks, weekly inspections, and monthly overhauls, becomes dramatically easier and more effective with the right Computerized Maintenance Management System like WorkTrek.
The Problem with Manual Tracking
Let’s be honest: maintaining paper checklists for CNC maintenance is tedious and error-prone. Technicians forget to document tasks, paperwork gets lost, and there’s no easy way to analyze trends or predict when problems might occur.
A 2024 survey by Plant Engineering found that 67% of maintenance teams still rely on some combination of paper records, spreadsheets, or memory to track maintenance activities.
The result? Missed scheduled tasks, inability to track parts usage accurately, and zero visibility into which machines are consistently problematic.
How WorkTrek Transforms CNC Maintenance
This is where WorkTrek changes the game for preventive maintenance programs. As a modern CMMS platform built specifically for manufacturing environments, WorkTrek makes it effortless to manage every aspect of CNC machine maintenance.
Automated Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
WorkTrek automatically generates preventive maintenance work orders based on calendar time, operating hours, or custom triggers. Your maintenance teams never miss a scheduled task because the system proactively reminds them when maintenance is due.
For example, if your CNC lathe requires monthly coolant concentration testing, WorkTrek creates that work order automatically on the first of each month.
The assigned technician receives a notification, opens the work order on their mobile device, completes the task, and documents the results. The best part is that they can do all this without touching a piece of paper.
Comprehensive Maintenance Checklists
WorkTrek lets you create detailed, step-by-step maintenance checklists specific to each machine type. Your daily maintenance checklist for a CNC router differs from that for a CNC lathe, and WorkTrek handles that complexity effortlessly.
Each checklist item can include:
- Detailed instructions for the task
- Photos or diagrams showing what to inspect
- Acceptable parameter ranges
- Links to related procedures or manuals
- Required tools or materials
When a technician opens a preventive maintenance work order, they see exactly what needs to be done, how to do it, and what standards the results should meet.
Real-Time Asset Health Visibility
WorkTrek provides complete visibility into the condition of every CNC machine in your facility. You can instantly see:
- When each machine last received maintenance
- Outstanding maintenance tasks
- Maintenance history and trends
- Parts consumption by machine
- Mean time between failures
- Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
This visibility helps you make informed decisions about machine replacement versus repair, identify machines that need more frequent attention, and optimize your preventive maintenance plan based on actual performance data.
Intelligent Parts Management
Remember those daily tasks of checking coolant, hydraulic oil, and lubrication levels? WorkTrek automatically tracks parts and consumables usage and alerts you when inventory is running low.
Let’s say you’re checking the coolant tank and need to add five gallons of coolant. You document that in the work order, and WorkTrek automatically:
- Deducts five gallons from coolant inventory
- Updates the reorder point if inventory is getting low
- Tracks which machine used the coolant
- Builds a consumption history to predict future needs
No more emergency runs to the supplier because you ran out of critical supplies. No more stockrooms filled with unnecessary inventory because you’re ordering “just to be safe.”
Mobile Accessibility for Maintenance Teams
Your technicians don’t need to walk back to an office computer to complete paperwork. With WorkTrek’s mobile app, they can:
- Access work orders directly on the shop floor
- View maintenance checklists and procedures
- Attach photos documenting conditions or repairs
- Log time and parts used
- Update work order status in real-time
This eliminates the common problem of technicians completing maintenance tasks but forgetting to document them, leaving gaps in your maintenance history.
Powerful Analytics and Reporting
WorkTrek’s reporting capabilities transform your maintenance data into actionable insights. You can generate reports showing:
- Maintenance costs by machine or department
- Preventive vs. reactive maintenance ratios
- Most frequent failure modes
- Maintenance team productivity
- Compliance with preventive maintenance schedules
These reports help justify maintenance budgets, identify training needs, and demonstrate the value of your preventive maintenance program to management.
Common CNC Maintenance Challenges and Solutions
Even with the best preventive maintenance plan and the right CMMS, CNC maintenance comes with challenges. Let’s address the most common ones and how to overcome them.
Challenge 1: Coolant Management and Bacterial Growth
Coolant-related problems are among the most common maintenance issues in machine shops. Bacterial growth leads to foul odors, reduced coolant performance, and potential health concerns for operators.
The Solution: Implement a comprehensive coolant management program that includes:
- Regular concentration and pH testing
- Prompt removal of tramp oil
- Proper coolant mixing (never add concentrate directly to the tank)
- Periodic use of biocides when necessary
- Complete tank cleanouts on a semi-annual schedule
Master Chemical Corporation’s research indicates that maintaining proper concentration (typically 5-10%) and pH (8.5-9.5) can extend coolant life by 3-4 times compared to poorly managed systems.
Challenge 2: Hydraulic System Leaks and Pressure Issues
Hydraulic leaks are messy, create environmental concerns, and often result in inadequate clamping force, which can compromise safety and part quality.
The Solution:
- Implement weekly visual inspections of all hydraulic connections
- Use dye-based leak detection for slow leaks that are hard to spot
- Replace hydraulic hoses before they fail (typically every 3-5 years depending on usage)
- Maintain proper hydraulic oil filtration to prevent component wear
- Address any leak immediately rather than just adding more oil
A proactive approach to hydraulic maintenance prevents the majority of pressure-related issues before they impact production.
Challenge 3: Inconsistent Maintenance Documentation
When maintenance tasks aren’t properly documented, you lose the ability to analyze trends, predict failures, or demonstrate compliance with quality standards.
The Solution: This is where a CMMS like WorkTrek becomes indispensable. By making documentation automatic and mobile-friendly, WorkTrek ensures maintenance activities are captured consistently without adding burden to technicians’ workload.
Create a culture in which completing the documentation is as important as completing the task. WorkTrek’s mobile interface makes this so easy that there’s no excuse for incomplete records.
Challenge 4: Balancing Production Demands with Maintenance Needs
This is perhaps the most common complaint from maintenance managers: “Production won’t give me time to maintain the machines.”
The Solution: Frame maintenance in terms that production managers understand: uptime and output. Show them that:
- 15 minutes of daily maintenance prevents hours of unplanned downtime
- Preventive maintenance is scheduled during natural breaks or shift changes
- The cost of preventive maintenance is 1/5 the cost of reactive repairs
Use WorkTrek’s reporting capabilities to document how preventive maintenance has reduced downtime and costly repairs. Nothing convinces production managers like data showing improved overall equipment effectiveness.
Challenge 5: Keeping Up with Multiple Machine Types
A typical machine shop might have CNC lathes, vertical machining centers, CNC routers, and wire EDMs each of which have different maintenance requirements.
The Solution: WorkTrek excels here by allowing you to create machine-specific preventive maintenance templates. Each machine type gets its own customized maintenance checklist based on manufacturer recommendations and your operational experience.
The system automatically assigns the right checklist to the right machine, ensuring technicians always follow the appropriate procedures regardless of which equipment they’re maintaining.
Challenge 6: Skill Gaps in the Maintenance Team
As experienced technicians retire, newer technicians may lack the deep knowledge of CNC machine operations that comes from decades of hands-on experience.
The Solution: Use WorkTrek’s knowledge base features to capture institutional knowledge. Document procedures with photos, videos, and detailed instructions. When an experienced technician discovers a tricky repair technique or identifies an early warning sign of failure, that knowledge gets captured in WorkTrek and shared across the entire team.
Additionally, implement a structured training program that pairs new technicians with experienced technicians on complex maintenance tasks. Document these training sessions in WorkTrek to build a complete record of each technician’s skills and certifications.
Conclusion
Maintaining CNC machines at peak performance isn’t complicated, but it does require consistency, attention to detail, and the right tools to manage the process effectively.
Your daily tasks keep machines clean and identify obvious problems. Weekly and monthly maintenance catch developing issues before they cause breakdowns. Annual overhauls address long-term wear and maintain precision.
And throughout all of this, a comprehensive CMMS like WorkTrek ensures nothing falls through the cracks.
Your CNC machines are capable of incredible precision, remarkable productivity, and decades of reliable service. Give them the maintenance attention they deserve, supported by the right technology, and they’ll reward you with optimal machine performance year after year.
Ready to take your CNC maintenance program to the next level? Schedule a demo of WorkTrek and discover how easy preventive maintenance can be when you have the right CMMS supporting your maintenance teams.