Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKey Takeaways:
- Farm equipment repair costs have spiked 41% since 2020, nearly doubling in the past two decades.
- Preventive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime by 30% and can resolve 25% of service issues remotely.
- Unplanned breakdowns cost farmers approximately $3,348 per season in lost productivity and emergency repairs.
Picture this: It’s 5 p.m. on a Friday during harvest season. Your fields are ready, the weather forecast shows rain coming tomorrow, and you’re prepared to work through the night if necessary. But your combine refuses to start, your tractor needs a critical part, and your harvest equipment sits idle.
This scenario plays out on farms across the country every season, and the consequences extend far beyond a simple repair bill.
Farm equipment is one of the largest capital investments in modern agriculture, and proper maintenance is essential to protect that investment.

In this guide, we’ll explore ten essential tips for farm equipment maintenance that successful farmers use to maximize equipment reliability, minimize repair costs, and avoid unexpected breakdowns during critical operations.
1. Follow Manufacturer’s Maintenance Schedules
Your farm equipment comes with detailed maintenance procedures outlined in the operator’s manual, and there’s a compelling reason to follow them closely.
Manufacturers spend millions developing these maintenance procedures based on extensive testing and real-world performance data. These schedules account for the specific engineering tolerances, component wear patterns, and operational stresses your equipment faces.
Ignoring manufacturer’s recommendations can void warranties and lead to catastrophic failures that could have been prevented through routine maintenance.
Modern agricultural equipment features complex hydraulic systems, electronic components, and precision-engineered moving parts that require specific maintenance intervals. What worked for older, simpler machinery won’t keep today’s sophisticated farm machinery operating at peak performance.
Keep all equipment manuals organized and accessible, whether in a home office, workshop, or digital format on your phone.
Create a farm equipment maintenance checklist based on these schedules, noting daily tasks, weekly inspections, and seasonal maintenance requirements. For further guidance, review an effective maintenance plan with 10 key tips.

According to the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, following proper maintenance schedules keeps annual repair costs in the 2-4% range of original equipment cost, significantly lower than reactive maintenance approaches.
2. Perform Daily Pre-Operation Inspections
Before starting any piece of equipment, successful farmers conduct visual inspections that take just minutes but prevent hours of downtime.
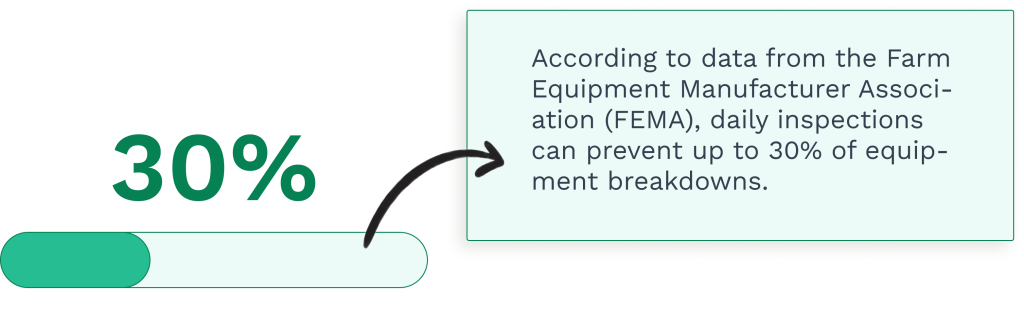
Daily inspections catch early signs of wear, leaks, or damage before minor issues escalate into major problems.
During critical operations like planting or harvest season, these quick checks ensure the equipment’s reliable performance when you need it most.
Your daily inspection routine should include:
- Walking around each piece of equipment to check for obvious damage
- Inspecting hoses and hydraulic systems for leaks or wear
- Checking fluid levels, including engine oil, hydraulic fluid, and coolant
- Examining belts and chains for proper tension and wear
- Verifying tire pressure on all equipment
- Testing all lights and safety features
- Looking for loose belts, damaged wiring, or accumulated dirt
Pay special attention to critical components that experience the most stress. On tractors, check engine oil levels and look for oil leaks. On harvest equipment and combines, inspect the header, belts, and cleaning systems.
These routine maintenance activities become second nature with practice, taking only 5-10 minutes per machine while providing invaluable peace of mind that your equipment is ready for efficient operation.
3. Change Fluids and Filters Regularly
Engine oil, hydraulic fluid, transmission fluid, and filters are the lifeblood of farm machinery, yet they’re often neglected until problems arise.
Regular oil changes dramatically extend equipment lifespan and prevent engine wear.
Dirty oil causes friction between moving parts, accelerates component wear, and reduces fuel efficiency. The cost of routine oil changes pales in comparison to the cost of engine rebuilds or premature equipment failure.
Don’t forget the filters. Air filters, fuel filters, oil filters, and hydraulic filters all require regular attention:
- Replace air filters when they show signs of restriction or when the manufacturer recommends it. Clean air filters ensure proper combustion and fuel economy.
- Change fuel filters to prevent contaminants from reaching fuel injectors and other critical components.
- Replace oil filters with every oil change to maintain proper lubrication.
- Service hydraulic filters to protect expensive hydraulic systems from damage.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that farm equipment repair costs have increased 41% since 2020. Regular fluid and filter changes represent a small investment that prevents the costly repairs this data reflects.
Consider implementing an oil analysis program. This simple test analyzes a small oil sample to detect early signs of engine wear, contamination, or other issues before they cause equipment to break down.
4. Lubricate All Moving Parts
Proper lubrication is a no-brainer, and one of the simplest yet most effective maintenance tasks you can perform to extend the lifespan of your agricultural equipment.
Farm machinery contains countless moving parts. This includes bearings, chains, hinges, pivot points, and gearboxes.
All of these parts require regular greasing to prevent friction and wear. Without adequate lubrication, these components generate excessive heat, wear prematurely, and eventually fail.

Use the right grease for each application. Consult your equipment manual to identify the correct lubricant type and grade for different components.
Using the wrong lubricant can be as harmful as using none at all.
Establish a regular lubrication schedule based on equipment use:
- Grease all lube points before and after heavy use periods
- Inspect chains and sprockets for proper lubrication
- Check gearbox oil levels regularly
- Lubricate pivot points on implements and attachments
- Grease wheel bearings according to the manufacturer’s intervals
Pay special attention to harvest machinery during busy seasons.
The combination of dust, chaff, and extended operating hours can quickly degrade lubrication, making frequent greasing essential for keeping your farm running smoothly.
Keep a well-organized supply of essential tools and the right grease types in your workshop. A few minutes spent greasing critical components can prevent hours of downtime and thousands in repair costs.
5. Monitor and Maintain Tire Pressure
This is one of the simplest maintenance tasks that you can perform regularly – check the tire pressure.
Tire pressure might seem like a minor detail, but it significantly impacts equipment performance, fuel efficiency, and operational costs.
Properly inflated tires on tractors, combines, and harvest equipment provide better traction, reduce soil compaction, and improve fuel economy.
Under-inflated tires increase rolling resistance, waste fuel, and accelerate tire wear. Over-inflation reduces the contact patch, decreasing traction and potentially damaging tires on rough terrain.
Check tire pressure weekly during active seasons and monthly during storage periods. Temperature changes affect pressure, so verify readings when tires are cold for accuracy.
The benefits of proper tire maintenance extend beyond the tires themselves:
- Improved fuel efficiency: Properly inflated tires can reduce fuel consumption by 3-5%
- Better traction: Correct pressure maximizes the contact patch for optimal grip
- Reduced soil compaction: Proper inflation distributes weight more evenly
- Extended tire life: Correct pressure prevents irregular wear patterns
- Higher resale value: Well-maintained equipment commands premium prices
Don’t forget spare parts inventory. Keep spare tires or at least tire repair supplies on hand to avoid delays during critical operations.
A flat tire during harvest season can cost more in lost productivity than years of tire maintenance.
Inspect tire treads regularly for excessive wear, cuts, or damage. Replace worn tires before they fail in the field, and consider rotating tires on equipment to ensure even wear across all positions.
6. Keep Equipment Clean
Keeping farm machinery clean might seem counterintuitive given the nature of agricultural work, but regular cleaning is a crucial maintenance procedure that pays significant dividends.
Accumulated dirt, mud, crop residue, and chemical buildup accelerate corrosion, hide damage, obstruct cooling systems, and attract moisture that promotes rust. What starts as harmless debris becomes a maintenance issue that shortens equipment lifespan.
Develop a cleaning routine that fits your operation:
- Remove crop residue, chaff, and plant material after each use
- Wash equipment thoroughly at season’s end before proper storage
- Pay extra attention to moving parts where debris can interfere with operation
- Clean under covers and shields where moisture and debris collect
- Remove fertilizer and chemical residue that can corrode metal surfaces
For harvest equipment, thorough cleaning between crops prevents contamination and removes abrasive materials that accelerate wear.
On tractors and general farm equipment, keeping the engine bay clean helps prevent overheating and makes leak detection easier during daily inspections.
Use a pressure washer for efficient cleaning, but avoid directing high-pressure water at electrical components, bearings, or other sensitive areas. A soft brush works well for removing stubborn residue from delicate parts.
Clean equipment also makes maintenance easier. When you can clearly see components, identifying worn parts, detecting leaks, and performing routine maintenance becomes much simpler and more effective.
7. Store Farm Machinery Properly
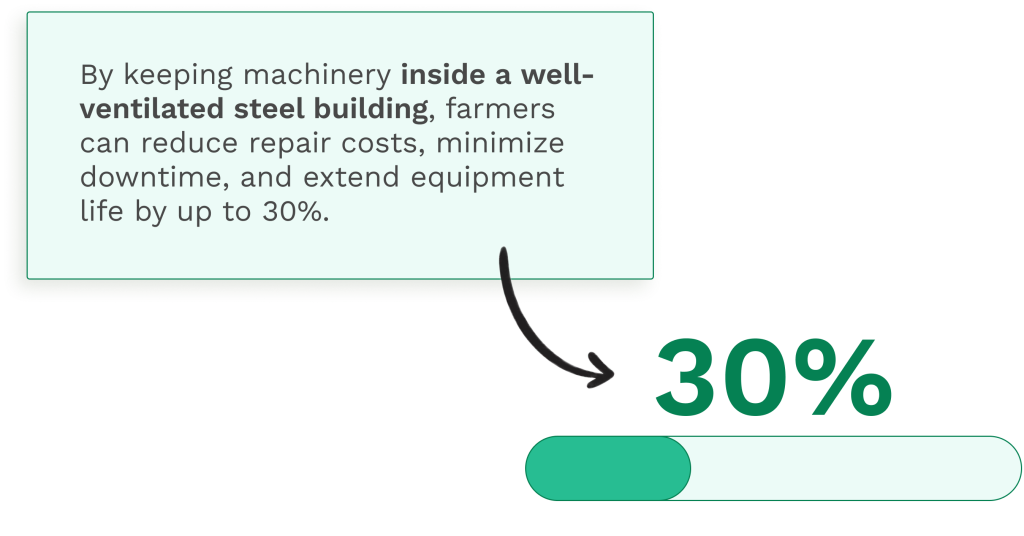
How you store equipment between seasons dramatically affects its condition and longevity. Exposure to sun, rain, snow, and temperature extremes accelerates wear and deterioration.
Indoor storage under a roof or in a dedicated shed provides the best protection. If indoor storage isn’t available for all equipment, prioritize protecting the most valuable pieces and those with sensitive electrical components.
For equipment that must remain outside:
- Use quality waterproof tarps to protect from precipitation
- Park on level, well-drained ground to prevent moisture accumulation
- Block or support equipment to take the weight off the tires and prevent flat spots
- Remove batteries and store them indoors in temperature-controlled conditions
- Drain fluids from sprayers and other systems that could freeze
Proper storage extends beyond just parking equipment. Take these additional steps before storage:
- Change oil and filters so the equipment isn’t sitting with contaminated fluids
- Fill fuel tanks to prevent condensation
- Apply rust preventative to exposed metal surfaces
- Disconnect batteries or use trickle chargers
- Cover exhaust and air intake openings to prevent pest intrusion
According to agricultural industry research, proper storage and preventive maintenance can reduce unexpected breakdowns significantly, avoiding the $3,348 average seasonal cost of equipment failures.
8. Inspect and Replace Worn Components
Proactive parts replacement prevents unexpected breakdowns at the worst possible times. Waiting for complete failure wastes time, increases repair costs, and risks damaging other components.
Regular inspections help identify parts nearing the end of their service life. Look for early signs of wear on belts, hoses, chains, bearings, and other high-wear components. These items have predictable lifespans and should be replaced on schedule, not after failure.
Key components requiring regular inspection include:
- Belts: Check for cracks, fraying, glazing, or improper tension
- Hoses: Inspect for cracks, bulges, leaks, or deterioration
- Chains: Look for stretch, worn pins, or damaged links
- Bearings: Listen for unusual noises indicating wear
- Cutting edges and blades: Replace when dull to maintain efficient operation
- Electrical components: Check wiring for damage or corrosion
Keep commonly needed spare parts in stock. During harvest season or other critical periods, having parts on hand eliminates the downtime associated with emergency ordering and shipping.
When you inspect hoses and other components, don’t just look at visible sections. Many critical hoses and belts are partially hidden, making thorough inspection important.
Use a flashlight and a mirror to examine hard-to-reach areas.

Document when parts are replaced to track component lifespan and predict future replacement needs. This data helps you stock the right spare parts and budget accurately for maintenance costs.
9. Document All Maintenance Activities
Focus on transforming reactive maintenance into proactive asset management. Detailed documentation helps track costs, identify patterns, predict failures, and maintain warranty coverage.
This process is greatly simplified if you implement a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) like WorkTrek.
Create a maintenance logbook for each piece of equipment that records:
- Date and hours of operation for all service
- Specific maintenance tasks performed
- Parts replaced with part numbers
- Fluids used and amounts
- Issues discovered during inspections
- Repair costs and labor hours
- Preventative maintenance completed
This information becomes invaluable when:
- Troubleshooting recurring problems
- Planning annual maintenance budgets
- Determining optimal replacement timing
- Negotiating trade-in values with dealers
- Providing documentation for warranty claims
- Training new operators on maintenance procedures
Digital maintenance software offers significant advantages over paper records. Modern CMMS solutions automatically track maintenance activities, send reminders for scheduled tasks, and generate reports showing equipment performance and cost trends.

Industry data shows that annual repair costs typically range from 2-4% of the original machine cost. Good records help you track whether specific equipment falls within this range or requires more frequent attention.
Historical data also helps identify whether equipment has become unreliable enough to justify replacement. When repair costs exceed a certain threshold relative to replacement cost, it’s time to consider upgrading to newer, more reliable machinery.
10. Train Operators on Equipment Use
Operator error causes a significant percentage of equipment failures. Improper operation accelerates wear, causes damage, and voids warranties.
All of which is preventable through proper training.

Every person who operates your farm equipment should receive thorough training on:
- Proper starting and shutdown procedures
- Daily inspection requirements
- Normal operating parameters
- Warning signs of problems
- Emergency shutdown protocols
- Basic troubleshooting techniques
- Safe operating practices
Many operators assume they know how to run equipment without reading the manual. This attitude leads to costly mistakes. New technology, updated safety features, and model-specific operational requirements make manual reading essential, not optional.
Encourage operators to report unusual sounds, vibrations, or performance changes immediately. These early warnings often indicate minor issues that can be addressed before causing equipment failure.
Create standard operating procedures for complex equipment. Written checklists ensure consistency and prevent operators from skipping important steps. Laminated checklists mounted in operator cabs provide a ready reference during operation.
For seasonal or temporary workers, invest time in proper training before turning them loose on expensive equipment. The few hours spent on training prevent thousands of dollars in damage from improper operation.
Remember that even experienced operators benefit from refresher training when manufacturers introduce new features or technologies.
Modern agricultural equipment includes sophisticated electronics and automated systems that require a thorough understanding to operate correctly and be adequately maintained.
Conclusion
Farm equipment maintenance isn’t just about preventing breakdowns. The goal is to protect your farm’s most valuable assets and ensure reliable operations during critical windows.
The ten essential tips covered in this guide provide a comprehensive framework for maintaining agricultural equipment at peak performance. From following manufacturer’s recommendations to implementing digital maintenance tracking, each strategy contributes to reduced repair costs, improved equipment reliability, and extended machinery lifespan.
With equipment repair costs rising 41% since 2020 and unplanned breakdowns costing thousands per season, the importance of preventive maintenance has never been clearer.
Successful farmers understand that time invested in routine maintenance activities saves far more time and money than constantly fighting equipment failures.
Start implementing these practices today, beginning with daily inspections and proper documentation. As your maintenance program matures, consider adding CMMS software to streamline processes and maximize efficiency.