Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeMaintenance workflow automation is transforming how businesses manage their equipment and facilities. This innovative approach aims to reduce unexpected downtimes and cut maintenance costs. Companies can boost efficiency at every maintenance process step by streamlining operations and leveraging technology.
The benefits of automating maintenance workflows are significant. It can lead to fewer errors, improved efficiency, and higher employee job satisfaction. Key elements like work identification, maintenance planning, and scheduling are crucial in keeping equipment running smoothly. Choosing the right Computerized Maintenance Management Software is essential for success.
Improving Maintenance Processes
Streamlining Upkeep Procedures
Maintenance procedures are key to keeping equipment running smoothly. Good upkeep practices help machines last longer and work better. When done right, these tasks can boost a factory’s performance.
Maintenance workflows cover all the steps needed to keep things in top shape. This includes:
- Checking equipment regularly
- Fixing problems quickly
- Keeping records of all work done
When teams follow clear steps, they get more done. They also make fewer mistakes. This leads to:
- Less downtime for machines
- Lower repair costs
- Happier workers who know what to do
Making Tasks Easier with Technology
Using tech to help with maintenance is a smart move. It takes away boring jobs and helps workers focus on what matters.
Automated workflows can:
- Send alerts when it’s time to check a machine
- Keep track of parts used
- Make reports on how well things are working
This saves time and cuts down on errors. It also gives bosses a clear picture of what’s happening.
Here’s a simple look at how it can help:
| Without Automation | With Automation |
|---|---|
| Manual schedules | Auto-reminders |
| Paper records | Digital logs |
| Slow reporting | Real-time data |
By using these tools, companies can work smarter, not harder. This leads to better results and less stress for everyone involved.
Optimizing Maintenance Workflows

Source: WorkTrek
Maintenance workflows form the backbone of effective equipment and facility management. These structured processes ensure smooth operations and prevent unexpected breakdowns. A well-designed workflow reduces costly failures and extends the life of important assets.
Key steps in a maintenance workflow include:
- Problem identification
- Task planning
- Priority assessment
- Execution
- Documentation
Maintenance teams use asset history to make smart decisions. This data shows past work and helps plan future tasks.
Regular upkeep tasks often follow this pattern:
- Choose preventive measures
- Set task frequency
- Schedule to minimize disruption
- Carry out the work
- Record details for future use
A good workflow balances proactive and reactive maintenance. This approach reduces emergency repairs, which often cost more and cause bigger disruptions.
| Workflow Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Work orders | Track tasks and assign staff |
| Checklists | Ensure consistent quality |
| Schedules | Coordinate activities |
| Asset records | Monitor equipment health |
Teams should review and update their workflows regularly. This helps them stay efficient and adapt to new challenges.
Effective maintenance workflows also:
- Improve safety
- Control costs
- Boost equipment performance
- Reduce downtime
Maintenance teams can create a system that keeps operations running smoothly and protects valuable assets by focusing on these areas.
Benefits of Automating Maintenance Processes
Main Advantages
Automating maintenance processes offers several key advantages. It boosts efficiency and productivity, freeing up staff to focus on high-value tasks. This leads to improved job satisfaction and better use of skills.
Automation also enhances equipment reliability. By scheduling regular maintenance, machines run smoother for longer. This cuts downtime and keeps operations running smoothly.
Here are some main benefits:
- Higher efficiency
- Better use of staff skills
- Improved equipment reliability
- Less downtime
 Source: WorkTrek
Source: WorkTrek
Minimizing Mistakes
Automated systems help reduce human errors in maintenance tasks. They ensure consistent task completion and set clear standards for all team members.
This leads to better quality control and fewer mistakes. Automation also makes it easier to track who did what and when. This improves accountability across the maintenance team.
Benefits of error reduction:
- More consistent work quality
- Clearer expectations for staff
- Better tracking of tasks
- Improved accountability
Lowering Upkeep Expenses
Automating maintenance workflows can significantly cut costs in several ways:
- Labor savings: Automation reduces manual tasks, letting staff focus on critical work.
- Less rework: Automated processes are more consistent, reducing costly mistakes.
- Predicting issues: Data analysis helps spot potential problems before they cause breakdowns.
- Smart resource use: Automation helps allocate tools, parts, and staff more efficiently.
- Longer equipment life: Regular, timely maintenance extends machine lifespan.
- Meeting regulations: Automated systems help comply with industry standards, avoiding fines.
- Better data: Accurate, real-time info leads to smarter spending decisions.
- Energy efficiency: Optimized equipment operation can lower utility bills.
| Cost-Saving Area | How Automation Helps |
|---|---|
| Labor | Reduces manual tasks |
| Rework | Improves consistency |
| Breakdowns | Predicts issues early |
| Resources | Optimizes allocation |
| Equipment Life | Ensures timely maintenance |
| Compliance | Meets industry standards |
| Decision-Making | Provides accurate data |
| Energy Use | Optimizes operations |
By improving these areas, automation leads to better asset performance and more scalable operations.
Elements for Maintenance Workflows
A well-designed maintenance workflow incorporates several key components to ensure smooth operations and optimal equipment performance. The process begins with identifying potential issues or areas for improvement. This step is crucial for catching problems early and preventing costly breakdowns.
Next comes the planning phase. Here, maintenance teams create detailed plans outlining specific tasks, required tools, and necessary resources. A critical part of this stage is developing a preventive maintenance schedule. This proactive approach helps extend equipment life and reduce unexpected downtime.
Prioritization is another vital element. Teams should conduct a criticality analysis to rank maintenance tasks based on their importance to operations and safety. This ensures that the most critical issues are addressed first.
Scheduling is essential for minimizing disruptions to normal operations. A well-crafted schedule balances maintenance needs with production demands.
The execution phase involves carrying out the planned maintenance activities. Technicians perform repairs or preventive tasks according to the established plans.
Documentation is the final key component. It involves recording all completed work and creating a historical record. This data is invaluable for future planning and analysis.
Here’s a summary of the main components:
- Issue identification
- Maintenance planning
- Preventive maintenance scheduling
- Criticality analysis
- Task scheduling
- Execution of maintenance activities
- Documentation and record-keeping
By incorporating these elements, organizations can create efficient maintenance workflows that improve equipment reliability, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency.

Implementing CMMS Software for Automated Systems
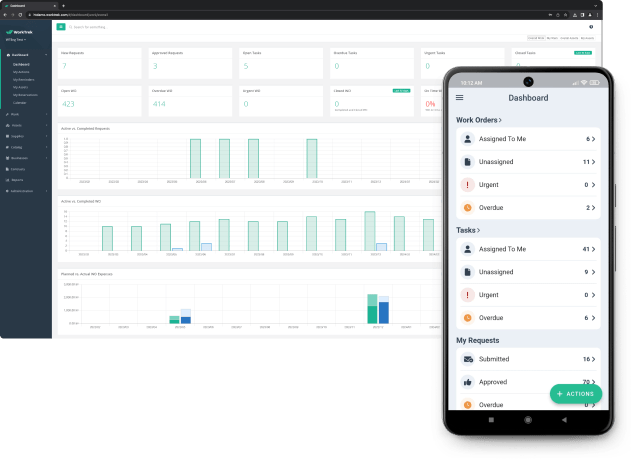 Source: WorkTrek
Source: WorkTrek
Picking the Best CMMS Software
Choosing the right upkeep software is key for smooth operations. Look for these features:
- Easy to use
- Mobile-friendly
- Good customer support
- QR code scanning
- IoT device connections
- Room to grow
A good system helps teams work better and gives quick insights. But be careful—there are many options, and picking the wrong one can cause problems.
Connecting Your CMMS System
Linking your maintenance software to other tools is important. It helps everything run smoothly, and new ways to connect systems make it easier to share data quickly.
When systems work together, you can:
- See all upkeep tasks in one place
- Work faster
- Get data quickly to make smart choices
Connected systems are a big part of fully automated upkeep.
To set up automated maintenance:
- Map out each step
- Make sure everyone knows the plan
- Set clear goals that fit your business
- Find places where machines can help
- Pick software that’s easy to use
- Connect your tools so they work as one
Good planning helps teams see what needs to be done. Clear targets keep everyone on track. The right software makes work easier for all. When tools talk to each other, workflows better.
Automated systems can save time and money. They help catch problems early. Teams can focus on big tasks instead of small ones. With the right setup, upkeep becomes smoother and more reliable.
Setting Up Effective Preventive Maintenance Systems
Asset Tracking and Documentation
A detailed inventory of all equipment is key to a strong preventive maintenance plan. This involves making a list of every machine, device, and service history. Adding barcodes or QR codes to important equipment can make tracking easier. Good records show where money is spent on repairs and work can be done more efficiently.
Equipment Priority Classification
Analyzing how important each piece of equipment is helps decide which items need the most attention. This process looks at different risks like how a breakdown might affect operations, costs, the environment, or safety. Knowing these priorities helps maintenance teams focus their efforts and budget where they matter most.
Streamlining Regular Upkeep
Using technology to automate regular maintenance tasks can improve the whole process. It’s important to set up a schedule that fits the equipment’s use. Some items might need checks at fixed times, while others should be inspected based on how much they’re used. This approach ensures everything gets the right amount of care without wasting time on unnecessary checks. A well-planned schedule helps prevent equipment from wearing out too quickly and balances the need for maintenance while keeping costs down.
Preparing Maintenance Teams for Automated Systems
Training maintenance personnel is crucial for smooth operations in automated environments. Well-trained technicians can spot issues early, preventing costly breakdowns. They also help extend equipment life through proper handling and upkeep.
Key benefits of training maintenance staff include:
- Faster problem identification
- Reduced unplanned downtime
- Improved equipment longevity
Maintenance teams should stay up-to-date with the latest automation technologies. This keeps their skills sharp and relevant.
Investing in staff education pays off by:
- Enhancing operational stability
- Maximizing return on automation investments
- Boosting overall productivity
Companies that prioritize training see fewer errors and smoother processes. This leads to more reliable automated systems and better performance overall.
Tracking and Fine-Tuning Automated Processes
Keeping a close eye on automated workflows is key to getting better results. Teams can use significant numbers to see how well things are working. These numbers include how long machines stay on, how well they work, and how fast repairs happen.
Putting sensors on machines can give useful info right away. This helps catch problems early and plan fixes better. It also means less downtime and lower costs.
Here are some benefits of using sensors:
- See machine health in real-time
- Spot issues before they get big
- Plan maintenance smarter
- Cut down on surprise breakdowns
- Know what’s up with important machines
Good reports turn data into smart choices, helping things run smoother over time. New tech lets experts check on machines from far away, which means faster fixes and less travel time.
Always watching and tweaking how things work keeps automated systems running well. It helps them stay quick and useful as needs change.
Improving Team Communication in Maintenance Operations
Effective communication is key to smooth maintenance operations. When teams work well together, they can prevent issues before they happen, leading to better asset care and fewer delays.
Managers play a big role in keeping things running. They must:
- Handle unfinished jobs
- Create task lists
- Make sure the equipment is ready
- Deal with all work requests
Good talk between team members prevents work from piling up and prevents people from doing the same job twice.
New computer systems help teams work better. These systems offer:
- Full views of important equipment
- Ways to manage work from anywhere
- Easy file sharing for upkeep papers
- Clear safety rules
- Views of all maintenance activities
- Less surprise repairs
- Better care for expensive tools
- Simple reports for checking data
These tools help bosses and workers manage systems better, leading to smoother work and less downtime.
With good teamwork, maintenance crews can:
- Fix problems faster
- Keep customers happy
- Share updates easily
- Be more open about their work
Teams that talk well get more done. They also make sure equipment stays in good shape for longer.
Hurdles and Remedies in Streamlining Maintenance Operations
Streamlining maintenance operations through automation presents several challenges. Data security stands out as a primary concern. Even automated systems can have weak spots that hackers might exploit.
Different tech setups across teams can make it difficult to implement one-size-fits-all solutions. This mix of tools and platforms adds to the complexity.
Money matters often slow progress. The upfront costs of new systems can make company leaders hesitate, and it takes time to see the payoff from these investments.
Another worry is how well these systems can grow and change with a business. Markets shift, and companies need tools that can keep up.
Workers may resist new tech. Some fear job loss, while others struggle to let go of old ways of doing things.
Fitting new systems into what’s already there can be tricky. This often leads to delays and other issues.
To tackle these problems, companies need to:
- Plan carefully
- Talk clearly with all staff
- Get support from every level of the company
Businesses can smooth out the bumps in adopting new workflow systems by taking these steps.
Maintenance Workflow Automation: Tomorrow’s Trends
AI and technology are reshaping how companies handle maintenance tasks. Smart systems now spot problems before they happen, using data to predict when machines might break down. This lets workers fix issues early, saving time and money.

Connected devices are changing the game, too. Machines talk to each other and share info about how they’re doing. This helps create better upkeep plans.
New tools are making repairs easier:
- Virtual guides that show step-by-step instructions
- Remote help from experts miles away
Companies can now set up automation without writing complex code. This makes it simpler to improve work processes.
Advanced AI is tackling tough jobs in specific industries. It’s handling tasks that used to need human experts.
These changes are making maintenance work faster and more accurate. They also help businesses grow and improve over time. As tech advances, we’ll see even more ways to make maintenance smoother and smarter.
Aspects of Maintenance Workflow Enhancement
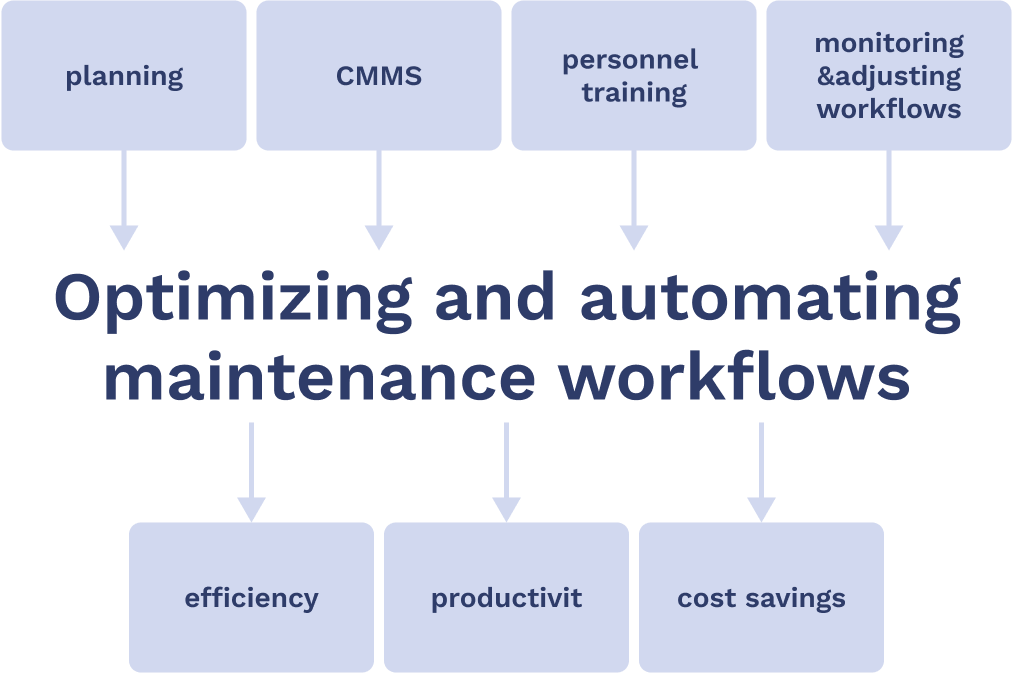
Maintenance workflow automation can greatly boost efficiency and cut costs in industrial settings. It requires careful planning and the right tools. Companies should pick suitable CMMS software and train their staff well. Regular checks and updates to the workflow are crucial.
Key steps include:
- Setting clear goals
- Choosing the best software
- Training employees thoroughly
- Monitoring results
As technology advances, maintenance methods will keep improving. Smart companies stay up-to-date with new trends. This helps them remain competitive and efficient.
The future of maintenance looks bright. More data and connectivity will lead to new ways to improve work. Companies that start improving now will be ready for what’s next.
Source: WorkTrek
Common Questions About Maintenance Workflow Automation
How to Diagram a Maintenance Workflow for Better Automation?
Diagramming a maintenance workflow helps visualize the process:
- Map out current steps
- Identify bottlenecks
- Note manual tasks
- Highlight decision points
- Show data flows
Use flowchart software to create a clear visual. Review with team members to ensure accuracy.
What Are the Steps to Automate a Maintenance Workflow?
- Analyze existing process
- Pick tasks to automate
- Choose automation tools
- Set up new workflow
- Train staff
- Test thoroughly
- Go live
- Monitor and adjust
Continuous improvement is key for long-term success.
Which Tools Work Best for Automating Maintenance Workflows?
Top tools include:
- Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
- Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software
- Workflow automation platforms
- Mobile apps for technicians
- Internet of Things (IoT) sensors
Pick tools that fit your needs and budget.
How Does Standardization Improve Maintenance Review Processes?
Standardization helps by:
- Creating consistent checklists
- Defining clear approval steps
- Setting uniform data entry methods
- Establishing regular review schedules
- Providing templates for reporting
This leads to more efficient and reliable reviews.
What Are the Main Advantages of Automated Maintenance Workflows?
Key benefits include:
- Increased efficiency
- Reduced human error
- Better data tracking
- Improved compliance
- Cost savings
- Faster response times
- Enhanced safety
Automation frees up staff to focus on critical tasks.
How to Measure Success of an Automated Maintenance Workflow?
Track these metrics:
- Equipment downtime
- Labor hours
- Maintenance costs
- Work order completion rates
- Asset lifespan
- Safety incidents
- Customer satisfaction