Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeMany organizations struggle with inconsistent maintenance practices, leading to increased downtime, safety hazards, and costly repairs. Without a standardized approach, teams often miss critical steps or perform tasks incorrectly, affecting productivity.
This inefficiency can lead to operational delays, unexpected equipment failures, and higher costs, ultimately hindering business growth and performance.
 Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Know Industrial Engineering
Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Know Industrial Engineering
Implementing Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) for maintenance ensures consistency, clarity, and compliance across the board. Organizations can reduce errors, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall efficiency by standardizing tasks, improving performance, and achieving cost savings over time.
Listen to this Article
What is Maintenance SOP?
Maintenance SOPs provide a structured approach to equipment care and facility upkeep. They ensure safety, efficiency, and consistency across maintenance tasks.
Definition of SOP
A maintenance SOP is a detailed guide that outlines specific steps for carrying out maintenance tasks. It sets clear standards for work quality and safety practices.
These documents are crucial for several reasons:
- They promote consistency in maintenance work
- SOPs reduce errors and improve safety
- They help train new staff quickly and effectively
- SOPs increase efficiency by standardizing processes

Source: WorkTrek
Maintenance SOPs also ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards. They create a system of accountability and help track maintenance history.
Core Components
Effective maintenance SOPs include several key elements:
- Scope and objectives
- Safety precautions
- Required tools and equipment
- Step-by-step procedures
- Quality control checks
A good SOP starts with clear goals and a defined scope. It lists all necessary safety gear and precautions. The procedure section breaks down tasks into simple, easy-to-follow steps.

Source: WorkTrek
Quality control measures ensure the work meets standards. SOPs often include checklists or sign-off procedures. They may also specify how to document completed work.
Regular reviews and updates keep SOPs relevant and effective, ensuring they reflect current best practices and equipment changes.
Developing Effective Maintenance SOPs
Creating useful maintenance SOPs involves getting input from workers, making clear documents, and improving them over time. Good SOPs help maintenance teams work better and keep equipment running smoothly.
Gathering Input From Stakeholders
Stakeholders play a key role in making SOPs. Talk to maintenance techs, supervisors, and operators. They know the jobs best.
Ask about common tasks, safety concerns, and equipment needs. Make a list of all maintenance activities.
Hold meetings to discuss procedures. Take notes on important steps and tips.
Look at past repair records to find problem areas. Check if any rules or laws apply to the work.
Get photos or videos of tasks being done right. These can go in the SOP later. Having input from many people helps make SOPs that work well in real life.
Creating SOP Documents
Write SOPs in simple, clear language. Use short sentences and bullet points. Start with the task’s goal. List needed tools and safety gear.
Break jobs into step-by-step instructions. Number each step. Use photos or diagrams to show key parts. Make a checklist for workers to follow.

Source: WorkTrek
Include these parts in each SOP:
- Task name and ID number
- Who does the task
- How often to do it
- Safety warnings
- Step-by-step directions
- What to do if something goes wrong
Use a standard format for all SOPs. This makes them easy to read and update.
Incorporating Feedback and Revisions
Test new SOPs before using them fully. Have workers try following the steps. Watch for any confusion or missed items. Ask for their thoughts on how to improve the SOP.
Provide a way for staff to give feedback anytime. Put a note box in the work area, or use a CMMS System to collect ideas. Review all suggestions regularly.
Update SOPs when equipment or methods change. Check quality standards to be sure SOPs still meet them. Revise steps that cause problems or delays.
Keep track of all SOP changes. Use version numbers. Tell workers about updates. Train them on new steps. Good SOPs grow and improve over time.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing maintenance SOPs requires a well-planned approach. This involves clear communication, defined roles, and proper resource allocation.
Communication and Training
Strong communication is essential for the effective implementation of maintenance SOPs. Teams must understand the new procedures and their importance.
Training sessions should be held to explain the SOPs in detail. These can include hands-on practice and Q&A periods.
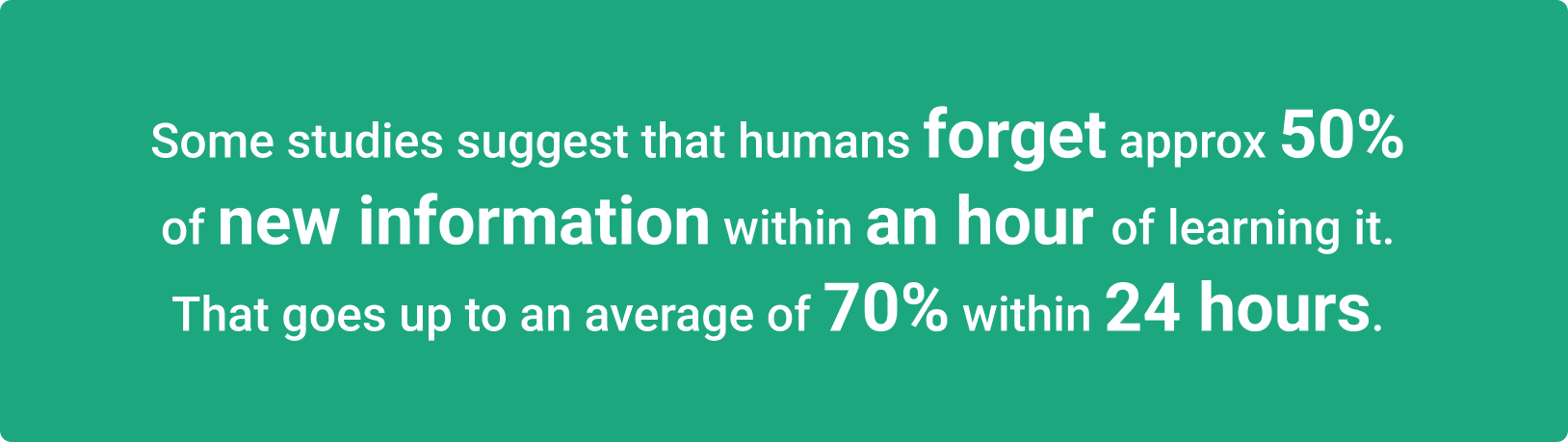
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Whale
Regular updates keep staff informed of any changes. This helps ensure everyone follows the latest procedures.
Feedback channels allow workers to voice concerns or suggest improvements. This creates a culture of continuous improvement.
Assigning Roles and Responsibilities
Clear role assignments are crucial for SOP success. Each team member should know their specific duties.
A responsibility matrix that lists tasks and the people accountable can help clarify who does what.
Supervisors should oversee SOP compliance. They can offer guidance and address any issues that arise.
Regular performance reviews can track how well staff follow SOPs. This helps identify areas for improvement or additional training.
Tools and Resources Allocation
Proper tools and resources are essential for effective SOP implementation. This includes both physical equipment and digital systems.
Maintenance management software can help track work orders and SOP compliance. It provides a central platform for accessing procedures.

Safety gear and specialized tools should be readily available. This ensures workers can follow SOPs without delay.
Budget allocation for ongoing training and equipment upgrades is important. This keeps the maintenance team up-to-date with best practices and technology.
Safety and Compliance
Safety and compliance are key parts of maintenance SOPs. They protect workers and keep things legal. Rules, safety steps, and industry standards all play a role.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements set the rules for maintenance work, and companies must know and follow them. OSHA standards often apply to maintenance tasks.
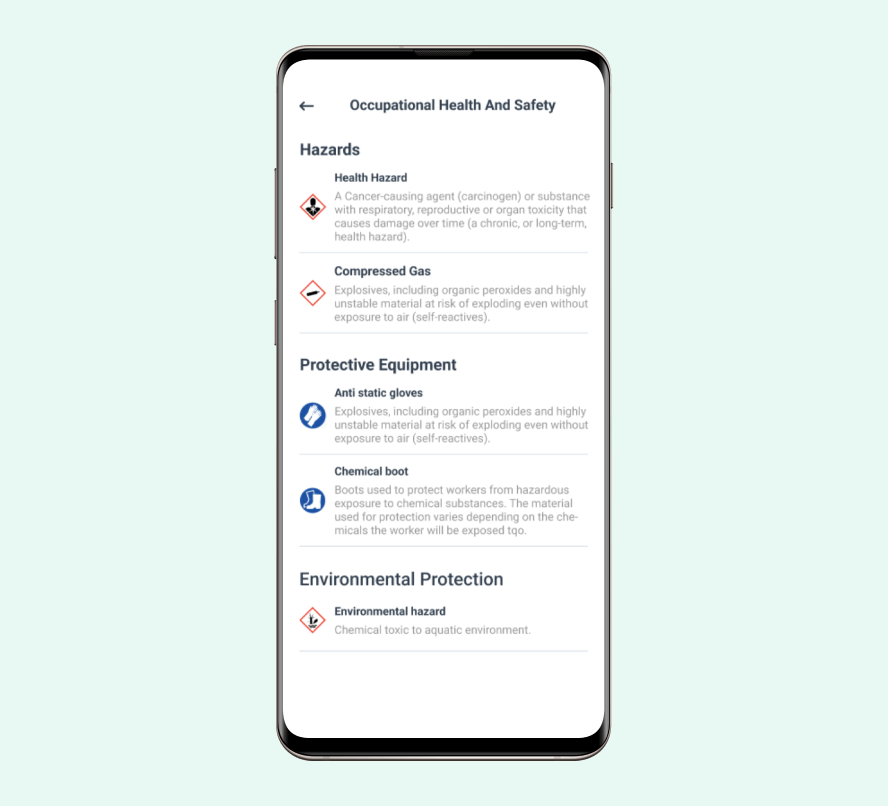
Source: WorkTrek
Some common rules include:
- Proper machine guarding
- Lockout/tagout procedures
- Electrical safety standards
Breaking these rules can result in fines or legal trouble. Therefore, it’s crucial to stay current on changing regulations.
Incorporating Safety Protocols
Safety protocols are steps to prevent harm. They should be a core part of every maintenance SOP.
Key safety measures include:
- Using the correct personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Following proper tool-handling procedures
- Identifying and marking hazards
Regular safety training helps workers remember these protocols. Review and update safety steps often.
Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards
Industry standards go beyond basic rules. They set best practices for maintenance work, and following these standards can improve safety and quality.
Common industry standards include:
- ISO 9001 for quality management
- ISO 14001 for environmental management
- ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety
Maintenance SOPs should align with these standards. This helps ensure work is done safely and correctly, making it easier to pass audits and inspections.
Regular reviews can help keep SOPs in line with changing standards. It’s important to document how the SOP meets each standard.
Maintenance Execution
Effective maintenance execution involves regular inspections, timely repairs, and proper documentation. These practices help keep equipment running smoothly and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
Conducting Inspections and Preventive Maintenance
Regular inspections are crucial for identifying potential issues before they become major problems. Maintenance teams should create checklists for each piece of equipment, noting key components to examine.
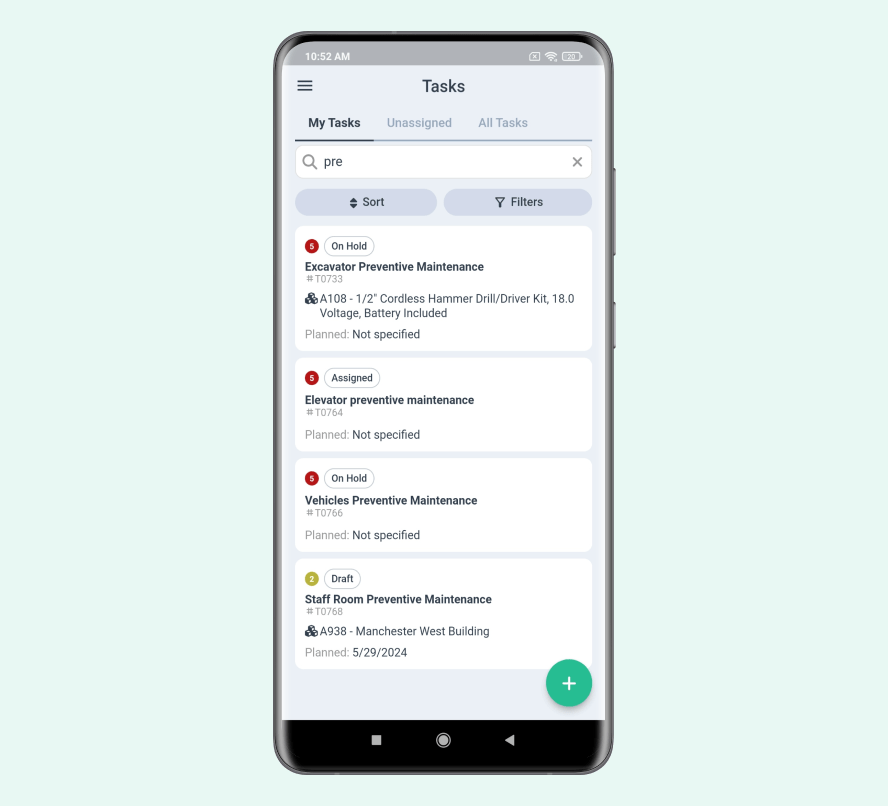
Source: WorkTrek
Preventive maintenance tasks may include:
- Lubricating moving parts
- Tightening loose bolts
- Cleaning filters
- Checking fluid levels
These tasks should be scheduled based on manufacturer recommendations and equipment usage patterns. It’s important to train staff on proper inspection techniques and safety procedures.
Maintenance teams should use digital tools to track inspection results and schedule follow-up actions. This helps ensure no issues are overlooked and allows for trend analysis over time.
Equipment Repair and Parts Management
When repairs are needed, technicians should follow standardized procedures to diagnose and fix issues. This may involve:
- Troubleshooting steps
- Repair instructions
- Safety precautions
- Potential safety hazards
Source: WorkTrek
A well-organized parts inventory is essential for quick repairs. Maintenance departments should:
- Keep commonly used parts in stock
- Track part usage and reorder points
- Store parts properly to prevent damage
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) can help streamline parts ordering and tracking, reducing equipment downtime and improving repair efficiency.
Recording and Reporting Procedures
Accurate maintenance records are needed to track equipment history and identify recurring issues. Technicians should document:
- Date and time of maintenance activities
- Work performed and parts used
- Equipment condition before and after maintenance
- Any unusual findings or concerns

Source: WorkTrek
Regular reporting helps management make informed decisions about equipment replacement and maintenance strategies. Monthly or quarterly reports should include:
- Equipment uptime and downtime statistics
- Cost of repairs and parts
- Trends in maintenance needs
Using digital tools for recording and reporting can improve data accuracy and make it easier to analyze maintenance performance over time.
Performance Evaluation and Improvement
Evaluating and improving maintenance performance is crucial for keeping operations running smoothly. Tracking key metrics, analyzing downtime, and implementing continuous improvement help boost efficiency and reliability.
Tracking Maintenance Metrics
Maintenance analytics in the form of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential for measuring and optimizing maintenance performance. Standard metrics include equipment uptime, mean time between failures, and maintenance costs.
Managers should track both leading and lagging indicators. Leading indicators predict future performance while lagging indicators show past results.
Key metrics to monitor:
- Equipment availability
- Planned vs unplanned maintenance
- Work order completion rate
- Spare parts inventory turnover
Regular review of these metrics helps identify trends and areas for improvement. Teams can use dashboards or reports to visualize data and spot issues quickly.
Analyzing and Addressing Downtime
Downtime analysis is critical for improving maintenance efficiency. Teams should track both planned and unplanned downtime and categorize reasons for equipment failures.
Steps to address downtime:w
- Collect detailed data on each incident
- Identify root causes using techniques like 5 Why analysis
- Develop action plans to prevent recurring issues
- Implement predictive maintenance where possible

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Trilio
Prioritize efforts on equipment that will have the highest impact on productivity. Cross-functional teams can collaborate to find innovative solutions to chronic problems.
Regular downtime review meetings help keep everyone focused on improvement goals. Teams should celebrate successes and learn from setbacks.
Continuous Improvement Process
Continuous improvement is vital for long-term maintenance success. It involves regularly reviewing and updating processes to adapt to changing needs and technologies.
Key elements of a continuous improvement process:
- Regular performance reviews
- Employee feedback and suggestions
- Benchmarking against industry best practices
- Training and skill development programs
Teams should set clear improvement goals and track progress over time. Small, incremental changes often lead to significant gains in efficiency and quality.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Manutan
Encourage a culture of innovation where staff feel empowered to suggest ideas. Pilot new approaches on a small scale before fully implementing them.
Technology can support improvement efforts through better data collection and analysis. Consider investing in maintenance management software to streamline processes.
Maintenance Optimization
Maintenance optimization improves efficiency, reduces costs, and extends equipment life. It focuses on using technology, streamlining workflows, and enhancing reliability.
Leveraging Technology and CMMS
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) play a key role in maintenance optimization. These systems help track equipment, schedule tasks, and manage resources.
CMMS software stores equipment data, maintenance history, and spare parts inventory. This information helps managers make better decisions about maintenance needs.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Flowdit
With CMMS, teams can set up automatic alerts for scheduled maintenance. This ensures tasks are done on time, reducing the risk of breakdowns.
Mobile apps linked to CMMS allow technicians to access information and update records in real-time, improving accuracy and speeding up work completion.
Streamlining Maintenance Workflows
Efficient workflows are crucial for optimizing maintenance processes. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) provide clear guidelines for maintenance tasks.
SOPs outline step-by-step instructions for each maintenance job. This helps ensure consistency and quality in work performed.
Prioritizing tasks based on equipment criticality is important. Teams should focus on high-priority items first to minimize downtime.
Cross-training staff allows for more flexible scheduling and ensures that critical tasks can always be completed, even if specific team members are unavailable.
Regular team meetings help identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. This ongoing feedback loop is essential for continuous optimization.
Extending Equipment Lifespan and Reliability
Planned Maintenance Optimization (PMO) strategies help extend equipment life and improve reliability. PMO involves analyzing maintenance data to create targeted maintenance plans.
Predictive maintenance techniques use sensors and data analysis to detect potential issues before they cause breakdowns. This approach can significantly reduce unexpected failures.
Regular inspections and preventive maintenance tasks keep equipment in good condition. Follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance schedules.
Proper lubrication, cleaning, and equipment calibration are simple yet effective ways to extend its lifespan. Train staff on these basic maintenance tasks.
Tracking and analyzing equipment performance data helps identify patterns and potential problems. This information guides decisions about repairs or replacements.
Documentation and Manuals
Good documentation and manuals are key to effective maintenance. They provide clear instructions, help with training, and keep everyone on the same page.
Creating Visual Aids and Flowcharts
Visual aids and flowcharts make complex procedures easier to understand. They break down tasks into simple steps. Use clear diagrams to show equipment parts and how they fit together.
Flowcharts help organize decision-making processes and guide workers through troubleshooting steps. Create charts for common problems and their solutions.
Use colors and symbols to highlight important points. Keep designs simple and easy to read. Test visuals with staff to ensure they are helpful.
Updating Manuals as per Manufacturer Recommendations
Manuals need regular updates to stay useful. Check for new info from equipment makers often. This keeps procedures safe and up-to-date.
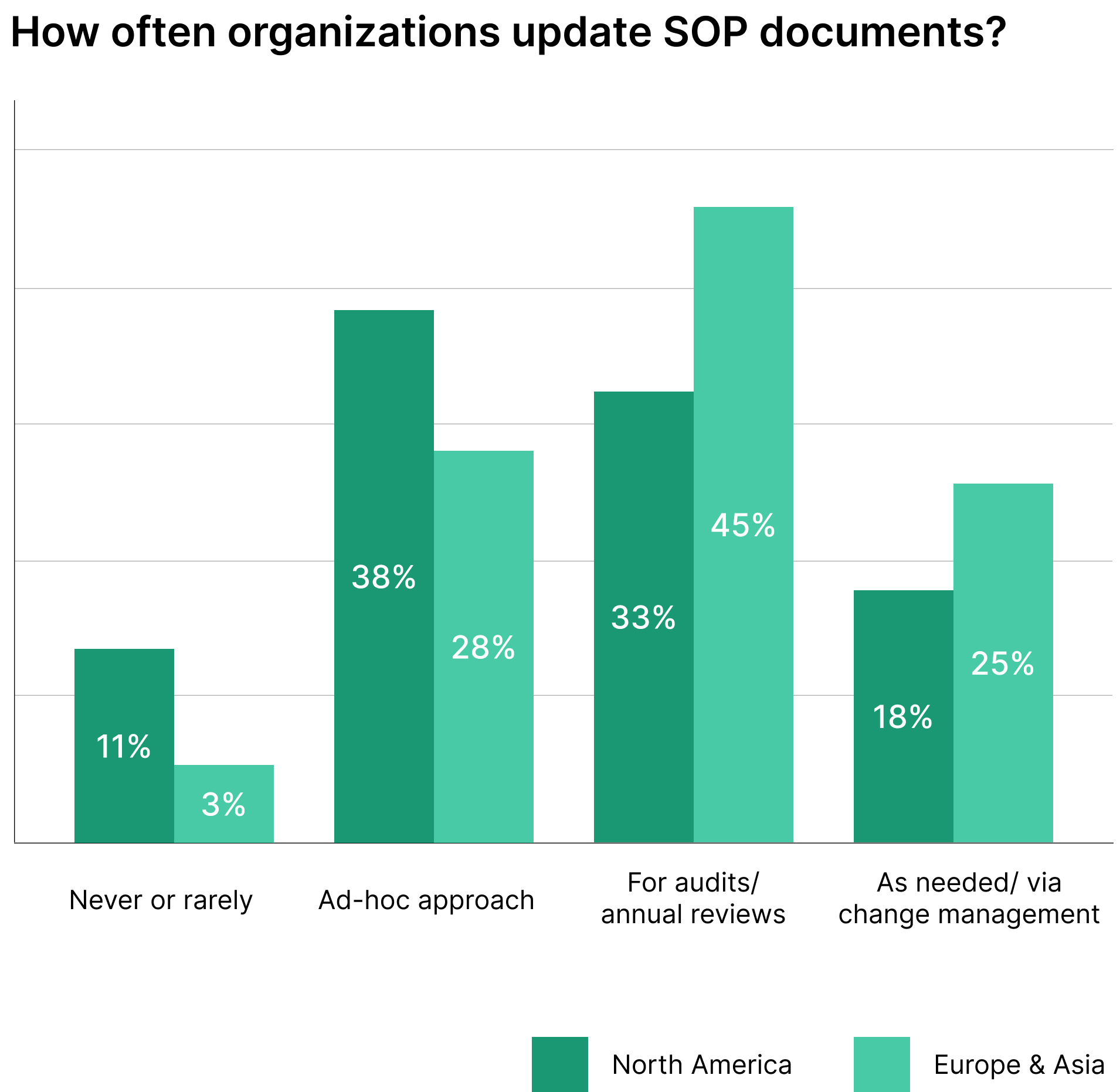 Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Infotech
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Infotech
Set a schedule to review manuals. Look for changes in:
- Safety guidelines
- Operating instructions
- Maintenance schedules
- Maintenance processes
- Emergency procedures
- Part numbers
Add notes about common issues found on-site. This will make the manuals more helpful for your team. Share updates with all staff quickly.
Document Control and Record Keeping
Good record-keeping is vital for maintenance. It helps track work done and plan future tasks. Set up a system to organize all documents.
Use a central database for easy access. Include:
- Equipment manuals
- Repair histories
- Inspection reports
- Safety procedures
Control who can edit documents. This keeps info accurate. Use version numbers to track changes.
Keep backup copies of all records. This protects against data loss. Train staff on how to use and update the system properly.