A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a software solution specifically designed to streamline maintenance processes and enhance asset management within an organization. Its primary function is to empower maintenance managers by enabling them to efficiently schedule, track, and analyze work orders, inventory, and maintenance tasks. By harnessing the capabilities of a CMMS, organizations can achieve several benefits, including minimizing downtime, prolonging the life of assets, optimizing labor resources, and overall improvement in maintenance operations.
A CMMS essentially serves as the central hub for maintenance and reliability programs, acting as a repository for crucial data. Maintenance teams leverage CMMS software to oversee their work and gain insights into machine health and reliability. It is particularly well-suited for managing industrial facilities where machine assets are critical for production.
CMMS software enhances the utilization, availability, and longevity of various assets, including equipment, machinery, fleets, infrastructures, facilities, and operations.
Modern CMMS solutions are typically cloud-based and offer cutting-edge features such as mobile CMMS applications, tools for regulatory compliance, and the ability to operate across multiple sites or languages. They can also seamlessly integrate with other applications, like ERP purchasing software, or access isolated production data from systems such as SCADA, PLC, and BMS.
Leading CMMS platforms can connect with condition monitoring sensors and software, enabling predictive maintenance.
The terms CMMS system, solution, platform, and software are interchangeable; they all refer to digital systems for effective maintenance management.
By adopting CMMS software, organizations can save time, simplify their work processes, prevent downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and bolster the reliability of their assets.

Maintenance: While no computer can replace skilled labor in completing maintenance tasks with speed, efficiency, and precision, a CMMS software system is invaluable for maintenance teams. It allows them to efficiently schedule work orders, manage parts and supplies inventories, and utilize data for informed maintenance decisions.
Computerized: In the digital age, most operations have transitioned to computers. It was only a matter of time before the traditional clipboard and pen were replaced by modern technology. Leading CMMS software providers facilitate the integration of previous hard-copy records into the computerized interface, ensuring that no data is lost during the transition to a computerized maintenance management software solution.
Management: A CMMS is pivotal in helping management plan, schedule, and report on maintenance work. It empowers leadership to create forecasts and provide insights into completions, compliance, audits, and other maintenance key performance indicators.
System: CMMS software does not aim to replace maintenance workers; instead, it complements existing practices and enhances the efficiency of labor completion. Software like eMaint CMMS seamlessly integrates with current maintenance processes, enabling users to customize features to suit their needs.
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software is a powerful tool that helps organizations efficiently manage their day-to-day maintenance operations while facilitating the integration of new maintenance solutions, such as condition monitoring.
Try WorkTrek CMMS 30 days for Free
How Such Software Operates
CMMS software performs a range of functions to enhance maintenance management. It acts as work order software, tracking maintenance orders and scheduling tasks, which is pivotal for maintenance teams in managing their workflows and reducing downtime. Furthermore, through seamless integrations with tools such as vibration sensors and condition monitoring devices, CMMS allows continuous monitoring of machine health and conditions, facilitating the implementation of condition-based maintenance strategies.
Key integrations of CMMS, like Enterprise Resource Planning software, enable maintenance teams to connect their operations with the purchasing and inventory functions used elsewhere within an organization. As modern organizational environments demand smooth collaboration between various business systems, a CMMS must communicate seamlessly with these systems.
Today’s maintenance managers turn to CMMS systems to improve maintenance programs, streamline processes, and enhance the tracking and analysis of maintenance Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). CMMS also enables the accurate documentation of maintenance activities, a crucial requirement for heavily regulated industries that undergo audits.
CMMS functions as a comprehensive database, supporting various functions across different teams. It offers visibility into inventory status, costs, supply contracting, and other maintenance operations, benefiting teams in operations, finance, and beyond.
CMMS software empowers organizations to manage and streamline a wide range of functions, including:
- Resources and labor allocation
- Asset lifecycle management
- Prioritization and scheduling of work orders
- Implementation of preventive maintenance
- Materials and inventory control
- Audits and compliance tracking
- Reporting and dashboarding for data analysis
- Mobile maintenance functionality for on-the-go management
- Condition monitoring for real-time health assessment
- Customized training and support
Book a free WorkTrek CMMS Demo
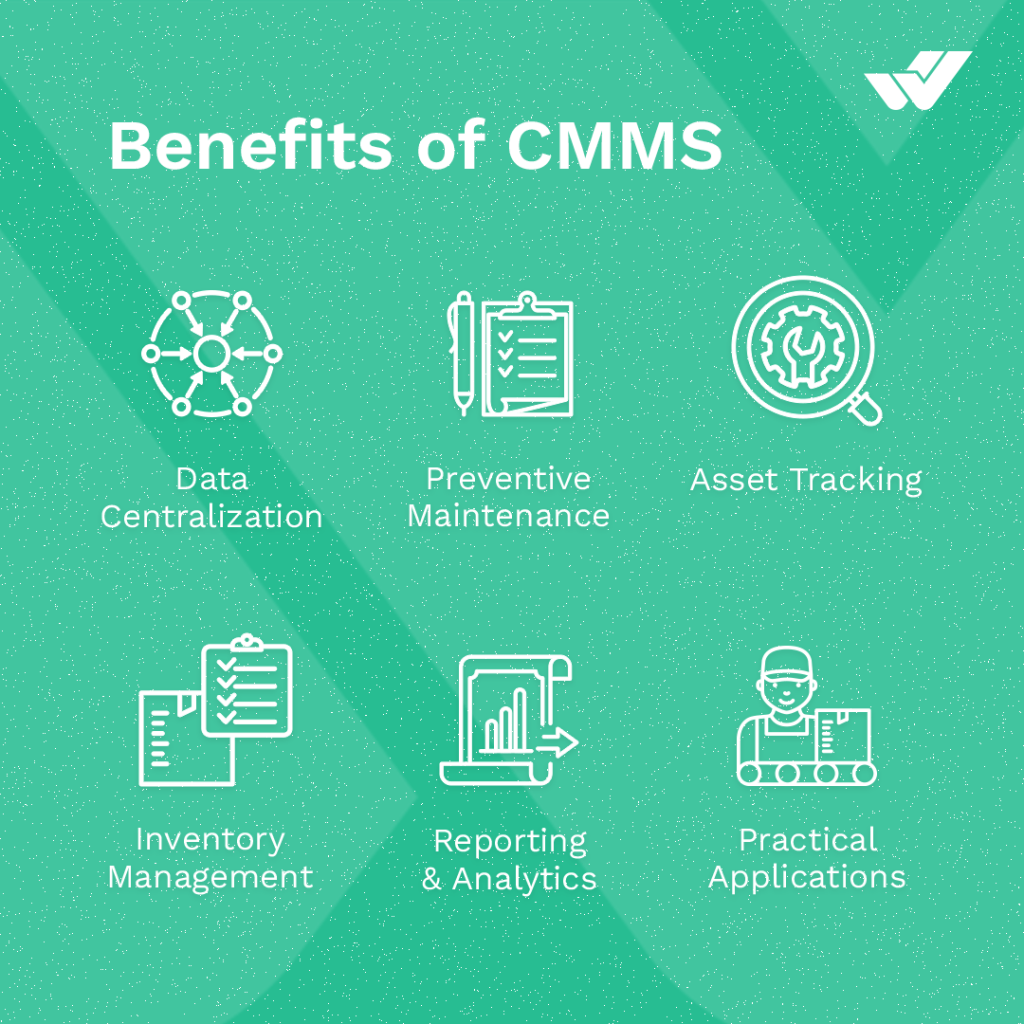
Benefits of Utilizing CMMS Software
Implementing CMMS software offers a plethora of efficiency and lifecycle advantages. It allows maintenance teams to align their practices and activities with other departments and broader business objectives. When a system facilitates the sharing of data across departments, everyone’s work becomes more efficient.
Some of the key benefits of CMMS software include:
- Healthy and Safe Environments:
A CMMS can enhance safety, health, and environmental compliance by global, national, state, or local regulations. Timely and proper maintenance reduces the likelihood of asset failures that could jeopardize workers’ well-being. CMMS software provides reports on incidents, defects, corrective action histories, and process change management. - Workflow Visibility and Work Order Management:
Work order software enables teams to visualize actions through dashboards and reports, allowing workers at all levels to assess the current status and improve work order completion rates. Maintenance teams can swiftly determine the asset’s location, required parts, and task assignments. - Mobile Workforce:
Managing field workers on the move can be challenging and costly, but advanced CMMS software offers robust mobility connectivity for users who seldom need to return to the office. With software that supports mobile workers, deploying teams remotely becomes seamless. - Automation and Process Enhancement:
Numerous processes are ideal for automation, including inventory reorders, shift scheduling, and work order assignments based on availability. Transitioning to a CMMS database enables the automation of these processes, resulting in time savings, reduced human error, and increased efficiency. - Asset Lifecycle Visibility:
CMMS software empowers teams to monitor and manage asset health and lifecycles from pre-installation planning and engineering to decommissioning. By clearly understanding assets’ active status, organizations can better plan, schedule, and execute work. - The Path to Prescriptive Maintenance:
The software assists teams in transitioning from reactive and preventive maintenance to a prescriptive maintenance strategy. Maintenance teams gain insight into asset health by integrating data from sensors, usage statistics, and more. Subsequently, the software can provide AI-enhanced analytics to determine the most appropriate actions and timing. - Regulatory Compliance and Audits:
Compliance regulations established by local, regional, state, national, and global organizations can make keeping up with audits challenging. However, it can ensure regulatory compliance and create the digital paper trail necessary for compliance audits to evaluate an organization’s adherence to all required standards. These standards encompass health and safety, IT, energy and environmental management, and quality management, among others, applicable across various industries.
Advantages of CMMS Software
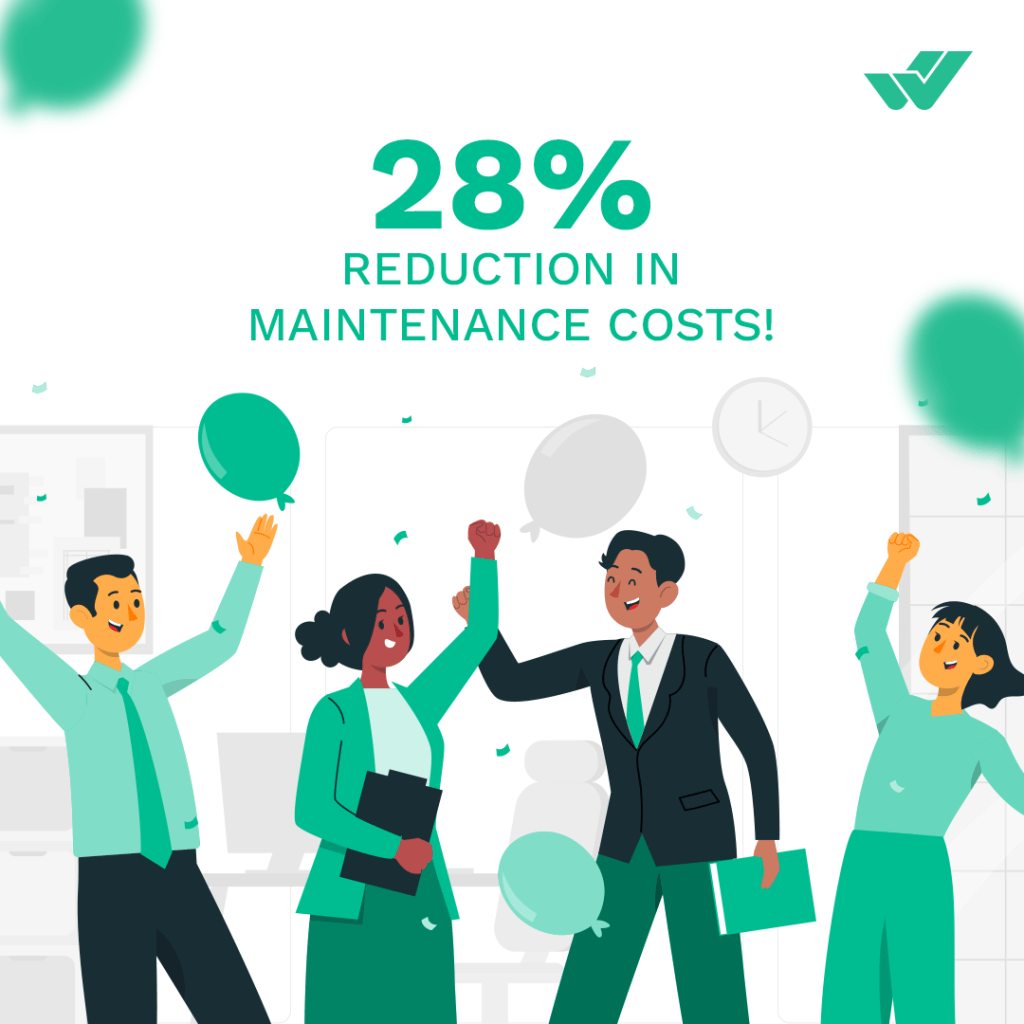
CMMS software offers numerous advantages for maintenance and reliability teams looking to save time, enhance efficiency, maximize uptime, and strengthen reliability. Integrating CMMS software doesn’t simply digitize maintenance management; when utilized effectively, it can significantly improve core Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), reduce maintenance costs, and boost production. In the era of AI, IIoT, and smart factories, such software is essential for streamlining and managing your maintenance team.
Here are some of the key advantages that maintenance programs using CMMS software have over the competition:
- Reduce downtime with preventive and predictive maintenance.
- Save time on management, organization, scheduling, data entry, and reporting.
- Increase overall reliability and extend equipment lifespan with asset management, tracking, and analysis.
- Ensure compliance with regulatory and safety standards through maintenance standardization across teams and worksites.
- Boost work order completion rates with efficient work order management.
- Track and reduce maintenance costs through integration with purchasing software.
- Monitor and enhance productivity while reducing labor costs through work order scheduling.
- Simplify reporting by tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and providing user-friendly reports and dashboards.
Common Features
Modern CMMS software typically encompasses the following capabilities:
- Work order management: Create, assign, and complete work orders and work requests.
- Asset management: Track assets, monitor their current status, and access detailed maintenance history.
- Preventive maintenance: Schedule recurring preventive maintenance for assets, including tasks, procedures, and required parts. Advanced platforms often offer interactive drag-and-drop calendars for simplified preventive maintenance planning.
- Parts and inventory management: Reserve spare parts for work orders and associate them with relevant assets. Keep an eye on inventory levels and receive alerts for reordering parts.
- Reporting and analytics: Generate reports on maintenance activities and establish dashboards to gain insight into key processes and KPIs.
- Mobile CMMS app: Manage maintenance tasks from mobile devices, covering work orders and part reservations. Premium apps may even support offline work that syncs later.
- Regulatory compliance: Easily construct audit dashboards to demonstrate compliance. Review and report on records stored in a comprehensive audit trail and secure key actions with electronic signatures.
- Integrations: Seamlessly integrate your software with core business software, ranging from SAP to Power BI, through API connections or low-code integration. Additionally, connect to SCADA and PLC systems to access condition data.
- Predictive maintenance: Connect with condition monitoring sensors and software to automate work orders based on condition data, evolving your strategy into predictive maintenance.
- Multi-site capabilities: Enterprise-friendly software allows you to manage multiple sites, standardize maintenance strategies, and facilitate global reporting. Multi-site CMMS platforms generally support multiple languages, time zones, and currencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the best CMMS software?
The best software supports training and deployment, offers customization options, and provides users with mobility. - What’s the difference between CMMS and EAM?
A computerized Maintenance Management System facilitates maintenance functions. At the same time, EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) is a broader strategy that often uses CMMS or other EAM software to plan, manage, and execute maintenance operations. - Who uses CMMS software?
Maintenance teams utilize software, including entry-level technicians, supervisors, and senior leadership or corporate owners. - How do I learn about CMMS?
Learning about a Computerized Maintenance Management System often begins with a discussion with sales experts who can assess your needs. With input on your requirements, sales teams can guide you in understanding the functions and features most crucial for your operations. - What kind of CMMS training is available?
The best software providers offer ongoing education and training. These sessions are tailored to your needs, showcasing a commitment to supporting your journey towards maintenance efficiency. - Can I get CMMS Certified?
Leading software providers often offer certification programs. These certifications help increase software adoption and usage and provide recognition and incentive for maintenance professionals.




