What is Drop Shipping?
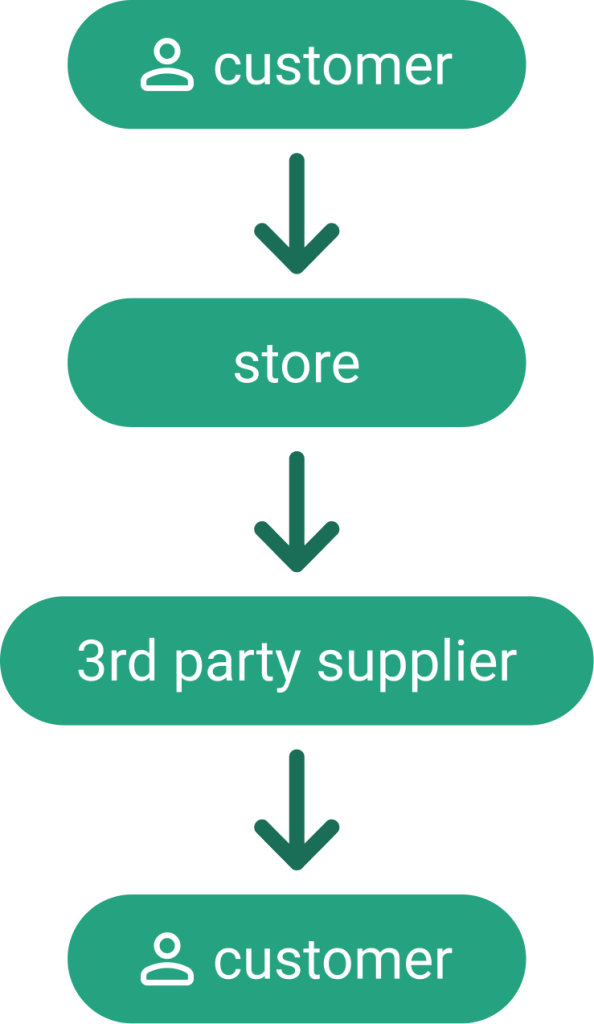
Drop shipping is a fulfillment method where a store does not keep the products it sells in the warehouse. Instead, when a customer orders, the store purchases the item from a third-party supplier, who then ships it directly to the customer.
The retailer acts as an intermediary, handling sales and customer service while outsourcing storage and shipping.
Drop shipping can eliminate physical inventory, making it a low-cost way to start an online store. Retailers do not have to worry about managing stock or handling fulfillment logistics, which reduces overhead costs. The main advantages of dropshipping include low startup costs, flexibility in product offerings, and minimal risk of overstocking or unsold inventory.
However, dropshipping has drawbacks, such as lower profit margins and less control over product quality and shipping times.
It is a popular model for e-commerce businesses looking to minimize upfront investment, focus on marketing, and offer a wide range of products.
Pros and Cons of Drop Shipping for Maintenance Organizations
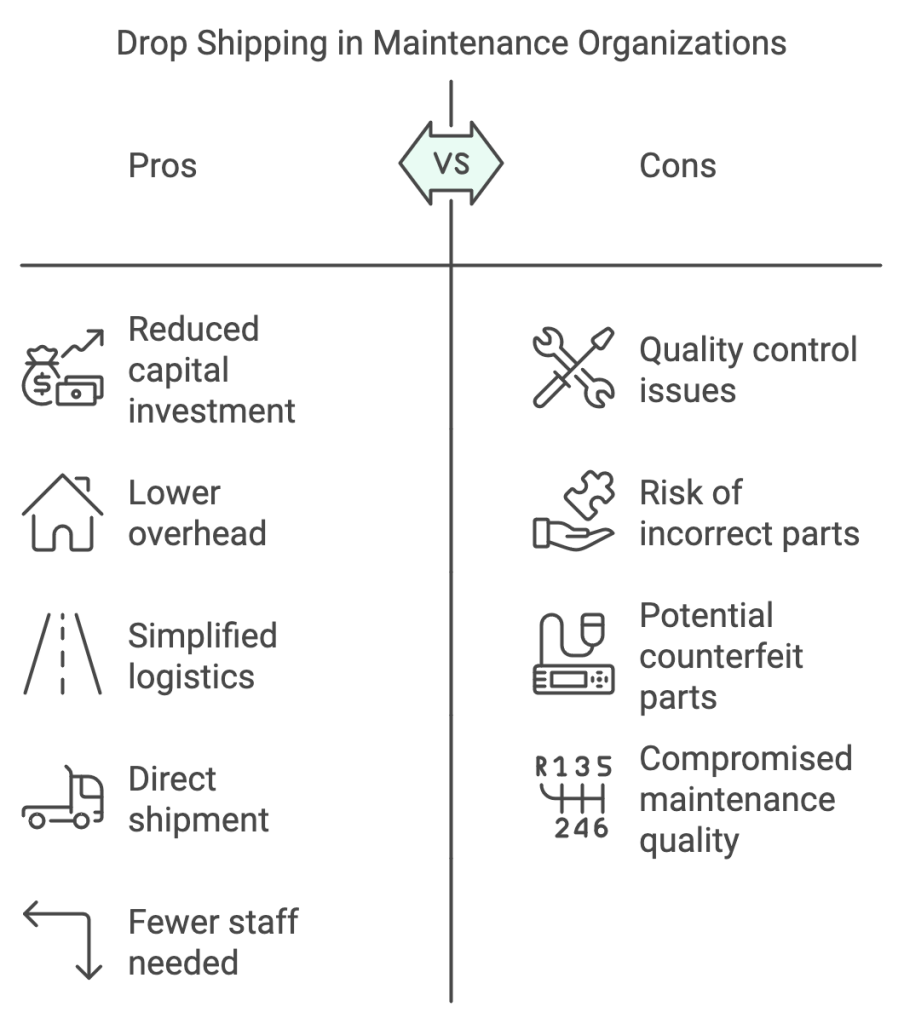
Drop shipping in maintenance organizations offers significant benefits but comes with notable challenges that need careful consideration.

From a financial perspective, drop shipping reduces capital investment by eliminating the need for warehouse space and inventory carrying costs. Organizations can operate with lower overhead and maintain financial flexibility since they’re not tied to large parts inventories that might become obsolete.
Operationally, the model simplifies logistics by enabling direct shipment to work sites and reducing the need for internal handling. This streamlines the procurement process and requires fewer staff to manage logistics operations.
However, quality control becomes more challenging as organizations cannot inspect parts before they reach the work site. This creates vulnerability to receiving incorrect or potentially counterfeit parts, compromising maintenance quality.
Time Management
Time management presents another significant challenge. The inability to maintain local stock can lead to longer wait times for parts, potentially extending equipment downtime. This is particularly problematic for emergency repairs or critical equipment failures where immediate access to parts is essential.
Heavy reliance on suppliers increases business risk. Organizations become vulnerable to supplier stockouts and shipping delays and have less negotiating power on individual orders. The returns process becomes more complex when parts must be replaced or exchanged.

Hybrid Model
A practical approach for maintenance organizations is to implement a hybrid model. This involves maintaining the stock of critical spares while using drop shipping for predictable maintenance items. This balance helps mitigate risks while still capturing the financial benefits of drop shipping for appropriate items.
Success with drop shipping requires robust supplier relationships, clear service level agreements, and strong integration between ordering systems and maintenance management software. Organizations should also maintain relationships with local suppliers as a backup for emergencies.
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



