What is Maintenance SOP?
A Maintenance Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is a detailed, written document that establishes the steps to perform specific maintenance tasks consistently and safely. Maintenance standard operating procedures are essential written instructions that guide maintenance workers in performing their tasks efficiently and effectively.
Think of it as a carefully crafted recipe book for maintenance activities, where each “recipe” ensures that work is performed the same way every time, regardless of who performs it.
Definition and Importance
Standard operating procedures (SOPs) for maintenance are detailed, with written instructions outlining the steps to perform specific maintenance tasks. These procedures ensure consistency, efficiency, and safety in maintenance operations.
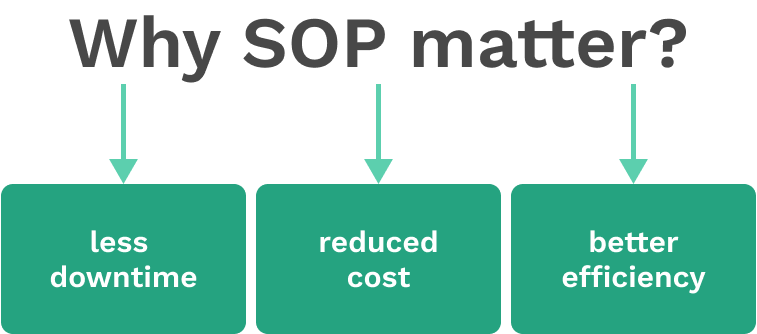
By following SOPs, maintenance teams can minimize the risk of equipment failure or downtime, reduce costs, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
Think of maintenance SOPs as the backbone of a well-oiled machine. They provide a clear roadmap for maintenance personnel, ensuring every task is performed correctly and consistently. This helps maintain equipment reliability and optimizes maintenance teams’ performance.
The core components of a maintenance SOP
Purpose and Scope
This section clearly defines what the procedure accomplishes and when it should be used for routine maintenance tasks.
For example, an SOP for maintaining a commercial air conditioning system would specify that it covers routine maintenance, filter changes, and basic troubleshooting but might exclude major repairs requiring specialized certification.
Safety Requirements
Before diving into the actual procedure, SOPs detail all necessary safety precautions. This includes required personal protective equipment (PPE), safety equipment, lockout/tagout procedures, and specific safety protocols. Consider how an SOP for electrical equipment maintenance would first require verification that power is disconnected and proper insulating equipment is worn.
Required Tools and Materials
Much like a recipe lists ingredients before the cooking steps, an SOP lists every tool, part, and material needed before work begins. This prevents situations where technicians must interrupt work to fetch missing items, which can compromise safety and efficiency.
Step-by-Step Instructions
The heart of the SOP provides detailed, sequential instructions written in clear, actionable language. Each step should be specific enough for someone with appropriate training to follow it without additional guidance.
For instance, rather than saying, “Check the belt,” an SOP might specify, “Inspect the drive belt for signs of wear, cracking, or misalignment, belt deflection should not exceed 1/4 inch when pressed with 5 pounds of force.”
Quality Control Measures
SOPs include checkpoints and verification steps to ensure work meets required standards. This might involve specific measurements, testing procedures, or inspection criteria.
For example, after bearing replacement, an SOP might require temperature monitoring during the first hour of operation.
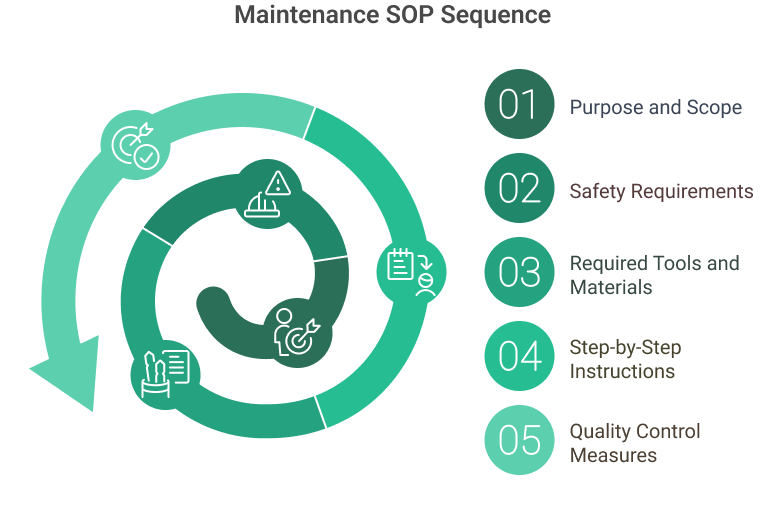
Documentation Requirements
The SOP specifies what information must be recorded, where it should be logged, and who needs to sign off on the work. This creates an audit trail and helps track maintenance history. Proper documentation is also crucial for ensuring regulatory compliance.
The process of developing effective maintenance SOPs involves:
- Initial Assessment: Analyze the maintenance task, identifying critical steps, potential risks, and required expertise levels. This often involves consulting experienced technicians who understand the nuances of the work.
- Documentation Creation: Write the procedure using a standardized format in clear, concise language. Include diagrams, photos, or illustrations where they add clarity. For instance, a diagram showing the torque sequence for bolts is clearer than written instructions alone.
- Review and Validation: Before implementation, have multiple qualified individuals, including supervisors and frontline technicians, review the SOP. This helps identify potential gaps or unclear instructions.
- Testing: Conduct a trial run of the SOP under controlled conditions, observing whether technicians can follow it effectively. This real-world testing often reveals necessary adjustments.
- Implementation: Roll out the SOP through proper training and ensure all necessary resources are available. This might include creating quick-reference guides or checklists derived from the full SOP.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update SOPs based on feedback, technological changes, or identified inefficiencies. For example, if technicians consistently find a better way to perform a step, the SOP should reflect this improvement.
Benefits of Maintenance SOPs
Implementing maintenance SOPs can bring numerous benefits to an organization, including:
Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Maintenance SOPs streamline maintenance processes, reducing the time and effort required to complete tasks.
By following standardized procedures, maintenance teams can work more efficiently, complete tasks faster, and minimize downtime. This, in turn, can lead to increased productivity and improved overall operational efficiency.
For example, consider a manufacturing plant with maintenance SOPs for routine equipment checks. These SOPs ensure that maintenance technicians follow the steps and use the right tools and materials, which can help reduce equipment downtime.
As a result, tasks are completed more quickly, and the likelihood of errors is minimized. This boosts the maintenance team’s productivity and ensures the equipment remains in optimal working condition, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns.
Enhanced Safety and Compliance
Maintenance SOPs ensure safety and compliance in maintenance operations. By outlining specific safety procedures and protocols, SOPs can help prevent accidents and injuries and reduce the risk of regulatory non-compliance.
Additionally, SOPs can help organizations comply with industry standards and regulations, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
For instance, an SOP for electrical maintenance might include detailed safety procedures such as lockout/tagout protocols and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
By adhering to these safety procedures, maintenance personnel can avoid potential safety hazards and ensure a safe working environment.

Moreover, compliance with regulatory requirements is maintained, safeguarding the organization from legal and financial repercussions.
How to Implement Maintenance SOP
Technology Integration
Modern maintenance management systems can incorporate SOPs into digital workflows, making them easily accessible on mobile devices and enabling real-time documentation.
Training Requirements
Develop training programs that ensure maintenance staff understand the steps and reasoning behind them. This deeper understanding leads to better compliance and problem-solving ability.
Compliance Tracking
Establish methods to verify that SOPs are being followed consistently. This might include supervisor oversight, quality checks, or automated monitoring systems.
Emergency Procedures
Include clear instructions for handling unexpected situations or complications during maintenance tasks. This helps maintenance staff respond appropriately to unusual circumstances while maintaining safety and quality standards.
Assigning Roles and Responsibilities
Assigning clear roles and responsibilities is essential for effective maintenance SOP implementation. By defining specific tasks and responsibilities, organizations can ensure that maintenance teams know their duties and can work together seamlessly to complete tasks.
This can help reduce confusion, improve communication, and enhance maintenance efficiency.
In maintenance operations, assigning roles and responsibilities involves:
- Identifying specific maintenance tasks and procedures
- Defining the roles and responsibilities of maintenance personnel
- Establishing clear lines of communication and authority
- Providing training and support to ensure that maintenance teams are equipped to perform their duties effectively
For example, in a facility with a comprehensive maintenance SOP for HVAC systems, roles might be assigned as follows: one technician is responsible for filter changes, another for coil cleaning, and a third for belt inspections.
By clearly defining these roles, the maintenance team can work more efficiently and ensure that all preventive maintenance tasks are completed on schedule.
This enhances maintenance efficiency and ensures that the equipment operates reliably and safely.
By assigning clear roles and responsibilities, organizations can ensure that maintenance SOPs are implemented effectively and that maintenance operations are carried out safely, efficiently, and in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Types of Maintenance SOP
Let me explain the different types of maintenance SOPs that organizations typically develop and implement. These procedures form the backbone of an effective maintenance program.
Equipment-Specific Maintenance SOPs
These are the most common maintenance SOPs, focusing on individual equipment or machinery. For example, a manufacturing facility might have specific SOPs for each CNC machine, detailing daily startup procedures, routine maintenance checks, and shutdown protocols.
These SOPs account for the unique characteristics and requirements of each piece of equipment, much like how different vehicles require different maintenance approaches despite all being forms of transportation.
Safety and Emergency SOPs
These procedures focus specifically on maintaining safety systems and responding to maintenance-related emergencies. Think of these as your emergency response playbook.
For instance, a chemical plant would have detailed SOPs for maintaining emergency shower stations, including weekly testing requirements, water temperature verification, and proper inspection documentation. They also include procedures for responding to equipment failures that could create hazardous conditions.
Preventive Maintenance SOPs
These procedures outline scheduled maintenance activities designed to prevent breakdowns before they occur. Consider them like a health checkup schedule for your equipment.
A building’s HVAC system might have preventive maintenance SOPs that specify quarterly filter changes, annual coil cleaning, and bi-annual belt inspections.
These SOPs typically include detailed inspection checklists and condition assessment criteria.
Predictive Maintenance SOPs
These are more sophisticated procedures that guide the use of monitoring equipment and analysis of performance data.
For example, a power generation facility might have SOPs for conducting vibration analysis on turbines, including specific procedures for sensor placement, data collection intervals, and interpretation of results.
These SOPs often incorporate technology-driven elements like infrared cameras or ultrasonic testing equipment.
Corrective Maintenance SOPs
These procedures guide repairs when equipment fails or malfunctions. They’re like your repair manual but with much more detail.
For instance, a packaging line might have specific SOPs for addressing common issues like seal failures or belt misalignment, including troubleshooting steps, repair procedures, and post-repair testing requirements.
Calibration and Testing SOPs
These procedures ensure the accuracy of measuring and testing equipment. In a quality control laboratory, for instance, these SOPs would detail how to calibrate scales, spectrometers, and other precision instruments, including the frequency of calibration, acceptable tolerance ranges, and documentation requirements.
Documentation and Record-Keeping SOPs
These procedures govern how maintenance activities are recorded and tracked. They ensure consistency in record-keeping across all maintenance activities, much like accounting procedures ensure consistent financial record-keeping.
These SOPs specify what information must be recorded, where it should be stored, and how long records must be maintained.
Training and Certification SOPs
These procedures outline how maintenance personnel should be trained and certified for specific maintenance tasks.
For example, an aerospace manufacturer might have SOPs detailing the training required before technicians can perform maintenance on critical components, including classroom instruction, hands-on practice, and competency verification requirements.
Environmental Compliance SOPs
These procedures ensure maintenance activities meet environmental regulations. A manufacturing facility might have specific SOPs for maintaining pollution control equipment, including guidelines for filter changes, emissions monitoring, and proper disposal of maintenance waste.
Quality Assurance SOPs
These procedures verify that maintenance work meets quality standards. They’re similar to quality control in manufacturing but focused on maintenance activities.
For instance, after replacing bearings in a critical pump, the SOP might require vibration testing, temperature monitoring, and performance verification before returning the equipment to service.
What should be included in a maintenance SOP?
Each type of maintenance SOP should include:
- Clear scope and applicability statements
- Required qualifications for personnel performing the work
- Detailed lists of necessary tools and materials
- Step-by-step procedures with appropriate detail level
- Quality control checkpoints and acceptance criteria
- Documentation requirements
- References to related procedures and supporting documents
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



