What is DFMEA?
In maintenance organizations, Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (DFMEA) is a structured approach for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential failures during the design phase.
DFMEA is designed to proactively address weaknesses before production or deployment. The goal is to ensure that designs are reliable, safe, and easy to maintain.
Eliminating design flaws is particularly valuable for organizations seeking to reduce downtime, extend asset life, and improve operational efficiency. Many design flaws could eventually become maintenance headaches if not implemented in the design process.
So, how does it all work? The process starts by identifying potential failure modes. That is followed by a detailed evaluation of each failure’s effects on overall performance, safety, and maintenance.
This is followed by assigning a Risk Priority Number (RPN) based on the failure’s severity, occurrence, and detection. This process is designed to help organizations prioritize high-risk issues that require immediate attention.
Benefits to Maintenance Organizations
Maintenance organizations benefit from DFMEA by ensuring asset designers don’t forget maintenance issues when designing products.
For instance, components prone to wear can be made more accessible for service technicians. They can be designed so that technicians don’t have to disassemble much of the equipment to get to them.
Additionally, designers can improve maintenance performance by directly implementing sensors and diagnostics equipment in their design philosophy.
DFMEA also helps minimize maintenance costs by reducing the frequency and complexity of repairs, enhancing maintainability.
Creating an Action Plan
One additional outcome of DFMEA is creating a corrective action plan to address potential design flaws. This should be done before equipment is commissioned.
This approach reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures and ensures that maintenance teams can perform tasks efficiently when issues arise.
DFMEA also promotes continuous improvement by providing a framework for reviewing and refining designs over time.
Overall, DFMEA helps maintenance organizations integrate reliability and maintainability into the design process. This can help reduce asset downtime and ensure long-term performance.
This proactive approach ultimately leads to safer, more efficient operations and lower lifecycle costs.
What are the benefits of DFMEA?
DFMEA (Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a proactive risk management tool used to identify and assess potential failure modes in a product or process design and to develop strategies for mitigating or eliminating those risks. Implementing DFMEA can provide several significant benefits for organizations, including:
- Early Identification of Potential Failures:
- DFMEA helps identify potential failure modes early in the design process when changes are easier and less expensive. By considering potential failures upfront, teams can design more robust and reliable products and processes.
- Reduced Product Development Costs:
- By catching and addressing potential issues early, DFMEA can help reduce the need for costly design changes and rework later in the development process. DFMEA can also help optimize designs for manufacturability, reducing production costs and improving quality.
- Improved Product Quality and Reliability:
- DFMEA helps teams focus on the most critical potential failure modes and develop targeted strategies for preventing or mitigating those failures. By systematically addressing potential failures, DFMEA can help improve overall product quality and reliability, reducing warranty claims and customer complaints.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:
- DFMEA can help improve customer satisfaction and loyalty by delivering more reliable products better suited to customer needs. It can also help teams anticipate and address potential customer use scenarios, reducing the risk of product misuse or dissatisfaction.
- Compliance with Standards and Regulations:
- DFMEA can help organizations demonstrate compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949. By documenting the risk management process and the actions taken to address potential failures, DFMEA provides a robust audit trail and evidence of due diligence
- Improved Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- DFMEA typically involves a cross-functional team of experts from design, engineering, manufacturing, quality, and other disciplines. DFMEA can foster better organizational communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing by bringing diverse perspectives and expertise together.
- Knowledge Capture and Continuous Improvement:
- DFMEA provides a structured framework for capturing and documenting knowledge about potential failure modes and effective mitigation strategies. This knowledge can be leveraged for future product development efforts, enabling continuous improvement and organizational learning.
- Reduced Warranty and Liability Costs:
- By identifying and addressing potential failures early, DFMEA can help reduce the risk of product defects and failures in the field. This can significantly reduce warranty claims, product recalls, and potential liability costs.
- Improved Resource Allocation:
- By prioritizing potential failure modes based on their risk and potential impact, DFMEA helps teams allocate resources more effectively. This ensures that the most critical risks are addressed first and resources are not wasted on low-priority or low-impact issues.
- Enhanced Stakeholder Confidence:
- By demonstrating a robust and proactive approach to risk management, DFMEA can help build confidence among key stakeholders, such as customers, regulators, and investors. This can lead to improved relationships, increased business opportunities, and a stronger reputation in the market.
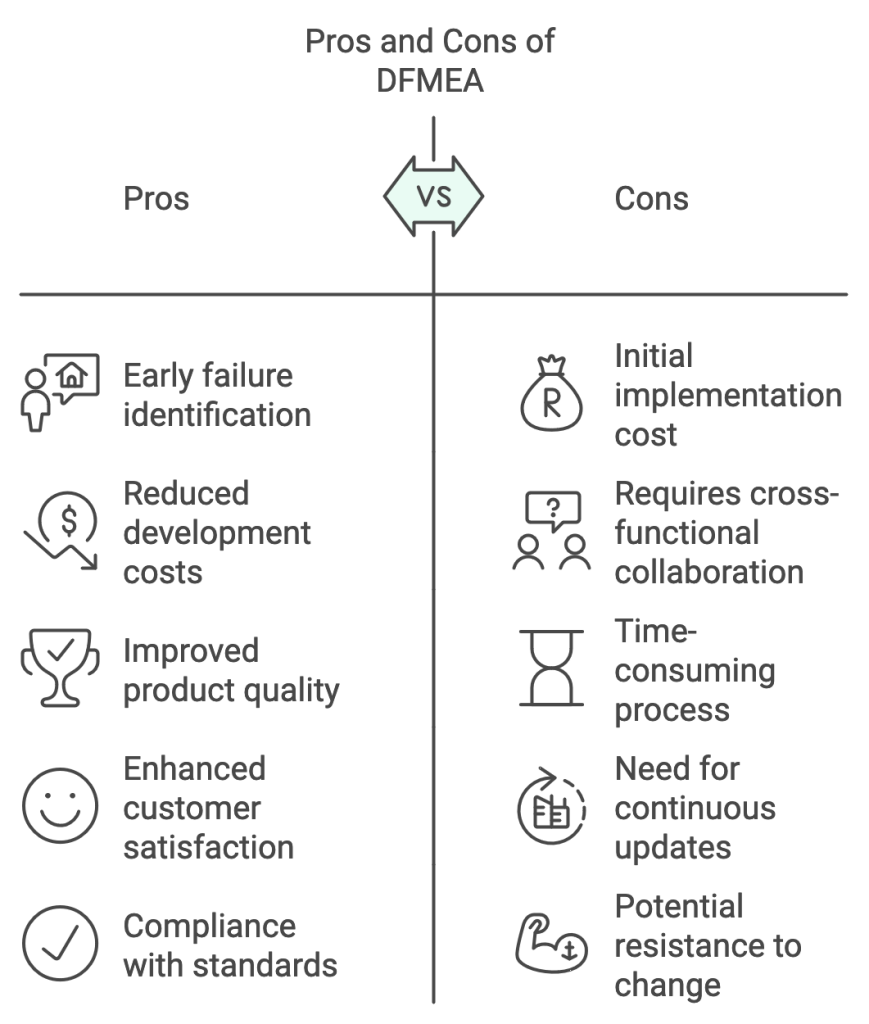
While implementing DFMEA does require an investment of time and resources, the long-term benefits can be substantial. By making DFMEA an integral part of their product development and risk management processes, organizations can improve product quality, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction, ultimately driving better business performance and competitiveness.
Tools to help implement DFMEA
Organizations can use various tools to support implementing DFMEA (Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) in their maintenance operations. These tools can help streamline the DFMEA process, facilitate collaboration among team members, and provide a centralized repository for DFMEA data and documentation. Some common tools used for DFMEA implementation include:
- Spreadsheet Software: Basic spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets can be used to create and manage DFMEA templates. These tools allow teams to input failure modes, effects, causes, and risk rankings and perform basic calculations such as Risk Priority Number (RPN). However, spreadsheets can become cumbersome for complex systems or large teams.
- Dedicated DFMEA Software: There are specialized software packages designed specifically for DFMEA, such as:
These tools provide a more structured and user-friendly interface for conducting DFMEAs, with features like built-in libraries of failure modes and effects, customizable templates, and automated RPN calculations. They also often include capabilities for generating reports and visualizations.
- Quality Management Software: Many quality management software platforms, such as ETQ Reliance, MasterControl Quality Excellence, and Intellect eQMS, include modules for FMEA. These tools allow organizations to integrate DFMEA into their overall quality management processes and provide a centralized platform for managing DFMEA data alongside other quality-related information.
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) Software: PLM software, such as PTC Windchill, Siemens Teamcenter, and Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE, often include FMEA capabilities as part of their product development and manufacturing process management features. These tools can help integrate DFMEA into the broader product lifecycle and facilitate collaboration between design, engineering, and maintenance teams.
- Maintenance Management Software: Some Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) software, such as WorkTrek, include features for conducting FMEAs on maintainable assets. These tools can help integrate DFMEA results into maintenance planning and scheduling processes.
- Collaboration and Project Management Tools: General collaboration and project management tools, such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, Asana, or Trello, can support the DFMEA process by facilitating communication and task management among team members. These tools can help ensure that DFMEA activities are coordinated and that all team members can access the latest information.
When selecting tools for DFMEA implementation, organizations should consider factors such as:
- Ease of use and learning curve for team members
- Integration with existing maintenance and quality management systems
- Scalability and ability to handle complex systems and large teams
- Customization options for templates, failure mode libraries, and risk ranking criteria
- Reporting and visualization capabilities
- Collaboration and communication features
- Data security and access control
- Cost and licensing models
Ultimately, the choice of tools will depend on the organization’s specific needs, existing technology infrastructure, and the scope and complexity of their DFMEA implementation. By selecting the right tools and ensuring that team members are properly trained, organizations can effectively support the implementation of DFMEA in their maintenance operations and drive continuous improvement in asset reliability and performance.
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



