What is a Work Request?
A maintenance work request is the formal initiation mechanism within maintenance management systems. It is the critical first step that triggers the entire maintenance workflow.
It is a formal document submitted to a maintenance team indicating tasks requiring attention and resolution. It is a crucial step in the maintenance workflow, as it helps identify the work needed and ensures that it is properly documented.
More than just a simple notification, a work request creates a documented trail that captures the essence of an issue requiring attention, establishes accountability for both the requester and responder, and provides the foundation for all subsequent maintenance actions.
Work requests serve important contextual information that maintenance teams require to address issues effectively. They capture the nature of the problem, its location, the affected assets, the impact on operations, and the urgency of resolution.
This comprehensive documentation allows maintenance personnel to arrive prepared with the appropriate tools, parts, and expertise. The level of detail often determines how efficiently the subsequent maintenance activities will proceed.
Core Components of a Work Request
At its core, a work request form represents the translation of an observed deficiency into an actionable maintenance task. When equipment malfunctions, facilities deteriorate, or systems underperform, the work request transforms these problems from informal observations into formally recognized issues within the maintenance ecosystem. This documentation process ensures that maintenance needs don’t remain as fleeting observations but become persistent records that demand resolution.
A typical work request includes:
- Requester information (name, department, contact details)
- Date and time of submission
- Location of the issue or work needed
- Asset or equipment identification
- Description of the problem or work required
- Priority levels or urgency
- Requested completion date
- Any supporting documentation (photos, manuals, etc.)

Source: WorkTrek.com
Key Elements of an Effective Work Request
An effective work request typically includes five key elements: issue description, maintenance needs, priority level, location, and budget. These elements contribute to a work request that communicates an issue and identifies the maintenance needs created by that issue.
The more detailed the documentation, the more likely the operations manager will approve the maintenance request. A well-structured work request helps prevent misunderstandings and miscommunication between maintenance personnel and other stakeholders.
Types of Work Requests
Work requests can be categorized in several ways, each serving different maintenance needs. Maintenance tasks are crucial for tracking efficiency and departmental costs and should be prioritized based on urgency and type of request.
By Service Type
- Corrective Maintenance Requests: These address equipment or facility failures that have already occurred, such as a broken HVAC unit, malfunctioning production machine, leaking pipe, or snow removal.
- Preventive Maintenance Requests: These are scheduled maintenance activities to prevent breakdowns before they occur. They’re typically generated automatically based on time intervals, meter readings, or condition monitoring.
- Emergency Maintenance Requests: These high-priority requests require immediate attention due to safety concerns, production stoppage, or potential for significant damage.
- Modification or Improvement Requests: These involve changes or upgrades to existing equipment or facilities to enhance performance, efficiency, or functionality.
- Compliance or Regulatory Maintenance: These activities must meet industry regulations, safety standards, or legal requirements.

Source: WorkTrek.com
By Origination Method
- User-Initiated Requests: Submitted by employees, tenants, or facility users who notice an issue or need.
- System-Generated Requests: Automatically created by the CMMS based on predetermined schedules or IoT sensor data indicating a potential issue.
- Inspection-Generated Requests: Created following routine inspections that identify maintenance needs.
By Priority Level
- Critical/Emergency: Requires immediate attention (within hours)
- High: Should be addressed within 24-48 hours
- Medium: Should be addressed within one week
- Low: Can be scheduled during routine maintenance
Categorizing work requests by priority levels helps manage and prioritize tasks based on their impact on an organization’s financial health, stakeholder safety, and operational continuity.
Organizational Work Requests
From an organizational perspective, work requests establish clear lines of communication between those who identify maintenance needs and those responsible for addressing them. This formalized communication channel prevents maintenance requirements from being lost in casual conversations or email threads.
It creates a standardized approach for requesting maintenance assistance that works consistently across departments and facilities. Additionally, tracking work requests back to departments aids in properly allocating costs and contributes to more accurate end-of-year financial assessments.
The Role of the Maintenance Department
The maintenance department maintains facilities, grounds, equipment, vehicles, and other assets. Maintenance workers are skilled in various areas, including routine cleaning and preventive maintenance.
The maintenance department supports various customer needs, which can add to regular, scheduled work. Maintenance must operate with a clear workflow to manage and validate tasks effectively.
Evolution of Work Requests
In modern maintenance management, work requests have evolved from paper forms to sophisticated digital records that integrate with enterprise systems. They now serve as nodes in a complex network of maintenance information that connects to inventory systems, procurement processes, financial tracking, and regulatory compliance.
This integration allows maintenance activities to be viewed not as isolated tasks but as integral components of organizational operations with measurable impacts on productivity, safety, and financial performance. Utilizing a CMMS helps handle work requests, ensuring a streamlined and efficient workflow.
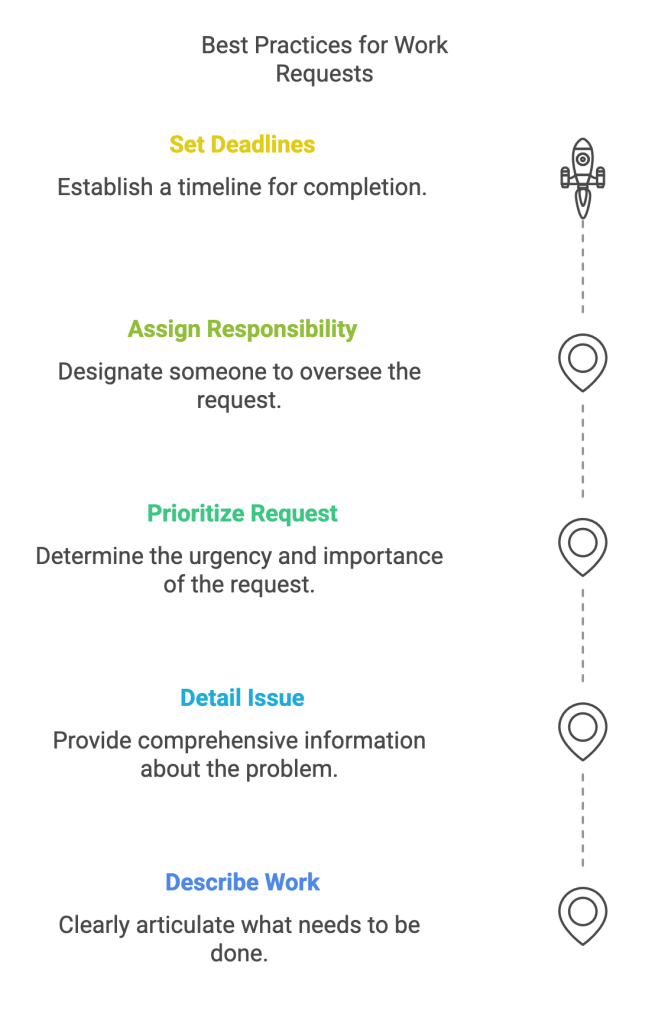
Best Practices for Creating Work Requests
Using the following best practices can help ensure that work requests are approved and completed quickly:
- Clearly describe the needed work
- Provide detailed information about the issue
- Prioritize the request
- Assign a responsible person to follow up on the request
- Set deadlines for completion
Source: WorkTrek.com
Best practices can help streamline the work request process and improve organizational efficiency. It is also important to use a work request form that includes all the necessary fields, such as request field, location field, priority level field, budget estimate field, department field, and date field.
Common Challenges in the Maintenance Process
One of the common challenges in the maintenance process is the confusion between work requests and work orders. A work request is not a work order but a pre-creation stage that signals a fault or anomaly.
In contrast, a work order represents the step following the issue of a request for intervention, through which the request is taken on board by organizing the intervention. Another challenge is the mismanagement of work orders, which can lead to severe disorganization.
CMMS software like WorkTrek can help streamline and automate the work request process, improve organizational processes, and ensure a safe, productive, and well-maintained work environment.
Work Requests in CMMS
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) significantly enhances the work request process through:
- Streamlined submission: Users can easily submit work requests through a user-friendly interface.
- Improved tracking: All requests are logged and tracked, ensuring nothing falls through the cracks.
- Enhanced communication: Maintenance teams receive instant notifications for quicker response times.
Additionally, maintenance technicians can incorporate budget estimates in request documents, which facilitates maintenance planning and aids in managing accounting and finance records.
Creation and Submission
CMMS platforms provide user-friendly interfaces for submitting work requests through:
- Web portals accessible to all employees
- Mobile applications with photo/video upload capabilities
- QR code scanning for specific equipment
- Integration with IoT sensors for automatic request generation
For example, a facility user might scan a QR code on a problematic piece of equipment, which opens a pre-populated work request form on their mobile device. They can add details, attach photos of the issue, and submit it directly to maintenance.

Tracking and Management
Once in the CMMS, work requests follow a structured lifecycle:
- Submission: The requester creates and submits the work request
- Review/Approval: Maintenance supervisors review the request for completeness and validity
- Prioritization: The request is assigned a priority level based on urgency and impact
- Work Order Creation: Approved requests are converted into formal work orders
- Scheduling: Resources (personnel, parts, tools) are allocated, and the work is scheduled
- Execution: The maintenance team performs the required work
- Completion and Feedback: The work is marked complete, and the requester may be notified
It is common for novice maintenance workers to confuse work requests with work orders, emphasizing the distinct roles each plays in maintenance processes.
Data Reporting and Analysis
CMMS systems can generate valuable insights from work request data:
- Mean time between failures for specific equipment
- Common failure modes or maintenance issues
- Departments or areas generating the most maintenance requests
- Average response and resolution times
- Maintenance backlog analysis
- Resource utilization metrics
For instance, a CMMS might reveal that 60% of emergency work requests involve a particular production line, indicating a need for more intensive preventive maintenance or potential equipment replacement.
Integration with Other Systems
Modern CMMS platforms often integrate work requests with:
- Inventory management systems to check parts availability
- Procurement systems for ordering needed materials
- Human resources systems for labor allocation
- ERP systems for cost accounting and financial impacts
- Building management systems for automated monitoring
This integration provides a comprehensive view of maintenance operations and their impact on the organization.
By implementing a work request system within a CMMS, organizations can transform reactive maintenance practices into proactive, data-driven maintenance management that improves asset reliability, extends equipment life, and optimizes maintenance resources.
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



