Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeSmart maintenance is changing how companies maintain their equipment and facilities. This approach uses data and technology to prevent problems before they happen rather than fixing things only when they break down.
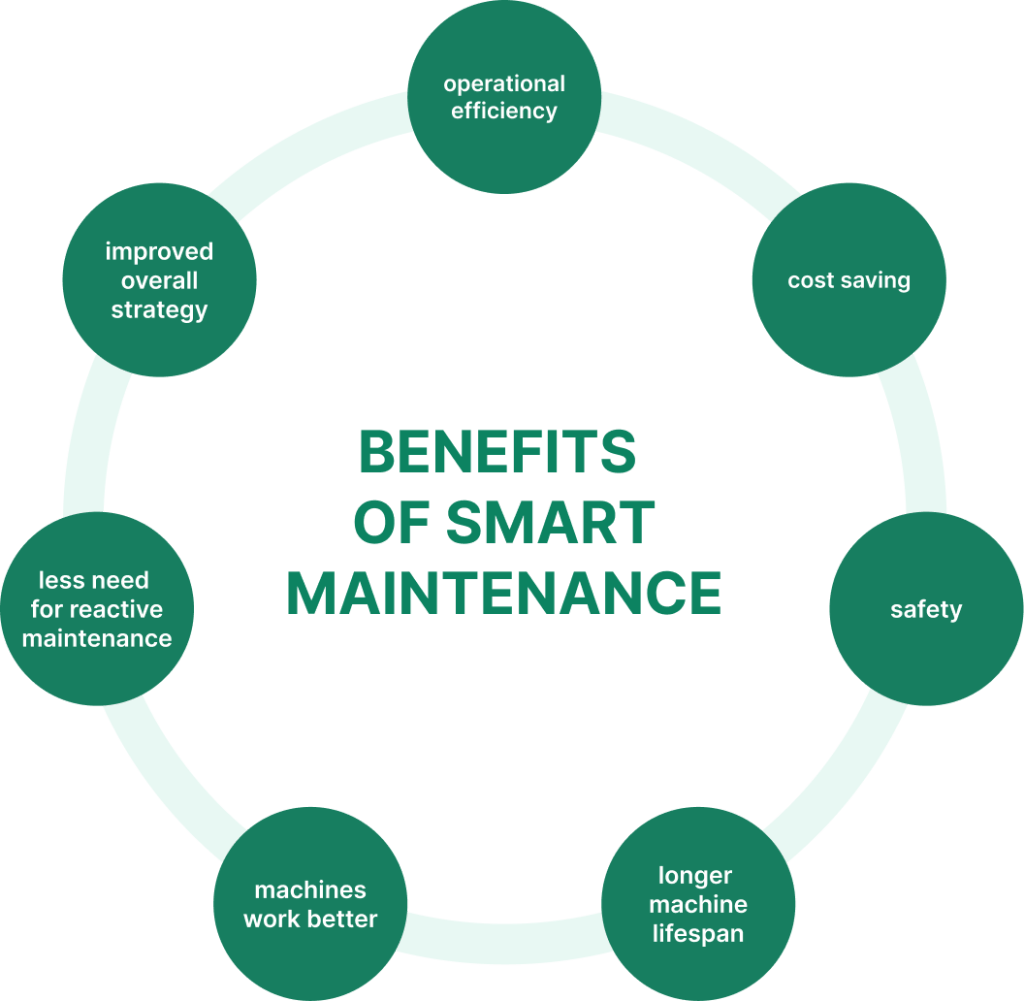
Smart maintenance can reduce maintenance costs, enhance operational efficiency, and make work safer, leading to significant cost savings. Companies that use it often see big improvements. They have less downtime, fewer surprise breakdowns, and lower repair costs.
The benefits of smart maintenance go beyond just saving money. It can help machines last longer and work better, reduce instances of reactive maintenance, and improve overall maintenance strategy. It can also make factories and other workplaces safer for employees. These advantages are why more businesses are starting to use smart maintenance methods.
Source: WorkTrek
Defining Smart Maintenance
Smart maintenance uses data and technology to predict and prevent equipment failures. Through proactive strategies, it aims to maximize uptime and reduce costs. Maintenance management plays a crucial role in leveraging technology to enhance operational efficiency by facilitating better scheduling, data analysis, and overall management of maintenance tasks.
Evolution of Maintenance Strategies
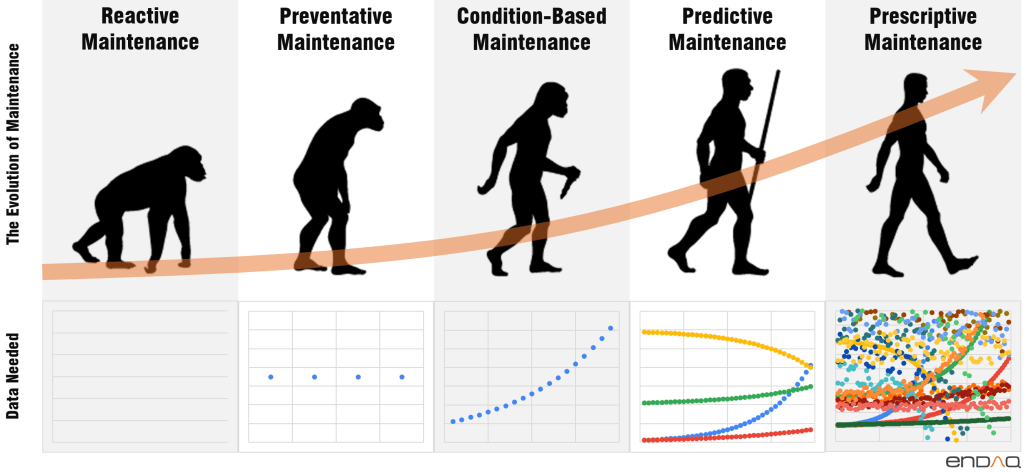
Maintenance approaches have changed over time. In the past, companies fixed machines only when they broke down. This led to unexpected downtime and high repair costs.
Next came preventive maintenance. Technicians serviced equipment on a set schedule. This helped but didn’t account for each machine’s unique needs.
Now, smart maintenance uses sensors and data analysis. It tracks how machines work in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance, which fixes issues before they cause problems.
To implement predictive maintenance effectively, you will need a robust maintenance strategy. This approach helps monitor equipment in real time, analyze data for potential failures, and take proactive measures to reduce downtime and enhance operational efficiency.
Smart systems learn from past data and improve their ability to spot potential failures. This preventive maintenance plan leads to fewer surprises and less wasted effort.
Source: Endaq
Core Components of Smart Maintenance Systems
Smart maintenance relies on several key parts working together. Sensors attached to machines collect data on things like temperature, vibration, and performance.
This information goes to a central system, where powerful computers analyze it using specialized Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence software.
The software looks for patterns that might signal future problems. Predictive maintenance technologies play an important role here, shifting from reactive to proactive strategies and significantly reducing maintenance costs, improving equipment effectiveness and machine downtime.
Data analysis helps make smart decisions. It shows which machines need attention and when. This helps teams plan their work better.
Using mobile devices lets maintenance workers see this information anywhere. They can quickly respond to alerts and fix issues. Over time, the system learns and gets even better at predicting problems.

Source: WorkTrek
Enhanced Reliability and Reduced Downtime
Smart maintenance boosts equipment reliability and cuts downtime. It uses advanced tech to spot issues early and keep machines running smoothly.
Maintenance managers can leverage data-driven insights to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules, preventing unplanned downtime and enhancing overall equipment productivity.
Predictive Analytics for Predictive Maintenance
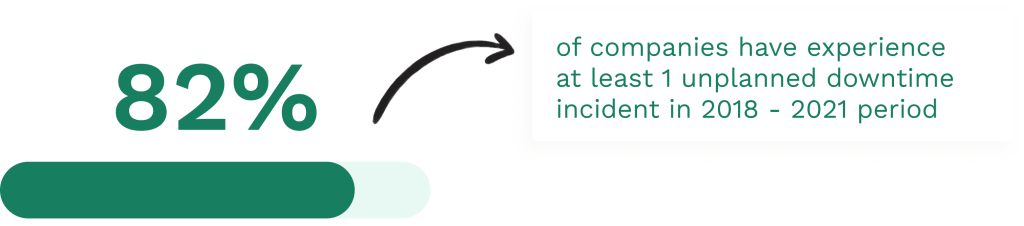
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Forbes
Predictive analytics helps catch problems before they happen. It looks at data from sensors and past breakdowns to guess when parts might fail, letting teams fix things before they break.
Predictive maintenance strategies effectively reduce maintenance costs and downtime, particularly in sectors like automotive, where data from connected cars enhances maintenance capabilities.
Smart systems can tell when a machine part is wearing out. They track things like heat, vibration, and power use. When signs of trouble show up, the system sends an alert.
This reduces unexpected breakdowns and keeps work flowing. It also saves money on extensive repairs, reducing operating costs. Teams can plan fixes at reasonable times, not during busy periods.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Real-time monitoring keeps a constant eye on equipment. Sensors track how machines are working every second. If something starts to go wrong, the system knows right away. Teams can also perform maintenance based on real-time data, ensuring timely interventions. All of this can lead to minimizing downtime.
Quick alerts let staff act fast. They can stop a small issue from turning into a big problem. This cuts down on surprise breakdowns that stop work.
Smart systems can also spot energy waste. They tell workers when machines are using too much power. Fixing these issues saves money and helps machines last longer.
Real-time data helps teams make better choices. They can see which machines need the most care, helping them use their time and resources wisely.
Cost Efficiency and Return on Investment
Smart maintenance brings major financial advantages to businesses. It cuts costs and boosts returns through better planning and resource use. A preventive maintenance program reduces costs, avoids equipment downtime, and maintains operational efficiency.
Optimizing Resource Allocation and Reduce Maintenance Costs
Smart maintenance helps companies use their resources more wisely. By scheduling upkeep at the correct times, it reduces maintenance costs by 12-18% compared to reactive approaches.
Companies avoid costly emergency repairs and waste from being fixed too early. Smart systems track equipment health in real time, allowing teams to act immediately. A well-planned preventive maintenance schedule minimizes disruptions and enhances overall workplace efficiency.

Labor costs go down, too. Workers spend less time on needless checks and focus on truly important tasks. Properly maintained parts last longer, cutting spending on replacements.
Source: WorkTrek
Long-Term Financial Benefits of preventive maintenance
The payoff of smart maintenance grows over time. Studies show a 400% return on investment is possible, resulting from avoiding breakdowns and extending equipment life.
Energy bills shrink as machines run more efficiently. One case found a monthly savings of around $18,000 after fixing system faults. Productivity rises when equipment works reliably.
Smart maintenance also helps plan for the future. It provides data on asset performance over time. This guides smarter choices about when to repair or replace items. Companies avoid overspending on new equipment too soon.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: ROI
Operational Performance Improvements
Smart maintenance boosts operational performance in manufacturing plants. It enhances efficiency and product quality through advanced technologies and data-driven approaches.
Streamlining Maintenance Processes
Smart maintenance maximizes the lifespan of machines and equipment. It uses real-time data to predict when repairs are needed, preventing unexpected breakdowns and costly shutdowns. Additionally, preventive maintenance tasks are crucial in avoiding downtime by addressing specific asset vulnerabilities.
Automated systems constantly track equipment health and alert technicians before problems occur. This proactive approach reduces downtime and keeps production running smoothly.
Smart maintenance also optimizes maintenance schedules. It ensures repairs happen at the best times, minimizing disruptions to production and improving overall efficiency.
Digital tools help technicians work faster and more accurately. They have instant access to equipment manuals and repair histories. This speeds up maintenance tasks and reduces errors.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Deloitte
Quality Assurance
Smart maintenance plays a key role in maintaining product quality. It helps detect and prevent issues that could affect output.
Advanced sensors monitor production processes in real-time. They spot deviations quickly and alert operators, allowing immediate corrections and reducing defects and waste.
Predictive maintenance improves throughput and quality. It ensures machines operate at peak performance, producing more consistent product quality and fewer rejects.
Data analysis helps identify recurring quality issues. Maintenance teams can address the root causes effectively, resulting in long-term quality improvements across production lines.
Safety and Compliance
Smart maintenance is crucial in enhancing workplace safety and ensuring regulatory compliance. It helps identify potential hazards before they become severe and keeps facilities updated with changing standards.
Minimizing Safety Risks
Smart maintenance systems use data and sensors to detect equipment issues early, preventing accidents caused by faulty machinery. For example, vibration sensors can spot loose parts before they break off and hurt someone.
Relying solely on reactive maintenance can lead to increased downtime, higher costs due to urgent repairs, and a negative impact on operational efficiency and equipment lifespan.
Regular upkeep, guided by smart systems, keeps equipment in top shape, reducing the chance of failures that could harm workers.
Predictive maintenance programs also help avoid sudden breakdowns. These could otherwise lead to dangerous situations on the work floor.
Smart systems track maintenance history. This lets managers know which machines need extra attention to stay safe. They can then prioritize fixes on high-risk equipment.

Source: JobSiteCare
Adherence to Regulatory Standards
Smart maintenance helps facilities comply with safety regulations. It keeps detailed records of all maintenance activities, making it easy to show inspectors that safety checks are done on time.
The systems can alert managers when equipment is due for required safety inspections, ensuring that nothing falls through the cracks.
Digital maintenance tools make it simple to update procedures when regulations change. New safety rules can be quickly added to checklists and work orders.
Smart systems can also track employee certifications. This ensures only qualified staff work on specialized equipment, as many safety standards require.
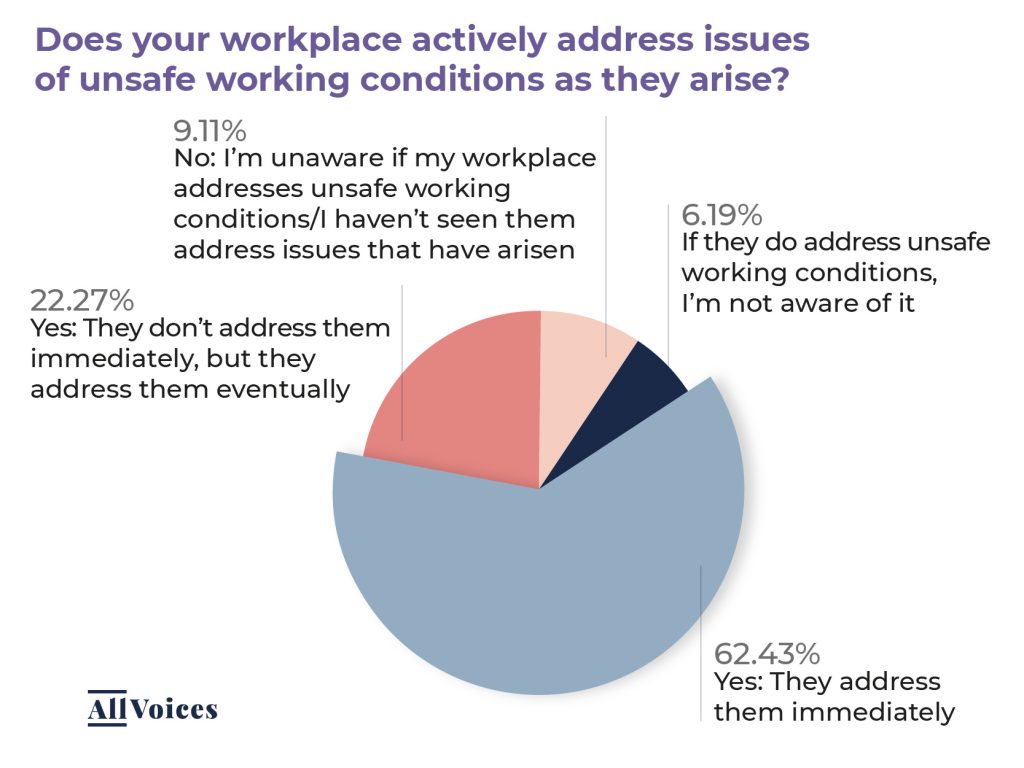
Source: All Voices
Data-Driven Decision Making
Smart maintenance relies on data to guide choices. This approach improves equipment upkeep and helps businesses plan for the future.
Leveraging Big Data and IoT
Data-driven decision-making uses information from many sources, including sensors, machines, and databases. The Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices to gather real-time data.
This data helps spot patterns and predict issues. For example, it can show when a part might fail. Maintenance teams can then fix problems before they cause breakdowns.
Big data analysis also helps compare different machines. It shows which ones work best and which need more attention, letting companies focus their efforts where they’re most needed.
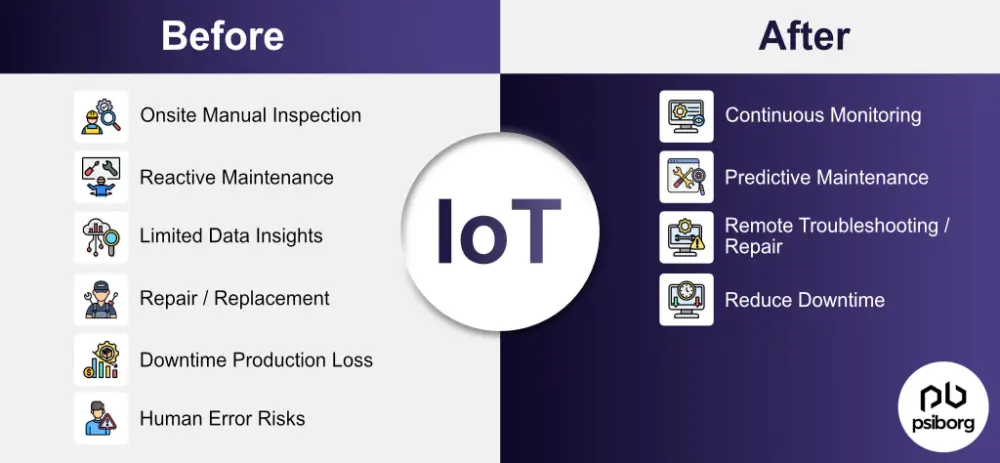
Source: Psibord
Informed Strategic Planning
Smart maintenance data guides long-term planning. It shows trends in equipment performance over time, helping to predict future needs and costs.
Companies can use this info to make better budget choices. They can plan for replacements or upgrades at the right time. This reduces the risk of sudden failures that could stop work.
Data also helps decide between repair and replacement. It shows the total cost of keeping old equipment running, making choosing the most cost-effective option easier.
Environmental Sustainability
Smart maintenance practices offer significant benefits for environmental sustainability. These approaches help companies reduce their ecological footprint while improving operational efficiency.
Energy Efficiency
Smart maintenance systems use sensors and data analytics to optimize energy use. They detect inefficiencies in equipment and suggest timely repairs. This leads to energy savings of 10-30% in many buildings.
These systems adjust heating, cooling, and lighting based on real-time needs. They also automatically turn off unused machines, which provides cost savings. Smart scheduling ensures maintenance happens at the right time, preventing energy waste from poorly functioning equipment.
Predictive maintenance catches issues early. This stops small problems from becoming big energy drains. It also extends the life of equipment, reducing the need for replacements and the associated energy costs of manufacturing new parts.

Source: Sustainability Success
Waste Reduction
Smart maintenance drastically reduces waste. It uses data to predict when parts will fail, allowing for just-in-time replacements and reducing excess inventory.
Digital work orders and reports eliminate paper waste. Remote monitoring cuts down on unnecessary site visits, saving fuel. Precise diagnostics mean fewer wrong parts are ordered or replaced.
Smart systems help track and manage hazardous materials better. This prevents spills and improper disposal. They also optimize the use of cleaning products and other consumables.
Smart maintenance extends equipment life, reducing the amount of machinery sent to landfills. It also promotes the reuse and recycling of parts when possible.
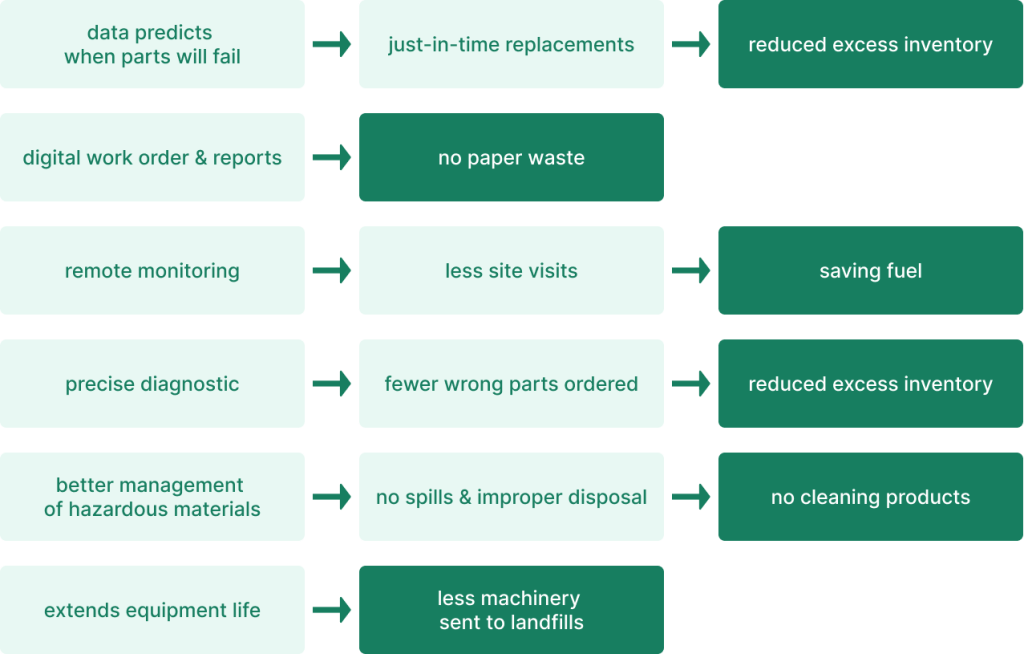
Source: WorkTrek
Future-Proofing and Scalability
Smart maintenance systems adapt to new technologies and grow with organizations. They provide long-term solutions that stay relevant as industries evolve and companies expand.
Adapting to Technological Advances
Smart maintenance keeps pace with rapid tech changes. It uses cognitive automation to stay current. These systems can self-diagnose problems and learn from past data.
As new tools emerge, smart maintenance easily integrates them. This might include:
- Advanced sensors
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning algorithms
Companies don’t need to overhaul their entire system when upgrading. Smart maintenance allows for modular updates. This saves time and money while keeping systems modern.
Scaling With Organizational Growth
Smart maintenance grows with a company. It handles increased workloads without major changes. As businesses expand, these systems scale up smoothly.
Key scaling features include:
- Cloud-based storage for unlimited data
- Flexible software that adds new assets easily
- Remote monitoring for multiple locations
Virtual training solutions help staff learn new processes quickly, keeping teams skilled as the company grows. Smart systems also share data across departments, improving company-wide efficiency.










