Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIdentifying the appropriate KPIs for maintenance is pivotal to your operational strategies. Efficient resource use, improved dependability, and proactive asset management are all contingent on the insightful application of these measurements.
This article outlines essential KPIs for maintenance operations, delineating their impact and offering actionable insights on leveraging them for operational excellence. ey maintenance KPIs like MTBF, MTTR, OEE, and PMP are essential for assessing equipment health and maintenance efficiency and balancing preventative and reactive maintenance. They are also critical for informing maintenance strategies and providing insights into equipment reliability, cost management, and the effectiveness of maintenance tasks.
Understanding Maintenance KPIs
Source: WorkTrek
An effective maintenance operation is grounded in the strategic selection of maintenance KPIs. These key performance indicators go beyond simple data points and steer the maintenance team toward enhanced reliability, cost savings, and longer equipment life.
These KPIs lay a foundation for developing and fine-tuning advanced maintenance strategies. They indicate how well maintenance management processes perform by shedding light on various aspects contributing to informed decision-making and strategy formation for the management team and maintenance staff.
These key performance indicators are the cornerstone of any successful organization’s maintenance plans.
Maintenance performance metrics
The process isn’t about randomly choosing metrics but involves picking those pertinent to your organization’s unique goals and obstacles within its operational framework. Some examples of KPIs to track are:
- Maintenance cost
- Maintenance metrics
- Maintenance Backlog
- Asset performance metrics
- Asset uptime
- Preventive maintenance compliance
Choosing the appropriate set of KPIs ensures that every action taken by a company is intentional and guided by accurate data analysis, thereby making achievements measurable with precision.
What is a Maintenance KPI?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) serve as measurable values that assess and track the success of maintenance processes. They provide essential insights for maintenance professionals to gauge.
- Their alignment with the planned maintenance percentage
- Their capability to control maintenance costs
- Their proficiency in performing their designated maintenance tasks.
These KPIs illuminate various aspects of the operational workflow, such as adherence to preventive or reactive approaches within a given timeframe.
The clarity offered by these metrics assists in formulating an effective strategy for conducting repair work and routine upkeep, all while ensuring meticulous budget management.
Why are Maintenance KPIs Important?
Maintenance KPIs are crucial tools for maintenance departments, functioning like a compass that guides their strategies and measures progress. When these KPIs align with an organization’s operational objectives, it guarantees that every action the team takes propels the company toward excellence.
The Equipment Availability KPI particularly reveals how healthy assets perform and their uptime, which can significantly affect profitability.
By focusing on pertinent KPIs, maintenance teams improve their strategic planning and practical execution. This focus nurtures an environment dedicated to ongoing enhancement and development within the department.

Source: WorkTrek
Essential Maintenance KPIs to Track
In the pursuit of exceptional maintenance management, several performance metrics are vital indicators of accomplishment. Key among these are:
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), which measures the efficiency with which repairs are carried out
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), an indicator of how reliably equipment operates
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), providing a comprehensive perspective on production efficacy
- Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) that reflects how effectively maintenance planning is being executed
These metrics collectively give a broad insight into various aspects of maintenance, ranging from the extent of pending tasks in the backlog to nuanced details related to equipment effectiveness and overall maintenance performance.
Through diligent tracking and analysis of these KPIs, maintenance managers can drive their departments toward reducing unplanned downtime while improving preventive and unplanned maintenance activities within their programs.
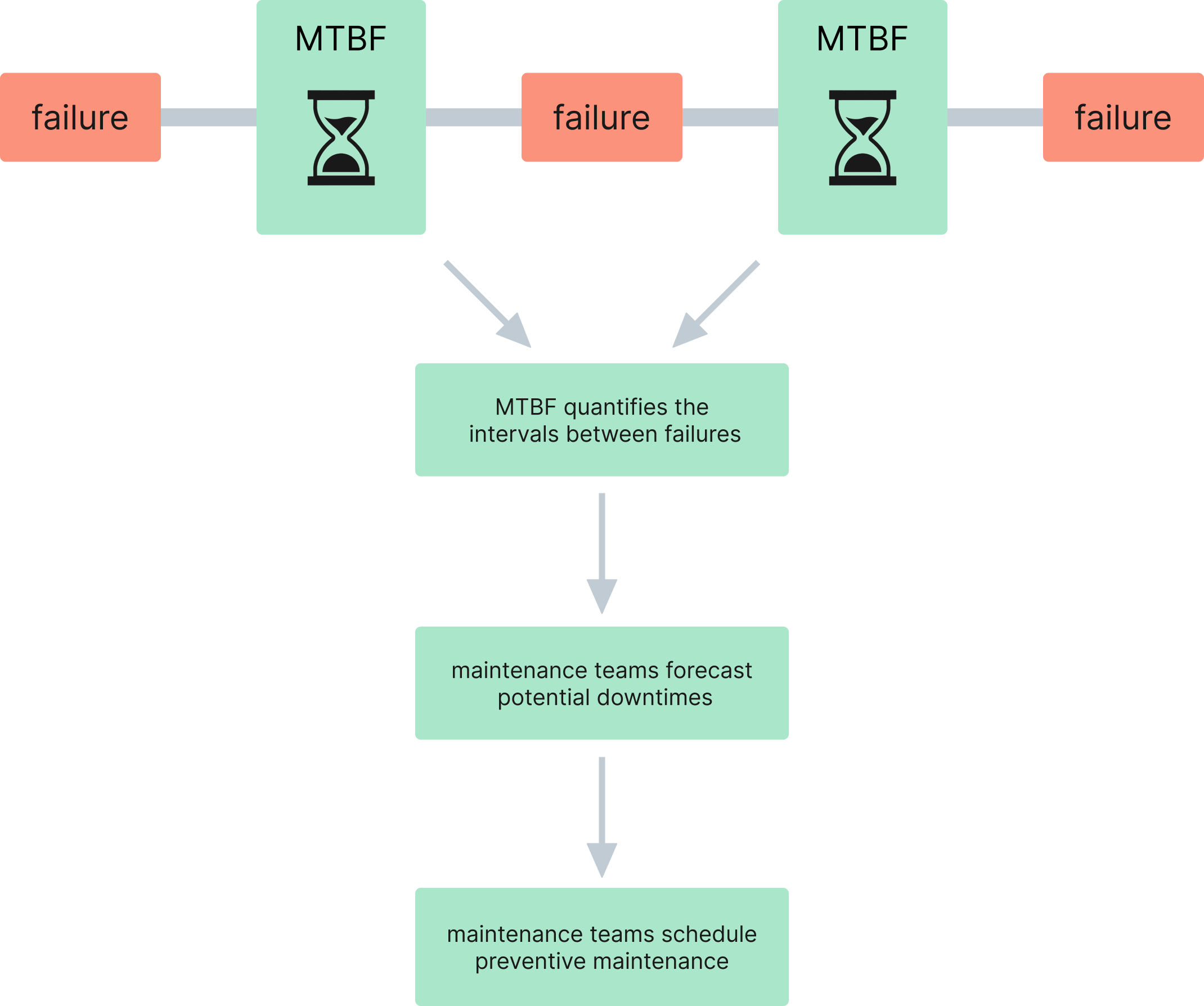
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a critical indicator of machine reliability, illuminating the longevity and robustness of your assets. It offers insight into equipment operation, anticipated operational continuity, and possible inherent design weaknesses that may precipitate unexpected failures.
MTBF adds a predictive dimension to maintenance planning by revealing the regularity with which machinery can execute its tasks without disruption. By quantifying the intervals between failures, MTBF enables maintenance teams to forecast potential downtimes and schedule preventive maintenance accordingly.
Source: WorkTrek
Most manufacturers do not publish official MTBF numbers for their equipment since it depends on variables such as operating environments that are out of their control. The best way to track MTBF is by collecting and analyzing historical data and repair history in your Work Order Management System.
This forward-looking approach helps minimize unexpected breakdowns and contributes to better resource allocation and inventory management.
Understanding equipment failure patterns through MTBF analysis can lead to more informed decisions regarding equipment replacement or upgrades, ultimately enhancing operations’ overall reliability and efficiency.
Nevertheless, it’s essential to recognize the constraints associated with MTBF. It depends upon statistical means and might not accurately forecast actual failure occurrences in scenarios where breakdowns do not happen randomly.
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR)
The Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) metric provides insight into maintenance effectiveness by indicating the average time equipment remains out of service during repair periods.
This measure shows a maintenance team’s ability and the impact of strategy on equipment functionality. MTTR is not only easy to calculate but also has significant implications. It demonstrates the quickness and skill of maintenance personnel can resurrect an asset after downtime.
Monitoring MTTR gives maintenance managers valuable information for task prioritization and procedure optimization, ensuring peak operation efficiency.
Difference Between MTBF and MTTR
Understanding the difference between Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) is crucial for maintenance teams aiming to optimize equipment reliability and minimize downtime.
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a reliability metric that measures the average time between non-scheduled maintenance incidents or failures of a system. It is a crucial indicator of how frequently a piece of equipment is likely to fail and is typically used to track the reliability of assets over time. A higher MTBF indicates better reliability and fewer disruptions in operations due to equipment failure.
On the other hand, Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) is a performance metric that represents the average time required to repair a failed component or piece of equipment and return it to operational status. This metric reflects the maintenance team’s efficiency in responding to and fixing issues when they arise. A lower MTTR means that the maintenance team is able to address failures quickly, reducing the impact of downtime on overall productivity.
In short, MTBF relates to the time equipment operates without interruption, while MTTR focuses on the speed and efficiency of returning equipment to service after a failure. Both are critical for developing a comprehensive maintenance strategy, providing insights into equipment reliability and responsiveness. By improving MTBF and MTTR, organizations can achieve a more effective and reliable maintenance operation.
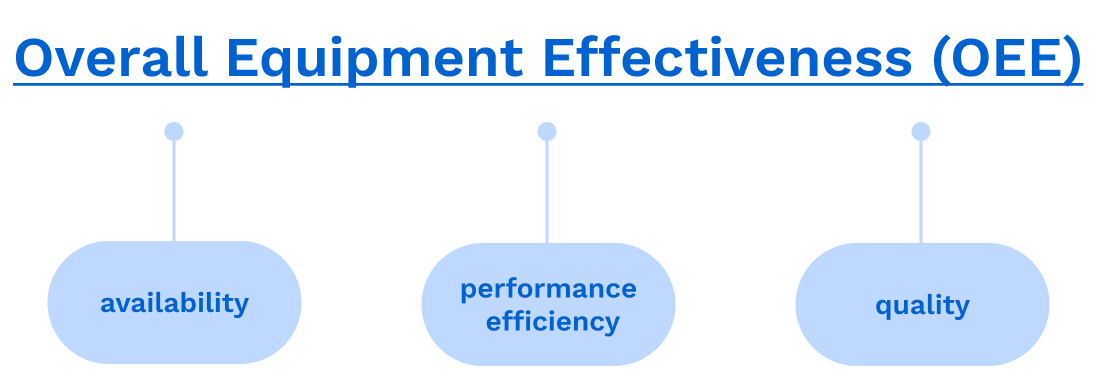
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Source: WorkTrek
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) includes three essential elements: availability, performance efficiency, and quality. These key aspects amalgamate to create a holistic measure as the foundation for evaluating machinery’s productivity.
Calculating OEE can seem complicated. However, it yields clear and practical insights—the score obtained from an OEE assessment is an immediate indicator of operational expenses and labor productivity.
OEE’s strength rests in its ability to distill multifaceted characteristics of equipment efficacy into one digestible number. This provides maintenance managers a focused directive for curtailing operational costs while enhancing machine dependability.
Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)
The Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) indicates the equilibrium between proactive measures and emergency responses in maintenance operations. It acts as a barometer for assessing how well a maintenance department can anticipate and prepare by contrasting the number of scheduled work orders with those prompted by unexpected equipment breakdowns.
A PMP ratio that aligns with best practices indicates a maintenance strategy centered on prevention rather than just reacting to crises.
Accordingly, industry standards propose that having 90% planned maintenance compared to 10% reactive is ideal. Nevertheless, achieving an 80% planned versus 20% reactive ratio also reflects positive progress towards more foresightful operations within the maintenance team over what’s typically seen.
Implementing Maintenance KPIs: Best Practices
Crafting maintenance KPIs is a nuanced art form that demands planning and alignment with company goals. Turning abstract goals into measurable milestones—like curtailing downtime or enhancing asset reliability—the resulting KPIs become crucial navigational beacons for the maintenance crew.
Focusing narrowly on core KPIs integrated into the enterprise’s strategic fabric ensures that resources and attention remain undivided, maximizing their impact.
By delineating explicit metrics accompanied by a defined schedule, maintenance managers gain a powerful tool to monitor advancements systematically. Each carefully selected KPI is an incremental advance toward achieving peak operational performance.
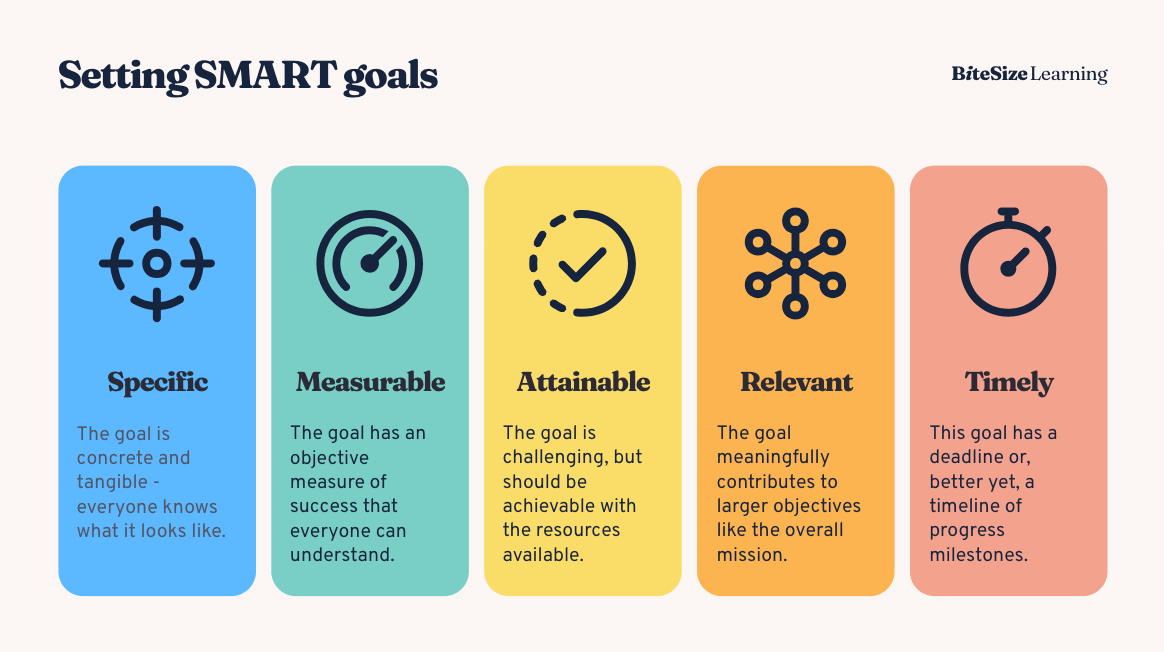
Set SMART Goals
Effective KPIs for maintenance hinge on the establishment of SMART goals, which are characterized by the following:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Achievable
- Realistic
- Time-bound
This ensures that such goals can be acted upon and yield significant advancements. Conforming to these SMART standards provides a precise framework for setting maintenance objectives, allowing teams to craft bold and attainable strategic aims.
Incorporating SMART goals within maintenance KPIs enables teams to focus on enhancing operational dependability and reducing expenses, among other expansive targets, thereby providing distinct guidance and intent.
Source: BiteSize Learning
Monitor and Adjust
The key performance indicators (KPIs) for maintenance are dynamic and should adapt as an organization’s goals and needs transform. The maintenance team is responsible for determining which metrics most effectively reflect their achievements and fine-tuning their focus on these essential KPIs accordingly.
It’s essential to strike a balance between leading and lagging indicators. Where leading indicators predict future maintenance requirements, lagging ones offer insight into historical performance.
To remain relevant to evolving corporate objectives, it’s imperative that a mix of tools, processes, and skilled personnel consistently review and adjust these maintenance KPIs.
Involve Your Team
Involving the maintenance team in the KPI process is crucial to fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. Active participation from maintenance managers and technicians in establishing and monitoring KPIs promotes an environment of openness and teamwork, resulting in improved work completion rates and increased efficiency within operations.
By adopting this shared strategy for managing KPIs, each team member gains clarity about their contribution to meeting departmental objectives, solidifying their dedication to perpetually advancing the standards of maintenance operations through continuous improvement.
Leveraging Technology for Maintenance KPI Tracking
In today’s digital landscape, leveraging technology such as Computerized Maintenance Management Software (CMMS) is essential for efficiently tracking and observing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to maintenance.
The functionality of CMMS extends well beyond mere tracking. It empowers teams to define, compare against benchmarks, and monitor their maintenance objectives accurately.
Work Order Management Software like WorkTrek Reporting delivers various reporting dashboards within the solutions, offering insights that forecast the evolution of maintenance operations. This future-focused perspective ensures that every choice is data-driven and every approach is tuned for peak operational efficiency.
Source: WorkTrek
Benefits of CMMS Software
CMMS software provides a wealth of advantages, such as:
- In-depth analyses
- Intuitive dashboards designed to demystify the intricate world of maintenance metrics
- Enabling enterprises to document their progress concerning maintenance KPIs
- Promoting an environment where data is the cornerstone of decision-making processes.
- Visibility to total maintenance costs
- Access to all maintenance history and total maintenance hours
- Centralized view for all maintenance backlogs
- Dashboards to quickly access both preventive and scheduled maintenance tasks
Thanks to its user-friendly design, CMMS software like WorkTrek removes obstacles, allowing technicians and managers to track, document, and evaluate KPIs effortlessly. The actual value delivered by CMMS implementation extends beyond mere statistics—it culminates in enhanced maintenance results characterized by increased rates of work completion and improved equipment effectiveness.
Choosing the Right CMMS Solution
Selecting the right CMMS system is crucial for enhancing the maintenance team’s productivity and meeting its key performance indicators. When making this decision, it’s essential to prioritize aspects like user support, the ability to integrate with other systems, and ease of use.
If a CMMS fits the team’s requirements well and effectively augments their current workflows, your team will likely embrace and use it. This alignment significantly contributes to more effective maintenance results.
Summary
Navigating maintenance KPIs is pivotal for achieving precision, efficiency, and strategic foresight in any organization. Embedding these crucial performance metrics into the core of maintenance operations goes beyond mere comprehension. It’s about integrating them thoroughly to guide daily practices.
Critical insights from MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) and MTTR (Mean Time To Repair), combined with the holistic perspective provided by OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) and equilibrium suggested by PMP (Preventive Maintenance Percentage), serve as essential tools that steer maintenance teams toward outstanding performance.
When applied through SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound objectives—with consistent monitoring and team engagement at its heart, the result is a robust maintenance program aligned with an organization’s strategic vision.
The role of CMMS software cannot be overstated—it is a valuable technological companion that equips teams with critical data to surpass expectations continually.
As success stories circulate within this community, they illuminate pathways for other professionals eager to refine their operational tactics. They are fully equipped with indispensable knowledge that enables transformation across their processes, resulting in unprecedented achievements by these skilled teams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main benefits of tracking maintenance KPIs?
By monitoring maintenance KPIs, organizations can enhance the reliability of their equipment, achieve cost-effectiveness, align with corporate objectives strategically, measure performance accurately, increase productivity levels, and optimize maintenance planning and efficiency—all contributing to the overall triumph in operations.
How can I ensure that the maintenance KPIs I select are effective?
Choose a handful of essential metrics that align with your business goals and strategic direction. Establish these maintenance KPIs by applying SMART objectives, an explicit scheme featuring particular metrics, and a schedule for monitoring advancement to guarantee they yield effective results.
What role does technology play in maintenance KPI tracking?
Technology is pivotal in maintaining KPI (Key Performance Indicator) tracking. Utilizing CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) software is crucial since it equips users with capabilities for establishing benchmarks and goals while offering comprehensive reporting features and consolidated data management to facilitate decisions based on informed insights.
What is the importance of involving the maintenance team in the KPI process?
Integrating the maintenance team into the KPI process is essential because this inclusion enhances transparency, responsibility, and operational efficiency. Such integration results in improved work completion rates and provides critical insights.
By doing so, there will be a considerable enhancement in how effectively the organization performs its functions.
Can maintenance KPIs change over time, and how should they be adjusted?
Maintenance KPIs must be adaptable to align with an organization’s shifting goals. Maintenance teams must consistently examine and update their KPIs to continue mirroring the evolving business environment.










