What is Benchmarking for Maintenance?
Benchmarking in maintenance refers to comparing an organization’s maintenance practices, performance, and costs against industry standards or best-in-class peers.
This process allows organizations to evaluate their maintenance efficiency, identify areas of improvement, and set performance targets to enhance their operations. By understanding how their maintenance efforts compare to others, businesses can adopt best practices and drive continuous improvement.
Benchmarking typically involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) like mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), maintenance cost as a percentage of asset value, and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). These metrics are compared to industry averages or those of top-performing companies to gauge performance.
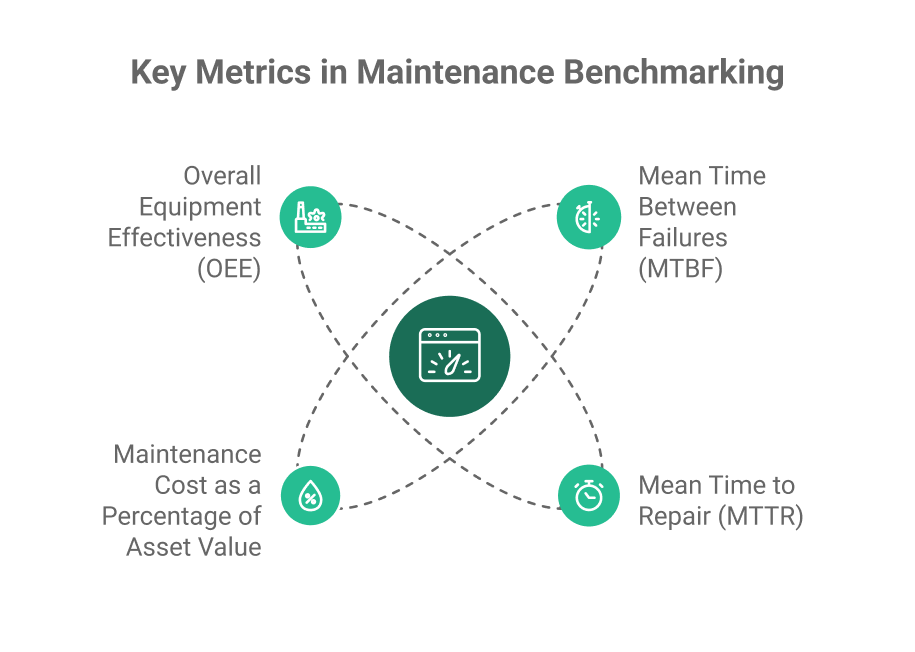
The purpose of benchmarking is to reveal performance gaps and to find opportunities for optimizing maintenance processes. It can lead to the adoption of better technologies, improved maintenance planning, or more effective resource allocation. For example, if a company finds its downtime significantly higher than its competitors, it might review its preventive maintenance schedules or invest in predictive maintenance tools.
Examples of How Maintenance Companies Use Benchmarking to Improve Operations
Benchmarking helps maintenance companies evaluate their performance against industry standards or competitors to identify areas for improvement. Here are some practical examples:
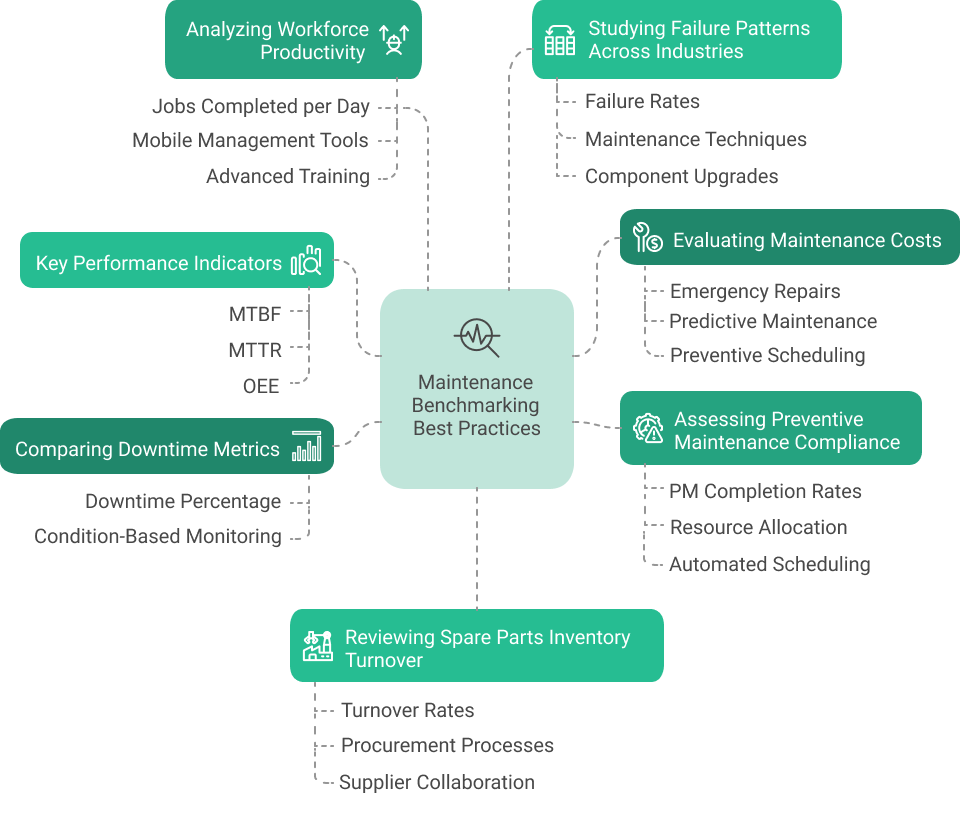
1. Comparing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Maintenance companies often benchmark critical KPIs such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Mean Time to Repair (MTTR), and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). For instance, a company might find that its MTTR is 20% higher than the industry average, prompting it to streamline repair processes, improve technician training, or invest in better diagnostic tools
2. Evaluating Maintenance Costs
Companies can identify inefficiencies by comparing their maintenance costs as a percentage of total operating expenses with their industry peers. For example, If a company spends 15% of its budget on emergency repairs, compared to the industry standard of 5%, it might focus on enhancing predictive maintenance and preventive scheduling.
3. Assessing Preventive Maintenance Compliance
Benchmarking preventive maintenance (PM) completion rates helps ensure assets are serviced on time. For instance, a maintenance firm discovers its PM completion rate is 70%, while top-performing companies achieve 95%. This insight drives them to optimize resource allocation or automate PM scheduling.
4. Comparing Downtime Metrics
Measuring downtime as a percentage of scheduled operating time against competitors helps identify weaknesses in maintenance strategies. For example, if a competitor achieves only 1% downtime and the company experiences 3%, they may implement condition-based monitoring systems to catch issues earlier.
5. Analyzing Workforce Productivity
Benchmarking technician productivity, such as jobs completed per day, reveals inefficiencies in workflow or skill gaps. Set organization benchmarks and track them. The company might introduce mobile workforce management tools or advanced training programs if technicians complete three jobs per day compared to the benchmark of five.
6. Reviewing Spare Parts Inventory Turnover
Benchmarking spare parts turnover rates ensures inventory is optimized without overstocking. A constant review will help you identify if your turnover rate is slower than average, leading to an overhaul of procurement processes and closer collaboration with suppliers.
7. Studying Failure Patterns Across Industries
Benchmarking failure rates of similar equipment across industries can highlight design or usage improvements. If peers using the same machinery experience fewer breakdowns, a company might adopt their maintenance techniques or upgrade specific components.
Best Practices for Benchmarking Maintenance Organizationsxg
Benchmarking is a powerful tool for improving maintenance operations by identifying gaps, setting goals, and implementing best practices. Below are some best practices companies use to benchmark their maintenance organization effectively:
1. Define Clear Objectives
- Establish what you want to achieve through benchmarking, such as reducing downtime, improving asset reliability, or lowering maintenance costs.
- A company may aim to decrease Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) by 15% within a year.
2. Identify Relevant Benchmarks
- Focus on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with organizational goals, such as:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
- Maintenance cost as a percentage of asset replacement value (ARV)
- Preventive Maintenance (PM) completion rates
- Use industry standards or data from top-performing organizations for comparison.
3. Gather Accurate Data
- Ensure data collection is consistent and reliable by standardizing methods across teams.
- Leverage tools like CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) to automate data capture and reduce errors.
4. Use Internal and External Comparisons
- Conduct internal benchmarking across departments, facilities, or business units to identify inconsistencies.
- Compare performance with industry leaders or similar organizations for external benchmarking.
5. Involve Stakeholders
- Engage maintenance teams, operators, and managers to provide insights and ensure the data reflects on-the-ground realities.
- Collaborate with external experts or peer organizations for an unbiased perspective.
6. Focus on Root Causes, Not Just Symptoms
- Use benchmarking data to identify root causes of inefficiencies, such as recurring equipment failures or skill gaps in the workforce.
- If MTBF is lower than industry averages, investigate whether poor operator training or insufficient maintenance schedules are contributing factors.
7. Regularly Review and Update Benchmarks
- Maintenance needs and industry standards evolve. Periodically reassess benchmarks to ensure they remain relevant.
- Incorporate new metrics as technologies like IoT and predictive maintenance become standard.
8. Establish Actionable Improvement Plans
- Use insights from benchmarking to develop specific, measurable actions for improvement.
- If Preventive Maintenance (PM) completion rates are below benchmarks, implement automated scheduling and better resource planning.
9. Leverage Technology
- Adopt analytics dashboards, IoT sensors, and machine learning to streamline data analysis and provide deeper insights.
- Predictive maintenance systems can provide real-time benchmarking on equipment performance.
10. Monitor Progress Continuously
- Set milestones and monitor performance to track progress against benchmarks. Adjust strategies based on ongoing results.
- Use a feedback loop to refine processes and sustain improvements.
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



