Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKey Takeaways:
- Organizations with effective preventive maintenance programs reduce equipment failures by 70-75% and cut maintenance costs by 25-40%
- 88% of manufacturing facilities deploy what they consider an effective preventive maintenance plan, but only 35% execute it correctly.
- Successful programs achieve 90%+ PM compliance rates and 10x ROI within 12-18 months
- The right combination of technology, training, and continuous improvement transforms maintenance from reactive to proactive
Your preventative maintenance program exists, but is it actually working?
This question keeps maintenance managers awake at night, and for good reason.
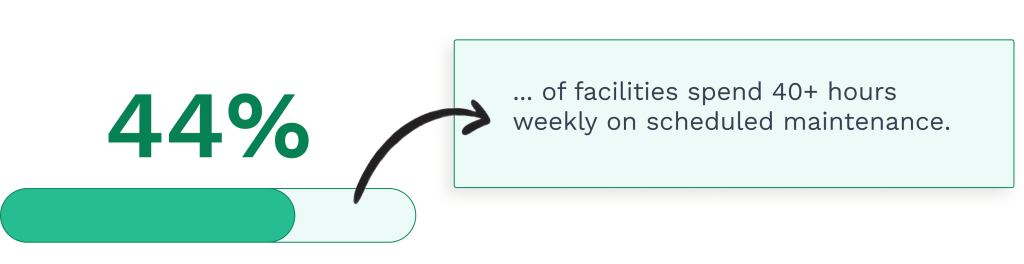
While 88% of manufacturing companies claim to use preventive maintenance, research shows that only 35% spend most of their maintenance time on scheduled activities. The rest remain trapped in reactive maintenance cycles, fighting fires instead of preventing them.
The disconnect is staggering.
Despite having preventive maintenance procedures in place, most organizations still experience unexpected equipment failures, costly repairs, and unplanned downtime that drain budgets and disrupt operations.
That’s because having a preventative maintenance program isn’t enough. You also need an effective one.
The difference between mediocre and exceptional preventive maintenance programs lies in execution, optimization, and continuous improvement.
These 10 tips will transform your existing maintenance operations from reactive chaos to proactive control.
1. Start with Asset Criticality Analysis
Not every piece of equipment deserves equal attention in your preventative maintenance schedules and program.
Spreading resources evenly across all assets is a recipe for inefficiency and equipment failures, which hurt most when they occur.
Prioritize Your Critical Equipment
Research shows that critical assets typically make up only 20% of total equipment, yet they drive 80% of your operation’s value.
The key to success is to focus your preventive maintenance activities here first.
Categorize your assets based on:
- Production impact: Single points of failure that halt operations
- Safety risks: Equipment whose failure could cause injury
- Replacement costs: High-value assets requiring major capital investment
- Regulatory requirements: Equipment subject to compliance standards
- Customer impact: Assets affecting service delivery or product quality
WorkTrek’s asset management features enable you to systematically classify and prioritize equipment, ensuring maintenance resources flow to where they matter most.
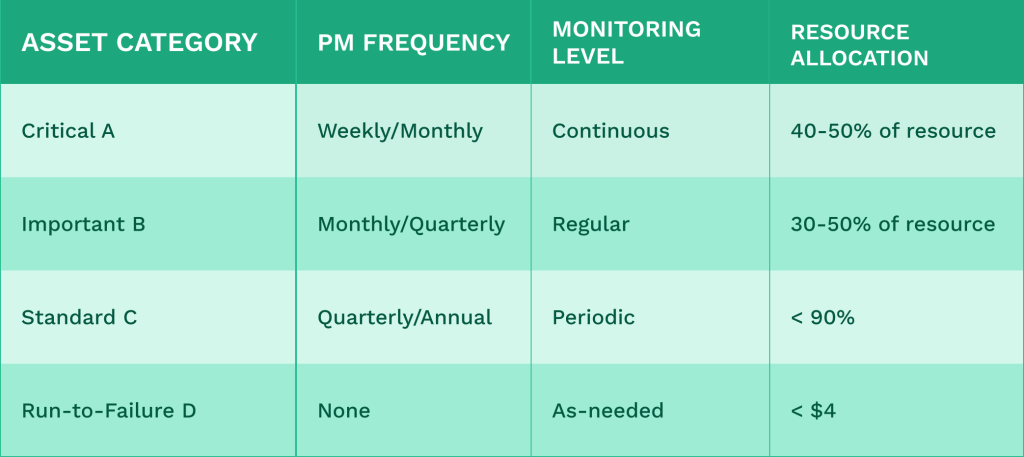
Tailor Maintenance Intensity by Criticality
Once classified, adjust your maintenance approach:
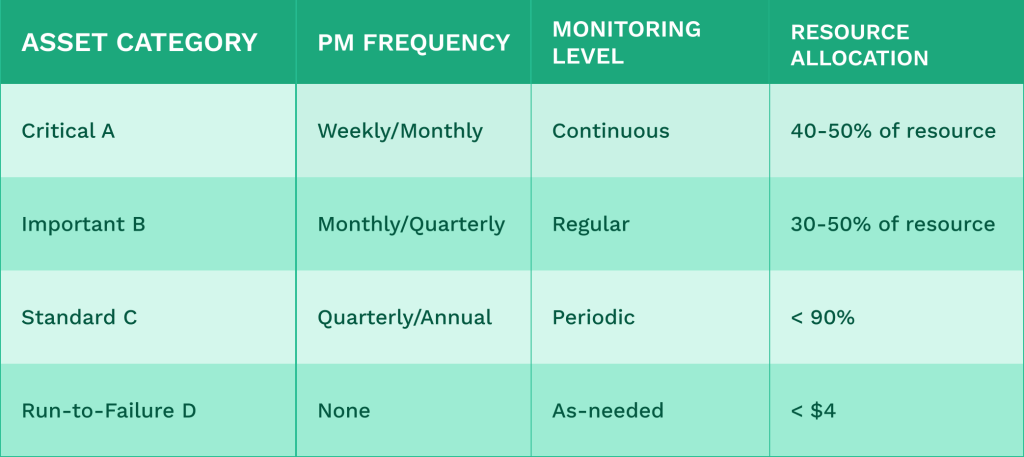
This approach ensures critical equipment receives the attention needed to prevent costly failures while avoiding over-maintenance of less essential assets.
2. Leverage a Computerized Maintenance Management System
Manual maintenance management is a losing battle and time-consuming.
Paper-based systems and spreadsheets can’t handle the complexity of modern preventive maintenance programs.
The CMMS Advantage
Industry data shows that 53% of facilities now use a CMMS to monitor their maintenance, and for good reason.
Organizations that implement CMMS software see the following benefits:
- 20% increase in equipment availability
- 30% reduction in maintenance costs
- 25% decrease in emergency repairs
- 50% improvement in schedule compliance
A computerized maintenance management system like WorkTrek transforms maintenance operations by:
- Automating preventive maintenance schedule generation
- Providing mobile access for maintenance technicians
- Tracking maintenance history automatically
- Managing spare parts inventory
- Generating key performance indicators instantly
Choose Technology That Works
Not all maintenance software is built the same. Look for solutions that offer:
- User-friendly interfaces that technicians actually use
- Mobile capabilities for field updates
- Integration options with existing systems
- Scalability to grow with your needs
- Comprehensive reporting for data-driven decisions
3. Establish Clear, Measurable Goals
A successful preventive maintenance program requires concrete objectives.
Without specific targets, you can’t measure progress or demonstrate value.
Define Success Metrics
Set specific goals for your preventive maintenance program. Some goal examples include:
Reliability Goals:
- Reduce equipment failures by 50% within 12 months
- Achieve 95% equipment availability for critical assets
- Decrease the mean time between failures by 30%
Cost Goals:
- Cut emergency repair costs by 40%
- Reduce overtime expenses by 25%
- Lower total maintenance costs by 20%
Efficiency Goals:
- Achieve 90% PM compliance rate
- Complete 80% of maintenance tasks within the scheduled time
- Reduce maintenance backlog by 60%
Research indicates that organizations with clear maintenance goals are 3x more likely to achieve successful preventive maintenance outcomes.
Track Progress Relentlessly
Establish key performance indicators and review them regularly:
- Weekly team reviews of PM compliance
- Monthly analysis of equipment effectiveness
- Quarterly cost-benefit assessments
- Annual program optimization reviews
WorkTrek’s analytics dashboard automatically tracks these KPIs, providing real-time visibility into program performance.
4. Create Detailed Preventive Maintenance Procedures
Vague and unclear maintenance instructions lead to inconsistent execution and equipment failures.
Your maintenance technicians need clear, step-by-step guidance for every preventive maintenance task.
Develop Comprehensive Documentation
Every PM procedure should include:
- Specific steps in logical sequence
- Required tools and equipment
- Safety guidelines and PPE requirements
- Time estimates for planning
- Pass/fail criteria for inspections
- Escalation procedures for issues found
Leverage Manufacturer Resources
Equipment manufacturers can provide deep insight into their own products. Incorporate their recommendations:
- Review service manuals for recommended intervals
- Follow specified lubrication requirements
- Use approved replacement parts
- Adhere to warranty maintenance requirements
Studies show that 77% of manufacturers rely on OEM guidelines for maintenance management, yet many fail to document these requirements properly in their procedures.
Standardize Across Similar Equipment
Define and create template procedures for similar equipment types:
- All pumps follow consistent inspection steps
- HVAC systems use standardized checklists
- Electrical systems follow uniform testing protocols
This standardization improves efficiency, reduces training requirements, and ensures consistent quality.
5. Implement Smart Scheduling Strategies
Poor scheduling can undermine even the best preventive maintenance plans.
Your preventive maintenance schedule should balance the equipment’s needs with operational demands.
Optimize Maintenance Intervals
Move beyond simple calendar-based scheduling to more sophisticated approaches:
Schedule tasks based on actual equipment usage rather than time. A machine running 24/7 needs different intervals than one used sporadically.
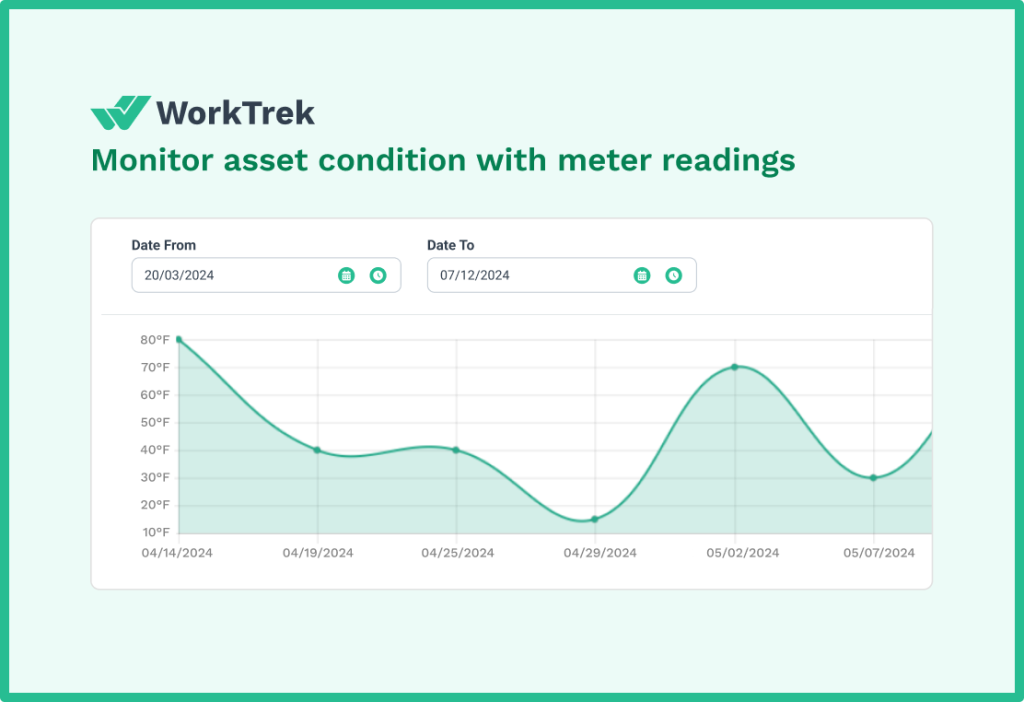
Condition-Based Maintenance:
Use equipment condition indicators to trigger maintenance. Implementing condition monitoring can reduce unnecessary maintenance by 30% while improving reliability.
Seasonal Scheduling:
Align maintenance with natural downtimes:
- HVAC system maintenance during mild weather and when subcontractors are more available
- Production equipment during slow seasons
- Outdoor equipment before harsh weather
Coordinate Across Departments
Effective scheduling requires collaboration:
- Production provides equipment availability windows
- Maintenance technicians confirm resource availability
- Spare parts availability from the inventory
- External contractors for specialized tasks
WorkTrek’s scheduling features automatically coordinate these factors, ensuring maintenance happens when planned, not when convenient.
6. Invest in Training and Skills Development
Your maintenance team is your greatest asset and, at times, can be your most significant limitation. Without adequate training, even the best preventive maintenance procedures fail.
Develop Technical Competencies
Studies show that only 29% of facility managers believe their technicians are “very prepared” for modern maintenance challenges.
Address this gap through:
- Equipment-specific training from manufacturers
- Latest maintenance techniques workshops
- Predictive maintenance technology training
- Safety certifications and updates
- Software training for CMMS and other tools
Build a Knowledge-Sharing Culture
Create systems for capturing and sharing expertise:
- Document lessons learned from equipment failures
- Establish mentorship programs for younger employees
- Create video tutorials for complex procedures. This can be included in each work order.
- Hold regular knowledge-sharing sessions
- Build a centralized database of solutions
This knowledge transfer is critical as 58% of manufacturing employees have worked in the industry for over 20 years and will soon retire.
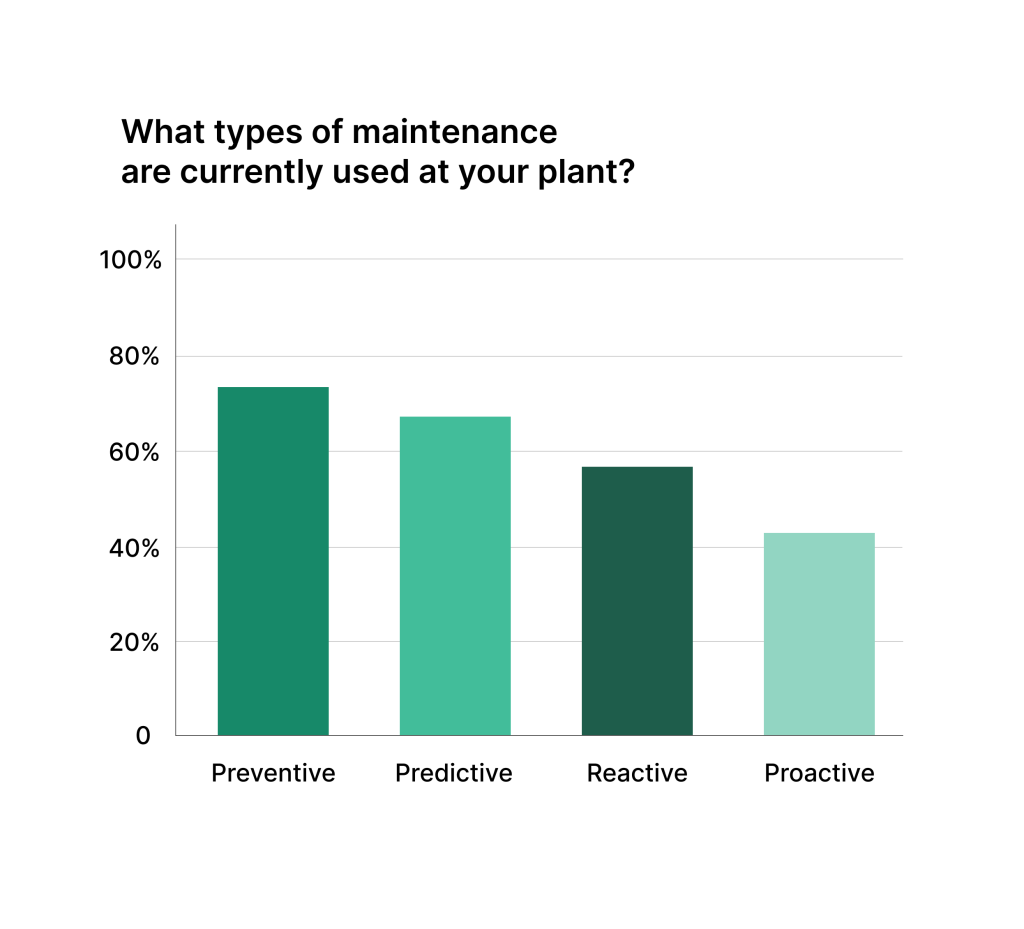
7. Balance Preventive, Predictive, and Corrective Maintenance
The most effective maintenance programs aren’t purely preventive. They strategically blend different maintenance strategies for optimal results.
The Right Mix
Industry leaders achieve this maintenance balance:
- Preventive Maintenance: 45-55% of activities
- Predictive Maintenance: 25-35% of activities
- Corrective Maintenance: 10-15% of activities
- Emergency Repairs: <5% of activities
Implement Predictive Technologies
Add predictive maintenance capabilities to enhance your program:
Vibration Analysis: Detect bearing wear and misalignment before failure. ROI typically exceeds 10:1.
Oil Analysis: Identify contamination and wear particles. Extends equipment life by 20-30%.
Thermography: Find hot spots in electrical systems. Prevents 70% of electrical fires.
These technologies provide 8-12% additional cost savings beyond preventive maintenance alone.
Know When Corrective Maintenance Makes Sense
Some equipment doesn’t justify preventive maintenance:
- Non-critical assets with low failure impact
- Equipment near end-of-life
- Assets with unpredictable failure modes
- Low-cost, easily replaced items
Strategic run-to-failure decisions free resources for critical equipment maintenance.
8. Ensure Adequate Resources and Spare Parts
Even the most effective preventive maintenance procedures fail without adequate resources.
When equipment breaks down, you don’t want to spend a lot of time waiting for critical parts or finding the right maintenance technician to fix it.
Optimize Inventory Management
The studies are clear. Boston Consulting Group research shows robust inventory management improves spare parts efficiency by 15%.
Implement these practices:
- Critical spare analysis: Stock parts for critical equipment
- Min/max levels: Automate reordering
- Vendor partnerships: Ensure rapid delivery for non-stocked items
- Kitting: Pre-package parts for common PM tasks
- Cross-reference lists: Identify alternative parts
WorkTrek’s inventory management integrates with maintenance schedules, ensuring parts availability before work begins.
Staff for Success
Labor can be expensive. However, understaffing can lead to deferred maintenance and equipment failures. Consider:
- Peak maintenance periods require additional resources
- Specialized equipment needs certified technicians
- Cross-training provides flexibility
- Contractor relationships fill skill gaps
9. Focus on Continuous Improvement
It is important to continuously review and improve your preventive maintenance program.
What works today may not be optimal tomorrow as equipment ages, technology advances, and operations change.
Analyze Failure Data
Every equipment failure is a learning opportunity for the organization:
Root Cause Analysis: Determine why failures occurred despite preventive maintenance:
- Was the PM interval too long?
- Were procedures inadequate?
- Did technicians miss warning signs and fail to document it?
- Were the wrong parts used?
Studies indicate that facilities that conduct regular RCAs reduce repeat failures by 65%.
Refine PM Tasks Based on Results
Use data analysis to optimize your program:
- Eliminate PMs that don’t prevent failures
- Increase frequency for high-failure equipment
- Decrease frequency for over-maintained assets
- Add new tasks for emerging failure modes
Research shows 30% of PM activities add little value and can be eliminated or modified.
Benchmark Against Industry Standards
Compare your performance metrics:
10. Create and Foster a Culture of Ownership
The best preventive maintenance programs succeed because everyone, from machine operators to senior management, takes ownership of equipment reliability.
Engage Machine Operators
Operators are your first line of defense against equipment failures.
Document and provide a communication channel if they notice:
- Unusual sounds or vibrations
- Performance degradation
- Leaks or loose components
- Operating parameter changes
Train and implement operator-based maintenance:
- Daily equipment inspections
- Basic cleaning and lubrication
- Simple adjustments
- Immediate problem reporting
This approach catches issues before they require maintenance technician intervention.
Create Accountability Systems
Clear ownership and accountability drive results:
- Assign equipment champions for critical assets
- Define maintenance responsibilities clearly
- Define equipment service personnel
- Track individual PM compliance rates
- Recognize exceptional performance
- Address accountability gaps quickly
- Identify any equipment that can pose safety risks
Communicate Value Continuously
Keep everyone informed about program success and not just the failures:
- Share cost savings from prevented failures
- Celebrate reliability improvements
- Highlight safety achievements from preventive measures
- Demonstrate productivity gains from reduced downtime
When people understand the value of preventive maintenance, they support and participate actively.
Conclusion
Building a better preventative maintenance program is about systematic improvement across multiple areas of your organization.
The data is compelling. Organizations that implement these 10 tips achieve remarkable results:
- 70-75% reduction in equipment breakdowns
- 545% ROI on maintenance investment
- 25-40% decrease in overall maintenance costs
- 95%+ equipment availability for critical assets
Yet despite these proven benefits, most maintenance programs operate far below their potential. The gap between average and exceptional isn’t about resources—it’s about execution.
Begin with these immediate actions:
- Assess your current state: Calculate your planned vs. reactive maintenance ratio
- Pick your priority: Choose one critical asset for intensive improvement
- Implement technology: Deploy a CMMS like WorkTrek for visibility and control
- Set clear goals: Define specific, measurable objectives for the next 90 days
- Track progress: Monitor KPIs weekly and adjust quickly
Your equipment is waiting. Your team is capable. The tools and knowledge exist.