Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIntroduction
The CMMS solution serves as a crucial tool for companies, enabling them to effectively manage their maintenance operations and consolidate all relevant information in a centralized database, benefiting all parties involved.
In the 1980s, the idea of CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System). This revolutionary concept brought about significant improvements in the working environment for maintenance personnel by enabling the computerization of work orders, efficient resource planning, and on-demand printing capabilities.
In the present day, CMMS incorporates not just various forms of maintenance (such as corrective, preventive, conditional, and predictive maintenance) but also encompasses supply management, operational assurance, and integration with production systems.
In order to enhance work planning efficiency, facilitate seamless information transfer through integration with accounting systems, and provide a range of other indispensable functionalities, CMMS has become an essential tool for any responsible business.
Industries that heavily rely on equipment and meticulous monitoring of operations, such as manufacturing, food processing, aviation, and transportation, find maintenance software to be exceptionally valuable. This software is applicable to any sector that necessitates the utilization of heavy machinery.

What is a Work Order?
A work order is a document used to detail the details of a request for goods or services received from a customer. In some industries, the work order is created using information obtained from a sales order prepared by the salesperson working with the customer. There are also situations where the sales order and the work order are the same document, with the terms used to identify the current status of the fulfillment of the customer’s request.
The exact structure of the work order will vary depending on the type of goods or services required. For example, the landlord can open a work order in response to a tenant’s request to have a room in their apartment painted. The owner will prepare the order in a way that documents the task at hand, the materials needed to complete the job, the time needed to handle the repainting, and the expenses involved in successfully completing the task. In this application, the work order essentially functions not only as a record of the client’s request, but also as the escalation list of steps needed to complete the job, and a record of how much it will cost the owner to comply.
The work order in a manufacturing plant is often prepared from data obtained from a customer order drafted by the sales department. Here, the order will include details of the product ordered, including size, number of units, color, and any other applicable information. The ticket will often include details of the delivery date agreed between the sales department and the customer. If the customer has expressed a preference regarding the method of shipping the items ordered, this information may also be included on the work order.
Regardless of the context, the purpose of the work order is to ensure that all parties involved in the fulfillment process know exactly what the customer has ordered, what it will take to fulfill that order, and when the order needs to be fulfilled. From this perspective, the order can be viewed as a necessary document that increases the potential for products to be prepared to customer specifications and delivered to the customer in a timely manner. For this reason, small and large businesses are very likely to use this type of document in one form or another.
Other phrases that business people could use in place of work orders are:
- Service ticket
- Job order
- Work ticket
- Job ticket
The Purpose of Work Orders
Such a document is only meant to serve the single function of maintaining a record of all work authorizations, service provider information, charges, and job completion times. A service ticket can be created by both internal and external clients, such as customers and staff.
Depending on whether it is an internal or external request for work, the paper is then sent to the appropriate team. Vouchers are frequently created by businesses using computer software and circulate through numerous physical or digital desks.
Find a quick list of the following work objectives here:
- Describe the problem, the fix, and the installation or delivery of the products
- The provision of materials and tools required for the task or maintenance work
- Provide thorough instructions on the work, job, or maintenance to the technicians
- Recording formally the resources, labor, and materials used to complete the work
- Track all repair and maintenance jobs that have been performed on each authorization
- Contains monetary data like cost, taxes, levies, cess, etc.
What Is Work Order Management?
The management of work orders encompasses the creation, tracking, and administration of these documents within a company. A work order serves as a written or digital record outlining the tasks, instructions, and prerequisites necessary to carry out a specific job or project. The process of work order management encompasses a range of activities, such as:
- Initiation of tasks or projects for employees, contractors, or service providers is facilitated through the creation of work orders. These orders encompass crucial information such as the nature of the work, location, deadline, necessary materials, and any specific instructions.
- When a work order is generated, it is then allocated to the suitable individuals or team who are accountable for carrying out the specified tasks. Assignments are determined by considering factors such as expertise, availability, and workload.
- The entire lifespan of a job or project involves the meticulous tracking of work orders. This entails closely monitoring the status of each individual work order, keeping tabs on the progress made, and meticulously documenting any alterations, setbacks, or complications that may occur during the execution of the work.
- Efficiently managing work orders requires effective scheduling and resource allocation to ensure timely and cost-effective completion. This often entails coordinating with various teams, departments, and external vendors to streamline operations and meet project deadlines while staying within budget.
- In work order management, it is crucial to have effective communication to keep all parties involved updated on the progress of work orders, any modifications to requirements, and any potential problems that may arise. This can be achieved through various communication methods, including emails, phone calls, and collaboration platforms.
- The process of work order management requires thorough documentation of pertinent details for each individual work order. This includes capturing information such as job specifics, costs associated with labor and materials, time allocation, and the status of completion. Precise and comprehensive documentation plays a crucial role in monitoring expenses, evaluating performance, and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
- The work order is considered finished and officially closed in the system after all necessary tasks have been completed. This closure triggers the generation of any final documentation or reports. Additionally, work order management includes the crucial step of evaluating the overall performance of the work order process. This evaluation aims to identify specific areas that can be improved upon and implement changes accordingly. The ultimate goal is to enhance both the efficiency and effectiveness of the work order system.

Work Order Management Terms
Work Approver – The assignment and authorization of maintenance requests for equipment management are handled by an administrative or a member of that team. The approver function may occasionally be performed by the warehouse manager and the front desk support for customer interactions.
Work Requester – The person or group that makes the request to execute a certain task is known as the requester. In the services and goods sector, customers generate task orders through online or in-person purchases. Business-to-business requests for work may originate from commercial clients or an internal team, such as when a manager of customer service operations demands workstation maintenance.
Field Technicians – Field technicians are engineers, millwrights, repair personnel, etc. who are qualified to carry out the task specified in the work order document in maintenance job tickets.
How To Effectively Manage Work Orders With a CMMS?
The management of work orders encompasses the creation, tracking, and administration of these documents within a company. A work order serves as a written or digital record outlining the tasks, instructions, and prerequisites necessary to carry out a specific job or project. The process of work order management encompasses a range of activities, such as:
Initiation of tasks or projects for employees, contractors, or service providers is facilitated through the creation of work orders. These orders encompass crucial information such as the nature of the work, location, deadline, necessary materials, and any specific instructions.
When a work order is generated, it is then allocated to the suitable individuals or team who are accountable for carrying out the specified tasks. Assignments are determined by considering factors such as expertise, availability, and workload.
The entire lifespan of a job or project involves the meticulous tracking of work orders. This entails closely monitoring the status of each individual work order, keeping tabs on the progress made, and meticulously documenting any alterations, setbacks, or complications that may occur during the execution of the work.
Efficiently managing work orders requires effective scheduling and resource allocation to ensure timely and cost-effective completion. This often entails coordinating with various teams, departments, and external vendors to streamline operations and meet project deadlines while staying within budget.
In work order management, it is crucial to have effective communication to keep all parties involved updated on the progress of work orders, any modifications to requirements, and any potential problems that may arise. This can be achieved through various communication methods, including emails, phone calls, and collaboration platforms.
The process of work order management requires thorough documentation of pertinent details for each individual work order. This includes capturing information such as job specifics, costs associated with labor and materials, time allocation, and the status of completion. Precise and comprehensive documentation plays a crucial role in monitoring expenses, evaluating performance, and ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements.
The work order is considered finished and officially closed in the system after all necessary tasks have been completed. This closure triggers the generation of any final documentation or reports. Additionally, work order management includes the crucial step of evaluating the overall performance of the work order process. This evaluation aims to identify specific areas that can be improved upon and implement changes accordingly. The ultimate goal is to enhance both the efficiency and effectiveness of the work order system.
Important Features of a CMMS Work Order Management System
When it comes to a comprehensive CMMS work order management system, it is crucial to incorporate the following key features:
- Effortlessly and effectively create work orders by providing specific information such as job description, location, priority level, deadline, and necessary materials or resources.
- To enhance efficiency and maintain uniformity, the creation process of work orders can be streamlined through the utilization of customizable templates, which are pre-designed for various types of tasks such as preventive maintenance, corrective maintenance, and inspections.
- Work order assignment and scheduling are crucial tools for effectively distributing tasks to maintenance technicians or teams. These tools take into account various factors, including skills, availability, and workload, to allocate work orders efficiently. Additionally, the system should enable seamless scheduling and dispatching of work orders to guarantee timely completion of tasks.
- Users can conveniently track the status of their work orders in real time, enabling them to stay updated on progress, receive timely notifications, and address any potential delays or issues that may arise.
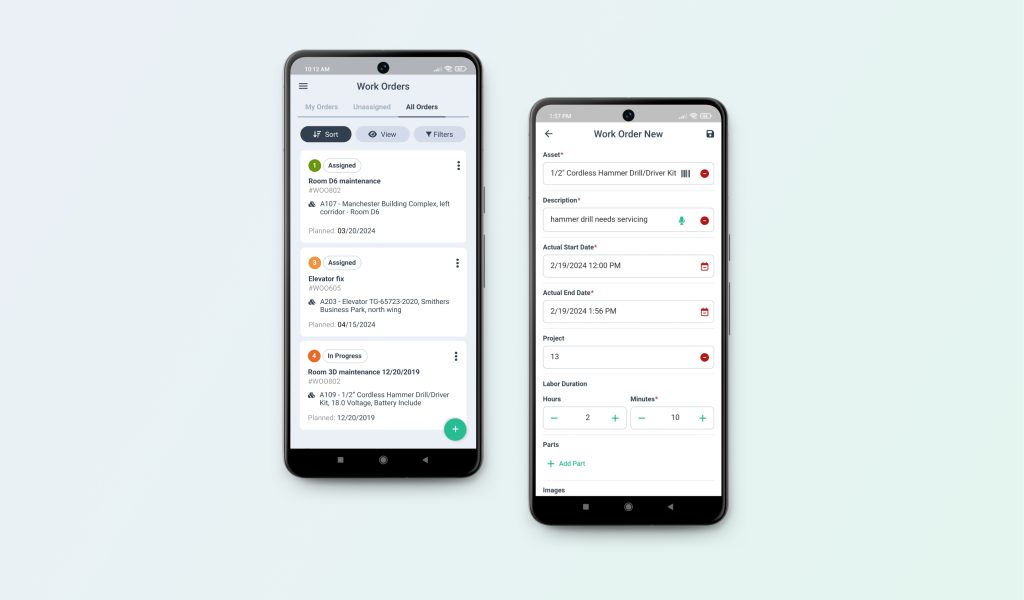
- The capability of accessing work orders through smartphones or tablets while in the field enhances mobile accessibility. This functionality enables technicians to view, update, and finalize work orders instantly, resulting in improved communication and efficiency.
- The integration of inventory management functionalities allows for tracking spare parts, tools, and materials necessary for maintenance tasks. The system should be capable of monitoring inventory levels, tracking stock, and automatically initiating reordering processes to guarantee the availability of essential components when required.
- The integration of asset management functionality enables the linking of work orders to specific equipment or assets that are in need of maintenance. This seamless connection allows users to conveniently access asset history, maintenance schedules, and pertinent documentation directly from the work order.
- The preventive maintenance scheduling feature offers a range of tools to streamline the process, such as built-in scheduling tools that allow users to set up recurring maintenance schedules, define task frequencies, and automatically generate work orders based on predefined criteria.
- The ability to include supporting materials such as documentation, manuals, schematics, and photos with work orders is a valuable feature. This functionality enables technicians to easily access and reference relevant information and instructions, enhancing their ability to efficiently complete tasks.
- Maintenance performance reports, key performance indicators (KPIs), and metrics can be generated through the reporting and analytics functionalities. Users have the ability to analyze various data points, including work order completion rates, downtime trends, and maintenance costs, in order to pinpoint opportunities for enhancement and optimization.
- To ensure seamless data sharing and maintain consistency throughout the organization, it is essential to integrate with external systems, including enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, asset management software, and accounting software.
- To safeguard sensitive information and maintain strict control over user access, role-based access control and security measures are implemented, allowing only authorized users to view, create, or modify work orders.

Benefits of a CMMS Work Order Management System
Organizations across different industries can reap numerous benefits from implementing a CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) work order management system.
- By utilizing CMMS work order management systems, the consolidation of all work orders into a single, user-friendly platform is achieved, leading to a reduction in paperwork and the elimination of manual procedures. This centralized method enhances organization and guarantees the streamlined tracking and efficient management of all work orders.
- CMMS systems enhance maintenance efficiency by optimizing the creation, assignment, and tracking of work orders. This streamlining process enables technicians to swiftly access work orders, prioritize tasks, and communicate updates in real-time. As a result, response times are accelerated, and downtime is minimized.
- CMMS work order management systems offer organizations the ability to optimize resource allocation through enhanced visibility into work order schedules, technician availability, and resource demands. This guarantees that tasks are assigned to the appropriate resources at the precise moment they are needed.
- The implementation of CMMS systems results in enhanced productivity for maintenance teams by automating workflows and optimizing processes. This allows technicians to allocate less time towards administrative duties and dedicate more time towards carrying out maintenance work, resulting in increased output and elevated service quality.
- The implementation of preventive maintenance is made easier with the assistance of CMMS work order management systems, which enable the creation and organization of preventive maintenance tasks. By proactively addressing potential problems and staying ahead of equipment failures, organizations can effectively reduce unplanned downtime and prolong the lifespan of their assets.
- Long-term financial benefits can be achieved through the implementation of CMMS work order management systems, which streamline maintenance processes, minimize downtime, and prevent expensive equipment breakdowns. Additionally, these systems provide enhanced visibility into maintenance costs, empowering organizations to pinpoint opportunities for cost reduction and operational efficiency.
- CMMS systems assist organizations in guaranteeing compliance with regulatory obligations and industry benchmarks by providing comprehensive records of maintenance operations and the history of work orders. These records serve as evidence of compliance during audits and inspections.
- The implementation of CMMS work order management systems enhances communication and collaboration within maintenance teams, supervisors, and other stakeholders. Through real-time updates, notifications, and messaging capabilities, seamless communication is achieved, resulting in enhanced coordination and teamwork.
- The utilization of CMMS systems enables organizations to gather essential data and gain valuable insights regarding maintenance performance, equipment reliability, and asset health. This data can be utilized to detect patterns, assess performance metrics, and make informed decisions based on data to enhance maintenance strategies and optimize overall operations.
- The ability to scale and adapt is a key feature of CMMS work order management systems. These systems can easily adjust to the evolving needs of organizations, whether they are overseeing a small facility or a large enterprise. With the capacity to accommodate growth and expansion, CMMS systems remain flexible and capable of supporting changing maintenance demands.
Conclusion
By effectively utilizing the features and functionalities of your CMMS system and following the steps outlined in this blog, you can optimize work order management, enhance maintenance efficiency, and extend the lifespan of your assets.










