Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeMany businesses find it challenging to manage inventory efficiently. Without the right systems, companies face stockouts, excess inventory, and wasted resources. These issues can disrupt operations, increase costs, and lead to unhappy customers.
This article provides 10 tips to help you implement an effective inventory management system.
Imagine losing sales because popular items are out of stock or having your cash tied up in unsold products that take up valuable space. Inaccurate inventory management can strain supplier relationships, create inefficiencies, and hurt your bottom line. As customer expectations rise and markets become more competitive, poor inventory practices leave businesses struggling to keep up.
The key to overcoming these challenges is mastering the best inventory control practices. By adopting proven techniques like ABC analysis, safety stock management, FIFO, and demand forecasting—and leveraging technology through inventory software and optimized warehouse layouts—businesses can streamline operations, cut costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
With the right strategies, companies can maintain precise stock levels, build stronger supplier relationships, and stay ahead in today’s fast-paced market.
Understanding Inventory Control
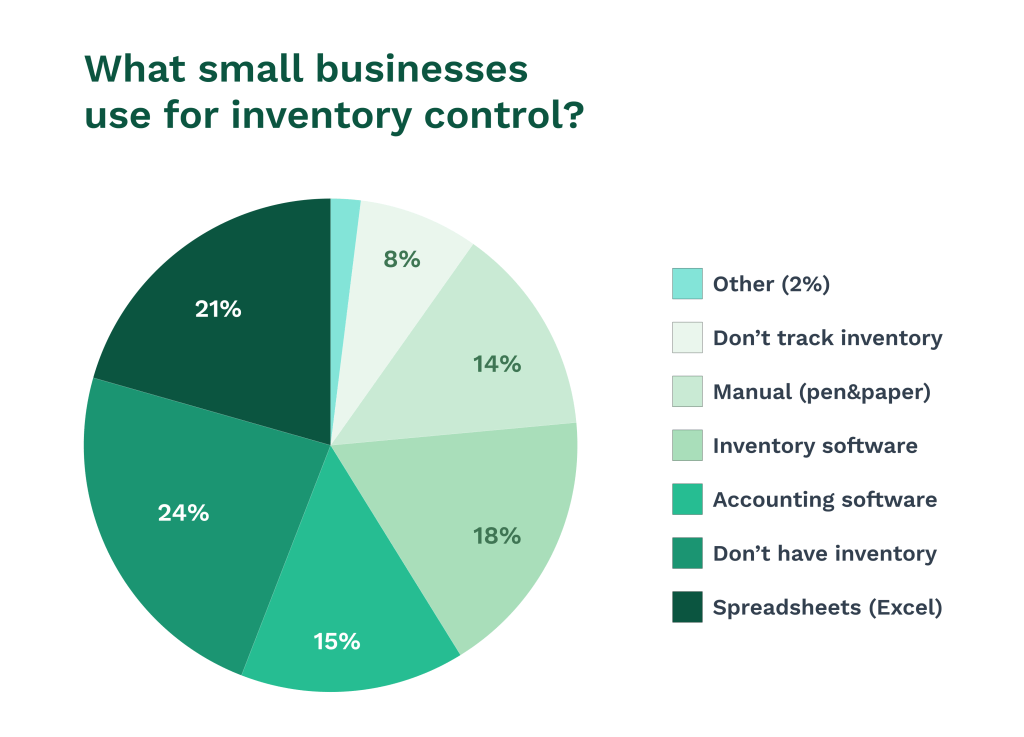
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Brahim Solutions
Having good inventory management operations can improve customer experience. Having the wrong quantity on hand or missing products can lead to customer dissatisfaction.
This can lead to missed deadlines, increased repair costs, and long wait times for maintenance organizations.
Improve Cashflow
A significant benefit of effective inventory control is the optimization of cash flow. By minimizing the excess funds in inactive inventory, businesses can free up capital to invest in areas like marketing initiatives or new product development.
Effective inventory control enhances operational performance, maximizing warehouse space efficiency.
Reduce Oversupply
Accurate monitoring and regulation of stock levels help prevent oversupply and protect against losses due to theft or spoilage. This careful oversight supports improved decision-making and reduces errors in inventory management.
Ensuring that adequate supplies are on hand mitigates risks associated with understocking—which leads to unfulfilled customer needs—and surplus stocks, which increase storage costs unnecessarily while posing potential loss threats from pilferage or deterioration.
An efficient strategy for maintaining these balances ultimately helps avoid scenarios where customers or maintenance managers encounter out-of-stock messages or delays resulting from backorders.
Companies can reduce inventory costs, simplify tracking inventory, and improve inventory accuracy with proper inventory management techniques.
1. Implement FIFO (First In, First Out)
The inventory management strategy known as First In, First Out (FIFO) prioritizes the sale of the oldest stock first. This is particularly advantageous for companies with limited shelf life or perishable products.
FIFO plays an important role in keeping goods fresh and minimizing financial loss due to expired or outdated items.
To implement FIFO, a clear labeling process must be developed, indicating the dates of receipt and expiration. This approach can help employees quickly identify which stock should be used or sold first. It also reduces spoilage for perishable items and can help you track inventory.
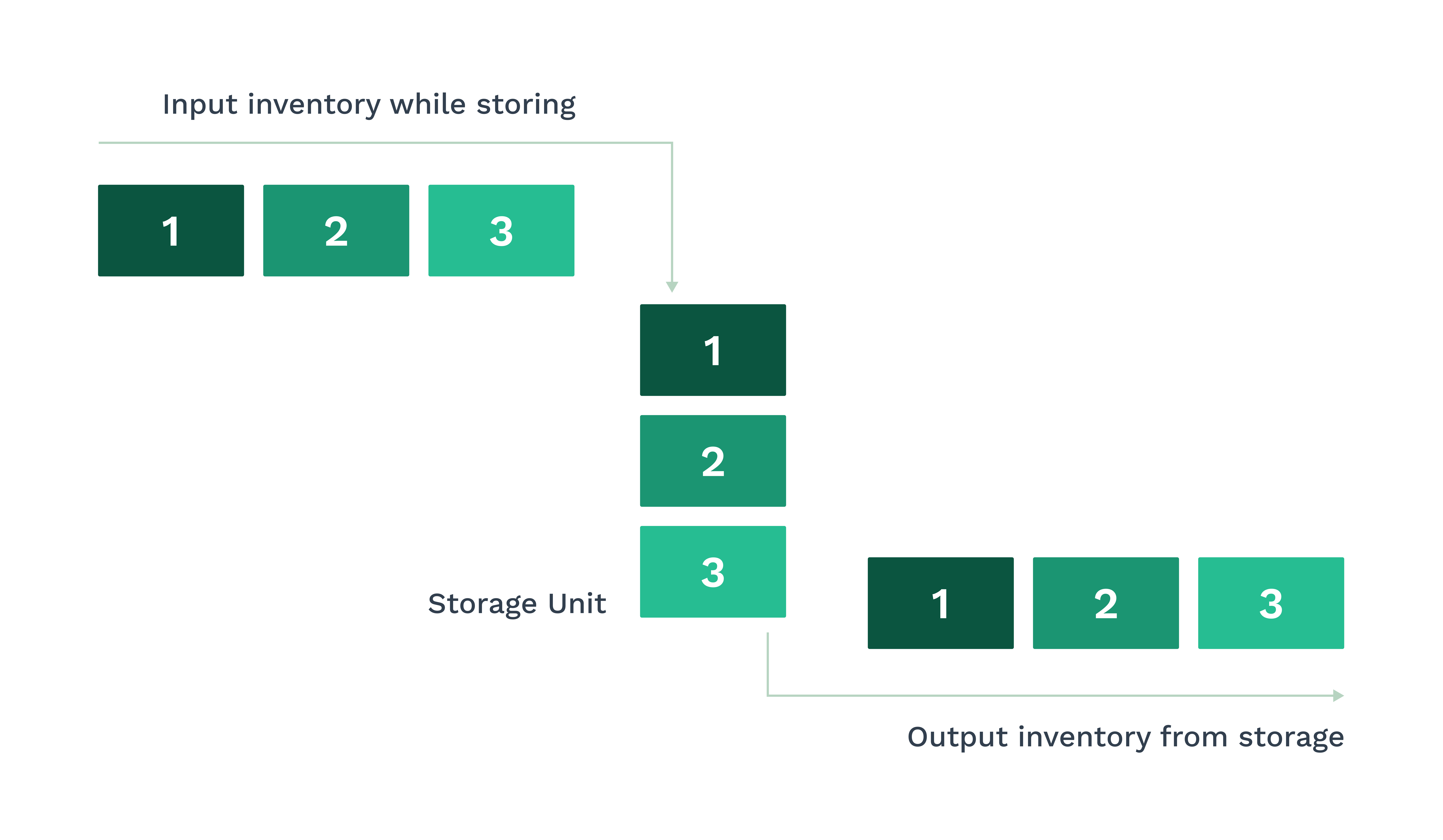
Source: mba SKOOL
Training employees can help smooth out the operation. You can also develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) that can provide a written guide for employees to follow.
Implementing FIFO in your inventory management methods can improve the production process and inventory lifecycle.
2. Perform Regular Inventory Audits
Implementing a regular inventory audit process can help provide accurate inventory counts. Consistent audits can help businesses spot inconsistencies between what is on the books and actual stock quantities, ensuring their inventory data remains current and trustworthy.
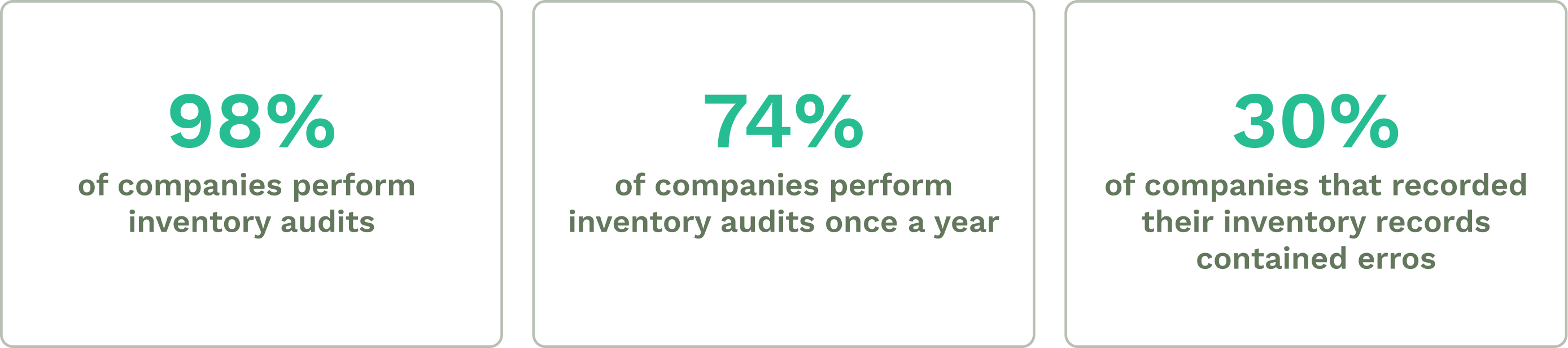
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: inFlow Blog
There are several popular approaches for auditing inventory items:
- Manual Count or Physical Inventory Audit: A complete physical count of all inventory items at a specific time (typically done annually or semi-annually). For example, a retail store conducts year-end physical inventory to reconcile discrepancies between records and on-hand inventory.
- Cycle Count Audit: Continuous inventory checks by counting smaller subsets of inventory on a rotating schedule (e.g., daily, weekly). For example, warehouse staff may count a different category of items every week to spot any differences early.
- ABC Analysis Audit: This is when inventory is divided into three distinct categories. For example, a pharmaceutical company may audit its most expensive drugs more frequently.
- A: High-value items with low sales frequency.
- B: Moderate value and moderate sales frequency.
- C: Low-value items with high sales frequency.
- Perpetual Inventory Audit: Inventory records are updated in real-time through a perpetual inventory system, and audits verify these records periodically. For example, retail stores that use POS systems can automatically adjust inventory levels and conduct spot checks to verify accuracy.
- Blind Count Audit: This is an approach where the audit staff cannot access the existing inventory records. This method can reduce bias when conducting inventory. For example, this is often used when companies hire third-party firms to validate a company’s inventory records.
- Reconciliation Audit: This audit compares recorded inventory levels with actual stock to identify discrepancies and their causes. The primary purpose is to reconcile differences between physical and recorded inventory. For example, a warehouse will conduct a reconciliation audit after sales events like Black Friday to account for shrinkage.
- Inventory Turnover Audit: This audit evaluates how quickly inventory is used and replaced. This approach can also help identify overstock or understock issues, guiding purchasing decisions. For example, a warehouse storing food might perform turnover audits to track perishable items and reduce waste.
- Internal vs. External Inventory Audit: Internal audits are performed by the company’s internal team to ensure compliance and accurate record-keeping. A third-party auditor conducts external audits to meet regulatory requirements or satisfy investors.
- Shrinkage Audit: The primary purpose of this audit is to identify lost, stolen, or damaged goods, reduce shrinkage, and improve inventory accuracy. Warehouse managers and retailers generally use shrinkage audits to find theft patterns and adjust their loss prevention strategies.

Source: WorkTrek
3. Implement Inventory Management Software
In today’s digital age, inventory management software can improve business processes. It simplifies product and material tracking while increasing control over various aspects of company operations.
One key benefit is providing real-time updates on inventory levels, helping businesses avoid overstocking and shortages.
Inventory management tools offer clear visibility into stock quantities and enable automated restocking processes. This automation maintains optimal inventory levels without constant manual monitoring, reducing errors caused by human involvement. These systems analyze data to identify potential problems and areas for improvement, facilitating more strategic decision-making.
If you are a maintenance organization, you can use CMMS tools such as WorkTrek, which offers a complete inventory management system, including low stock alerts.
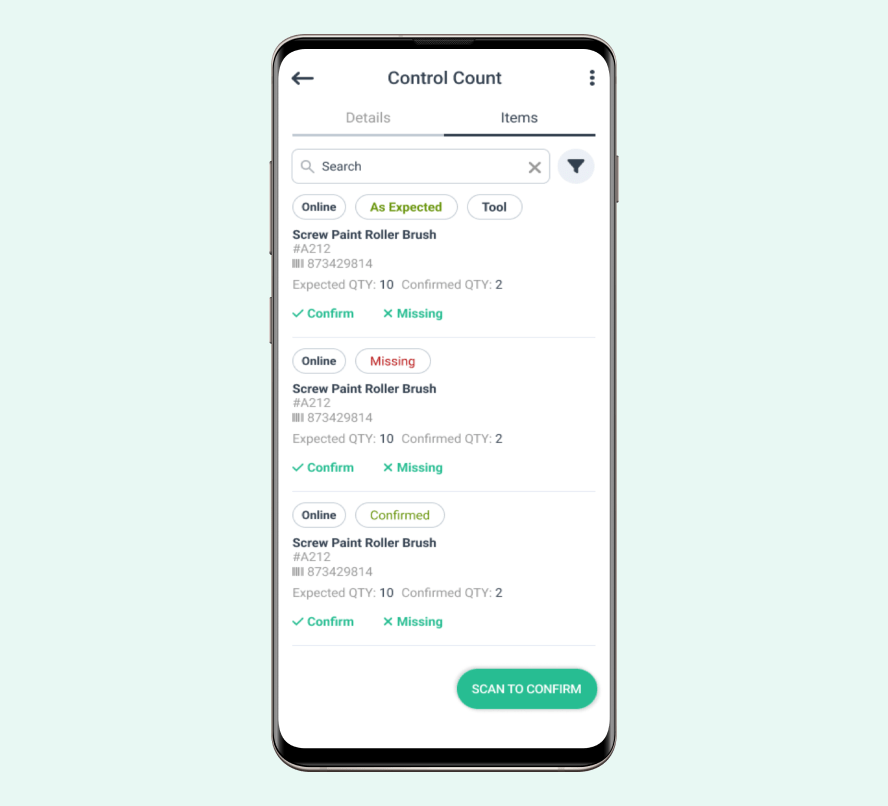
Source: WorkTrek
Comprehensive inventory management systems integrate customer order processing, real-time inventory monitoring, and supplier information in a single interface. This greatly enhances productivity by streamlining what would otherwise be a complex task when using separate platforms.
Consistent use of reliable inventory software promotes uniform practices across teams, ensuring accurate records and adherence to company protocols. This is essential for maintaining accurate records and ensuring all employees strictly follow established procedures.
Advanced features in these automated solutions cater to growing businesses by providing functionalities such as API integration with third-party logistics companies.
Investing in high-quality inventory management software helps companies streamline their workflows effectively. Quick access to stock position data enables precise tracking and supports informed operational strategies based on data-driven insights.
4. Closely Manage Safety Stock
Managing safety stocks can protect against demand fluctuations and supply delays. The primary role of safety stocks is to prevent stockouts, ensuring businesses can meet customer demands even during sudden spikes or supply chain disruptions.
They act as a buffer, providing peace of mind and greater control over inventory.
To determine the right safety stock level, analyze how maximum daily sales differ from the average and factor in supplier lead times.
This approach helps balance the need to meet customer expectations without incurring excess inventory costs.
You can also use forecasting based on historical sales data and future demand predictions. This ensures that safety stock levels are adjusted appropriately.
The proper safety stock improves customer service by ensuring consistent, on-time delivery. When businesses meet demand reliably, they build trust and loyalty, leading to repeat sales and referrals.
Proper stock levels also ease vendor relationships by reducing the need for last-minute orders, which can cause financial strain and disrupt partnerships.
However, holding too much safety stock can lead to unnecessary expenses. Storage costs, insurance, and risks like product expiration or obsolescence are all concerns, especially with perishable goods.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting safety stock levels based on market trends and supplier performance gives businesses a strategic edge. This approach optimizes inventory management, minimizes costs, and ensures smooth operations, improving overall efficiency.
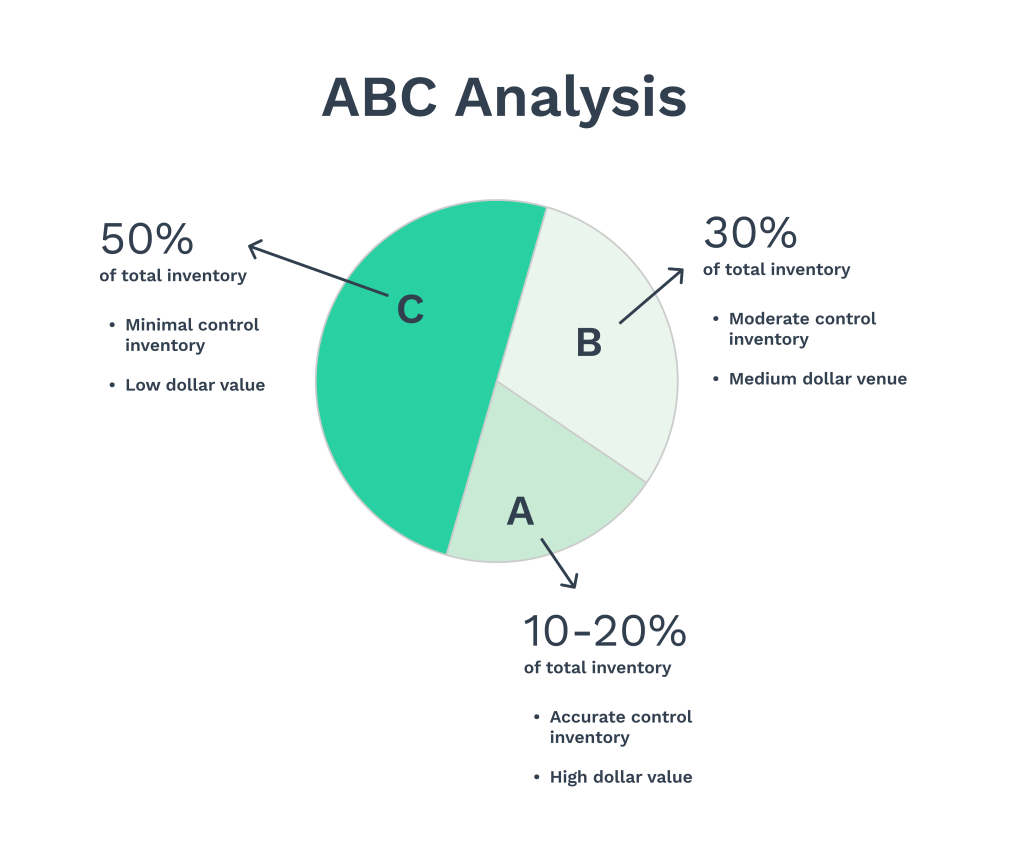
5. Perform ABC Analysis for Inventory Categorization
Based on importance, ABC analysis divides inventory into three groups: A, B, and C. It follows the Pareto Principle, which suggests that a small portion of inventory generates most of the revenue. By focusing on these key items, businesses can improve inventory management and allocate resources more efficiently.
- Class A items comprise 10-20% of stock but account for 70-80% of consumption value. These items need close monitoring and frequent reviews to ensure availability.
- Class B items represent about 30% of stock and contribute 15-20% to annual usage. Compared to Class A, they require moderate oversight.
- Class C items comprise 50% of inventory but only contribute around 5% to consumption value. These can be tracked with minimal effort.
Using ABC analysis, companies can focus on essential items while optimizing stock levels and costs to efficiently meet customer needs.
Source: impact.
This method also supports better decision-making by ensuring high-demand products are always available. There are several key benefits:
- Better supplier negotiations – Businesses can secure favorable deals by focusing on Class A items critical for operations.
- Adaptable product management – Regularly revisiting categories ensures inventory stays aligned with shifting market demands and new product launches.
- Improved productivity through automation – Technology simplifies categorization, increases reliability, and ensures smooth handling and storage, meeting customer expectations.
ABC analysis allows companies to manage inventory effectively, balancing costs while maintaining the availability of key products. This strategic approach ensures smoother operations and better customer satisfaction.
6. Develop Effective Supplier Relationships
Effective inventory management depends on building strong relationships with suppliers. These partnerships can add 23%-46% more value to a company. Reliable suppliers offer better long-term deals, stable pricing, and consistent supply, reducing the risk of disruptions in the supply chain.
Good supplier relationships also allow for faster stock replenishment, better pricing, and improved payment terms, which are beneficial during demand spikes. Close collaboration in negotiations helps businesses align minimum order quantities (MOQs) with demand forecasts, preventing overstock situations.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: inFlow Blog
Involving suppliers early in inventory and production planning improves efficiency. Sharing insights on demand forecasts and production timelines ensures both parties are prepared to meet customer needs. Prompt payments build trust, leading to prioritized services and greater reliability across the supply chain.
Using vendor-managed inventory (VMI) systems can further improve inventory control. In this model, vendors monitor stock levels using the business’s real-time data and sales forecasts. This collaboration eases the burden of inventory management, allowing companies to focus on other priorities while staying ready to meet customer demands.
Building strong supplier relationships improves inventory control by fostering trust, streamlining processes, and enhancing the ability to respond quickly to market changes
7. Create Demand Forecasting Techniques
Demand forecasting, or demand planning, involves predicting future inventory needs based on historical data and upcoming events. It helps businesses estimate product demand accurately to meet customer orders without creating excess stock.
Anticipating needs improves cash flow and reduces the costs of holding surplus inventory.
To forecast effectively, companies must consider several factors, including current stock levels, past sales trends, and expected changes in demand.
Analyzing sales history reveals recurring patterns, helping businesses adjust inventory levels accordingly. Along with internal trends, external factors—like market changes, promotions, or seasonal shifts—should also be part of the forecast.
Combining trend analysis, visual data tools, and qualitative judgment improves forecasting accuracy. Automated tools with machine learning can refine predictions over time, making inventory management more efficient.
Real-time stock monitoring gives businesses timely insights for proactive supply chain decisions. Maintaining open communication with suppliers about shifts in customer behavior allows companies to adapt quickly when demand changes.

Effective forecasting helps companies maintain the right balance—avoiding stockouts and overstock situations. With precise predictions, businesses can increase turnover, minimize risks, and stay ready to meet evolving customer needs. This forward-looking approach ensures smoother operations and better alignment with market trends.
8. Optimize Warehouse Layout
An optimized warehouse layout improves productivity and operational efficiency. Key areas include zones for receiving, storage, packing, and shipping.
Try strategically placing these zones to ensure smooth movement of products, staff, and equipment, minimize congestion, and improve workflow.
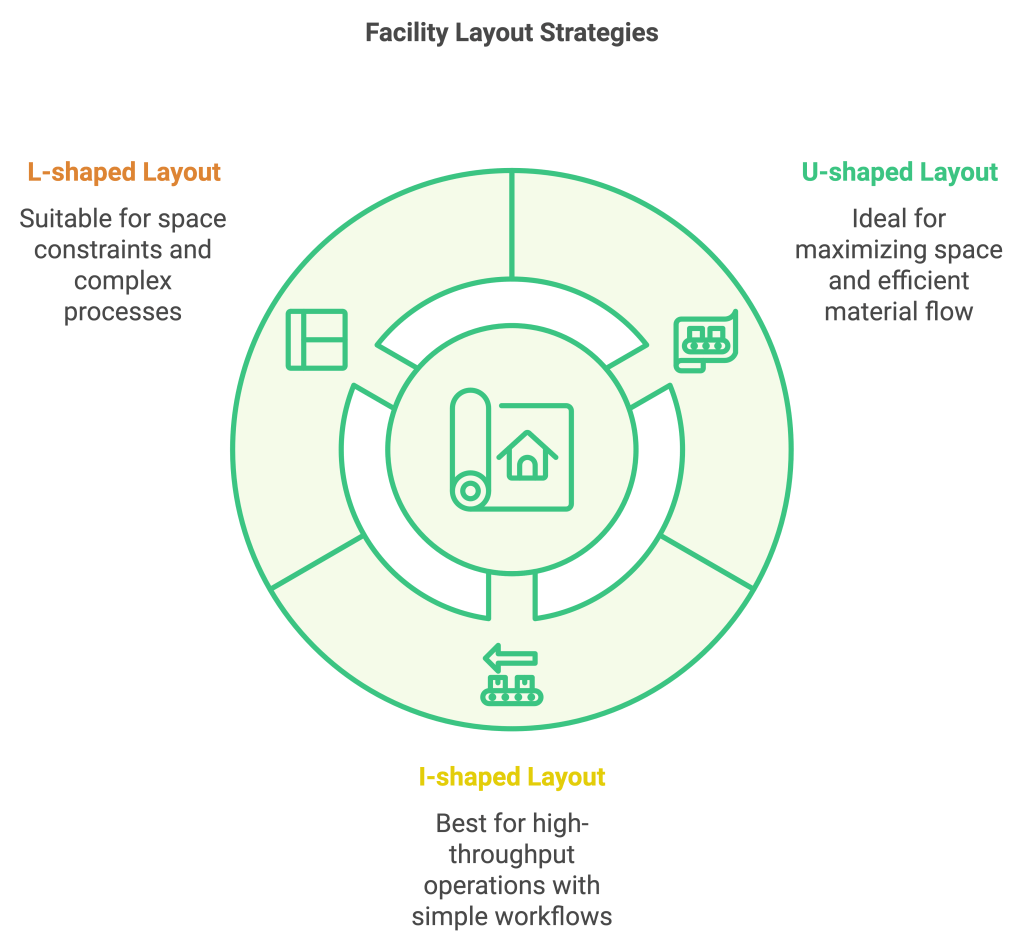
There are three main warehouse layouts: U-shaped, I-shaped, and L-shaped. Each serves different needs:
- U-shaped layout maximizes space and supports efficient material movement.
- I-shaped layout works well for high-throughput operations with simple workflows.
- L-shaped layout suits businesses with specific space constraints or complex processes.
Source: WorkTrek
An adjustable racking system can offer flexibility, accommodating changing inventory levels and product sizes. Clear visibility and easy access within storage areas help employees work efficiently, reducing frustration. Well-organized layouts with proper signage also speed up stock-related tasks and improve accuracy.
Safety is essential in any warehouse design. Proper lighting, designated walkways, and separate paths for people and machines reduce risks and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Consistent safety features across multiple sites improve both operations and staff well-being.
Optimizing a warehouse layout is crucial for effective inventory control. It promotes faster workflows, safer environments, and better stock management. A well-designed layout supports smoother operations, helping businesses meet goals and manage logistics more precisely.
9. Leverage Technology for Inventory Tracking
Technology is essential for improving the accuracy and efficiency of inventory tracking. High-value items and sensitive products often use RFID tags, which automatically update stock information. This reduces human error and simplifies inventory management.
IoT devices provide real-time insights into stock levels and locations, increasing transparency throughout the supply chain. These devices can also monitor temperature and humidity, ensuring goods are stored properly. With up-to-date data, businesses can quickly adjust to changes in inventory.
For smaller businesses, QR codes offer a simple, cost-effective solution. Employees can scan these codes to track item movements and update inventory systems with real-time availability.
![]()
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: zhenhub
Advanced technologies like RFID, IoT sensors, and QR codes improve inventory accuracy and support best practices. Real-time tracking enables businesses to make smarter decisions and optimize operations.
Modern innovations have transformed how companies manage inventory. These technologies offer greater precision, improve the inventory management process, and enhance customer satisfaction, driving success and growth.
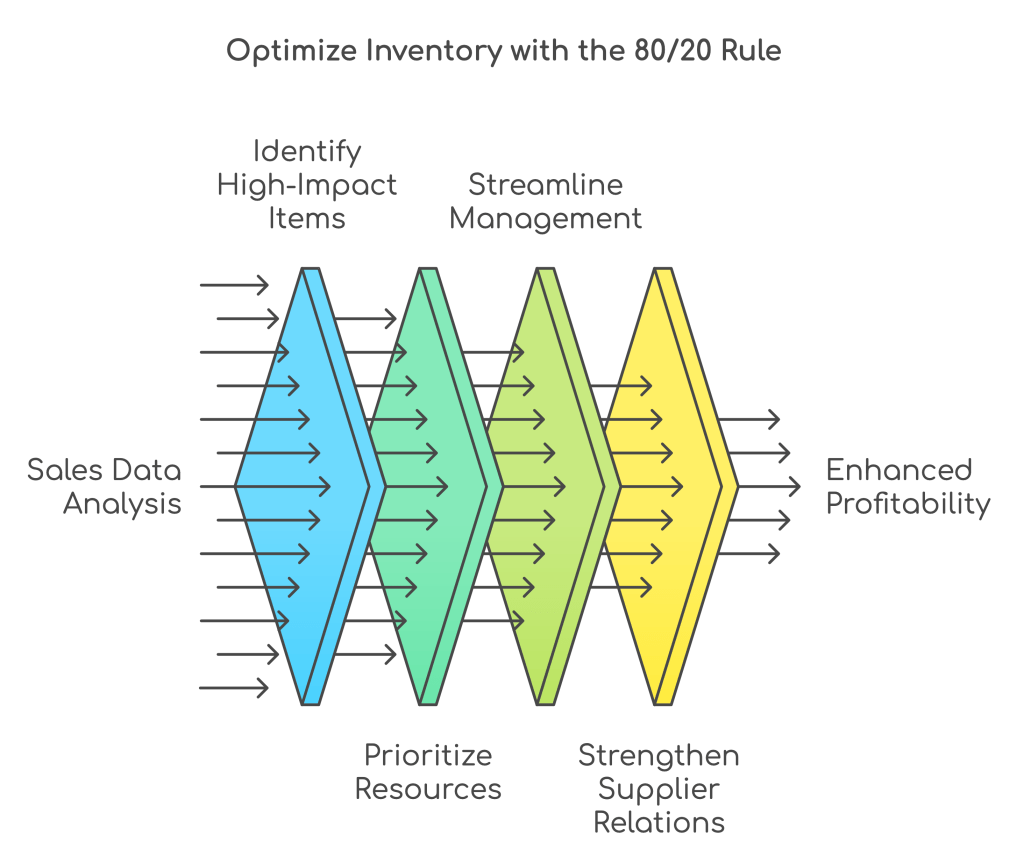
10. Understand and Employ 80/20 Rule
The 80/20 rule, or Pareto Principle, is a powerful strategy for improving inventory management. It suggests that 80% of a company’s revenue comes from just 20% of its inventory. By identifying and focusing on these critical items, businesses can manage inventory more efficiently and allocate resources more effectively.
Applying the 80/20 rule starts with analyzing sales data to find the products that contribute the most to revenue. Once identified, these high-impact items should be prioritized in stock levels, marketing, and customer service. Ensuring these key products are always available maximizes sales and improves customer satisfaction.
Focusing on top-performing items also streamlines inventory management. It reduces excess stock, lowers carrying costs, and improves cash flow. With fewer low-performing items to manage, businesses can use warehouse space more strategically. Prioritizing high-value products can also strengthen supplier relationships, leading to better terms and pricing.
Incorporating the 80/20 rule helps businesses boost efficiency and make smarter decisions. This approach minimizes waste, maximizes returns, and ensures companies are ready to meet customer demand. By focusing on what matters most, businesses can drive growth and profitability.
Source: WorkTrek
Summary
This guide has explored best practices for effective inventory management, providing businesses with strategies to transform their stock management. It emphasizes mastering inventory basics while adopting advanced technologies to enhance control and efficiency.
Effective inventory management streamlines cash flow, reduces costs, and meets customer needs. Businesses can achieve precise stock levels and improve operations by using techniques like first-in-first-out (FIFO), routine audits, maintaining safety stocks, ABC analysis, and demand forecasting. Integrating robust inventory management software and optimizing warehouse layouts further strengthens these efforts.










