Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKey Takeaways:
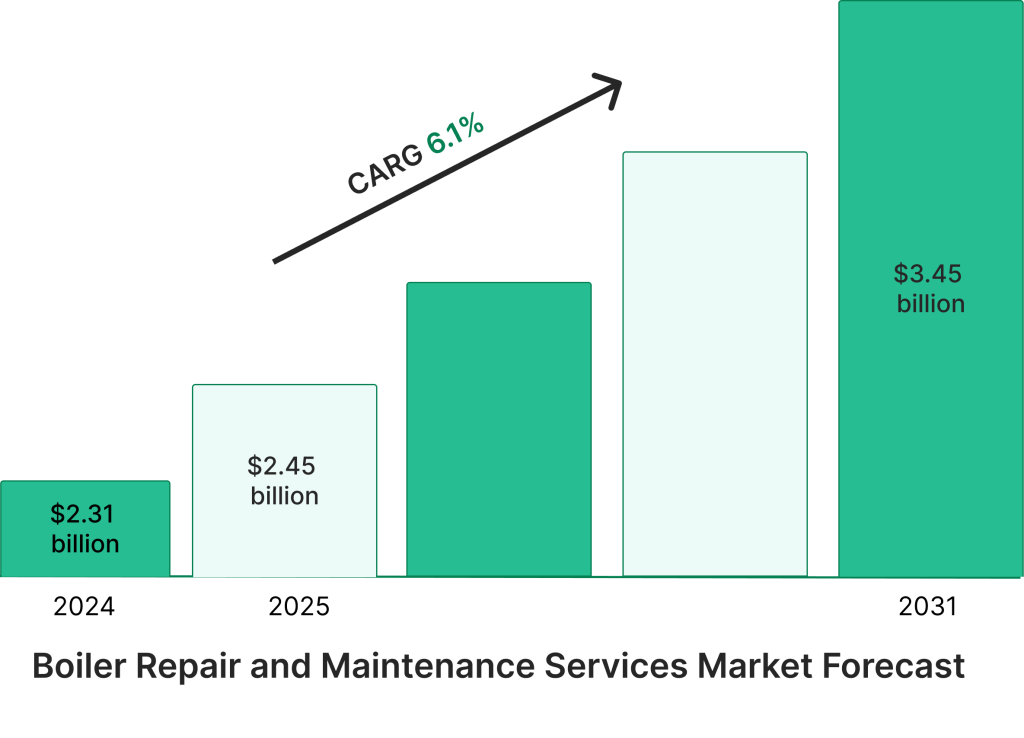
- The industrial boiler maintenance market reached $22.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at 4.6% CAGR through 2034
- Industrial boilers account for approximately 85% of steam production in the manufacturing sector
- Without proper maintenance, boiler efficiency can drop by 10-20% within just one year
- Water-tube boilers account for 60% of maintenance demand due to their use in high-pressure steam applications
Industrial boiler maintenance isn’t just about keeping equipment running. It is also about protecting one of your facility’s most critical assets while maximizing energy efficiency and preventing costly downtime.
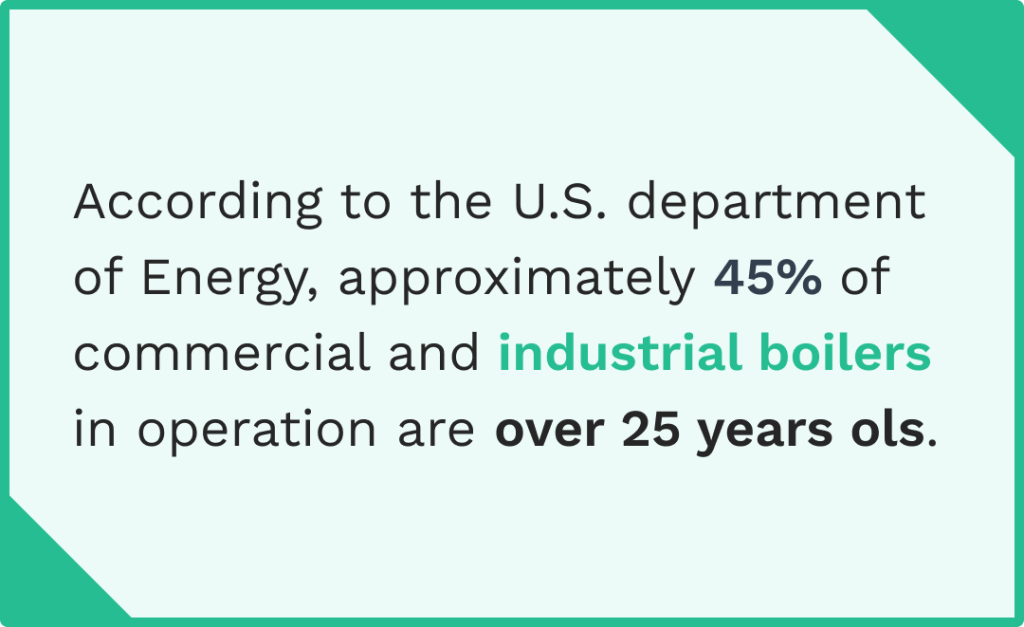
Industrial steam boilers power everything from manufacturing processes, hot water to heating systems, making proper boiler maintenance essential for facility managers and boiler operators alike. Yet many organizations treat boiler systems as “set it and forget it” equipment until something goes wrong.
That approach can be catastrophic.
A poorly maintained boiler not only wastes energy but also creates safety hazards, drives up energy costs, and can lead to complete system failure when you need it most. The consequences range from minor inefficiencies to major boiler emergencies that shut down entire operations.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about industrial boiler maintenance, from understanding different boiler types to implementing a preventive maintenance plan that keeps your heating system running smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding Industrial Boiler Systems
Before diving into maintenance specifics, it’s important to understand what makes industrial boiler systems so critical to operations.
Industrial boilers are pressure vessels designed to generate steam or hot water by burning fuel—typically natural gas, fuel oil, or biomass—in a combustion chamber. The heat from combustion gases is transferred through heat exchangers to water, creating steam or hot water for various industrial processes.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, industrial boilers account for approximately 85% of steam production used in the manufacturing sector. Streamlining maintenance with solutions like work order software can help manage these industrial assets efficiently.

That’s a staggering figure that underscores why proper boiler maintenance can’t be treated as an afterthought.
Role of Boiler Technicians
Boiler service technicians conduct thorough inspections of boilers, identifying potential issues and assessing their severity. Technicians perform routine maintenance tasks, including cleaning, lubrication, and parts replacement.
Safety is paramount in boiler service, and technicians test and calibrate safety devices to ensure they function correctly. Technicians perform routine maintenance tasks, including cleaning, lubrication, and parts replacement.
Technicians maintain detailed records of boiler inspections, maintenance, and repairs to track the boiler’s history and compliance with safety regulations.
Modern boiler systems include several critical components working together:
- Combustion chamber: Where fuel burns to create heat
- Heat exchanger: Transfers heat from hot combustion gases to water
- Control systems: Regulate pressure, temperature, and fuel usage
- Water treatment system: Maintains water quality to prevent corrosion and scale buildup
- Burner’s pilot tube and ignition system: Initiates and maintains combustion
- Pressure relief valves and safety valves: Protect against excessive pressure
Each component requires specific maintenance attention to ensure the boiler’s performance remains optimal.
Types of Industrial Boilers
There are many types of industrial boilers. However, they fall into two primary categories:
Fire Tube Boilers
In fire tube boilers, hot combustion gases pass through tubes surrounded by water. These are typically used for lower-pressure applications and smaller capacities.
Fire-tube boilers are simpler in design and generally easier to maintain, but they have limitations in pressure capacity and steam output.
Water Tube Boilers
Water tube boilers reverse this configuration—water flows through tubes while hot gases surround them. These boilers can handle high-pressure steam demands and are commonly found in power generation and large industrial facilities. For information on pricing plans related to asset and inventory management solutions, see the WorkTrek pricing page.
According to Global Market Insights, water tube boilers account for approximately 60% of the industrial boiler maintenance market share, driven by their ability to produce high-pressure steam efficiently.
Water tube boilers require more specialized maintenance due to their complexity, but they offer superior heat transfer efficiency and can handle much higher capacities than fire tube boilers.
Other Boiler Types
Beyond these main categories, you’ll also encounter:
- Electric boilers: Use electricity rather than combustion, eliminating the combustion chamber and reducing emissions
- Condensing boilers: Recover heat from exhaust gases to improve efficiency
- Packaged boilers: Pre-assembled units that arrive ready to install, offering maintenance and cost-saving opportunities
Each type has unique maintenance requirements, though the fundamental principles of regular inspection, cleaning, and preventive maintenance apply to all.
Key Components Requiring Regular Maintenance
Effective industrial boiler maintenance requires understanding which components need attention and why.
Burner and Combustion System
The burner controls the air-to-fuel ratio and ensures proper combustion. Regular burner tuning prevents inefficient fuel usage and excessive emissions.
According to Coal Biomass Boiler, improving combustion quality can increase boiler efficiency by 3-8%, resulting in substantial fuel savings and extended equipment life.
Poor combustion leads to wasted fuel, increased emissions, and carbon buildup that reduces heat transfer efficiency.
Heat Exchanger and Tubes
The heat exchanger is where energy transfer happens. Over time, scale buildup and corrosion can significantly reduce efficiency.
Research shows that every 1 mm of scale buildup results in 2-3% heat transfer loss.
This means a neglected boiler with substantial scaling can lose 10-15% efficiency or more, dramatically increasing energy costs.
Regular cleaning and water treatment are essential for maintaining optimal heat transfer efficiency.
Water Treatment and Chemical Feed Systems
Water quality directly affects boiler longevity. Poor water treatment leads to:
- Corrosion that weakens boiler components
- Scale buildup that reduces heat transfer
- Foaming that affects steam quality
- Priming issues in steam systems
A proper water treatment system includes chemical feed pumps, water softeners, and deaerators to remove oxygen and maintain proper pH levels. For businesses interested in system optimization beyond water treatment, you can also explore 15 types of inventory management systems in this comprehensive guide.
Control Systems and Safety Devices
Modern boiler control systems monitor and adjust multiple parameters:
- Steam pressure and temperature
- Fuel and air flow rates
- Water level
- Combustion efficiency
Safety devices like pressure relief valves, flame safeguards, and low-water cutoffs must be tested regularly to ensure they’ll function when needed.
Malfunctioning controls can lead to reduced efficiency, unstable operation, or dangerous conditions.
The Importance of Routine Boiler Maintenance
The case for regular boiler maintenance isn’t just theoretical—it’s backed by compelling data.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Without a proactive maintenance plan, boiler efficiency can drop by 10-20% within just one year, resulting in substantial fuel waste, costly downtime, and reduced equipment lifespans.
For a facility spending $500,000 annually on fuel, a 15% efficiency loss means $75,000 in wasted energy.
Proper maintenance, including routine boiler maintenance tasks like cleaning heat transfer surfaces, optimizing combustion, and maintaining water chemistry, can prevent these losses and keep your heating system running efficiently.
Safety Risks and Regulatory Compliance
Neglecting boiler maintenance creates serious safety hazards:
- Pressure vessel failures from corrosion or overpressure
- Gas leaks from deteriorated seals
- Carbon monoxide poisoning from incomplete combustion
- Explosions from fuel accumulation
Industrial boilers operate under high pressure and temperature, making safety protocols non-negotiable.
Regulatory bodies require annual or biannual inspections, depending on jurisdiction and boiler class. Failure to maintain proper documentation and pass inspections can result in fines, forced shutdowns, or legal liability.
Minimizing Downtime
Unplanned boiler failures cause production disruptions that far exceed the direct repair costs.
Research from Siemens found that annual downtime costs at large automotive plants can reach $695 million, driven largely by critical equipment failures, including boiler systems.
Preventive maintenance helps identify issues before they cause failures, allowing you to schedule repairs during planned downtime rather than dealing with emergency repairs when production is at stake.
Extended Equipment Life
Boilers represent major capital investments. A well-maintained industrial boiler can operate efficiently for 25-30 years or more, while a neglected system may require replacement in half that time.

Regular maintenance prevents accelerated wear, protects against corrosion, and ensures components operate within design specifications—all factors that contribute to longer equipment life.
Essential Routine Maintenance Tasks
A comprehensive boiler maintenance checklist should include tasks at various intervals.
Daily Maintenance Tasks
Daily checks keep boiler operators aware of any developing issues:
- Monitor boiler pressure, temperature, and fuel consumption
- Inspect the pilot light and flame quality through sight ports
- Check for unusual noises, vibrations, or odors
- Verify proper water levels and flow rates
- Review control system readings for abnormalities
- Inspect for visible leaks (steam, water, or fuel)
- Test safety alarms and indicators
These quick checks take minimal time but can catch problems before they escalate.
Weekly Maintenance Activities
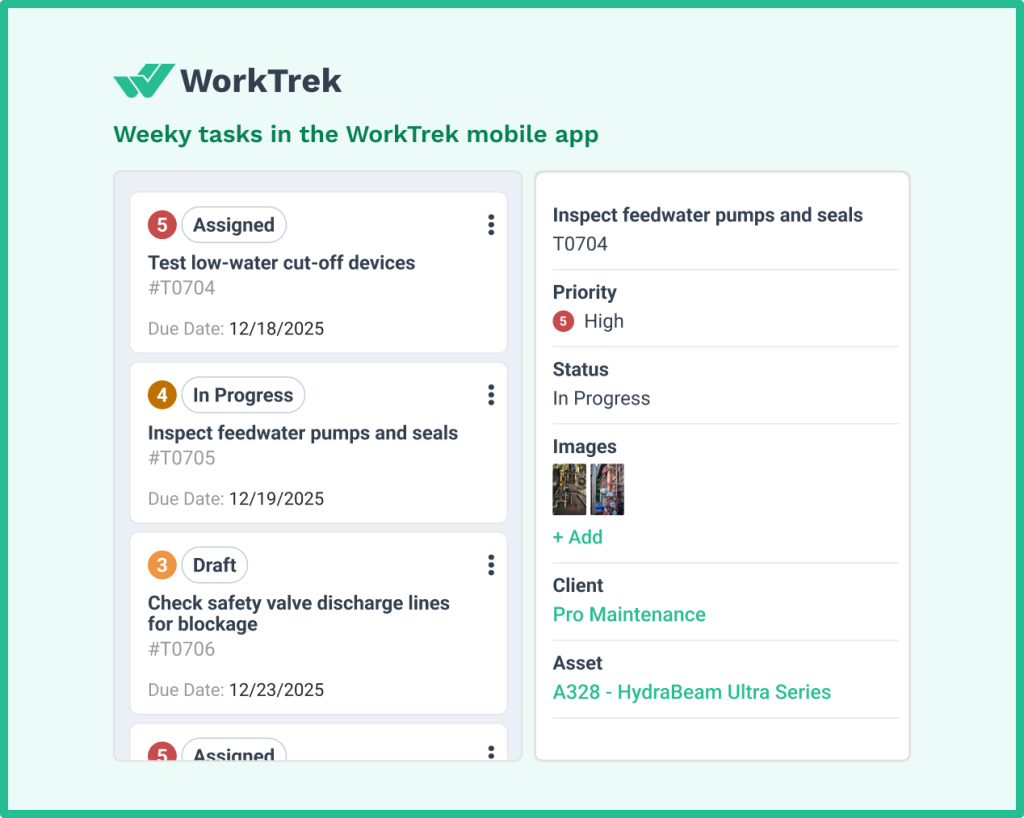
Weekly tasks provide a more thorough assessment:
- Test water quality and adjust chemical treatment as needed
- Inspect fuel supply lines and valves for leaks
- Blow down the boiler to remove sediment
- Test pressure relief valves and safety controls
- Check combustion air intake for obstructions
- Inspect insulation for damage
- Review operating logs for trends
Monthly Inspection and Cleaning
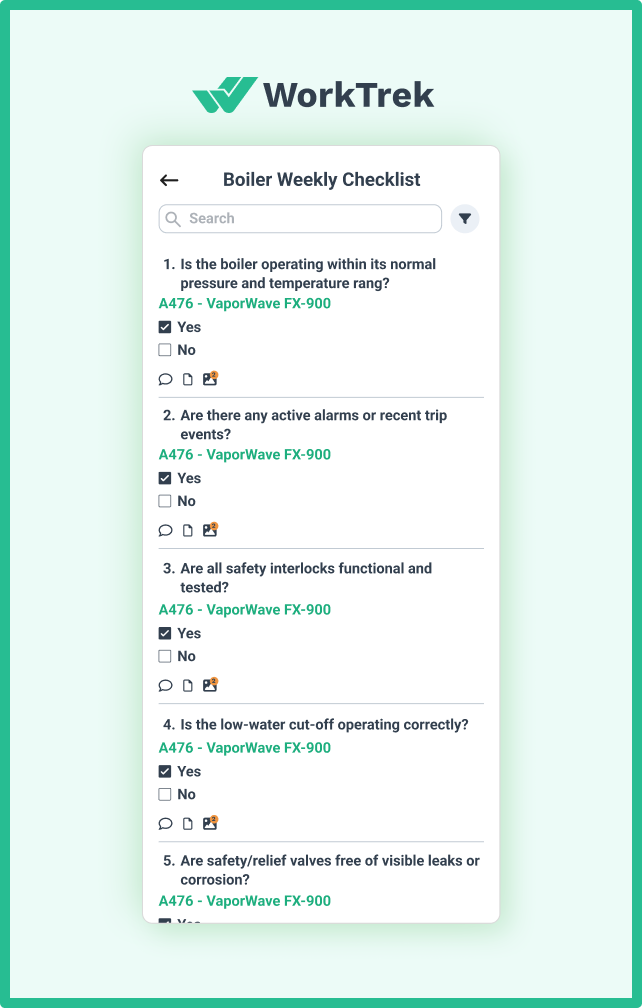
Monthly maintenance includes a deeper inspection:
- Clean burner components and check the ignition system
- Inspect and clean flame sensors and thermocouples
- Check electrical connections and control wiring
- Inspect refractory and insulation for deterioration
- Test and calibrate control instruments
- Review maintenance schedules and upcoming tasks
- Perform combustion analysis to verify efficiency
Semi-Annual and Annual Maintenance
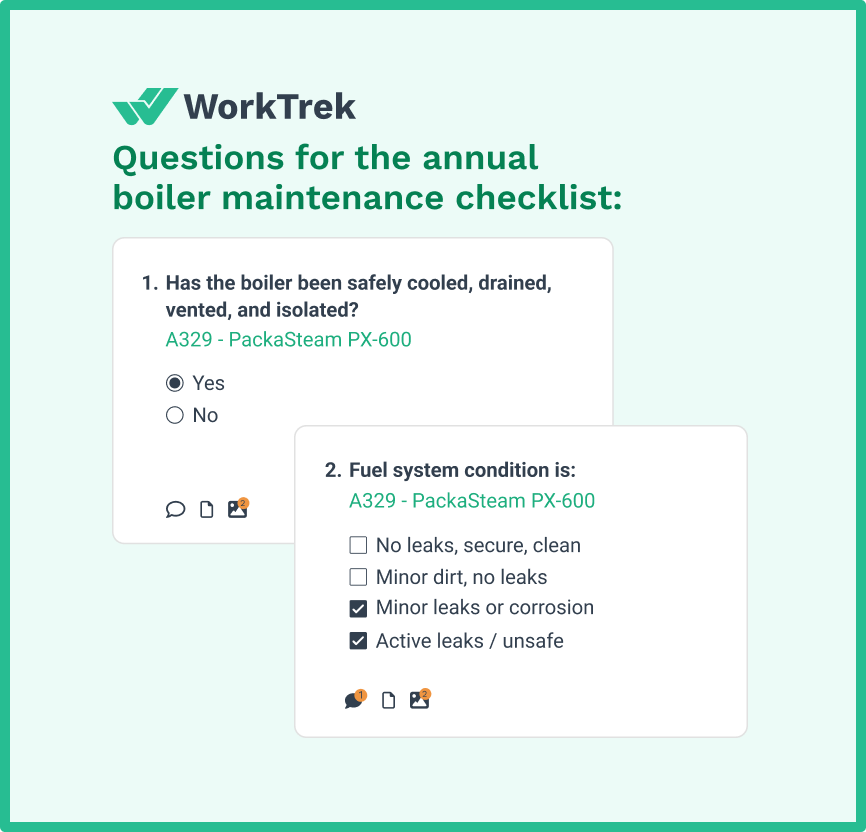
These comprehensive maintenance schedules should include:
- Complete boiler shutdown and internal inspection
- Clean fireside and waterside heat transfer surfaces
- Inspect tubes for corrosion, erosion, and scaling
- Non-destructive testing of critical components
- Inspect and test all safety devices
- Overhaul or replace worn components
- Recalibrate control systems
- Comprehensive pressure testing
- Review and update maintenance documentation
Common Boiler Problems and Solutions
Even with regular maintenance, boilers can develop issues. Recognizing problems early is key to preventing costly repairs.
Corrosion and Scale Buildup
Corrosion attacks metal surfaces, weakening pressure vessels and tubes. Scale buildup acts as insulation, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
Solution:
Implement proper water treatment with chemical dosing, maintain appropriate pH levels (typically 10.5-11.5 for boilers), and schedule regular cleaning. Deaerators and softeners help remove oxygen and hardness minerals that contribute to these problems.
Low Boiler Pressure Issues
Low pressure can result from leaks, faulty pressure controls, or insufficient water supply.
Solution:
Systematically check for leaks in the system, inspect pressure relief valves for proper operation, verify makeup water supply, and test pressure controls for accuracy. Address the root cause rather than just increasing operating pressure.
Reduced Efficiency and Higher Energy Costs
Efficiency losses typically stem from fouling, poor combustion, or air leakage.
Solution
Regular combustion analysis helps optimize the air-fuel ratio. Clean heat exchangers remove insulation created by soot and scale. Seal air leaks in the boiler shell and ductwork. Consider upgrading combustion air fans to variable-frequency drives to match load requirements.
Ignition Problems
Difficult ignition or flame instability indicates problems with the ignition system, fuel supply, or combustion air.
Solution:
Clean burner components, including the burner’s pilot tube; check fuel pressure and quality; verify proper draft and airflow; and test ignition transformers and electrodes. Replace worn components as needed.
Water Level Issues
Both high and low water levels create problems. Low water can cause tube overheating and failure, while high water can lead to priming and carryover.
Solution:
Test level controls and sensors for accuracy, clean level gauge glasses, check feedwater pumps for proper operation, and inspect steam traps and condensate return systems.
Create a Comprehensive Maintenance Plan
An effective maintenance plan balances preventive tasks with reactive maintenance while documenting everything for analysis and compliance.
Establishing Maintenance Schedules
Base your schedule on:
- Manufacturer’s recommendations for your specific boiler model
- Operating hours and duty cycle
- Fuel type and quality
- Water conditions
- Previous maintenance history
- Regulatory requirements
Higher utilization and challenging operating conditions require more frequent maintenance.
Prioritizing Critical Components
Not all components require equal attention. Focus on:
- Safety-critical items (pressure relief valves, safety controls)
- High-wear components (burners, igniters)
- Efficiency-impacting parts (heat exchangers, tubes)
- Regulatory inspection items
This risk-based approach ensures you address the most important items first.
Training and Personal Protective Equipment
Boiler maintenance requires trained personnel who understand:
- Safe operating procedures
- Lockout/tagout protocols
- Hot work permits and fire safety
- Water chemistry fundamentals
- Combustion principles
- Regulatory requirements
Proper personal protective equipment includes heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, hearing protection, and respirators for working in confined spaces.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Maintain detailed records including:
- Daily operating logs
- Maintenance task completion records
- Water treatment test results
- Combustion analysis data
- Inspection reports
- Repair histories
- Parts replacement tracking
- Safety test results
This documentation proves compliance during inspections and provides valuable data to identify trends and optimize maintenance strategies.
Safety Considerations and Regulatory Compliance
Industrial boiler safety cannot be overstated. Boilers are pressure vessels operating at high temperatures with combustible fuels—a combination that demands respect and proper procedures.
Critical Safety Protocols
Before any maintenance:
- Follow lockout/tagout procedures to isolate energy sources
- Allow adequate cooling time
- Verify zero pressure before opening
- Test the atmosphere in confined spaces
- Obtain necessary permits for hot work
- Post warning signs and barriers
Never bypass safety devices or pressure controls, even temporarily.
Regulatory Requirements
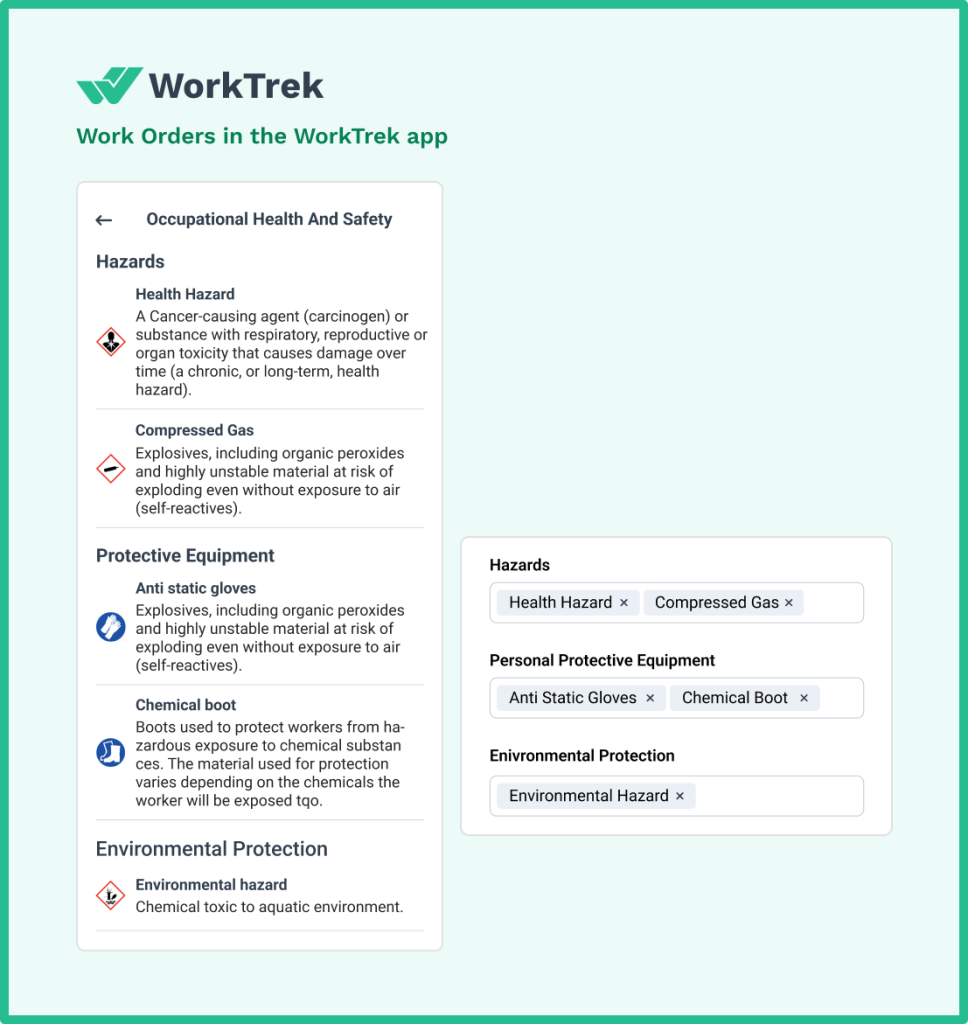
Boiler operations are governed by multiple agencies:
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code: Design and construction standards
- OSHA regulations: Worker safety requirements
- EPA rules: Emission standards and environmental compliance
- State and local codes: Inspection frequency and certification requirements
- Insurance requirements: Minimum maintenance standards
Regular inspections by authorized inspectors verify compliance and maintain insurance coverage.
How CMMS Software Transforms Boiler Maintenance
While traditional paper-based systems or spreadsheets can track basic maintenance, they fall short for modern industrial boiler operations. This is where Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) become game-changers.
Automating Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
Manual scheduling leads to missed tasks, especially with multiple boilers and complex maintenance schedules.
A CMMS like WorkTrek automatically generates work orders based on calendar dates, operating hours, or condition-based triggers. This ensures routine maintenance tasks never slip through the cracks.
For example, WorkTrek can schedule:
- Daily blowdown and log reviews
- Weekly water quality tests
- Monthly combustion analysis
- Quarterly safety valve testing
- Annual internal inspections
The system sends notifications to assigned personnel, eliminating the risk of forgotten tasks that could lead to efficiency loss or safety hazards.
Centralizing Boiler Documentation
Industrial boilers generate mountains of paperwork: inspection reports, test results, repair histories, manufacturer manuals, and regulatory documentation.
WorkTrek centralizes all this information in one accessible location. Maintenance technicians can access:
- Complete equipment history and specifications
- Standard operating procedures
- Manufacturer maintenance recommendations
- Previous repair notes and solutions
- Parts lists and inventory levels
- Safety documentation and permits
This instant access to information speeds up troubleshooting and ensures technicians have everything they need before starting work.
Tracking Maintenance Costs
Understanding the true cost of boiler operation requires tracking more than just fuel expenses.
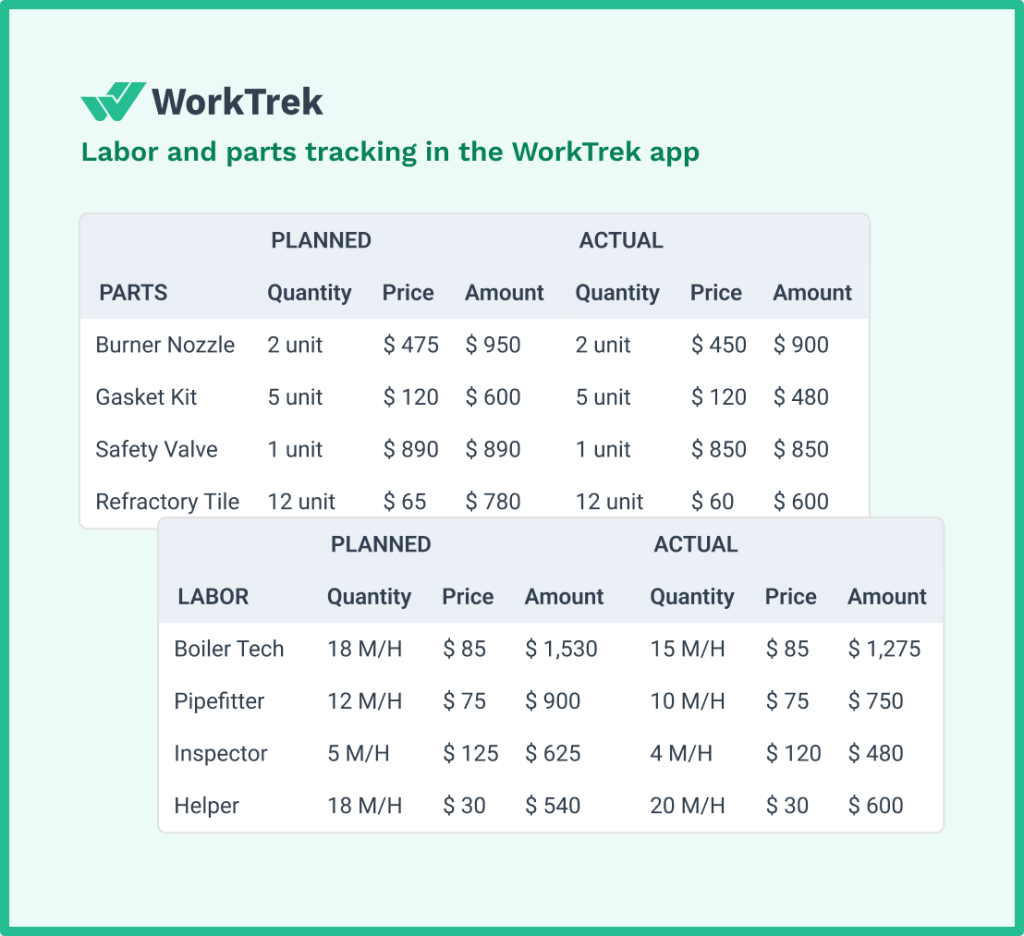
WorkTrek’s comprehensive cost tracking includes:
- Labor hours for maintenance tasks
- Parts and materials used
- Contractor and service costs
- Energy consumption trends
- Downtime impact on production
This data helps justify maintenance budgets, identify cost-saving opportunities, and make informed decisions about repair versus replacement.
Improving Compliance and Audit Readiness
Regulatory inspections require proof of proper maintenance. Paper records get lost, and spreadsheets lack the detail inspectors need.
WorkTrek maintains a complete audit trail showing:
- When maintenance was performed and by whom
- What tasks were completed
- Test results and measurements
- Parts replaced
- Safety checks conducted
This documentation is instantly accessible during inspections, reducing stress and proving compliance.
Optimizing Spare Parts Inventory
Running out of critical spare parts during a boiler emergency can lead to extended downtime. Overstocking ties up capital in unused inventory.
WorkTrek’s inventory management tracks:
- Parts consumption patterns
- Reorder points based on usage
- Vendor information and lead times
- Parts costs and budget impact
- Critical spare part availability
When a maintenance task requires parts, the system automatically deducts them from inventory and flags low stock levels for reordering.
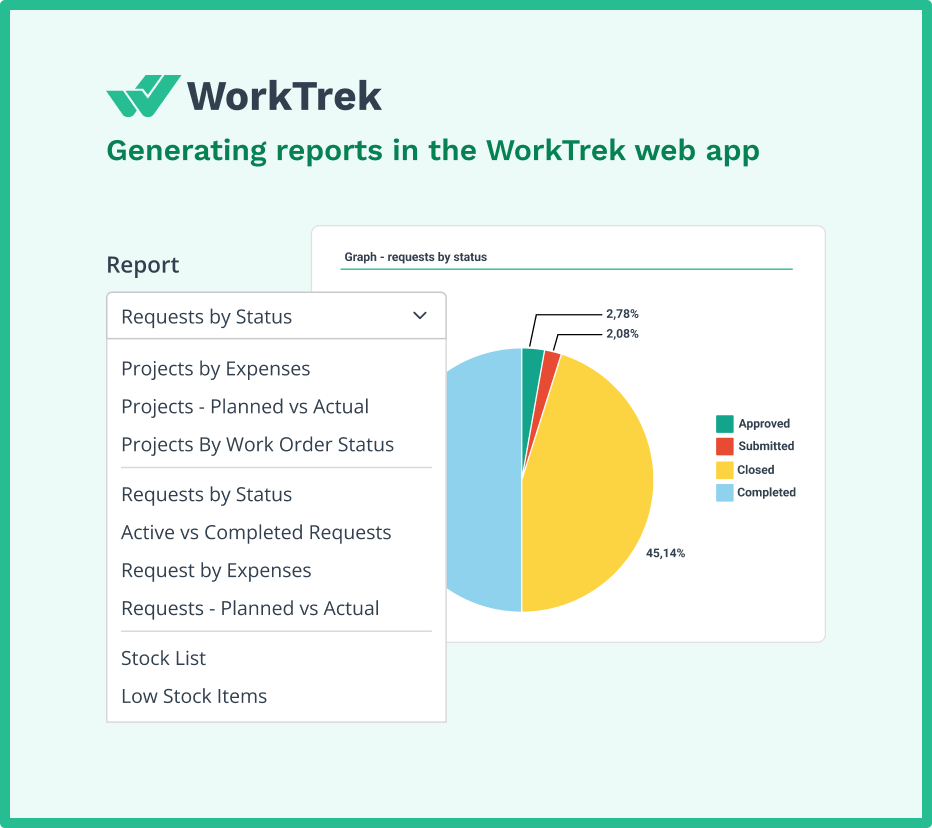
Enabling Data-Driven Decisions
The real power of a CMMS lies in the insights it provides.
WorkTrek’s reporting and analytics capabilities help facility managers:
- Identify recurring problems requiring root cause analysis
- Compare boiler performance across multiple units
- Track efficiency trends over time
- Calculate return on investment for maintenance activities
- Optimize maintenance schedules based on actual performance
For instance, if combustion efficiency data shows gradual decline between cleanings, you can adjust cleaning frequency to maintain optimal performance while avoiding unnecessary maintenance.
Supporting Mobile Maintenance Teams
Boiler operators and technicians work in the field, not behind desks.

WorkTrek’s mobile app puts maintenance information in technicians’ hands:
- Access work orders and checklists on smartphones or tablets
- Record readings and test results directly in the system
- Attach photos of problems or completed work
- Update task status in real-time
- Access equipment manuals and diagrams
For more information on maintenance strategies, including reactive and preventive maintenance, visit our detailed article.
This eliminates double-entry, reduces paperwork, and ensures accurate, timely data capture.
The WorkTrek Advantage for Boiler Maintenance
What sets WorkTrek apart for industrial boiler maintenance?
Intuitive interface
Technicians can start using WorkTrek with minimal training, reducing implementation time and resistance to adoption.
Comprehensive functionality
From preventive maintenance scheduling to inventory tracking to compliance reporting, WorkTrek handles all aspects of boiler maintenance on a single platform.
Scalability
Whether you’re managing a single boiler or a fleet across multiple facilities, WorkTrek grows with your needs.
Outstanding support
WorkTrek’s implementation team ensures smooth setup and provides ongoing assistance to maximize your return on investment.
Integration capabilities
WorkTrek connects with other business systems, eliminating data silos and improving overall operational efficiency.
Organizations that implement WorkTrek for boiler maintenance typically see:
- 20-30% reduction in unplanned downtime
- 15-25% decrease in maintenance costs
- Improved boiler efficiency and lower energy costs
- Better regulatory compliance and faster inspections
- Extended equipment life through consistent preventive maintenance
In an era where industrial facilities face pressure to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and maintain stringent safety standards, WorkTrek provides the tools to achieve all three.
Conclusion
Industrial boiler maintenance is required for efficient, cost-effective operations.
The data is clear: proper boiler maintenance prevents efficiency losses of 10-20%, extends equipment life, reduces energy costs, and protects against catastrophic failures. With the industrial boiler maintenance market exceeding $22 billion and growing steadily, organizations worldwide recognize the strategic importance of keeping their boiler systems in peak condition.
The key elements of an effective maintenance program include:
- Understanding your specific boiler type and its maintenance requirements
- Implementing comprehensive maintenance schedules covering daily, weekly, monthly, and annual tasks
- Training personnel in proper procedures and safety protocols
- Maintaining detailed documentation for compliance and analysis
- Addressing problems promptly before they escalate
- Investing in modern tools like CMMS software to optimize maintenance operations
Whether you operate fire-tube or water-tube boilers, burn natural gas or fuel oil, produce hot water or high-pressure steam, the principles remain the same: regular inspections, proper water treatment, combustion optimization, and proactive repairs keep your boiler running smoothly.
The alternative—reactive maintenance that addresses problems only after failures occur—inevitably costs more in the long run through emergency repairs, production disruptions, safety incidents, and shortened equipment life.
By implementing the practices outlined in this guide and leveraging tools like WorkTrek to streamline your maintenance operations, you can transform your boiler maintenance from a necessary expense into a value-creating activity that pays dividends through improved reliability, efficiency, and safety.