What is Turnaround Maintenance?
Turnaround maintenance refers to a planned, periodic shutdown of an entire facility, plant, or unit where normal operations cease completely to allow for comprehensive inspection, repairs, replacements, and upgrades of equipment and systems.
This strategic maintenance approach involves extensive planning, turnaround schedules, coordination, and execution of maintenance activities. This effort takes place within a shutdown period to reduce production downtime.

Definition and Overview
A turnaround is a planned period of non-production during which industrial facilities perform maintenance, inspection, repair, and upgrade activities. The primary purpose of a turnaround is to ensure the facility’s continued safe, efficient, and reliable operation.
Regular turnarounds help prevent equipment failures, reduce the risk of accidents, and maintain regulatory compliance. By systematically addressing potential issues before they escalate, turnarounds play a crucial role in extending the lifespan of equipment and optimizing overall plant performance.
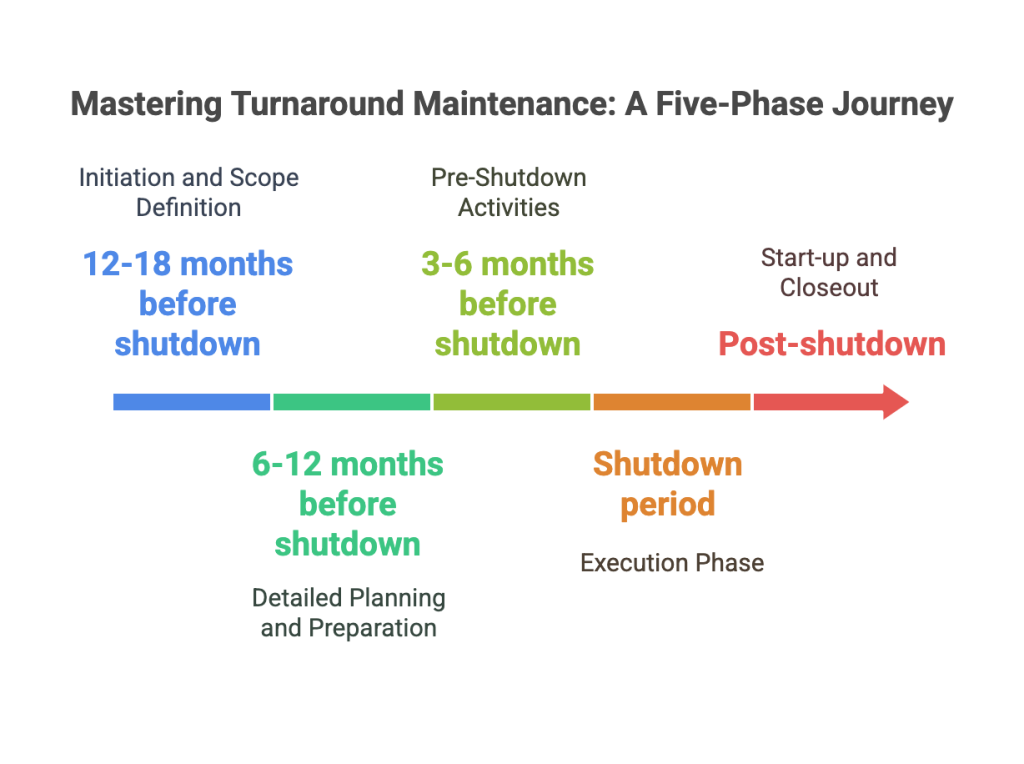
Five Phases of Turnaround Maintenance
Phase 1: Initiation and Scope Definition
The turnaround planning journey begins with thorough planning, typically 12-18 months before the shutdown.
A well-defined maintenance strategy is crucial during this phase to cover all aspects of the turnaround.
During this phase, maintenance managers work with operations, engineering, and other stakeholders to define the turnaround’s scope and improve the turnaround performance.
This involves reviewing equipment performance data, maintenance histories, and regulatory requirements.
For example, analyze equipment failure patterns in a chemical processing plant, identify critical assets requiring attention, and determine which upgrades or modifications should be included.
This evaluation phase will help you better understand the critical aspects of the plant’s operations.
The outcome of this turnaround process phase is a comprehensive scope document that outlines all work to be performed during the turnaround.
Don’t forget that turnaround success depends on a comprehensive scoping phase and a proper sequence.
Phase 2: Detailed Planning and Preparation
Once the scope is defined, the focus shifts to detailed planning and scope management.
This phase generally takes place 6-12 months before the shutdown and involves creating detailed work packages, project management plans, procurement plans, and resource schedules.
Maintenance managers develop precise execution strategies, including critical path analysis and contingency planning.
Consider a refinery turnaround: During this phase, we would create detailed specifications for each task, order long-lead items like specialized valves or heat exchanger tubes, and begin contracting discussions with specialty service providers.
Safety plans, process units, quality control procedures, and communication protocols would also be established during this period. The goal is to minimize unplanned outages.
Phase 3: Pre-Shutdown Activities
The pre-shutdown phase, which typically occurs 3-6 months before the main event, focuses on mobilization and preparation. Logistics coordination is crucial to ensure efficient resource management.
This includes setting up temporary facilities, staging equipment, and materials, and conducting pre-turnaround training.
This phase might involve constructing temporary workshops, positioning heavy lifting equipment, and conducting safety orientations for contract workers in a power generation facility.
Critical pre-shutdown activities, such as isolating systems that can be worked on while the plant is still running, are also executed during this phase.

Phase 4: Execution Phase
After months of planning, you’ve finally reached the main event. The execution phase, also known as maintenance execution, is the shutdown period during which the planned work is carried out.
This intense period requires precise coordination and control of numerous simultaneous activities.
Using a petrochemical plant as an example, the execution phase might involve multiple crews working around the clock on various tasks – one team performing vessel entries and inspections, another replacing catalyst materials, and others conducting preventive maintenance on rotating equipment.
Maintenance managers must strictly control work quality, safety protocols, and schedule adherence. Progress is typically monitored through daily coordination meetings and real-time tracking systems.
Phase 5: Start-up and Closeout
The final phase systematically returns the plant to normal operations, documenting the turnaround results. This phase is crucial for ensuring all systems are correctly recommissioned and operating as intended.
This would include, for example, equipment testing, safety system verification, and gradual production ramp-up in a manufacturing facility.
Maintenance managers oversee the completion of punch list items, the collection of quality documentation, and the preparation of final reports.
Lessons learned sessions are conducted to improve future turnarounds, and all documentation is archived for reference.
Each phase builds upon the previous one, creating a systematic approach to managing complex turnaround projects.
The success of a turnaround depends heavily on how well each phase is executed, with particular emphasis on the planning phases. Modern maintenance managers often enhance these phases with digital tools and analytics platforms to improve efficiency and decision-making.
The five phases are interconnected, and their careful execution ensures the completion of immediate maintenance tasks and the facility’s long-term reliability and efficiency.
Understanding and properly implementing each phase helps maintenance managers deliver turnarounds that meet safety, quality, schedule, and budget objectives while minimizing the impact on production operations.
Source: Worktrek.com
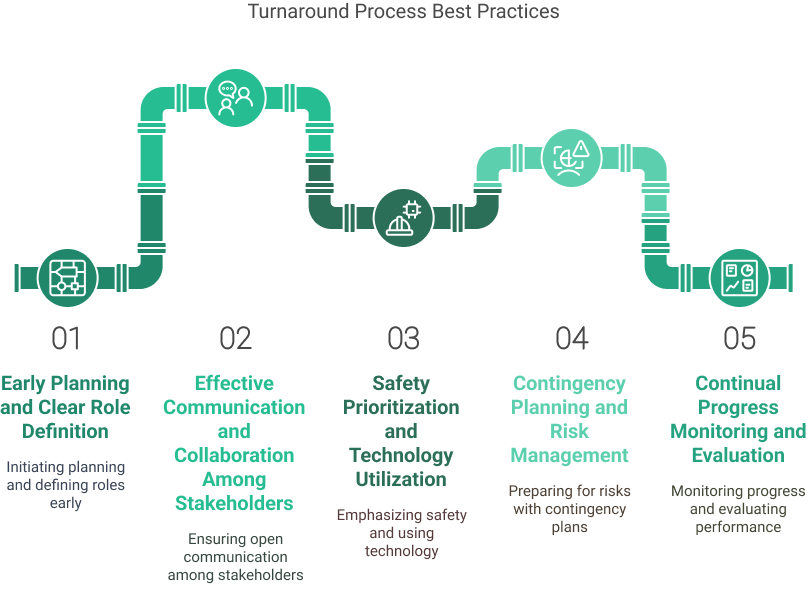
Turnaround Process Best Practices
Effective turnaround management is critical to ensuring the success of the turnaround and minimizing downtime. Best practices for turnaround management include:
- Early Planning and Clear Role Definition: Initiating the planning process well in advance and clearly defining roles and responsibilities ensures everyone understands their tasks and deadlines for the plant shutdown.
- Effective Communication and Collaboration Among Stakeholders: Open lines of communication and collaboration between all stakeholders, including operations, maintenance, engineering, and contractors, are essential for a smooth turnaround process.
- Safety Prioritization and Technology Utilization: Prioritizing safety through rigorous training and advanced technologies, such as digital monitoring tools, helps mitigate risks and enhance turnaround performance.
- Contingency Planning and Risk Management: Developing contingency plans and conducting thorough risk assessments prepare the team to handle unexpected challenges without significant disruptions.
- Continual Progress Monitoring and Evaluation: Monitoring progress and evaluating performance through key metrics allows for real-time adjustments and continuous improvement for common challenges.
Computerized Maintenance Management System for Turnaround Maintenance
Work Order Management and Planning
A CMMS like WorkTrek is the central hub for creating, tracking, and managing all turnaround-related work orders through an efficient work order system. During the planning phase, maintenance managers can use the CMMS to generate detailed work packages that include step-by-step procedures, required resources, and safety protocols.
For instance, when planning a refinery turnaround, the CMMS can help organize thousands of individual tasks into logical work packages, ensuring nothing is overlooked. It can also centralize information about past turnarounds and the necessary equipment for the plant’s operations.
The system can automatically generate work orders based on equipment maintenance histories, manufacturer recommendations, preventive maintenance tasks, and regulatory requirements.
Resource Management and Scheduling
The CMMS helps optimize resource allocation by providing detailed insights into labor requirements, contractor availability, and equipment needs.
For example, when scheduling a power plant turnaround, the system can help identify potential resource conflicts and optimize crew assignments. It can track specialized skill requirements for each task and match them with qualified personnel.
The scheduling capabilities allow managers to visualize the critical path, identify potential bottlenecks, and make real-time adjustments.
Inventory and Procurement Control
The CMMS helps ensure all necessary parts and materials are available when needed through integration with inventory management modules.
The system can automatically track stock levels, generate purchase requisitions for long-lead items, and monitor delivery schedules.
Consider a chemical plant turnaround: the CMMS can help identify all required spare parts months in advance, trigger automatic reordering when stock levels fall below predetermined thresholds, and track the arrival of critical components.
Documentation and Maintain Regulatory Compliance
Modern CMMS platforms enable organizations to maintain regulatory compliance and quality assurance by managing compliance documentation. They can store and organize equipment specifications, maintenance procedures, safety permits, and inspection reports. During a manufacturing facility turnaround, the CMMS can ensure all necessary permits are in place, track the completion of required inspections, and maintain detailed records of all work performed.
Real-time Progress Tracking
During the execution phase, the CMMS provides real-time visibility into turnaround progress monitoring. Maintenance managers can track completion percentages, monitor labor hours, and identify delays or issues requiring immediate attention. For instance, in a petrochemical plant turnaround, managers can use mobile CMMS applications to update work order status from the field, attach photos of completed work, and flag any safety concerns immediately.
Cost Control and Budget Management
The CMMS helps maintain tight control over turnaround costs by tracking labor hours, material usage, and contractor expenses in real time, facilitating effective budget tracking. It can compare actual costs against budgeted amounts and generate alerts when costs exceed predetermined thresholds. This functionality allows managers to make informed decisions about scope changes or resource allocation during the turnaround.
Historical Data Analysis and Future Planning
After completion, the CMMS becomes a valuable repository of historical turnaround data analysis. This information can be analyzed to improve planning for future turnarounds by identifying common issues, optimizing resource allocation, and refining cost estimates. For example, analysis of previous turnaround data might reveal patterns in equipment failures that could influence the scope of future maintenance activities.
Integration with Other Systems
Modern CMMS platforms can integrate with other enterprise systems to provide a more comprehensive view of turnaround activities. Integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems can improve procurement and cost tracking, while integration with condition monitoring systems can help refine maintenance scopes based on actual equipment conditions.
Performance Metrics and Reporting
The CMMS can generate detailed reports on performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) such as schedule compliance, cost variance, safety incidents, and quality metrics. These reports help maintenance managers demonstrate the value of turnaround activities to stakeholders and identify areas for improvement in future turnarounds.
Maintenance managers can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of turnaround maintenance activities by properly utilizing a CMMS. The system provides the structure and tools to plan, execute, and control complex turnaround projects while maintaining comprehensive documentation for future reference. Would you like me to elaborate on any specific aspect of CMMS implementation for turnaround maintenance?
Industry Trends and Innovations
The increasing role of digital technology in turnarounds is a key trend. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in risk assessment and scheduling is revolutionizing the way turnarounds are planned and executed. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, optimize resource allocation, and enhance decision-making processes. Additionally, the adoption of modular construction techniques to minimize on-site work is becoming more prevalent. By prefabricating components off-site, companies can reduce turnaround durations and improve safety and quality control.
Preparing for Industry 4.0
As we look toward the future, turnarounds will continue to evolve in response to emerging trends, technological innovations, and the challenges and opportunities of Industry 4.0. To prepare for Industry 4.0, companies should focus on:
- Implementing Digital Technologies to Improve Efficiency and Reduce Downtime: Leveraging digital tools and platforms can streamline turnaround planning and execution, leading to significant cost savings and enhanced turnaround success.
- Developing a Skilled Workforce with Expertise in AI, ML, and Data Analytics: Investing in training and development programs ensures that the workforce is equipped with the necessary skills to utilize advanced technologies effectively.
- Embracing Modular Construction Techniques to Minimize On-Site Work: Prefabricating components off-site can lead to more efficient and safer turnarounds, reducing the impact on normal operations.
- Prioritizing Safety and Environmental Considerations in Turnaround Planning and Execution: Ensuring that safety and environmental standards are met protects workers and the environment and helps maintain regulatory compliance and corporate reputation.
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



