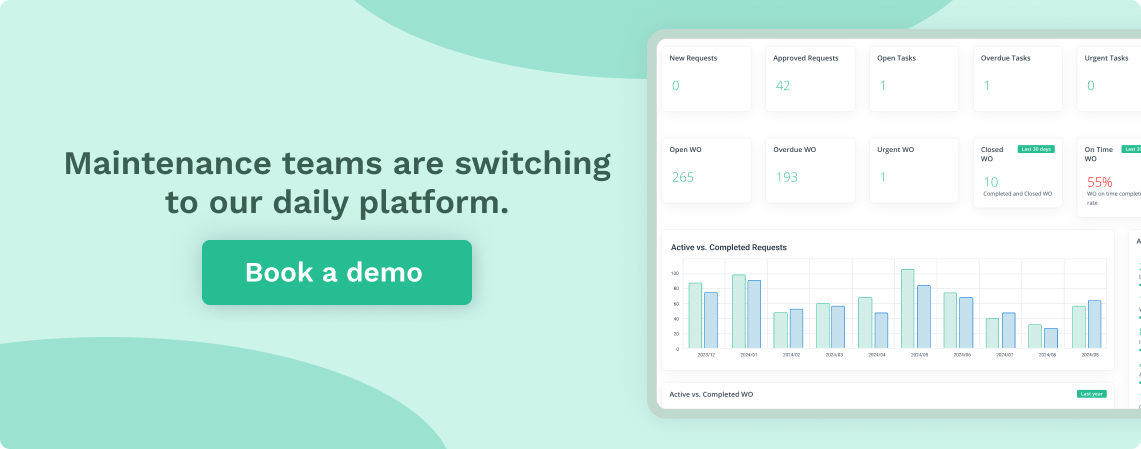
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeSmart maintenance is changing how businesses maintain their equipment. It refers to using digital tools and data-driven methods to make maintenance and servicing more efficient. Smart maintenance uses repair data and preventive care to extract more value from equipment.
This new approach helps companies save money and time. It stops big breakdowns that can shut down work. Smart maintenance also makes machines last longer.
With smart maintenance, workers can plan better. They know when to fix things and what parts they need, keeping everything running smoothly and safely.
The Concept of Smart Maintenance
Smart maintenance uses data and technology to keep machines running smoothly. It helps companies save money and avoid problems before they happen.
By integrating digital tools, maintenance data, CMMS, IoT, predictive analytics, machine learning, and Industry 4.0 methods, smart maintenance forms an efficient and value-creating maintenance strategy.
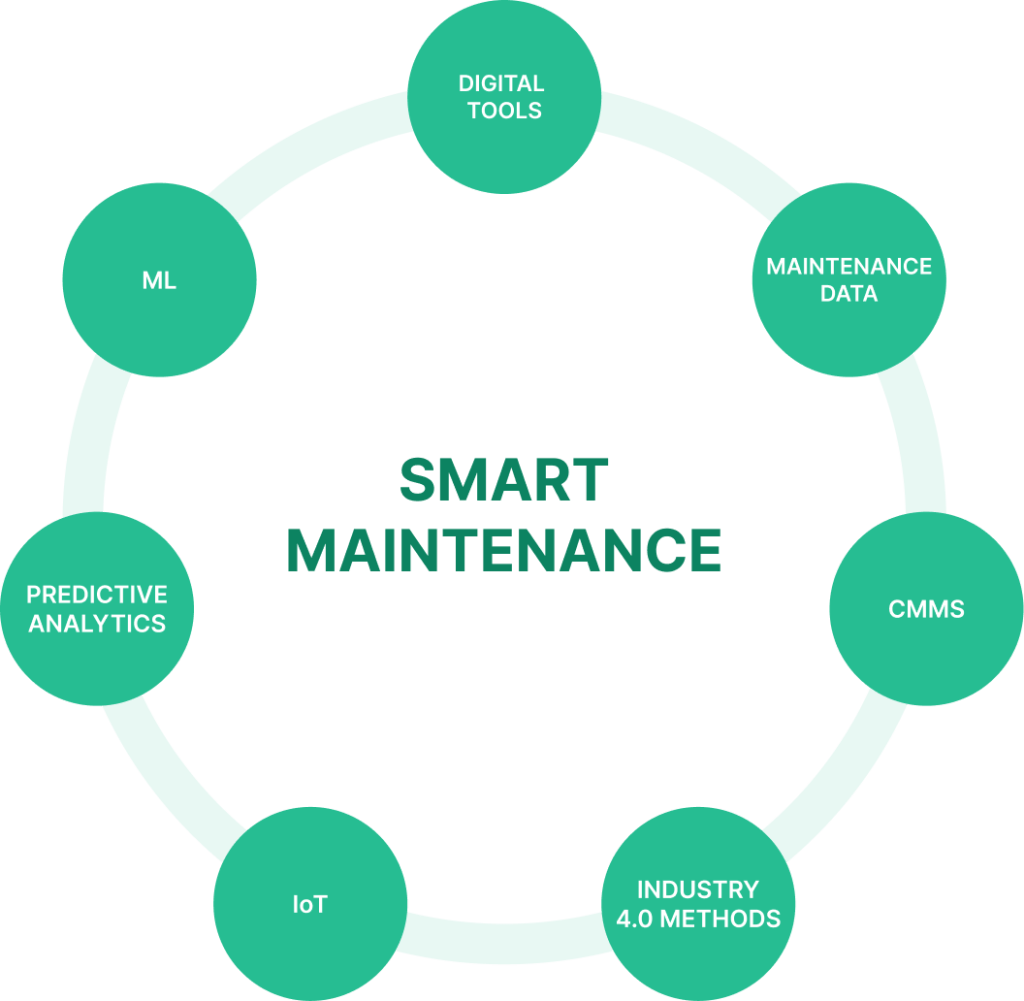
Source: WorkTrek
Defining Smart Maintenance
Smart maintenance is a modern approach to keeping equipment in top shape. It uses sensors, data, and computers to spot issues early, automating maintenance. This method checks machines all the time, not just when they break.
Smart maintenance looks at how machines work and predicts when they might need fixing. It uses special tools to collect and study information about equipment health.
This approach helps companies plan repairs at the best times. It aims to prevent breakdowns before they happen. Smart maintenance provides a much-improved asset performance.
Downside Of Traditional Methods
A smart maintenance strategy offers significant advantages over old ways of fixing things. It helps machines last longer and work better. Companies can save money by avoiding sudden breakdowns. Integrating lean, smart maintenance principles can reduce costs and increase process flexibility.
With smart maintenance, workers can fix problems faster. They know what’s wrong before they start, so they bring the right tools and parts. This means less downtime for machines.
Smart maintenance increases productivity by keeping machines running smoothly. It also improves safety by catching dangerous issues early. Companies can plan their work better when they know their equipment is reliable.
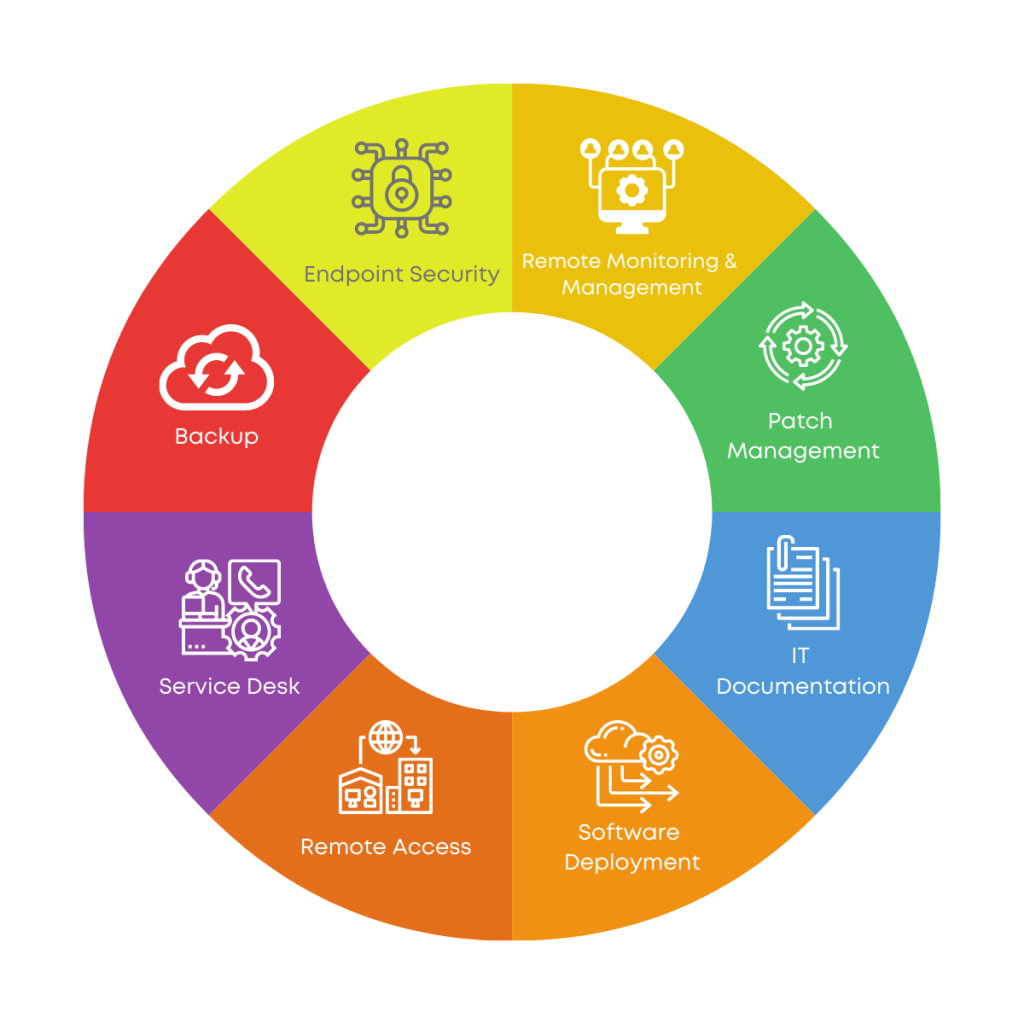
Technologies Powering Smart Maintenance
Smart maintenance relies on cutting-edge technologies to improve efficiency and reduce downtime. These tools work together to predict issues, guide repairs, and manage maintenance tasks effectively, which can reduce downtime.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Advanced technologies like AI plays a key role in smart maintenance. It analyzes data from machines and sensors to spot patterns and predict problems before they happen. This h nPredictive analytics, a branch of AI, uses machine data to forecast when parts might fail. This allows companies to replace components quickly, saving money and preventing surprise failures.

Source: WorkTrek
Integrating Augmented Realit to Smart Maintenance
Advanced Augmented Reality (AR) is changing how maintenance teams work. It overlays digital information onto the real world, making complex repairs easier to understand and perform.
Smart glasses are a standard AR tool in maintenance. They show step-by-step repair instructions right in the technician’s field of view, helping workers fix problems faster and with fewer mistakes.
AR can also connect remote experts with on-site teams. An expert can see what the technician sees and guide them through difficult repairs. This cuts travel costs and speeds up problem-solving.
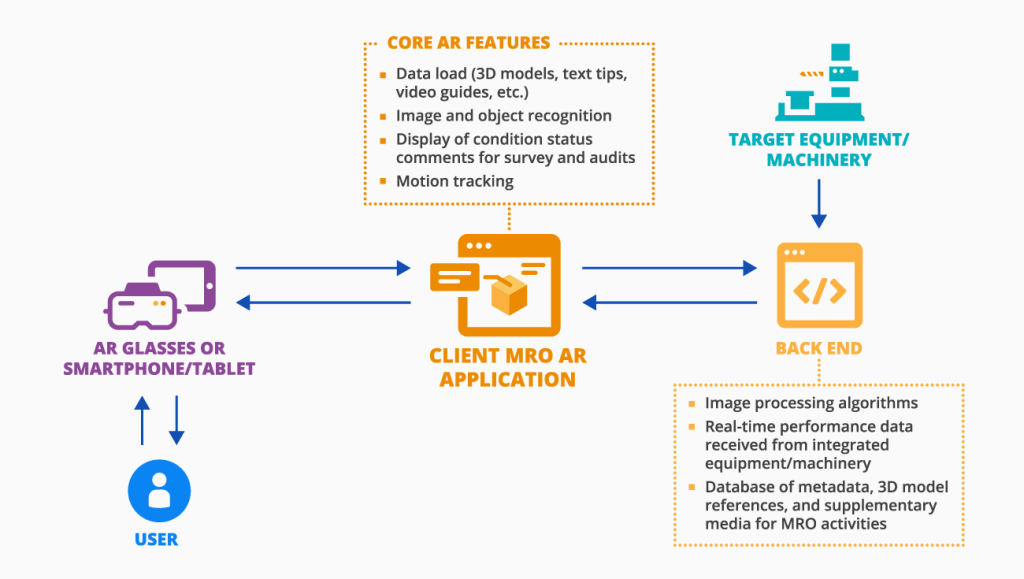
Source: ScienceSoft
Leveraging IoT and Smart Sensors
The Internet of Things (IoT) and smart sensors are key to smart maintenance. They collect real-time data on machine health, temperature, vibration, etc.
Smart sensors can detect early signs of wear or damage. They send alerts when machines need attention, helping prevent breakdowns before they happen.
Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) sensors are often used in smart maintenance. They’re small, energy-efficient, and can send data wirelessly over short distances.
This constant stream of data helps maintenance teams make better decisions. They can focus on the most urgent issues and plan maintenance more effectively.
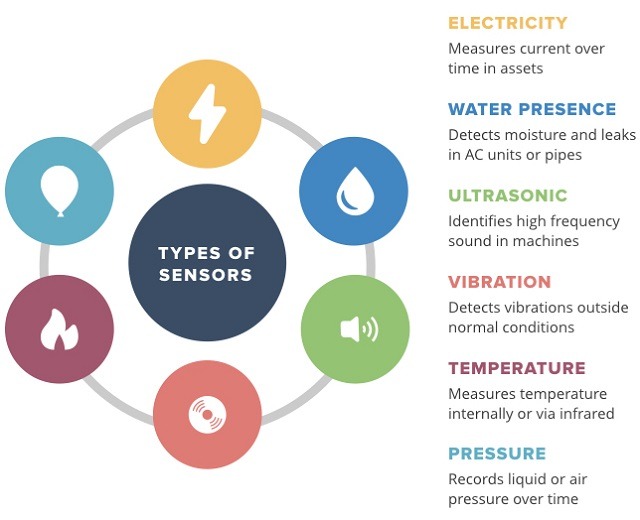
Source: Shangai SMEE
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are the backbone of smart maintenance. They encompass all technical and organizational measures aimed at using digital tools to make maintenance and servicing more efficient. CMMS stores and organizes all maintenance data in one place.
A CMMS tracks equipment history, schedules maintenance tasks, and manages spare parts inventory. This helps teams stay organized and ensures no maintenance task is overlooked.
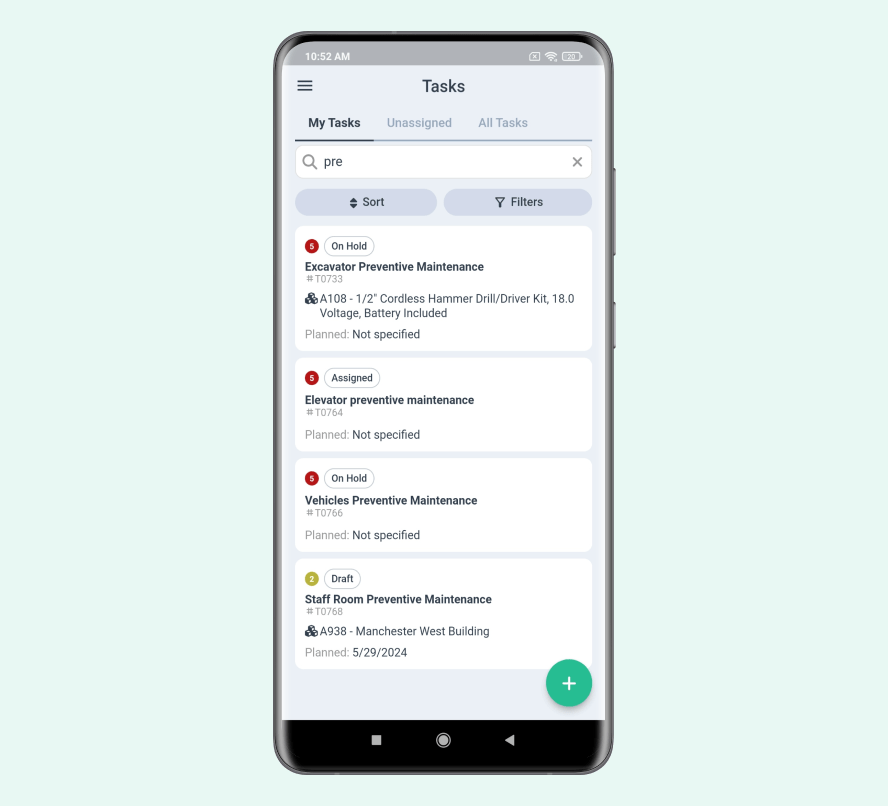
Source: WorkTrek
Modern CMMS software can integrate with other smart technologies. It can automatically use sensor data and AI predictions to create work orders.
CMMS also provides valuable insights through reports and dashboards that can help decision-making. Managers can easily see maintenance trends and make data-driven decisions in a centralized location to improve operations.
Data-Driven Maintenance Strategies
Smart maintenance uses data to improve equipment upkeep and prevent breakdowns. It helps companies make better choices about when to fix or replace parts.
A smart maintenance strategy leverages digital tools such as CMMS, IoT, predictive analytics, machine learning, and Industry 4.0 to drive insights from maintenance data and enable accurate decision-making.
Predictive vs Preventive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses real-time data to spot problems before they happen. Sensors track how machines work and warn about issues early.
Preventive maintenance follows a set upkeep schedule. Developing a preventive maintenance plan involves identifying a maintenance schedule and requirements for each piece of equipment. An ERP solution is often used to ensure timely and accurate maintenance processes.
Predictive methods can save money by fixing things only when needed. They also help avoid surprise breakdowns that stop work.
Companies often use both types. Predictive for complex machines and preventive for simpler ones.
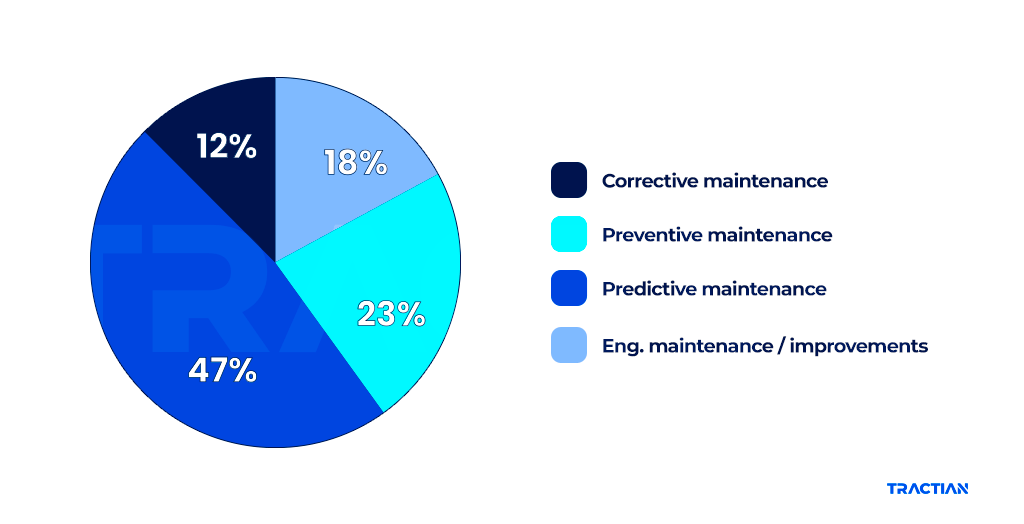
Source: Tractian
Using Data for Decision-Making
Data-driven decisions help maintenance teams work smarter. They examine information from sensors, past repairs, and machine performance.
This data shows patterns that humans might miss. It can tell when a part will likely fail or which machines need the most care.
Teams use this info to:
- Plan maintenance at the best times
- Order parts before they’re needed
- Focus on the most critical fixes first
Metrics like uptime and repair costs help track how well the strategy works.
Documentation and Compliance
Good records are key for smart maintenance. They help teams learn from past work and prove they follow the rules.
Digital tools make it easier to:
- Log all maintenance tasks
- Track parts used and costs
- Show when safety checks were done
- Give maintenance managers a centralized location for all work
- Reduce reactive maintenance
- It gives real-time visibility into all work being performed
This info helps with audits and planning. It also makes it simpler to train new workers.
Clear records can show if the maintenance plan is working well. They also help spot areas for improvement and save money.

Source: WorkTrek
Improving Maintenance with Smart Goals
Smart goals help maintenance teams boost efficiency and performance. They provide clear targets and ways to measure progress.
Setting and Tracking Goals
Smart maintenance goals are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. A good goal might be “Reduce equipment downtime by 15% in the next quarter.”
Managers should set goals that align with broader company objectives. Teams need the right tools to track their progress.
Modern software can help collect and analyze maintenance data, making it easier to see if goals are being met.
Regular check-ins keep everyone focused. Teams can adjust their approach if needed.
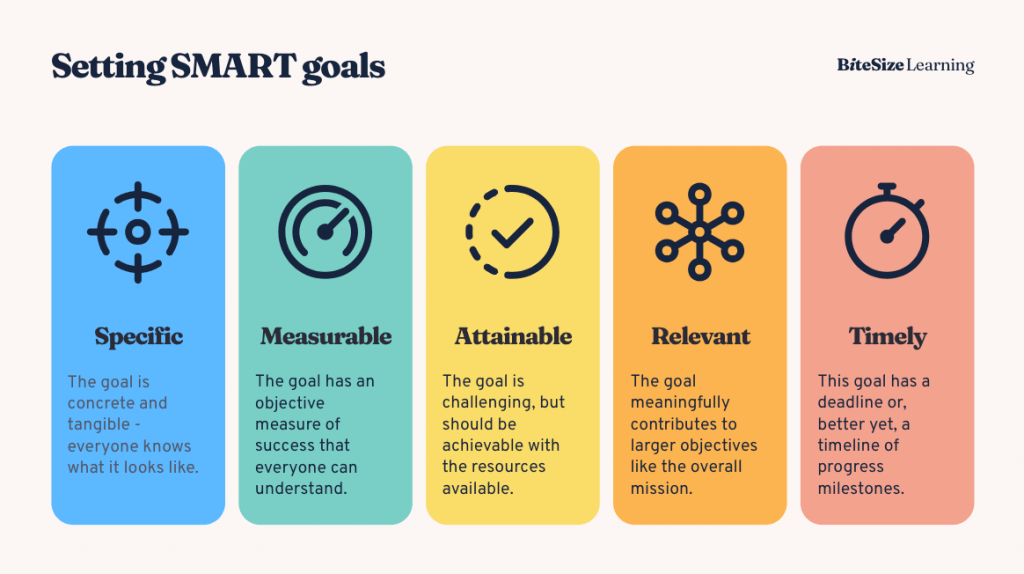
Source: BiteSize Learning
Balancing Cost, Quality, and Performance
Smart goals help maintenance teams balance different priorities. Cost, quality, and performance all matter.
A goal to cut costs shouldn’t harm quality or safety. For example: “Reduce maintenance costs by 10% while maintaining a 98% equipment uptime rate.”
Quality goals might focus on reducing defects or complaints. “Decrease customer complaints about facility cleanliness by 25% this year.”
Performance goals often target efficiency. “Complete 95% of scheduled maintenance tasks on time each month.”
Safety should always be a top concern. “Achieve zero workplace injuries for 365 consecutive days.”
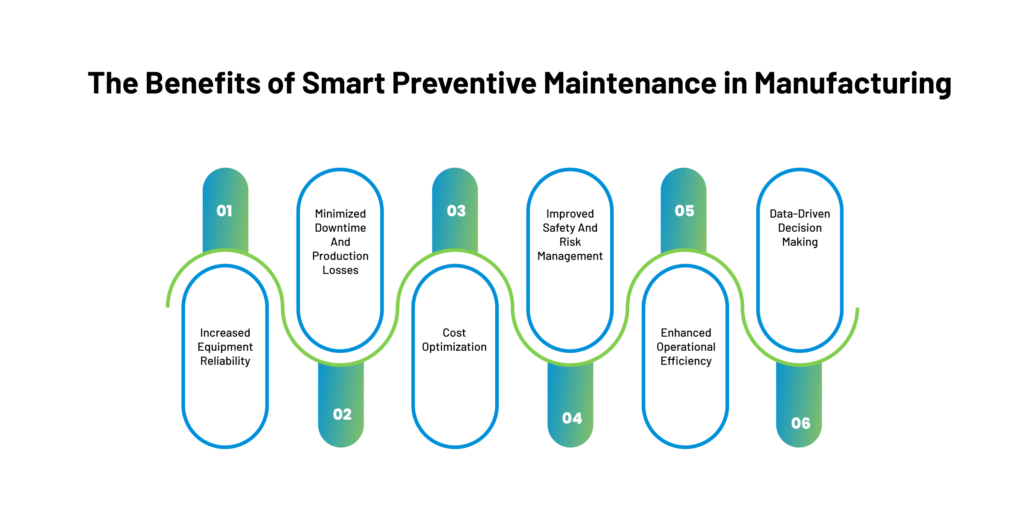
Operational Impacts of Smart Maintenance
Source: WorkTrek
Smart maintenance significantly changes manufacturing operations. It substantially affects equipment performance, costs, and energy use.
Minimizing Downtime
Smart maintenance helps reduce unexpected machine breakdowns. It uses sensors and data to spot issues early, allowing repairs to be made before failures happen.
Smart maintenance impacts plant performance by cutting unplanned downtime. Predictive algorithms flag potential problems in advance, and technicians can fix them during planned stops.
Real-time monitoring also speeds up repair times. It pinpoints exact failure points quickly. This cuts diagnostic work and gets machines running faster.
Maximizing Equipment Uptime
Smart systems boost machine uptime and output. They track performance data to find the best operating conditions.
Automated maintenance schedules keep equipment in top shape. Smart technologies, such as AI, optimize these plans based on actual wear and tear.
Remote monitoring allows quick responses to issues. Experts can advise afar, avoiding travel delays. Software updates can often fix problems without stopping production.
Better uptime leads to higher throughput. Factories can produce more with the same machines.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Smart maintenance cuts energy waste and expenses. It finds inefficient machines that use too much power.
Sensors detect air leaks, bearing issues, or other problems that waste energy. Fixing these quickly can save money on utility bills.
Data analysis reveals the best times to run equipment for the lowest energy costs. It can shift power-hungry tasks to off-peak hours.
Smart systems also reduce spare parts inventory. They order only what’s needed when needed, cutting storage costs and preventing overbuying.
Labor costs drop, too. Technicians spend less time on routine checks and more on critical tasks.
Source: CopperDIGITAL
Smart Maintenance in Action
Smart maintenance uses advanced tech to keep factories and vehicles running smoothly. It helps spot problems early and fix them fast.
Remote Monitoring and Maintenance
Smart maintenance lets experts fix things from far away. A wind farm uses remote access to turbines. Techs could change settings and restart systems without climbing towers.
Oil rigs use video links to get help. Rig workers connect with onshore experts, who guide repairs step-by-step. This cuts repair time and boosts safety.
Smart factories link machines to the cloud. Engineers can check machine health from anywhere. They spot trends and plan fixes before breakdowns happen.
Source: information solutions
Handling Complex Malfunctions
Smart systems help solve tricky problems. A power plant used AI to diagnose a weird noise. The AI checked sensor data and past issues. It found a rare fan problem that humans missed.
Smart maintenance tools guide repairs. Techs use tablets with 3D guides, which show how to disassemble and fix complex machines. This helps new techs work like pros.
Some systems can fix themselves. A smart building network found a broken AC unit. It switched to backup cooling and automatically ordered a new part.
The Human Element in Smart Maintenance
People play a key role in smart maintenance systems. Workers need new skills and training to use advanced technology, and they must also continue to focus on customer needs.
Training for Technical Expertise
Smart maintenance requires workers to learn new tech skills. Companies offer training on data analysis and using digital tools. This helps staff work with sensors, software, and connected machines.
Maintenance teams get hands-on practice with smart factory equipment. They learn to read data from machines and spot issues early. Workers also train to fix problems remotely when possible.
Regular updates keep skills fresh as technology changes. Online courses let staff learn at their own pace, and mentoring programs pair new workers with experienced techs.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Devlin Peck
Evolving Role of Maintenance Personnel
The job of maintenance workers is changing. They now do more than fix broken machines. Smart systems let them prevent issues before they happen.
Techs analyze data trends and look for ways to improve machine performance. Problem-solving skills become more important in this new role.
Workers are teaming up more with other departments. They share insights to help make better business choices and soft skills like communication grow in value.
Some tasks become automated. However, humans still make key decisions based on data and experience.
Maintaining Customer-Service Excellence
Even with smart tech, customer service stays crucial. Maintenance teams must keep a service mindset while using new tools.
Workers learn to explain complex tech issues in simple terms. They update customers on machine status and repair progress. Quick response times remain important, aided by smart alerts.
Techs gather feedback to improve service. They use digital tools to track customer satisfaction. The human touch helps build trust in smart maintenance systems.
Teams aim to balance tech efficiency with personal care. They find ways for smart systems to enhance, not replace, good service.

Source: WorkTrek










