Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeThere are two ways to standardize maintenance operations: develop your own procedures and guidelines or adopt already-established industry standards.
The latter is often more efficient, providing a reliable path to effective and safe maintenance practices, regardless of your specific industry.
However, with so many standards, figuring out which ones are right for you can take time and effort.
That’s why we explored ten essential standards every maintenance professional should know, offering a brief overview and explaining why they’re important.
Let’s get started.
ISO 55000: Asset Management Standards
Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 55000 serves as a foundation for more efficient asset management.
This is a family of three interconnected standards, each serving a unique purpose:
| ISO 55000 | Introduces the core concepts for developing a long-term asset management plan aligned with an organization’s goals, business policies, and stakeholder needs. |
| ISO 55001 | Provides a detailed framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and improving a successful asset management system. |
| ISO 55002 | Supports ISO 55001 implementation with additional clarification, examples, and guidance for setting up an asset management system in accordance with ISO 55001 requirements. |
If your company owns and manages any kind of assets, these guidelines can help you unlock greater value.
You can extend asset useful lives, reduce downtime, minimize risk, and more.
Consider the example of the Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority (MARTA), which became North America’s first transit agency to earn ISO 55000 certification in 2019.
According to David Springstead, former MARTA’s Chief of Rail Operations, the certification made a real difference.

To learn more about this series of standards and get certified yourself, it’s best to review the official ISO 55000 documentation.
It offers everything you need to set up an asset management system that complies with the standard, giving you a clear path to optimized asset performance and value.
ISO 13374 Standards: Condition Monitoring and Machine Diagnostics
The ISO 13374 series of standards establishes protocols for managing, processing, and communicating machine condition data.
This opens the door to smarter, more effective asset health tracking and maintenance scheduling.
The series is divided into several parts:
| ISO 13374-1:2003 | General guidelines for data processing, communication, and presentation specifications. |
| ISO 13374-2:2007 | Requirements for an effective data processing the condition monitoring architecture needs to adhere to. |
| ISO 13374-2:2007 | Requirements for efficient data communication within this system. |
| ISO 13374-4:2015 | Requirements for presenting information to support technical analysis and decision-making. |
Manufacturing, energy, and transportation industries where equipment reliability and efficiency are paramount particularly benefit from adopting ISO 13374 standards.
These guidelines ensure data from multiple sources is processed uniformly, offering a more accurate, reliable view of each asset’s health.
As a result, organizations can move from reactive to predictive or condition-based maintenance, where they can address issues before they lead to costly failures.
This directly translates to fewer disruptions, lower repair costs, and a big boost to overall operational efficiency.
ISO 18436 Standard: Competence Requirements for Condition Monitoring Personnel
This is another internationally accepted standard that helps organizations take asset condition monitoring to the next level.
It provides structured requirements for the training, experience, and testing personnel responsible for tracking and diagnosing machines’ health.
ISO 18436 divides into sub-standards for specific techniques, such as vibration analysis (ISO 18436-2), field lubricant analysis (ISO 18436-4), etc.
The standard also defines four competency levels for each of these skills:
| Category I | Basic data collection knowledge |
| Category II | Ability to conduct diagnostics under supervision |
| Category III | Proficient in condition-monitoring program diagnostics and management |
| Category IV | Expert level, capable of developing and optimizing condition-monitoring programs |
These guidelines help companies ensure employees are qualified to perform condition monitoring procedures efficiently and safely.
And this is more important today than ever before.
According to Andy Hancock, Global VP of SAP’s Digital Supply Chain Centre of Excellence, condition-monitoring tools are advancing rapidly.

Maintenance professionals must keep pace with these advancements.
That’s precisely where ISO 18436 comes in, keeping our maintenance technicians sharp, agile, and capable of delivering reliable insights about the assets’ health and performance.
ISO 14224: Equipment Reliability and Maintenance Data Standard
ISO 14224 instructs petroleum, natural gas, and petrochemical companies on effectively collecting reliability and maintenance (RM) data.
It covers the methodology for the information collection and what data needs to be collected.
The key data categories include:
| Equipment Data | e.g., equipment taxonomy and attributes |
| Failure Data | e.g., failure cause, failure consequence |
| Maintenance Data | e.g., maintenance action, resources used, maintenance consequence, downtime |
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), like WorkTrek, play a vital role in implementing ISO 14224 effectively.
These systems provide the digital infrastructure to automatically record, organize, analyze, and report all sorts of asset data, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing human error.
You get clean, standardized, and accurate asset lists with all vital insights, from equipment names and locations to their entire service histories.
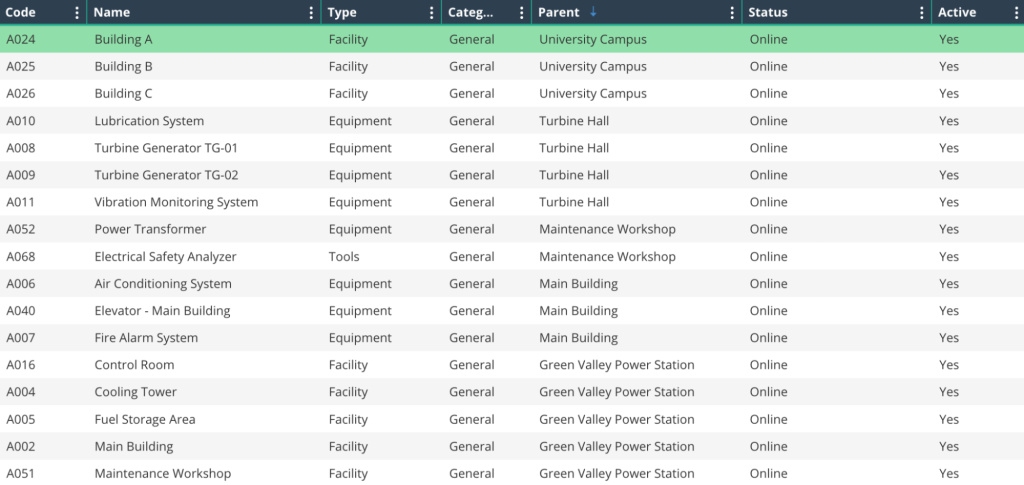
This consistency is crucial for meeting ISO 14224 requirements, driving better decision-making, and ultimately improving performance and reliability across the board.
ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety Standard
ISO 45001 sets concrete criteria for planning and implementing occupational health and safety (OH&S) policies.
By following these guidelines, companies can successfully identify various hazards, control risks, and reduce workplace injuries and incidents.
Currently, ISO 45001 is in the midst of a three-year revision project focused on more effectively addressing diversity, inclusion, and worker well-being.
Troy Winters, Senior Health & Safety Officer at the Canadian Union of Public Employees and the project leader, explains what the ISO 45001 standard is all about:

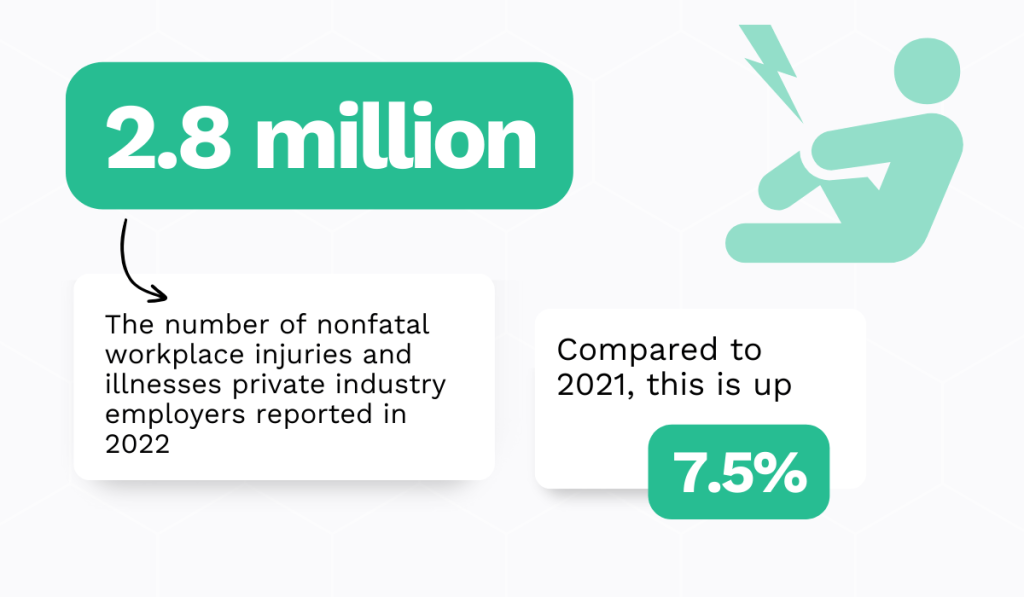
Considering that private sector employers reported 2.8 million nonfatal workplace injuries and illnesses in 2022, there’s a serious need for stronger safety standards.
Maintenance personnel, especially those working on high-risk tasks or with heavy equipment, must be particularly mindful of ISO 45001.
For them, safety protocols are not just a checklist item but a key to their well-being.
SAE JA1011 and JA1012: Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) Standards
Developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), The JA1011 standard was initially created to boost the reliability of assets and safety in commercial aviation.
However, its application has since broadened to other sectors.
Both standards are now used across many companies, establishing best practices and criteria for Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) processes.
According to SAE, an organization must answer the following seven questions to ensure adherence to RCM standards:
- What are the asset’s functions and desired performance standards in its current operating context?
- How can it fail to fulfill these functions (functional failures)?
- What causes each functional failure (failure modes)?
- What occurs when each failure happens (failure effects)?
- Why does each failure matter (failure consequences)?
- What proactive tasks and intervals should be set to predict or prevent each failure?
- What actions should be taken if a suitable proactive task cannot be identified (default actions)?
With JA1011 and JA1012 standards, companies can find effective answers to these questions.
SAE JA1011 establishes the foundational principles and methodologies for RCM, helping companies develop cost-effective upkeep strategies based on risk and criticality assessments.
Meanwhile, SAE JA1012 provides practical guidance on implementing the RCM process outlined in JA1011 through detailed explanations, interpretations, and examples.
Together, these standards empower organizations to identify necessary maintenance, prioritize, and execute it effectively.
The result is higher asset performance, reliability, and significant cost savings.
NFPA 70B: Electrical Equipment Maintenance Standard
NFPA 70B, developed by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), provides guidelines for efficient electrical equipment maintenance programs.
These guidelines apply to a range of settings, from plants and institutional and commercial buildings to large residential complexes.
The goal is the same regardless of the facility: improving the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Interestingly, NFPA 70B became an enforceable standard only recently.
Originally issued in 1973, it was considered a recommended practice until it gained enforceability last year.
Josh Knott, Director of Construction & Technical Sales at Leviton, explains why this change matters:
The NFPA 70B standard now prescribes the frequency and type of testing required for all electrical equipment, while also incorporating recommended practices to further enhance the resiliency and viability of the electrical infrastructure. It uniquely balances the priority of worker safety with protection against operational disruptions.
Making NFPA 70B a must-follow rule represents a big step forward.
This change not only boosts the reliability of critical electrical equipment but also significantly improves safety for those working with these systems.
ANSI TAPPI TIP 0305-34:2008 Standard for Maintenance Checklists
The ANSI TAPPI TIP 0305-34:2008 standard provides guidelines for organizations and upkeep personnel to develop daily, weekly, and monthly maintenance checklists.
This standard acts as a starting point. Maintenance engineers can customize the lists based on the company’s needs, asset configurations, and other factors.
Within the realm of upkeep, checklists are vital.
They ensure every component is thoroughly inspected, every task completed, and every issue resolved on time—keeping operations running smoothly and safely.
Asphalt plants are just one example of facilities relying on scheduled maintenance checklists.
Steve Elam, Operations Manager at Stansteel/Hotmix Parts, the company offering asphalt plant parts and services, elaborates:

By following such a systematic process, maintenance becomes more organized.
As a result, equipment stays in top condition for much longer.
Therefore, if you aim to streamline your maintenance management, consider implementing ANSI TAPPI TIP 0305-34:2008.
It could make all the difference in keeping your operations (and equipment) running at peak performance.
MIMOSA Open Information Standards
The Machinery Information Management Open Standards Association (MIMOSA) provides a detailed set of standards that support data exchange and integration across a broad range of Operations & Maintenance (O&M) systems.
At its core, MIMOSA drives interoperability. It aims to make systems, applications, and devices connect and communicate.
These interoperable systems are key to smarter decision-making, real-time monitoring, and breaking down data silos.
Brianna Perry, Product Marketing Manager at Fleetio, a fleet management platform, explains how harmful silos can be in the context of fleet maintenance.

Data silos can make the management of all kinds of assets less efficient.
MIMOSA, luckily, tackles all these inefficiencies head-on by empowering maintenance teams to share, analyze, and act on critical data across connected platforms and technologies.
Consequently, data flows freely, reaching the right people at the right time and facilitating faster, better-informed maintenance.
Industrial Internet Consortium Reference Architecture (IIRA) Standards
The Industrial Internet Reference Architecture (IIRA) is a framework from the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC), designed to empower easier development and integration of industrial IoT systems.
In a statement following its 2017 update, John Tuccillo, former Chairman of the IIC’s Steering Committee, perfectly summarized the core purpose of this series of standards:
Essentially, the IIRA enables organizations to adopt IIoT solutions confidently, mitigating concerns about designing systems from scratch or encountering compatibility issues.
This is particularly valuable for maintenance professionals, as IoT-based systems are the foundation for predictive maintenance and remote condition monitoring.
These systems pull live data from machinery (e.g., temperature, vibration, and wear) and send it to analytics platforms, where predictive models forecast potential problems.
In practice, service personnel can use IIRA-driven insights to access real-time conditions of their equipment and make proactive, data-backed decisions about repairs.
This allows them to avoid unnecessary work and keep critical assets running.
Conclusion
While this list doesn’t cover every maintenance-related standard, it provides a strong starting point to help you manage your maintenance process effectively.
When deciding which standards to implement, identify your primary maintenance challenges.
For example, if safety is a top concern, ISO 45001 could be a good choice.
If you struggle with data reliability, consider standards that address this, such as ISO 14224 or the MIMOSA standards.
Choosing the right standard becomes much simpler once you’ve pinpointed your key challenges.
From there, carefully review all relevant documentation, begin implementing, and watch your operations transform.
Before you know it, your maintenance will be smoother and more reliable.
Good luck!










