Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKeeping equipment running smoothly is a top priority for businesses across industries. Breakdowns cost money, waste time, and frustrate everyone involved. Predictive maintenance could be the solution to improve your maintenance operations.
Predictive maintenance offers a smarter approach by using data to spot problems before they cause failures. Unlike traditional maintenance methods that wait for equipment to break down or follow rigid schedules, predictive maintenance uses sensors, data analysis, and machine learning to anticipate exactly when maintenance is needed.

Getting started with predictive maintenance doesn’t have to be complicated. The process typically begins by identifying critical assets that would cause significant problems if they failed, followed by installing IoT sensors to collect data on how these assets perform.
This approach has transformed maintenance from a reactive necessity into a strategic advantage that reduces downtime, extends equipment life, and significantly cuts costs.
Key Takeaways
- Predictive analytics and IoT sensors to detect potential failures before they happen, reducing unplanned downtime by up to 50%.
- Implementation requires identifying critical assets, installing predictive maintenance solutions, and appropriate monitoring technology
- The future of maintenance strategies involves increasingly sophisticated AI algorithms, wider integration across industrial systems, and greater sustainability through optimized resource use.
Fundamentals of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance forms the backbone of modern industrial reliability strategies. It leverages data analytics to anticipate equipment failures before they occur, transforming traditional maintenance paradigms through technological innovation.
Definition and Concepts
Predictive maintenance is an advanced strategy that uses condition monitoring tools and data analysis to predict when equipment will need maintenance.
Unlike reactive maintenance, which addresses issues after failure, or preventive maintenance, which follows fixed schedules, predictive maintenance anticipates problems by analyzing equipment performance data.
The core concept relies on identifying patterns that indicate potential failures. This approach employs various technologies including:
- Vibration analysis
- Infrared thermography
- Oil analysis
- Ultrasonic inspection
- Motor circuit analysis
These techniques help maintenance teams detect anomalies in equipment behavior that might signal impending failures. The goal is to perform maintenance only when necessary, reducing costs while maximizing equipment uptime.
Evolution and History
Predictive maintenance has evolved significantly since its earliest applications in the mid-20th century. Initially, maintenance relied solely on human observation and basic tools to identify unusual equipment behavior.
The 1970s saw the introduction of computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), which allowed for better tracking of maintenance activities and equipment history.
With advances in sensor technology, condition monitoring techniques became more sophisticated by the 1980s and 1990s.

The true transformation occurred in the early 2000s with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and big data analytics. These technologies enabled:
- Real-time equipment monitoring
- Advanced pattern recognition
- Integration with enterprise systems
- Cloud-based data storage and analysis
Today’s predictive maintenance solutions incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve prediction accuracy, provide actionable insights, and predict potential failures.
Importance in Industry
Predictive maintenance delivers significant value across manufacturing, energy, transportation, and other industrial sectors.
Organizations implementing these strategies experience reduced unplanned downtime and optimized maintenance schedules.
The financial benefits of a proactive maintenance strategy are substantial:
- 25-30% reduction in maintenance costs
- 70-75% decrease in breakdowns
- 35-45% reduction in downtime
- 20-25% increase in production

Beyond cost savings, predictive maintenance enhances workplace safety by preventing catastrophic equipment failures and improving maintenance operations. It also extends asset lifespans by addressing issues before they cause significant damage.
Manufacturing operations particularly benefit as production interruptions can cascade through supply chains. Maintenance teams transition from reactive firefighting to strategic asset management, allowing organizations to optimize resources and improve operational reliability.
Technological Pillars of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance technologies transform raw data into actionable insights. These foundational elements enable organizations to anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance activities at optimal times.
Data Collection and Management
Data collection forms the backbone of any predictive maintenance program. Organizations need reliable systems to gather information from equipment through sensors and monitoring devices.
The quality and quantity of data directly impact the accuracy of predictions. High-quality data includes:
- Equipment parameters: Temperature, vibration, pressure, and flow rates
- Operational variables: Production rates, runtime hours, and load conditions
- Maintenance records: Past repairs, replacements, and failure incidents
Data management systems organize historical data in structured databases, making them accessible for analysis. Many organizations implement data-cleaning protocols to remove inconsistencies and errors that could affect analytical accuracy.
Effective data governance policies ensure proper information handling throughout its lifecycle, from collection to storage and analysis.
Machine Learning and Analytics
Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms process collected data to identify patterns that precede equipment failure. These tools can detect subtle changes in operational parameters that might escape human observation.
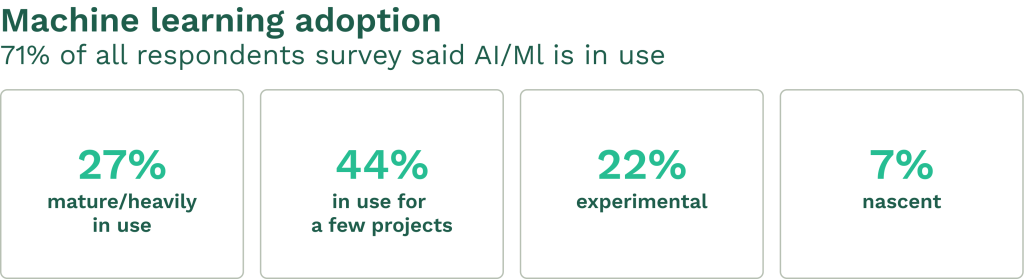
Predictive maintenance analytics typically involves several techniques:
- Anomaly detection: Identifying unusual patterns in equipment behavior
- Pattern recognition: Finding correlations between operational conditions and failures
- Failure prediction models: Calculating probability and timing of potential breakdowns
Machine learning models improve over time as they process more data, making predictions increasingly accurate. Organizations often start with simple statistical models before advancing to more complex neural networks and deep learning approaches.
The most sophisticated systems can differentiate between normal variations and warning signs of impending failure.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
IoT technology connects physical equipment to digital monitoring systems through networked sensors, creating a constant stream of real-time data about machine conditions and performance. These smart sensors are part
IoT integration enables:
- Real-time monitoring: Continuous assessment of equipment health
- Remote diagnostics: Evaluation of machinery status from anywhere
- Automated alerts: Instant notifications when parameters exceed thresholds

Modern sensors can measure multiple parameters simultaneously, including temperature, vibration, sound, and electrical current.
They are becoming increasingly affordable and compact, allowing extensive deployment across facilities.
Edge computing devices can process information locally before sending it to central systems, reducing bandwidth requirements.
Cloud Computing and Storage
Cloud platforms provide the computational power and storage capacity for predictive maintenance programs. They offer scalable resources that adjust to changing data volumes and analysis needs.
Key benefits of cloud-based predictive maintenance include:
- Scalable storage: Capacity to store vast amounts of historical and real-time data
- Powerful processing: Resources to run complex analytical models quickly
- Accessibility: Data and insights available across multiple locations and devices
- Cost efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models that eliminate large capital investments
Many organizations implement hybrid systems that combine on-premises solutions with cloud capabilities. This approach balances security concerns with the advantages of cloud computing.
Advanced security measures protect sensitive operational data while allowing maintenance teams and decision-makers appropriate access.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing predictive maintenance requires careful planning, appropriate tools, and organizational readiness. Businesses can achieve significant returns by following structured approaches addressing technical and operational aspects.
Assessing Readiness
Before implementing predictive maintenance, organizations must evaluate their current maintenance practices and technical infrastructure. This assessment helps identify gaps and establishes a baseline for improvement.
Start by examining your existing equipment and determining which assets would benefit most from predictive monitoring. Facility leaders should prioritize critical machinery that causes significant downtime when failures occur.
Next, assess your data collection capabilities. You’ll need:
- Sensors and IoT devices for data gathering
- Network infrastructure to transmit data
- Storage solutions for historical information
- Analytical tools for processing
Finally, evaluate your team’s technical skills. Staff may need training in data analysis, condition monitoring techniques, and new maintenance software platforms.
Creating a skills inventory helps identify where additional training or hiring might be necessary.
Creating an Implementation Plan
A structured implementation plan breaks down the predictive maintenance journey into manageable phases. Most successful programs start with pilot projects before scaling across operations.
Begin by establishing clear objectives with measurable outcomes, such as:
- Reduction in unplanned downtime (%)
- Decrease in maintenance costs ($)
- Extension of equipment lifespan (years)
- Improvement in overall equipment effectiveness (OEE)
Create a timeline with specific milestones for implementation. Effective strategies include starting with a small set of critical assets to demonstrate value quickly.
Allocate appropriate resources, including budget, personnel, and time. The plan should include stakeholder communication strategies to ensure buy-in from management, maintenance teams, and operators. Regular progress reviews help keep implementation on track.
Choosing the Right Tools and Platforms
Selecting appropriate technology forms the backbone of any predictive maintenance program. The market offers numerous solutions, from specialized sensors to comprehensive software platforms.
For data collection, consider these common sensor types:
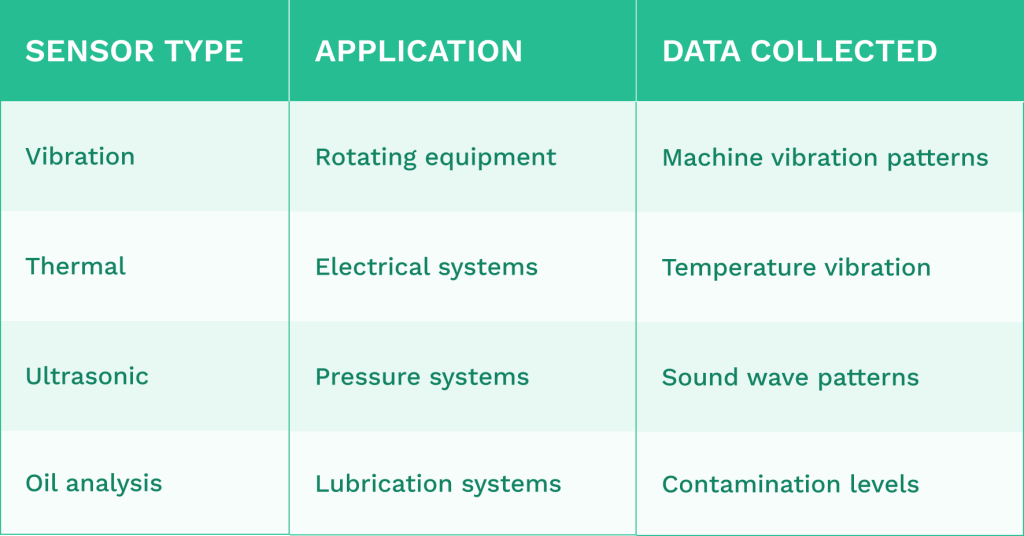
Predictive maintenance platforms should integrate with existing CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) for seamless workflow. Look for solutions offering:
- User-friendly dashboards
- Customizable alert thresholds
- Mobile accessibility
- Machine learning capabilities
Cloud-based solutions often provide greater scalability and easier updates than on-premises options. As a maintenance manager, when making selections, balance your immediate needs with future growth potential.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Implementing predictive maintenance inevitably presents obstacles. Understanding these challenges helps organizations prepare effective solutions in advance.
Data Quality
Data quality issues frequently undermine predictive models. Establish data governance protocols to ensure consistent collection methods and regular sensor calibration. Creating a “data dictionary” helps maintain standardization across systems.
Budget Constraint
Budget constraints can limit implementation scope. Address this by calculating and presenting ROI projections to leadership. Failure prevention and efficiency improvements typically justify the investment.
Acceptance to Change
Resistance to change from maintenance teams is common. Overcome this through comprehensive training programs and involving technicians in the implementation process. Highlight how predictive tools complement rather than replace their expertise.
Integration
Integration with legacy systems presents technical challenges. Consider middleware solutions or API connectors to bridge old and new platforms. Phased migration approaches minimize disruption to ongoing operations.
Predictive Maintenance Techniques
Effective predictive maintenance depends on using the right tools to monitor equipment conditions. These monitoring techniques detect early warning signs of equipment failure and provide data for making informed maintenance decisions.
Vibration Analysis
Vibration analysis is one of the most widely used predictive maintenance techniques. It measures the vibration patterns of rotating machinery to detect potential issues before they cause failure.
Equipment like motors, pumps, and turbines produce specific vibration signatures when operating correctly. When components wear or fail, these vibration patterns change in distinctive ways.
Technicians use specialized sensors and equipment to collect vibration readings. The data is then analyzed using specialized software that compares current readings to established baselines.
Common issues detected through vibration analysis include:
- Misalignment
- Imbalance
- Bearing failures
- Looseness
- Resonance issues
This technique is particularly valuable for detecting issues in rotating equipment where internal problems often manifest as changes in vibration patterns.
Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging uses infrared cameras to capture temperature variations across equipment. It detects abnormal heat patterns that often indicate electrical or mechanical problems.
These cameras create visual heat maps where color variations represent different temperatures. Hot spots in equipment often signal potential failure points or energy inefficiencies.
Real-time data from thermal sensors helps maintenance teams identify issues like:
- Overheating electrical connections
- Failing insulation
- Friction problems in mechanical components
- Blockages in pipes or cooling systems
- Overloaded circuits
Thermal imaging is non-invasive and can be performed while equipment runs, making it ideal for electrical systems, motors, and areas with multiple components.
Oil Analysis
Oil analysis involves examining lubricant samples to determine equipment condition. This technique is particularly valuable for machinery with lubrication systems, such as engines, gearboxes, and hydraulic systems.
Technicians collect oil samples and send them to specialized laboratories. The analysis examines several factors:
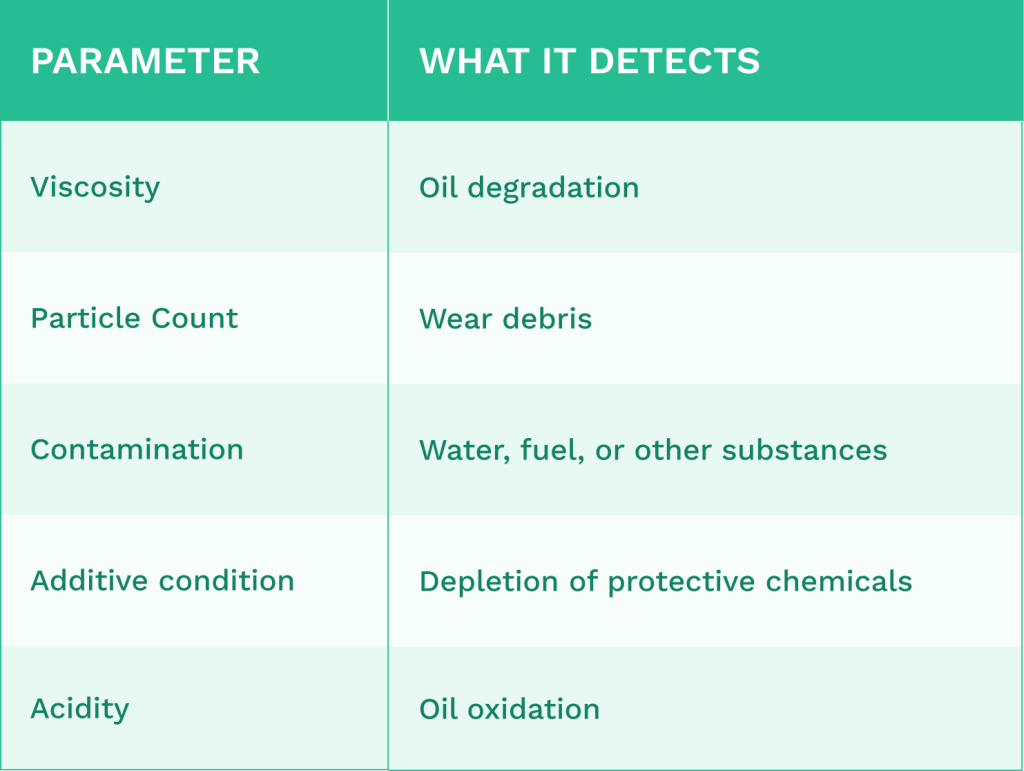
Results help identify issues like bearing wear, contamination, or inadequate lubrication before they cause catastrophic failure. Regular oil analysis also helps optimize oil change intervals, potentially reducing costs and downtime.
Ultrasonic Monitoring
Ultrasonic monitoring detects high-frequency sounds produced by equipment issues that are often inaudible to human ears.
This proactive maintenance approach identifies problems early in their development.
Specialized ultrasonic instruments convert these high-frequency sounds into audible ranges or visual displays. Technicians can then identify abnormal patterns that indicate potential problems.
Common applications for ultrasonic monitoring include:
- Detecting compressed air, gas, or vacuum leaks
- Identifying bearing issues before they appear in vibration analysis
- Checking steam trap functionality
- Evaluating electrical equipment for arcing or corona discharge
- Testing valve operation
This technique proves especially effective for detecting issues in pressurized systems and early-stage bearing failures before they cause significant damage.
Electrical Inspections
Electrical inspections employ various techniques to monitor the condition of electrical equipment and prevent unexpected failures. These inspections help identify potential issues before they lead to downtime or safety hazards.
Predictive maintenance for electrical systems typically includes:
Motor circuit analysis measures resistance, impedance, and other electrical parameters to detect developing issues. Changes in these readings often indicate problems like winding deterioration or insulation breakdown.
Power quality analysis monitors voltage, current, and power factor. Deviations can signal issues with the electrical supply or equipment performance.
Technicians collect data using specialized equipment, such as motor circuit analyzers, power quality meters, and insulation testers.
This data helps identify developing faults in motors, transformers, and other electrical components before failure.
Predictive Maintenance in Different Industries
Predictive maintenance strategies are implemented differently across various sectors, with each industry adapting techniques to match their specific equipment needs and operational challenges. The benefits of reduced downtime and extended equipment life are universal, but the applications vary significantly.
Manufacturing Sector
In manufacturing, predictive maintenance prevents failures, reduces costs, and significantly improves production efficiency. Factories employ vibration analysis sensors on motors, pumps, and assembly line equipment to detect anomalies before failure occurs.
Temperature monitoring helps identify overheating components in metal processing and chemical manufacturing. These early warnings prevent catastrophic breakdowns that could halt entire production lines.
Many manufacturers use AI-powered systems to analyze equipment performance data. These systems can predict when a CNC machine might fail or when robotic arms need servicing, often weeks before problems become apparent.
The ROI for manufacturing predictive maintenance is particularly impressive, with companies reporting:
- 25-30% reduction in maintenance costs
- 70-75% decrease in breakdowns
- 35-45% reduction in downtime
Implementation typically focuses on critical equipment first, gradually expanding to cover secondary machinery as the program proves successful.
Aerospace and Aviation
Aircraft maintenance demands exceptional precision and reliability. Predictive maintenance in aerospace uses advanced sensors and data analytics to monitor engine performance, structural integrity, and critical flight systems.
Engine health monitoring systems track vibration patterns, exhaust gas temperatures, and fuel efficiency metrics. These metrics help technicians identify potential turbine failures or combustion issues before they affect flight safety.
Airlines implement digital twin technology to create virtual replicas of aircraft components. These digital models simulate wear patterns and predict when parts will reach critical failure thresholds.
Flight data recorders provide valuable information for predictive algorithms. Maintenance systems can identify subtle patterns that precede component failures by analyzing thousands of flights.
Regulatory requirements make aerospace predictive maintenance particularly sophisticated. Systems must predict failures and document maintenance needs to comply with strict safety standards from aviation authorities.
Energy and Utilities
Power generation and distribution systems rely heavily on predictive maintenance strategies to deliver consistent service. In this sector, equipment failures can affect thousands of customers and create safety hazards.
Wind farms use vibration sensors and oil analysis to monitor turbine gearboxes and bearings. These technologies help technicians identify when a turbine needs maintenance before it stops generating electricity.
Power plants continuously monitor generator temperature, pressure, and vibration. AI systems analyze this data to predict failures in cooling systems, turbines, and electrical components.
Grid infrastructure benefits from infrared imaging technology that identifies hot spots in transmission lines. These hot spots often indicate connection problems that could lead to power outages if left unaddressed.
Smart meters and IoT devices throughout distribution networks create a comprehensive data picture. This data helps utilities predict where maintenance is needed most urgently, optimizing their maintenance resources.
Transportation and Transit
Public transportation systems and shipping fleets maintain complex equipment that must operate reliably under varying conditions. Predictive maintenance helps these organizations balance safety, reliability, and maintenance costs.
Rail operators use track-mounted sensors and train-based monitoring systems to collect data on wheel conditions, track integrity, and signaling system performance. This data feeds predictive models that schedule maintenance before derailments or service disruptions occur.
Commercial trucking fleets implement telematics systems that monitor engine performance, transmission health, and brake systems. These systems alert fleet managers when a vehicle shows signs of impending failure.
Maritime shipping employs hull integrity monitors and engine performance sensors. These technologies help prevent costly breakdowns while vessels are at sea, where repairs are difficult and expensive.
Bus transit systems use predictive maintenance to optimize engine performance and reduce emissions. By identifying fuel system issues early, these organizations maintain service schedules while meeting environmental requirements.
Healthcare Equipment
Hospital systems rely on predictive maintenance for critical medical equipment that directly impacts patient care. Downtime for these systems can delay treatment and create health risks.
MRI machines and CT scanners contain sophisticated cooling systems and moving parts that benefit from predictive monitoring. Sensors track helium levels, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical vibrations to prevent unexpected failures during patient procedures.
Patient monitoring systems undergo continuous performance checks. Predictive algorithms analyze signal quality and power system stability to ensure these critical systems function properly during emergencies.
Laboratory equipment like centrifuges and analyzers contain predictive maintenance capabilities that track motor performance and calibration drift. These features help maintain testing accuracy and prevent diagnostic errors.
Facilities management extends predictive maintenance to building systems that affect patient care. HVAC, water, and electrical systems are monitored to prevent environmental issues from compromising sterility in operating rooms or affecting sensitive equipment performance.
Benefits and ROI
Predictive maintenance delivers significant financial and operational advantages for organizations that implement it effectively.
Companies can expect concrete returns on their investment through several key pathways that impact both short-term budgets and long-term strategic goals.
Reducing Downtime
Unplanned downtime poses one of the costliest threats to manufacturing and industrial operations. Predictive maintenance directly addresses this challenge by identifying potential failures before they occur. Studies show that implementing predictive maintenance can reduce unplanned downtime by up to 50%, resulting in substantial productivity gains and cost savings.

Companies using predictive maintenance typically experience:
- 30-50% reduction in equipment failures
- 10-40% decrease in maintenance costs
- 25-30% reduction in maintenance labor hours
These improvements translate to real financial benefits. For example, a manufacturing facility that loses $10,000 per hour during equipment failures can save hundreds of thousands annually by preventing just a few major breakdowns.
The ROI is particularly evident in industries with high-value production processes with substantial downtime costs.
Extending Equipment Life
Predictive maintenance significantly increases the usable lifespan of valuable machinery and equipment. Organizations avoid premature replacement costs by addressing small issues before they escalate into major problems.
Equipment lifetime extensions typically range from 20-40%, representing enormous capital expense deferrals. A company that usually replaces a $500,000 machine every 10 years might extend its life by 3-4 years through consistent predictive maintenance.

This extension creates two financial benefits:
- Deferred capital expenditures
- Improved return on existing assets
The practice also optimizes maintenance scheduling by focusing resources on equipment needing attention rather than following arbitrary time-based maintenance schedules. This targeted approach extends equipment lifespan while reducing overall maintenance costs.
Improving Safety and Compliance
Predictive maintenance directly enhances workplace safety by reducing the risk of catastrophic equipment failures, which can lead to worker injuries, environmental incidents, and regulatory violations.
Key safety benefits include:
- Fewer emergency repair situations where technicians work under pressure
- Reduced risk of dangerous equipment malfunctions
- Better compliance with regulatory requirements
- Documentation of maintenance practices for audit purposes
Organizations in highly regulated industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and energy production gain particular value from these safety improvements. The predictive approach creates verifiable records of maintenance activities that satisfy regulatory requirements.
The ROI calculation must include potential costs avoided, such as workers’ compensation claims, regulatory fines, legal expenses, and production delays following safety incidents. These avoided costs often represent some of predictive maintenance programs’ most significant financial benefits.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Predictive maintenance transforms maintenance from a cost center to a strategic function that enhances overall efficiency. Organizations implementing these programs typically report:

- 10-20% increase in production capacity
- 20-25% reduction in maintenance overhead
- 35-45% decrease in spare parts inventory needs
The data gathered through predictive maintenance systems provides invaluable insights beyond maintenance alone. Production managers gain visibility into equipment performance patterns, allowing them to optimize operational parameters.
Resource allocation improves dramatically as maintenance teams focus on genuine issues rather than routine inspections of healthy equipment. This transition from reactive to predictive approaches makes maintenance personnel more productive and valuable to the organization.
The ROI calculation should include these efficiency gains alongside direct maintenance cost reductions. Many organizations find their maintenance teams become smaller yet more effective after implementing predictive maintenance.
Benchmarking Against Industry Standards
According to industry research, world-class maintenance organizations typically achieve:
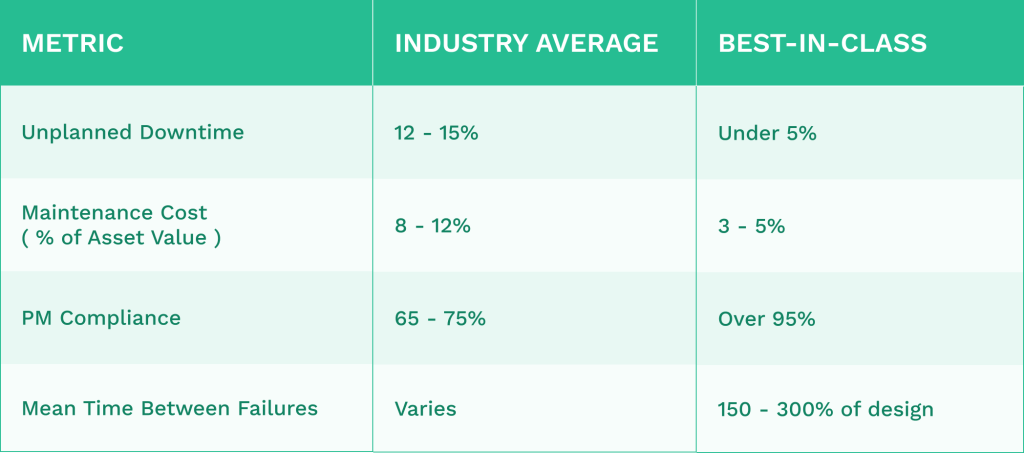
The best-performing organizations follow standardized inspection protocols and utilize comprehensive performance indicators. These indicators go beyond simple uptime measurements to include mean time to repair and maintenance cost per asset.
Effective benchmarking requires regular assessment of your maintenance program against these standards. Companies that review quarterly performance show 37% better results than those that benchmark annually.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Leading organizations establish dedicated improvement teams that regularly analyze performance data and recommend process adjustments. These teams typically meet weekly to review maintenance metrics and identify optimization opportunities.
Machine learning models benefit from continuous refinement with new data. Companies updating their predictive models quarterly achieve 40% better accuracy than static models.
AI-powered predictive maintenance continues to evolve with technologies like:
- Digital twins that create virtual replicas of physical assets
- Edge computing for real-time analysis without cloud connectivity
- Augmented reality tools for maintenance technicians
- Automated root cause analysis to prevent recurring issues
Organizations that allocate 5-10% of their maintenance budget to innovation initiatives consistently outperform competitors in equipment reliability and cost efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance and Sustainability
Predictive maintenance strategies extend beyond operational efficiency to deliver significant environmental benefits. Forward-thinking organizations now recognize how these approaches can reduce waste and promote more sustainable resource consumption.
Impact on Environmental Footprint
Predictive maintenance significantly reduces an organization’s environmental impact through multiple channels. Preventing catastrophic equipment failures minimizes the waste of materials, energy, and resources that would otherwise be consumed in emergency repairs.
Equipment running at optimal performance levels consumes less energy. Studies show that properly maintained machines can use up to 15% less electricity than those operating in suboptimal conditions. This translates to lower carbon emissions and reduced utility costs.
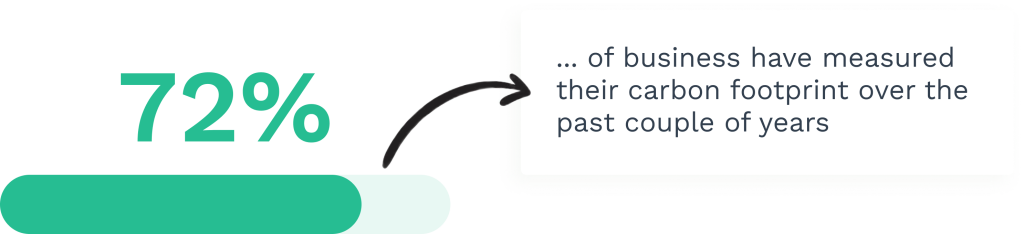
Advanced downtime tracking software helps organizations identify energy inefficiencies before they become significant problems. This proactive approach prevents the unnecessary waste of resources.
Predictive maintenance extends equipment’s lifespan, which means fewer machines are manufactured, and fewer end up in landfills. This reduces both upstream manufacturing impacts and downstream waste disposal issues.
Encouraging Responsible Consumption
Predictive maintenance enables businesses to make more informed decisions about resource allocation and equipment replacement. Rather than following fixed replacement schedules, companies can maximize the useful life of assets without compromising performance.
This approach aligns with circular economy principles by emphasizing repair and maintenance over replacement. Organizations can reduce maintenance costs through more efficient resource use while achieving sustainability KPIs.
Data-driven maintenance decisions lead to more precise ordering of replacement parts and supplies. This prevents overstocking and reduces waste from unused materials that may become obsolete.
By highlighting the connection between equipment performance and resource consumption, predictive maintenance creates awareness about sustainability throughout organizations. Maintenance teams become champions for both operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
The Future of Predictive Maintenance
With the explosion in AI and Machine learning, predictive maintenance is evolving rapidly. These technical innovations are reshaping how industries monitor and maintain their assets.
Several key developments will transform predictive maintenance practices in the coming years.
Emerging Technologies and Trends
Several emerging technologies are revolutionizing the predictive maintenance landscape.
Digital twins are creating virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing for real-time simulation and testing without disrupting operations. By analyzing historical and real-time data, these models can predict failures with increasing accuracy.
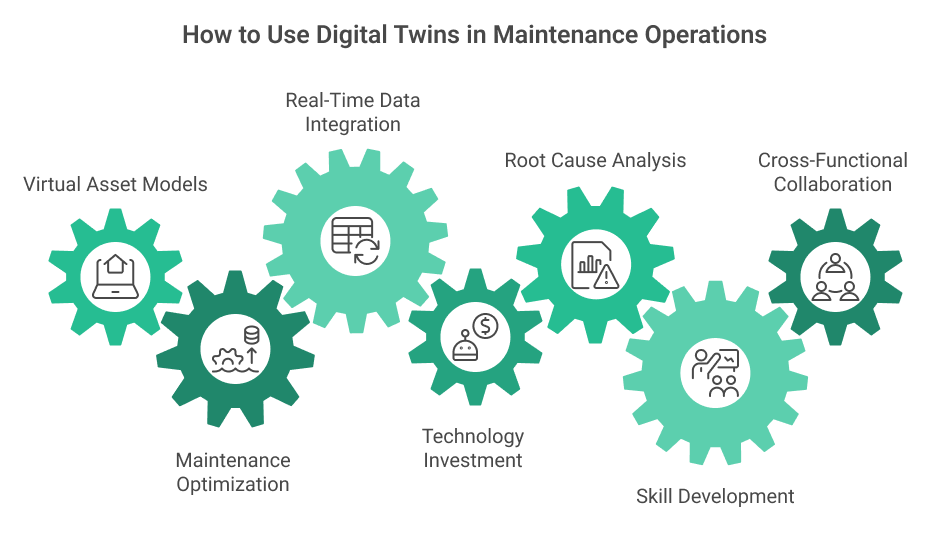
Edge computing is gaining traction by processing data directly on machinery rather than sending everything to the cloud. This reduces latency and enables faster decision-making for critical equipment.
IoT sensors are becoming smaller, more affordable, and more powerful. Modern sensors can detect subtle changes in vibration, temperature, and sound previously undetectable, providing earlier warning signs of potential failures.
Augmented reality (AR) tools are helping maintenance technicians visualize repair procedures and access real-time data while working on equipment, significantly reducing repair times and errors.
Integrating with Industry 4.0
Predictive maintenance is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0, where smart factories rely on interconnected systems. This integration creates unified data ecosystems where maintenance insights can influence production planning and vice versa.
Smart factories leverage predictive maintenance as part of their continuous improvement processes. These facilities can automatically adjust production schedules based on maintenance forecasts, minimizing downtime.
The convergence with supply chain management systems enables just-in-time spare parts delivery, reducing inventory costs and ensuring parts are available precisely when necessary for maintenance.
Key Industry 4.0 integration points include:
- Production planning systems
- Quality control processes
- Supply chain management
- Energy management systems
These integrations create feedback loops that enhance predictive algorithms and overall operational efficiency.
Potential for Artificial Intelligence Advancements
AI and machine learning will drive the next generation of predictive maintenance solutions. Current algorithms focus on detecting known failure patterns, but future AI will identify previously unknown relationships between operating conditions and equipment failures.
Unsupervised learning algorithms will recognize subtle anomalies without being explicitly programmed to look for them. This capability is particularly valuable for complex systems where failure modes may not be fully understood.
Natural language processing will enable maintenance systems to extract insights from unstructured data sources like technician notes, manufacturer documentation, and industry forums.
Explainable AI will provide clearer reasoning behind predictions, helping maintenance teams understand when and why a failure might occur. This transparency builds trust in AI recommendations and enables better human-machine collaboration.
Federated learning will allow organizations to benefit from industry-wide failure data while maintaining proprietary information security.
Preparing for the Skills of Tomorrow
The evolution of predictive maintenance is creating demand for new skill sets among maintenance professionals. Technical teams increasingly need data analysis capabilities alongside traditional mechanical and electrical knowledge.
Training programs are adapting to include:
- Data interpretation fundamentals
- Basic programming concepts
- Understanding of sensor technology
- Critical thinking about algorithmic recommendations
Cross-functional teams combining IT expertise with domain-specific maintenance knowledge are becoming standard in organizations implementing advanced predictive maintenance.
The human element remains crucial despite automation advances. Experienced technicians’ intuition and contextual understanding complement AI systems, creating more robust maintenance strategies than either could achieve alone.
Organizations that invest in upskilling current maintenance staff rather than simply replacing them with data scientists typically see more successful implementations and better retention of valuable institutional knowledge.
Summary
Predictive maintenance represents a paradigm shift in how industries approach equipment management. It offers a proactive maintenance strategy that leverages data, predictive analytics, and machine learning to anticipate and prevent equipment failures.

Organizations can significantly reduce maintenance costs, unplanned downtime, and equipment failures by identifying critical assets and implementing advanced predictive maintenance solutions. This comprehensive guide has explored the various predictive maintenance technologies, such as vibration analysis and oil analysis, that detect potential issues early, ensuring optimal equipment health and performance.
Integrating IoT sensors, cloud computing, and AI-driven predictive algorithms further enhances the ability to collect and analyze data in real-time, enabling maintenance teams to make informed decisions and schedule maintenance activities effectively.
As industries continue to embrace these technologies, predictive maintenance will be crucial in enhancing operational efficiency, extending asset lifespan, and promoting sustainability. It will ultimately transform maintenance strategies for a more reliable and cost-effective future.










