Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKey Takeaways:
- Preventive maintenance audits expose vulnerabilities that lead to catastrophic equipment failures and costly repairs
- Audit preparation time plummets when maintenance documentation is automated as part of daily workflows. One healthcare facility reduced audit prep from 2 weeks to under 2 hours while improving calibration compliance from 68% to 98%.
- CMMS delivers measurable financial impact: Organizations achieve 27% less downtime, 12-18% cost savings over reactive maintenance, and up to 8x ROI in the first year through reduced emergency repairs, extended equipment life, and improved labor efficiency.
Picture this: an auditor walks through your facility doors next Tuesday. Your maintenance team scrambles to locate work orders scattered across filing cabinets, spreadsheets, and half-forgotten notebooks.
Someone recalls that the compressor PM was completed last month, but no one can find the documentation. Meanwhile, the clock ticks, your heart races, and your entire maintenance operation hangs in the balance.
This scenario plays out in facilities worldwide, and it does not have to. A well-implemented computerized maintenance management system transforms preventive maintenance audits from anxiety-inducing ordeals into straightforward exercises in clicking “generate report.”
The difference between passing and failing an audit often comes down to one factor: whether your maintenance management approach relies on memory and paper or on structured, automated systems.
Why is Preventive Maintenance Audit critical?
A preventive maintenance audit is a detailed examination of your organization’s maintenance operations, procedures, and outcomes.
Unlike routine inspections that focus on individual assets, these audits evaluate your entire maintenance operation.
The objectives extend far beyond checking boxes. Audits assess whether your preventive maintenance schedules actually prevent equipment failures, whether your maintenance team follows established procedures, and whether your documentation meets regulatory compliance requirements.
They identify gaps between your intended maintenance strategies and your actual maintenance performance.
For facility managers and maintenance professionals, the audit process reveals the health of your maintenance management system:
- Are work orders completed on time?
- Does your maintenance history provide the traceability auditors demand?
- Can you demonstrate that critical assets receive the attention they require?
The Actual Cost of Reactive Maintenance
Before examining how CMMS software enhances maintenance operations, let’s look at what happens without it.
Organizations relying on reactive maintenance, fixing equipment only after it breaks, face a compounding set of problems that audits inevitably expose.
Understanding the Maintenance Audit Process
Successful preventive maintenance audits are a direct approach that evaluates multiple dimensions of your maintenance activities.
Understanding this process helps clarify why CMMS capabilities prove so valuable.
Documentation review
This forms the foundation. Auditors examine maintenance calendars, work order histories, and asset records to verify that scheduled maintenance occurs as planned.
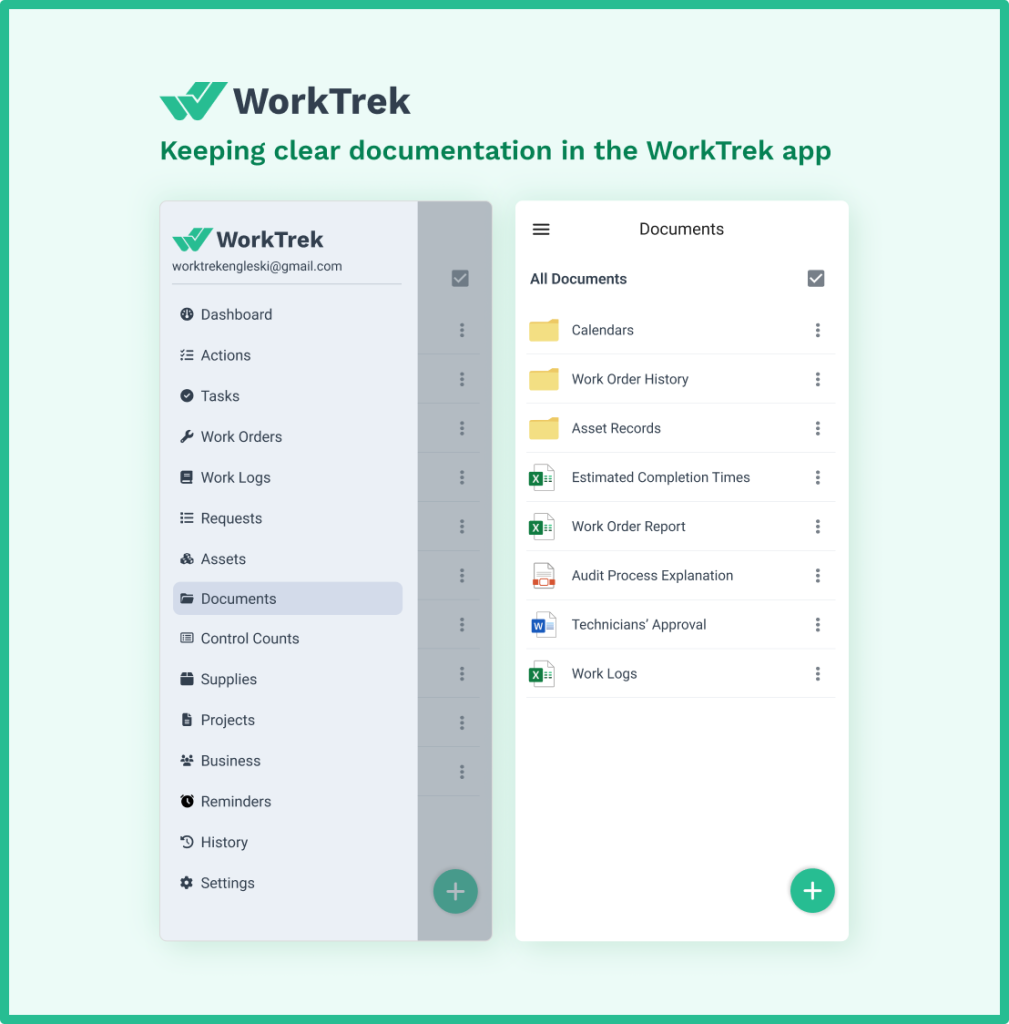
They look for evidence that your maintenance workflows include proper approvals, that technicians document their work thoroughly, and that your maintenance management system captures the information needed for traceability.
Equipment inspection
This provides ground truth. Auditors compare the documented condition of assets against their actual state.
A particular asset showing signs of neglect despite a complete maintenance history raises immediate red flags. This is where the integrity of your maintenance records faces its sternest test.
Data analysis
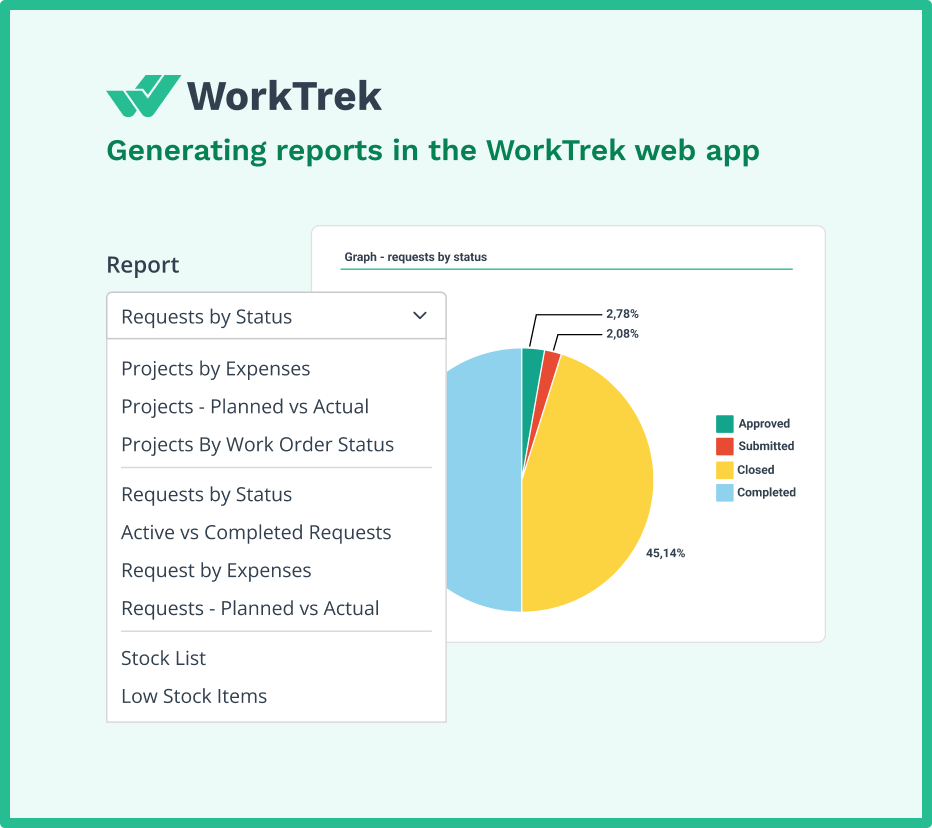
Can reveal interesting patterns. Auditors examine key performance indicators like equipment uptime, mean time between failures, and maintenance costs per asset. They compare your maintenance performance against industry benchmarks to identify areas requiring attention.
Organizations with mature maintenance management systems CMMS implementations can generate these reports instantly; those without scramble to compile data from disparate sources.
Performance evaluation
Can tie everything together. Here are the questions to consider:
- How effective is your preventive maintenance program at achieving its objectives?
- Are maintenance schedules based on equipment usage patterns and manufacturer recommendations, or arbitrary time intervals?
- Do your maintenance strategies evolve based on asset performance data, or remain static year after year?
How CMMS transforms preventive maintenance audits
A computerized maintenance management system like WorkTrek serves as the central nervous system for your organization’s maintenance operations.
Instead of scattered spreadsheets and paper records, CMMS software consolidates all maintenance activities into a single, searchable, auditable platform.
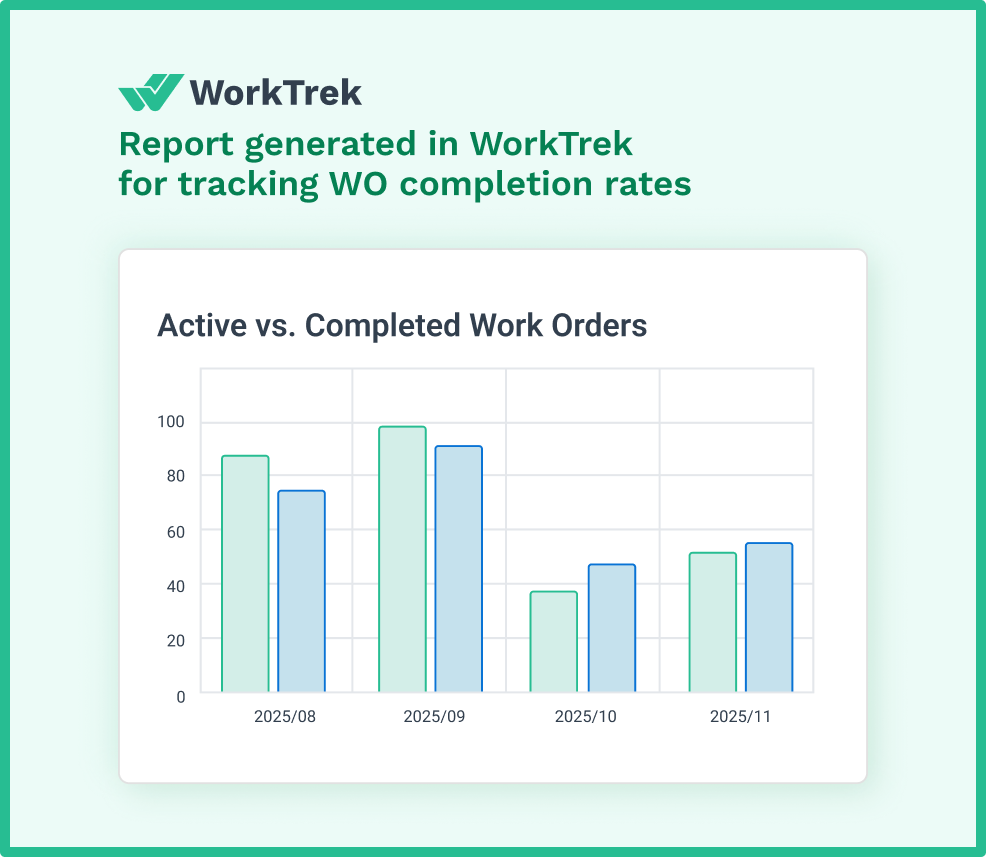
The transformation begins with centralized maintenance data. Every work order, every completed task, every part replacement, and every technician note lives in one system. When auditors request documentation for a particular asset, you retrieve its complete maintenance history with a few clicks. Asset histories that once required hours of manual compilation now appear in seconds.

Aberdeen Group research confirms that organizations using CMMS experience an average 27% reduction in downtime. This improvement stems directly from better visibility into maintenance performance—the same visibility that makes audits straightforward rather than stressful.
Automated scheduling eliminates the memory lapses that plague manual systems. CMMS platforms generate automated reminders when preventive maintenance schedules require attention. Rather than relying on someone to remember that the quarterly equipment inspection is due, the system alerts the appropriate technician and automatically creates the work order. Maintenance calendars stay current without constant manual intervention.
For healthcare facilities and other regulated environments, this automation proves especially valuable.
One healthcare CMMS implementation saw calibration compliance rise from 68% to 98% within six months, with audit preparation time dropping from two weeks to under two hours. The maintenance backlog decreased by 40% as automated workflows ensured nothing fell through the cracks.
Core CMMS features that streamline maintenance operations
Understanding specific CMMS capabilities clarifies why this technology delivers such significant audit benefits. Modern preventive maintenance software addresses every aspect of the audit preparation challenge.
Work order management and tracking
Every maintenance task flows through a documented work order system. Technicians receive assignments with clear instructions, required parts lists, and safety procedures.
They document their work upon completion, capturing timestamps, labor hours, and observations. This creates the continuous, verifiable record that auditors demand.
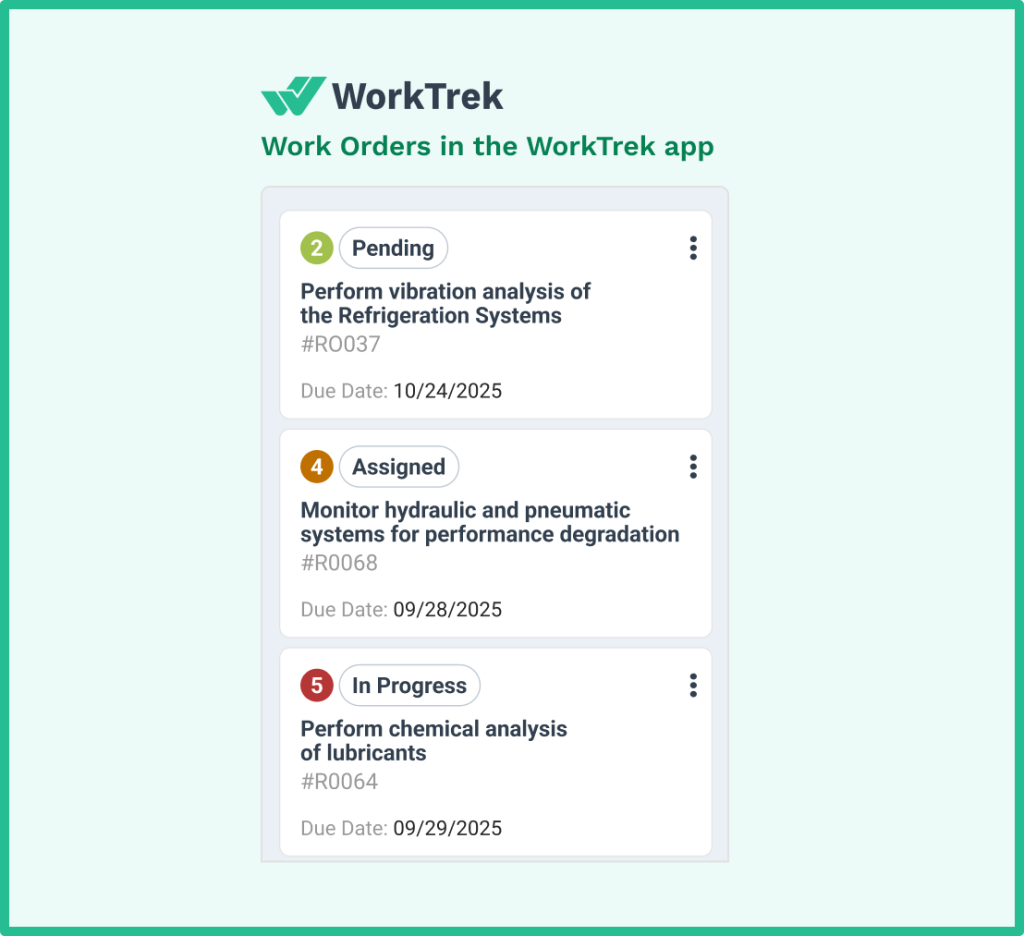
The ability to track maintenance tasks in real-time means supervisors always know the status of preventive maintenance activities. No more wondering whether that critical PM was completed—the system shows exactly when it happened and who performed it.
Asset management and tracking
Comprehensive asset management capabilities let you track every piece of equipment from acquisition through disposal. Asset tracking includes maintenance history, repair costs, parts consumption, and performance metrics.
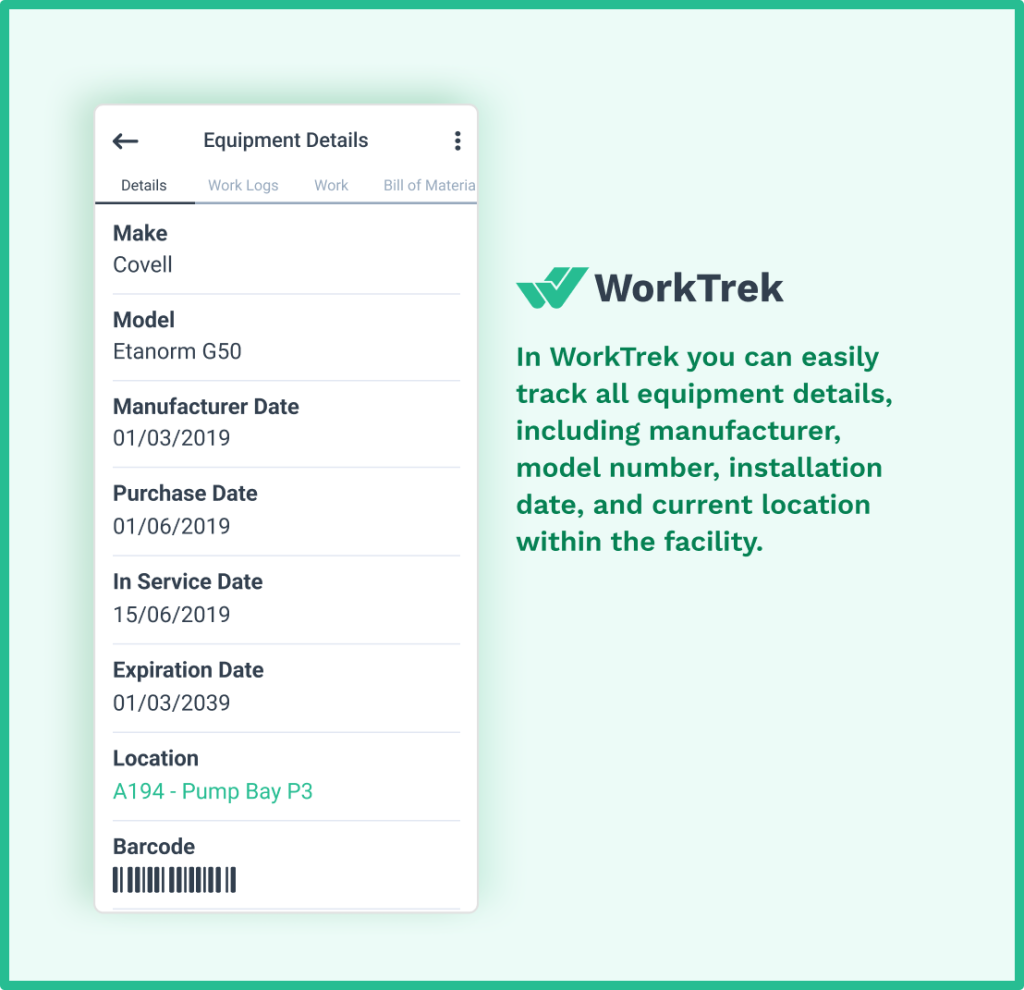
This longitudinal view helps optimize maintenance scheduling based on actual equipment behavior rather than generic guidelines.

For audit purposes, asset management documentation demonstrates that you understand your equipment portfolio and maintain it appropriately.
Inventory management integration
Parts availability determines whether routine maintenance tasks proceed on schedule or get delayed waiting for components.
CMMS inventory management features track inventory levels, automate reorder points, and associate parts with specific equipment. When a PM requires particular components, the system verifies availability before scheduling.
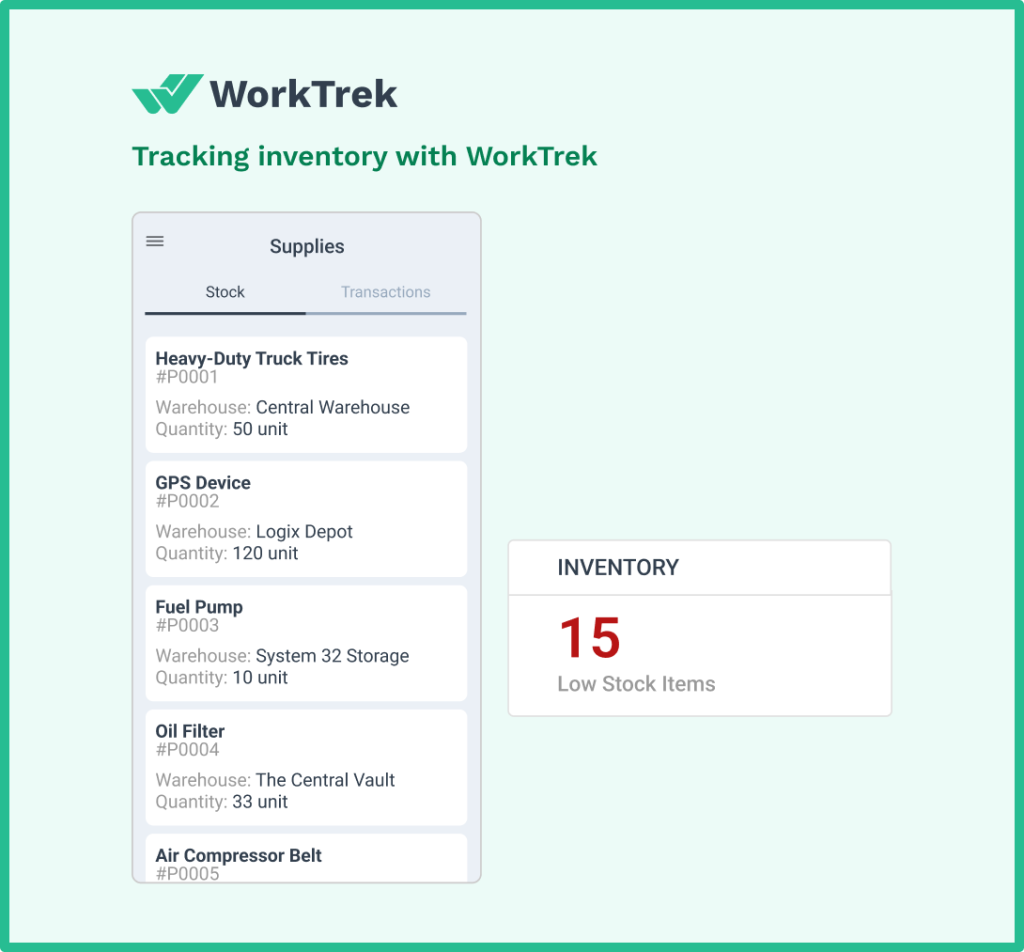
Research indicates that efficient inventory management with a CMMS can reduce maintenance costs by up to 30% by eliminating excess inventory and preventing costly emergency purchases.
Auditors appreciate seeing systematic inventory controls because they indicate mature maintenance management.
Reporting and analytics
The ability to generate comprehensive reports distinguishes CMMS from basic tracking tools. Built-in analytics calculate key performance indicators, including equipment reliability metrics, maintenance cost trends, technician productivity, and PM completion rates.
These data-driven insights help identify improvement opportunities before auditors do.
For compliance purposes, CMMS reporting capabilities produce the documentation auditors need in formats they expect, reducing manual work.
Mobile capabilities for field documentation
Modern CMMS platforms include mobile capabilities that enable technicians to document maintenance activities in real-time, directly from the equipment location. This eliminates the documentation gaps that arise when technicians complete field work but delay paperwork until they return to the office.
Mobile access also supports on-site audit procedures. When auditors inspect equipment, technicians can immediately pull up maintenance records on tablets or smartphones, demonstrating that your documentation reflects actual conditions.
Benefits of CMMS for regulatory compliance and audits
The compliance benefits of CMMS extend across regulated industries.
Whether your organization faces OSHA inspections, ISO audits, FDA reviews, or industry-specific requirements, computerized maintenance management provides the documentation infrastructure that regulators demand.
Building audit trails automatically
Every action in a properly configured CMMS creates an audit trail. Work order creation, assignment, completion, and approval all generate timestamped records.
Part usage, technician notes, and supervisor reviews leave permanent traces. This continuous documentation occurs automatically as part of normal maintenance workflows rather than requiring separate record-keeping.
When auditors request evidence that specific preventive maintenance occurred, you provide system-generated records showing exactly when, how, and by whom. The electronic trail eliminates concerns about falsified records or “pencil-whipping” that plague paper-based systems.
Meeting regulatory documentation requirements
Different industries face different compliance frameworks, but all share standard documentation requirements.
CMMS platforms support these requirements through:
Timestamped records that prove when maintenance activities occurred. FDA-regulated facilities need this to comply with 21 CFR Part 11. Manufacturing operations need it for ISO certifications. Healthcare facilities need it for Joint Commission reviews.
Electronic signatures and approvals that verify the identity of personnel performing and approving maintenance work. This satisfies chain-of-custody requirements for regulated maintenance activities.

Document control that maintains current versions of procedures, manuals, and specifications while preserving historical versions for reference. Auditors can verify that technicians followed the correct procedures in effect at the time maintenance was performed.
Reducing compliance risk and penalties
The National Safety Council estimates that companies can save an average of $120,000 per year by avoiding workplace safety violations through proper CMMS implementation.
Beyond direct penalties, compliance failures can trigger increased inspection frequency, operational restrictions, and reputational damage that far exceed the amount of fines.
How CMMS delivers measurable cost savings
The financial case for CMMS investment rests on measurable improvements across multiple cost categories. Understanding these savings helps justify implementation and demonstrates the business value of structured maintenance management.
Reduced maintenance costs through prevention
The fundamental economic principle underlying preventive maintenance holds that each dollar spent on prevention saves $5 in future costs. CMMS amplifies these savings by ensuring preventive maintenance actually happens as scheduled and by optimizing maintenance schedules based on actual equipment performance.
Industry research documents that over 20 years, organizations can achieve ROI of 545% by transitioning from reactive to preventive maintenance. CMMS makes this transition possible by providing the scheduling, tracking, and documentation infrastructure that sustained prevention requires.
Feature-rich CMMS software helps organizations save 5-15% of their maintenance budget according to FieldCircle analysis. These savings compound over time as better data enables better decisions about resource allocation, maintenance strategies, and equipment replacement timing.
Extended equipment life and reduced repair costs
Properly maintained equipment lasts longer and fails less dramatically. McKinsey research shows that predictive maintenance can extend equipment life by 20% to 40%, representing significant deferrals in capital expenditure.
Beyond lifespan extension, preventive approaches reduce repair costs by catching problems early. A small lubricant leak identified during a scheduled inspection costs far less to address than a seized bearing discovered during production. CMMS tracking ensures these inspections happen consistently rather than sporadically.
Labor efficiency improvements
CMMS software can increase work efficiency by 15-20% according to industry research. This efficiency gain translates to reduced overtime costs, lower labor expenses, and better utilization of your maintenance team.
The efficiency improvement stems from multiple factors. Technicians spend less time hunting for equipment information, parts, or previous work orders.
Supervisors spend less time manually assigning and tracking work. Administrative staff spend less time compiling reports and chasing documentation. All of this time savings redirects effort toward productive maintenance activities.
MaintainX reports that their clients keep equipment online 38% longer, repair it 37% faster, and increase technicians’ wrench time by around 12%. These metrics demonstrate how CMMS eliminates the administrative friction that consumes maintenance resources.
Energy cost reductions
The U.S. Department of Energy has documented that implementing CMMS can reduce facility energy consumption by 5-20%.

Properly maintained equipment operates more efficiently. Clean filters, calibrated sensors, and properly lubricated components all reduce energy waste.
Implementing CMMS for audit success
Transitioning to CMMS-based maintenance management requires a structured approach.
Start with asset data
Before CMMS can track maintenance, it needs accurate information about what you maintain. Asset data migration, such as entering equipment information, establishing hierarchies, and linking assets to maintenance requirements, forms the foundation for everything that follows.
Prioritize critical assets that are subject to the highest audit scrutiny. Production equipment subject to safety regulations, medical devices requiring calibration documentation, and environmental controls with monitoring requirements should be entered into the system first, with complete information.
Establishing maintenance schedules
Translate existing preventive maintenance schedules into CMMS-managed programs. This process often reveals gaps in current practices.

This can include equipment without documented PM requirements, schedules based on habit rather than manufacturer recommendations, or maintenance activities that no longer match current equipment configurations.
Use this transition to validate and optimize your preventive maintenance schedules. CMMS implementation requires documenting maintenance requirements that may have existed only in technicians’ memories.
Training for consistent usage
CMMS delivers benefits only when people use it consistently and with proper staff training.
Training should emphasize not just system mechanics but the reasons behind documentation requirements. Technicians who understand how their work order entries support audit compliance are more likely to provide complete, accurate information.
Include hands-on practice with realistic scenarios. Let technicians experience how easy mobile documentation can be. Show supervisors how reporting capabilities provide the visibility they lacked before. Build enthusiasm for the system by demonstrating its benefits rather than just mandating its use.
Monitoring adoption and refining processes
Post-implementation monitoring identifies usage gaps before they become audit problems. Track work order completion rates, documentation completeness, and PM compliance percentages. Address issues promptly rather than allowing bad habits to establish themselves.

Refine workflows based on actual usage patterns. If technicians consistently skip specific fields, determine whether those fields are necessary. If documentation takes longer than expected, investigate whether process changes could streamline entry without sacrificing audit requirements.
Measuring success and demonstrating ROI
Organizations implementing CMMS should establish metrics that demonstrate value and support continuous improvement of maintenance programs.
Core performance indicators
Track key performance indicators that reflect both maintenance effectiveness and audit readiness.
PM completion rates show whether preventive maintenance schedules translate into actual work. Documentation completeness rates indicate whether work orders capture required information.
Mean time between failures reveals whether preventive maintenance prevents equipment failures as intended.
These metrics serve dual purposes: they help optimize maintenance performance, and they demonstrate to auditors that your organization manages maintenance systematically and effectively.
Audit-specific metrics
Beyond operational metrics, track audit-related performance directly:
- How long does audit preparation require?
- How many findings result from each audit?
- How quickly can you retrieve specific documentation when requested?
Improvements in these metrics demonstrate the value of CMMSs in terms that resonate with executives concerned about compliance risk.
Reducing audit preparation from two weeks to two hours, as the healthcare case study documented, represents significant resource savings and risk reduction.
Financial impact tracking
Quantify cost savings wherever possible. Reduced maintenance costs should be identifiable in maintenance budgets. Equipment downtime reductions, measured through production records, confirm that preventive maintenance delivers operational benefits. Energy savings, while harder to isolate, often appear in utility cost trends.
Industry analysis from Limble suggests that organizations can achieve an ROI of approximately 8x their CMMS investment within the first year when accounting for downtime reduction, maintenance cost savings, and productivity improvements.
Your actual results can vary and depend on baseline conditions and implementation quality, but tracking these metrics helps demonstrate value and identify opportunities for improvement.
Conclusion
The question is no longer whether CMMS belongs in your preventive maintenance program but how quickly you can implement it.
As the data shows, manual tracking, scattered documentation, and reactive maintenance approaches expose your organization to audit risk, equipment failures, and preventable costs.
But the most powerful argument may be simpler: CMMS eliminates the stress of audit preparation by making audit-ready documentation a byproduct of normal operations rather than a separate administrative burden.
When your maintenance team documents work as they complete it, when preventive maintenance schedules automatically generate tracked work orders, and when asset histories accumulate without manual compilation, audits become non-events.
WorkTrek offers the preventive maintenance software capabilities your organization needs to transform maintenance operations and enhance operational efficiency. From automated scheduling to mobile documentation to comprehensive reporting, the platform provides the tools that make audit success achievable and sustainable.
The tools exist. The benefits are proven. Now is the time to make the transition.









