Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeWhat are some of the tips for managing a successful maintenance team? Effective management begins with setting clear SMART goals, which guide the team and ensure everyone knows their responsibilities within maintenance departments. This approach helps maintain focus and achieve desired outcomes efficiently.
Foster effective communication and collaboration among team members to build a cohesive team. Regular meetings and digital platforms for sharing insights and discussing challenges can significantly enhance teamwork.
Modern maintenance techniques and tools, such as WorkTrek CMMS, can improve the team’s productivity and reliability.
Understanding the Maintenance Landscape
To manage a successful maintenance team, understand the key elements that make up the team and the role of maintenance in maintaining production efficiency and equipment reliability.
This section covers essential components and the importance of a good maintenance strategy.
The Core Elements of a Maintenance Team
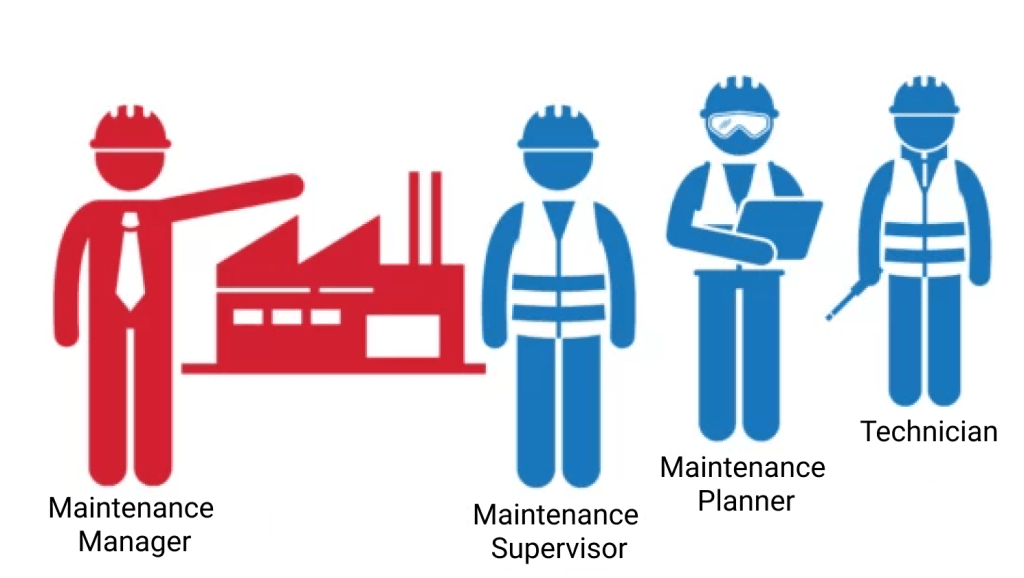
A well-structured maintenance team needs defined roles and responsibilities, good problem-solving skills, encouragement of collaboration, and the ability to follow the organization’s production goals.
This includes positions like maintenance managers, technicians, and planners. Each member should have precise tasks to avoid any overlaps or gaps.
Maintenance Managers oversee the entire operation, ensuring smooth operation and the team’s compliance with policies and procedures.
Technicians perform hands-on work, such as inspections, repairs, and servicing. Their skills are vital for equipment uptime and reliability.
Planners schedule and organize maintenance tasks. They ensure that the right resources are available and that work is done on time.
Maintenance Supervisors handle responsibilities within the maintenance team, particularly in smaller teams where the maintenance manager may manage these duties.
Effective communication within the team is also vital. Regular meetings to discuss progress, issues, and plans help keep everyone aligned.
Source: IDCON
Significance of Maintenance in Production
Good maintenance practices directly impact production. Routine inspections and preventive measures help keep machinery in top condition, reducing unexpected breakdowns.
Uptime is a key metric. The longer equipment can run without issues, the more productive the operation. Regular maintenance boosts equipment reliability, ensuring that production targets are met consistently.
A proactive maintenance program can prevent problems before they occur. Modern tools like condition monitoring can help identify potential issues early. Implementing a robust preventive maintenance (PM) plan and having a backup strategy for critical equipment failures are some practical steps.
Companies can also benefit by involving key stakeholders in planning. This helps address inconsistencies and fully utilize opportunities to optimize production efficiency.
Leadership and Management
Effective leadership involves empowering team members, ensuring clear goals, and fostering a cooperative environment. Management focuses on planning, coordinating tasks, and maintaining efficient workflows.
Roles of a Maintenance Manager
A maintenance manager ensures smooth operations by overseeing daily tasks and long-term projects. They coordinate with technicians, supervisors, and planners to manage resources effectively.
Key responsibilities:
- Scheduling and Planning: Ensure timely maintenance activities and minimize downtime.
- Resource Allocation: Manage spare parts and tools efficiently.
- Communication: Keep both team members and senior management informed.
- Training: Arrange ongoing training for team members to keep skills current.
- Safety: Implement and monitor safety protocols.
Tracking maintenance metrics such as mean time to repair (MTTR), planned maintenance percentage (PMP), and time vs. cost metrics is crucial for improving maintenance operations over time. A CMMS with advanced reporting capabilities can help analyze and act upon these metrics.
Maintenance managers play a critical role in building a high-performing team. They ensure the team’s success by emphasizing efficient planning, clear communication, and leveraging a computerized maintenance management system to organize and use necessary information.
Source: WorkTrek
Fostering a Positive Leadership Environment
Creating a positive leadership environment involves trust, respect, and engagement. Leaders encourage team members to take ownership of their tasks, fostering a sense of common purpose.
Strategies:
- Empowerment: Allow team members to make decisions and solve problems independently.
- Recognition: Highlight achievements and give credit where it’s due.
- Open Communication: Encourage feedback and provide clear, constructive responses.
- Team Building: Organize activities that build camaraderie and trust.
- Ongoing Support: Provide resources and support to help team members grow.
A positive environment leads to higher engagement and a more committed workforce. Influential team leaders focus on mutual respect and clear, goal-oriented strategies to ensure everyone works harmoniously toward shared objectives.
For more in-depth insights, check out the 9 Steps to a High-Performance Maintenance Team and learn how to elevate your maintenance team’s performance.

Source: WorkTrek / Data: teambuilding
Strategic Planning and Control
Effective strategic planning and control in maintenance management rely on developing a robust maintenance plan and leveraging data and KPIs for informed decision-making. These elements ensure a well-organized framework and efficient processes within the maintenance department.
Developing an Effective Maintenance Plan
A comprehensive maintenance plan is vital for any maintenance department. It should outline clear goals, responsibilities, and schedules. A maintenance planner should start by setting SMART goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. These goals help guide daily activities and long-term projects.
Involving key stakeholders during the planning phase can identify potential issues early. This ensures various perspectives are considered, enhancing the plan’s robustness. Maintenance personnel must understand their roles and the goals they are working towards.
The plan should also include an inventory of critical spare parts and a preventive maintenance schedule to minimize downtime. Proper resource allocation ensures the team is always prepared for any situation, greatly reducing the chance of unexpected failures.
Source: WorkTrek
Using Data and KPIs for Decision-Making
Data and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are crucial in maintaining effective control over maintenance activities. Maintenance planners can identify trends, predict equipment failures, and make proactive decisions by analyzing data from various sources.
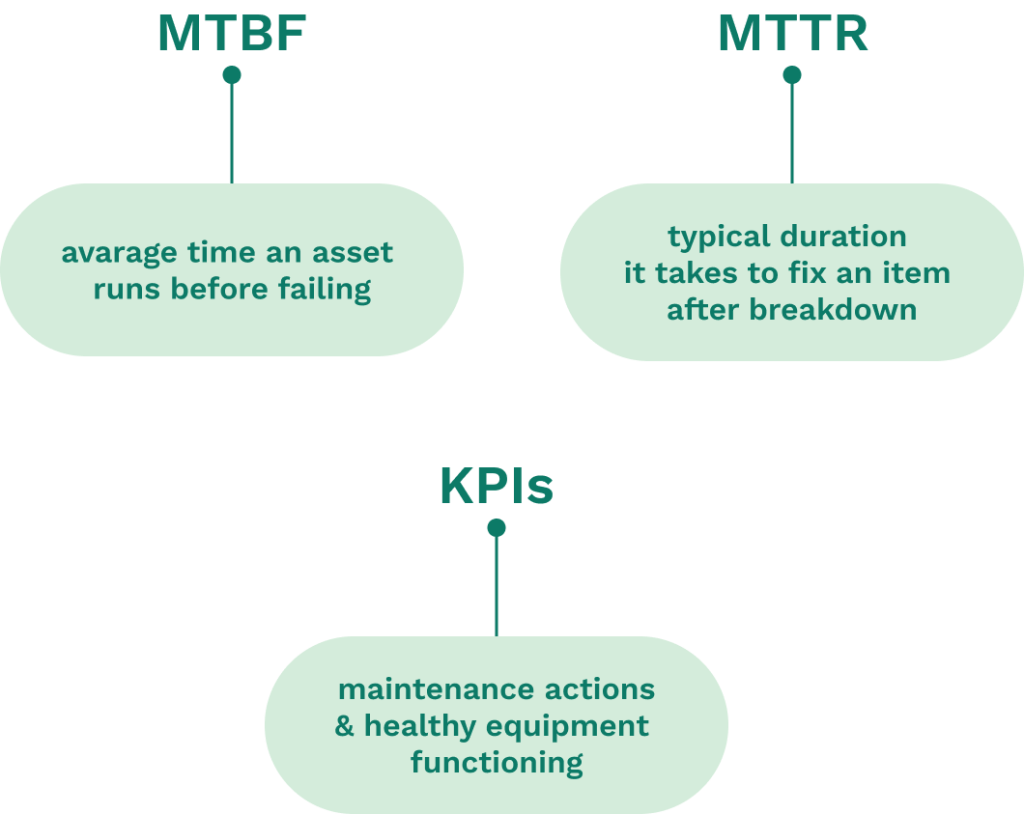
KPIs like Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) provide insights into equipment performance and reliability. These indicators help prioritize tasks and allocate resources efficiently. Consistent monitoring of KPIs allows the maintenance team to adjust strategies promptly.
Data collected from daily operations should be used to evaluate the success of the current maintenance plan. A maintenance planner can continuously analyze this information to improve processes and enhance overall performance. This approach ensures the maintenance team remains adaptive and efficient, effectively meeting the organization’s goals.
Source: WorkTrek

Maximizing Team Performance
Effective team management in maintenance relies on building strong synergy within the team and promoting continuous improvement through regular training. These strategies ensure the team operates efficiently and handles maintenance activities expertly.
Building Team Synergy
Creating a synergistic team involves more than just assembling skilled maintenance technicians; keeping maintenance team members motivated and engaged is crucial. It is important to foster communication and collaboration among team members.
Regular team-building activities can help strengthen bonds and improve teamwork. Encourage open dialogue and ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities clearly.
Management should establish procedures that facilitate smooth workflow and coordination. Hold regular meetings to discuss ongoing maintenance activities, challenges, and solutions. Setting up a mentorship program where experienced technicians guide newer team members and provide periodic feedback to reinforce good practices and correct errors can be beneficial.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Culture Monkey
Promoting Continuous Improvement and Training
Invest in your team’s continuous improvement through ongoing training and professional development to maintain high performance.
Schedule regular training sessions covering the latest maintenance techniques and safety protocols. Encouraging team members to pursue relevant certifications and further their education can also be advantageous.
Implement feedback mechanisms where team members can suggest improvements and share innovative ideas. Use performance evaluations to identify areas for improvement and tailor training programs accordingly. Encourage a culture of lifelong learning where technicians see value in continuously growing their skills through professional development opportunities.
Operational Excellence in Maintenance
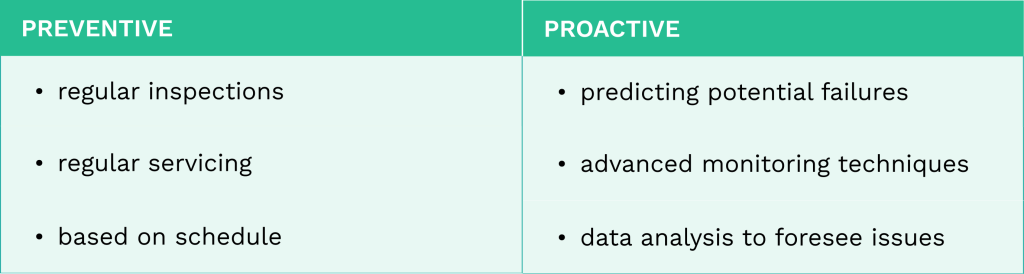
Achieving operational excellence in maintenance involves prioritizing both preventive and proactive strategies. It requires focusing on efficiently and effectively handling equipment and machinery to maintain reliability and performance.
Implementing Preventive and Proactive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance can improve the longevity of machinery and equipment. Regular inspections and maintenance tasks, such as lubrication and part replacements, can prevent unexpected breakdowns, reduce downtime, and extend asset lifespan.
Proactive maintenance goes further by identifying potential issues before they become serious problems. Using technologies like predictive analysis and condition monitoring, maintenance teams can anticipate failures and address them early. This method improves overall reliability and minimizes repair costs.
A balanced approach combining preventive and proactive maintenance ensures assets remain in top condition. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement and operational efficiency.
Source: WorkTrek
Efficiency and Effectiveness in Equipment Handling
Efficiency in equipment handling means performing tasks with the least wasted time and resources. Well-planned procedures and schedules help maintenance teams stay organized, reduce idle time, and maximize productivity.
Effectiveness focuses on doing the right tasks to achieve the desired outcomes. Using the right tools and techniques when handling equipment ensures high-quality work. Proper training and clear communication among team members contribute to this goal.
Reliable systems and processes are essential for maintaining efficiency and effectiveness. Implementing standardized procedures and best practices enhances consistency and improves the maintenance team’s overall performance and reliability.
By addressing both efficiency and effectiveness, organizations can achieve higher levels of operational excellence in their maintenance practices.
Resource Management and Optimization
Effective resource management can maximize productivity and control costs. This involves careful budgeting, maintenance scheduling, and resource allocation to ensure efficient operations.
Budgeting and Cost Control
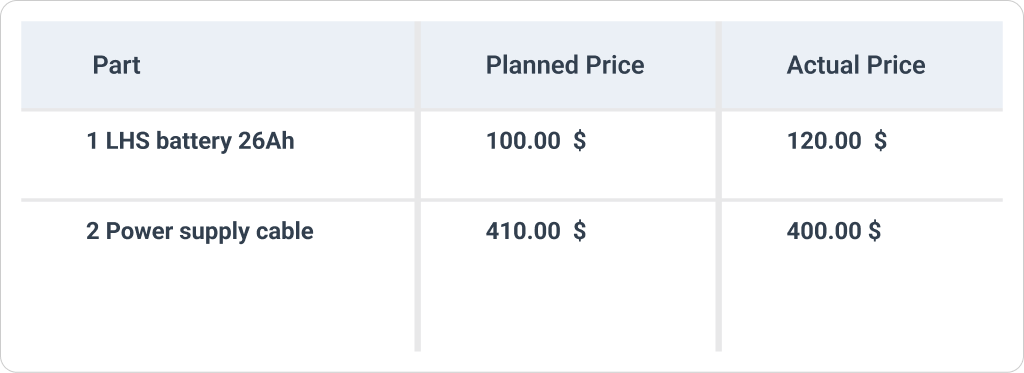
Developing a budget can help keep costs predictable and under control. This should include funds for regular maintenance, unexpected repairs, and optimization efforts. Proactive maintenance approaches, like predictive maintenance, can help reduce future costs.
Allocating resources for these activities beforehand is important.
A good practice is to set improvement goals, aiming for a small progress rate, such as 1-2% per year. Tracking expenses against the budget helps identify areas where cost savings can be achieved without compromising on the quality of maintenance work.
Source: WorkTrek
Maintenance Scheduling and Resource Allocation
Proper scheduling ensures that all maintenance activities are carried out without disrupting operations. A robust preventive maintenance plan includes regular inspections and repairs of critical equipment. This minimizes downtime and extends the life of assets.
Another key aspect is efficiently allocating resources. This means assigning personnel, materials, and equipment to each task. Tools and staff should be distributed based on the maintenance schedule to avoid bottlenecks and ensure each task receives attention.
Balancing the workload among team members can prevent burnout and maximize efficiency. Relying on reliable third-party contractors for temporary needs can also help meet resource demands.
Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration are crucial for managing successful maintenance teams. These elements ensure that team members understand their roles, can share feedback, and work together efficiently.
Enhancing Team and Cross-Department Communication
Clear communication within the maintenance team and across departments is vital. Recognizing and celebrating the team’s success through company-wide shout-outs, team-building activities, and time off can significantly boost morale and productivity.
Regular team meetings help ensure that everyone is on the same page. These meetings provide a platform for discussing ongoing projects, scheduling, and potential issues that may arise.
Using tools like a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), teams can track maintenance activities, report problems, and update task statuses in real-time. This promotes transparency and ensures that necessary information is easily accessible.
Feedback is essential. Encouraging team members to give and receive constructive feedback helps to identify and address challenges promptly, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Clear communication channels and regular updates minimize misunderstandings and improve overall efficiency.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Rock Blog
Collaboration for Streamlined Workflows
Collaboration within the team and with other departments is key to streamlined workflows. Encouraging a culture of teamwork can help resolve complex issues more efficiently. Integrating collaborative practices into daily routines, such as joint problem-solving sessions or shared responsibilities, can enhance productivity.
Tools and technology can also support collaboration. Utilizing a CMMS can facilitate better resource planning and coordination. This system allows for scheduling work orders, monitoring equipment status, and ensuring maintenance tasks are completed on time.
Shared Goals
Shared goals and responsibilities help build a cohesive team. When all team members understand their roles and how they contribute to their success, they are more likely to collaborate effectively. Establishing these goals and regularly reviewing progress can keep everyone aligned and motivated.
Effective communication and collaboration are the cornerstones of a successful maintenance team. By implementing these strategies, teams can enhance their productivity and achieve better outcomes.
Safety and Compliance
Safety and compliance are prioritized in maintenance teams, and strict adherence to protocols and regulations is required. Proper training and regular monitoring ensure a safe and secure work environment.
Establishing and Monitoring Safety Protocols
Safety protocols can help prevent accidents and injuries. All team members must be trained in these protocols to ensure they are familiar with the procedures.
Training should cover the proper use of tools and equipment, recognizing hazards, and emergency response actions.

Regular safety drills help reinforce these protocols. Drills simulate real-life scenarios, allowing the team to practice their response. Additionally, supervisors should perform routine inspections to identify potential safety hazards.
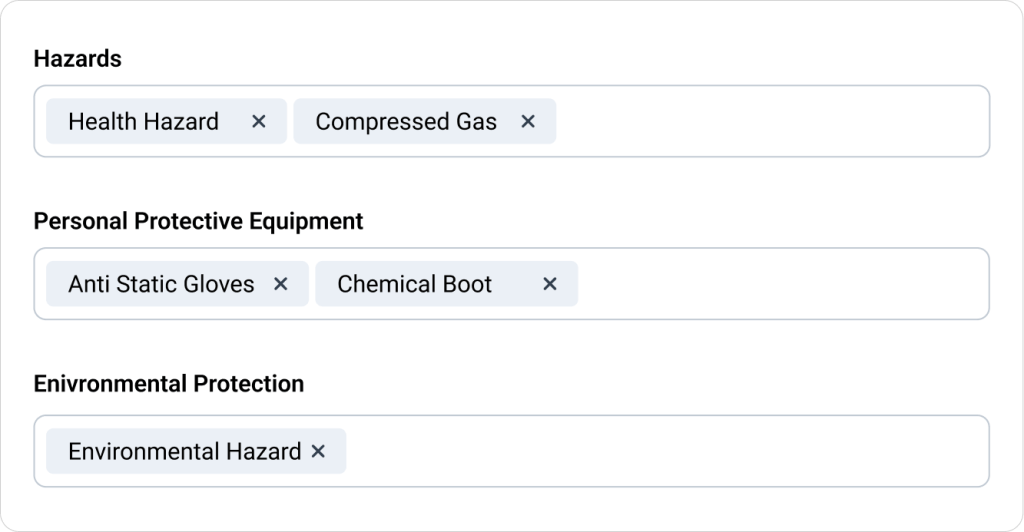
Use safety equipment such as helmets, gloves, and eye protection. Ensure the work area is well-lit and free from hazards like spills or debris. Implementing a safety-first culture encourages team members to report unsafe conditions without fear of repercussions.
Compliance with Standards and Regulations
Compliance with standards and regulations is crucial for maintaining a high-performance maintenance team. This involves adhering to industry-specific standards, such as OSHA regulations, to ensure safety and health in the workplace.
Document all policies and procedures. This documentation serves as a reference for team members and helps maintain compliance. Regular audits and inspections ensure that all practices meet required standards and corrective actions are implemented promptly.
Equipment should be inspected regularly to meet safety standards. For example, tools should be suitable for their environment and ergonomic to prevent strain or injury.
This ensures compliance and secures a safe working environment for the maintenance team. Ensuring compliance minimizes risks and promotes a culture of responsibility and professionalism within the team.
Source: WorkTrek
Enhancing Work Culture
Building a solid work culture for a maintenance team involves fostering motivation and providing clear growth opportunities. This includes creating a supportive work environment and offering consistent recognition and development.
Creating a Motivating Work Environment for Your Maintenance Teams
A positive work environment can improve team morale. Clear roles and responsibilities help employees understand what is expected, reducing confusion and boosting confidence.
Celebrating each team member’s success through company-wide shout-outs and team-building activities can significantly enhance individual motivation and overall team spirit.
Having well-maintained facilities can also contribute to a positive atmosphere.
Regular communication is essential. Effective performance reviews offer feedback and show employees how they contribute to the organization’s success. It’s important to empower team members by involving them in decision-making processes.
Providing defined roles ensures everyone knows their specific duties, which allows for better teamwork and cooperation. Regular meetings and open floor discussions can help address any issues quickly and efficiently.
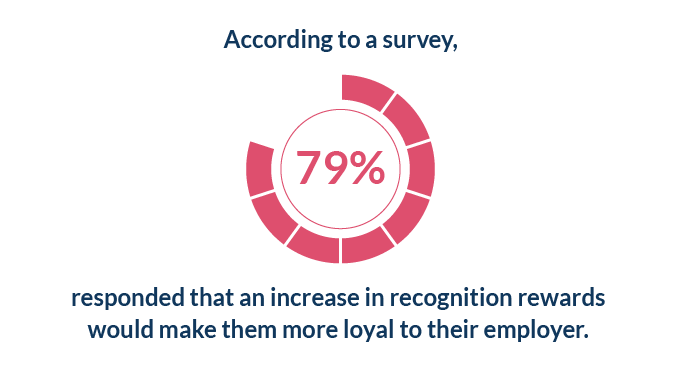
Recognition and Development Opportunities
Recognition of hard work and achievements can significantly increase motivation. Publicly acknowledging team efforts creates a sense of value and encourages others to strive for excellence. Regularly scheduled performance reviews help identify outstanding contributions and areas for improvement.
Offering professional development opportunities is also important. Training programs and workshops provide employees with the skills needed to excel. Encouraging attendance at industry conferences or certification courses can further enhance their knowledge.
Setting up a structured path for career advancement keeps employees engaged. When team members see a clear route for growth, they are more likely to stay motivated and committed to the organization.
Source: Ventage Circle
Overcoming Challenges in Maintenance
Effective maintenance management requires addressing common issues swiftly and preventing team turnover. Below, we explore methods for troubleshooting and retaining skilled workers.
Troubleshooting Common Maintenance Issues
Maintenance troubleshooting involves quick and accurate problem-solving. Teams should start with a detailed inspection and diagnostics, using tools like thermal imagers or vibration analyzers to identify issues. Regular training on the latest technologies also helps staff stay updated.
Another crucial step is preventive maintenance. This means scheduling regular checks on equipment to catch problems before they escalate. By addressing minor issues early, the team can avoid costly repairs.
Documentation
Additionally, consistent documentation is vital. Keeping detailed records of past problems and solutions allows for faster detection and resolution of recurring issues. Utilizing maintenance management software can streamline this process, making it easier to access needed information.
Finally, encourage open communication within the team. Problem-solving becomes more effective when everyone can share insights and suggestions, leading to a more resilient maintenance strategy.
Strategies for Reducing Turnover and Building Resilience
High turnover can disrupt workflow and lead to productivity losses. To reduce turnover, focus on creating a positive work environment. Competitive salaries and benefits are essential to attract and retain skilled workers.
Building a sense of belonging is equally important. Regular team-building activities and recognizing achievements can boost morale. When employees feel valued, they are less likely to leave.
Clear career paths and ongoing professional development opportunities also play a key role. Offering training for skill development and career advancement can keep employees engaged.
Lastly, it fosters resilience by promoting adaptability. Encourage your team to be open to organizational changes and new approaches.
Providing the necessary support during transitions can strengthen the team and make it capable of handling future obstacles. This ensures a high-performing maintenance team that can effectively overcome challenges.

Source: WorkTrek










