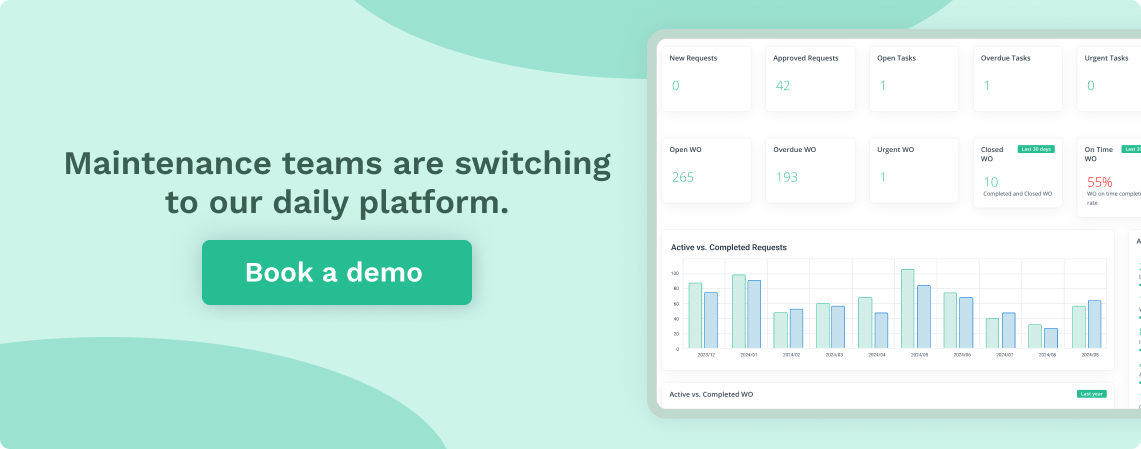
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKeeping your company’s financial health demands strict controls, detailed records, and regular audits.
The same goes for your physical assets.
You likely know the frustration of unexpected equipment breakdowns, plant shutdowns, and rising maintenance costs.
A thorough maintenance audit is the solution to prevent these issues.
With a comprehensive audit, you’ll gain a clear picture of your assets’ health, how well you plan and schedule maintenance, whether your technicians follow maintenance procedures, and much more.
Curious to learn more?
Keep reading to discover everything you need to know about maintenance audits and how the right tools can make them easier.
Maintenance Audit Basics
A maintenance audit is a thorough examination of your maintenance practices and procedures.
Think of it as a health check for your equipment and maintenance operations.
It identifies what’s working well and what needs improvement.
The primary purpose of a maintenance audit is to ensure you’re doing the right things that make your equipment run efficiently and reliably, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
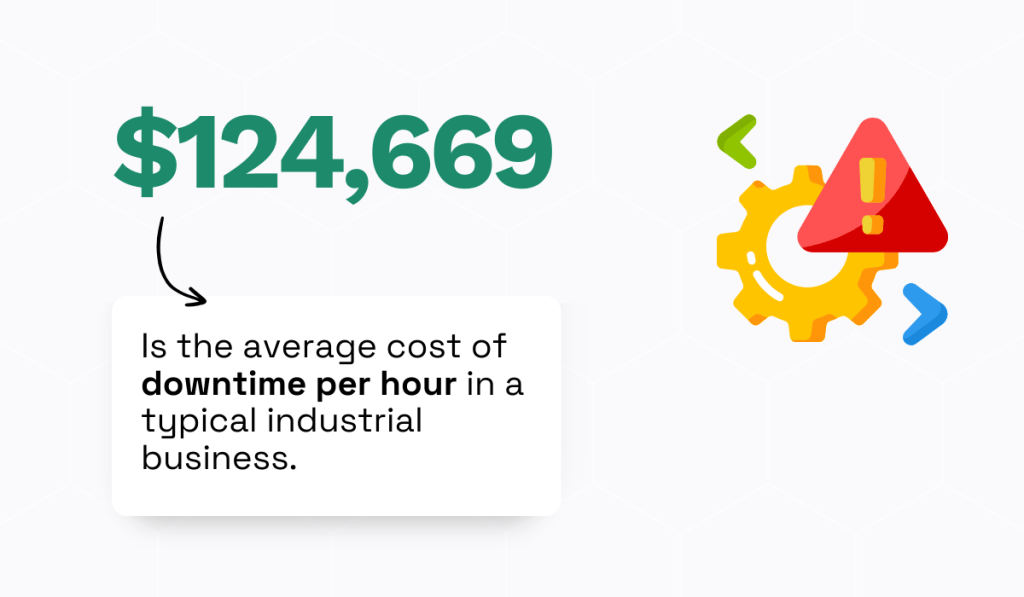
As per the latest statistics, unplanned downtime costs manufacturers more than $120,000 per hour.
That’s a significant hit to the budget—and productivity.
A maintenance audit helps prevent these costly disruptions by identifying potential issues before they become real problems.
It ensures your maintenance teams follow best practices, keep detailed records, and adhere to safety standards.
This saves you money, prolongs your equipment’s lifespan, and improves overall efficiency.
Beyond cost savings and efficiency, maintenance audits also ensure regulatory compliance.
In different industries, various regulatory bodies conduct audits to make sure companies follow quality, health, and safety regulations.
Maintenance audits are an important part of these larger checks.
If you fail to comply with them, you face legal issues, damage to your company’s reputation, and hefty fines.
For instance, penalties from the US Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) currently range from $16,000 to over $160,000 per violation.
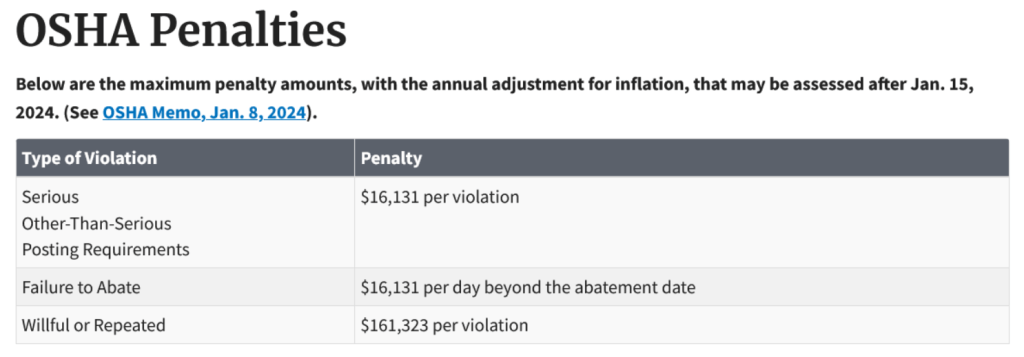
A maintenance audit helps you stay ahead of the industry requirements, ensuring you meet all necessary standards and avoid potential penalties.
How often these audits occur depends on who conducts them.
If the quality team within your organization does it, they have the authority to schedule them based on internal needs and goals.
And if we’re talking about external audits by regulatory bodies, their frequency may increase in response to past issues or compliance failures.
Extreme circumstances, like workplace injuries or product failures, might trigger immediate audits as part of an investigation.
The table below sums up maintenance audit basics:
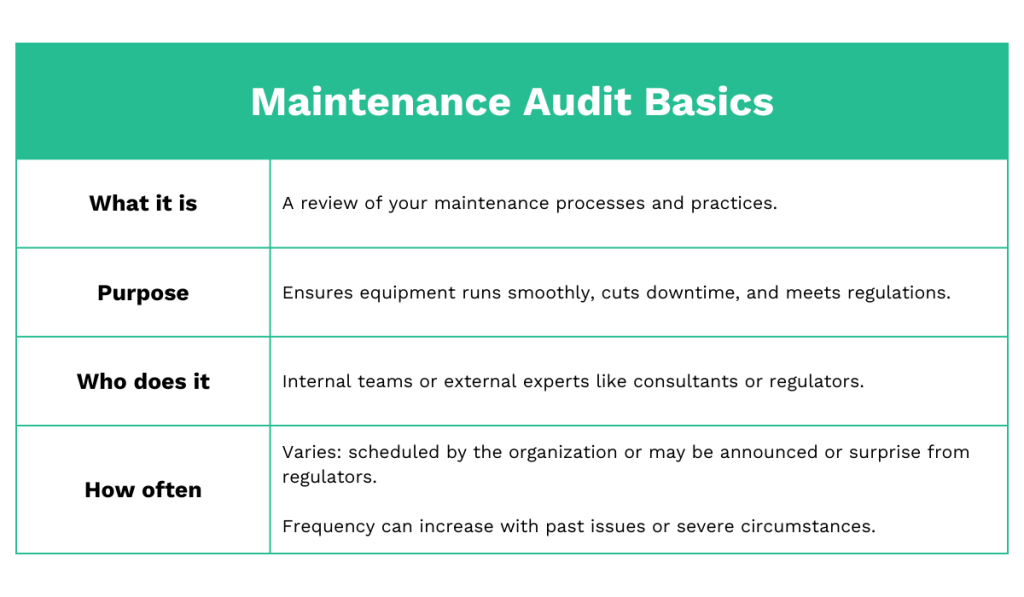
All in all, getting a grasp of these basics is the first step towards conducting maintenance audits correctly.
Let’s now explore different types of maintenance audits.
Different Types of Maintenance Audits
Since maintenance audits come in several flavors, each serving a distinct purpose, let’s take a closer look at the main types of maintenance audits and how they can impact your operations.
Mandatory
These audits are non-negotiable and are conducted by government agencies to ensure you’re complying with industry regulations.
They are essential for maintaining operational standards and avoiding legal trouble.
For example, OSHA might show up for a safety audit.
Part of their examination could include how your maintenance team handles equipment repairs.
They could also check if there is a departmental safety program, including courses on topics like forklift safety, lockout/tagout, electrical hazards, and compressed gasses.
Similarly, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) audits the pharmaceutical industry to ensure adherence to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (CGMP).
Marie Getsug, an experienced maintenance and reliability subject matter expert, explains what exactly the FDA checks during these audits:
Well-documented asset logs of failures—with appropriate strategies implemented to prevent the failure in the future, a robust record of technician training—adding confidence that the implemented changes were executed appropriately, and lists of equipment specification, detailing the safety and efficacy of using such equipment, are areas of focus within this regulated industry that are fundamental to a successful maintenance program.
Overall, these mandatory audits often encompass a broad review of your company’s policies and procedures, including maintenance practices, as seen in the example below.

To stay ahead of these audits, you should keep your maintenance records detailed and up-to-date.
This will prepare you for any inspection and avoid potential fines or compliance issues.
You can do this most easily with a good computerized maintenance management system, which we will discuss later on.
Voluntary
Voluntary audits usually happen when a company wants to evaluate the efficiency and compliance of its facilities and equipment.
They are your chance to showcase excellence and earn certifications for committing to high industry standards.
While these certifications (and, therefore, audits) aren’t required by law, they can boost your company’s credibility and competitiveness.
For instance, if you aim for ISO 55001 certification, which standardizes effective asset management practices, or LEED certification for sustainable building practices, you’ll undergo a series of self-audits to prove you meet these high standards.
Take a quick look at what obtaining an ISO 55001 certification looks like at the Bureau Veritas certification company.
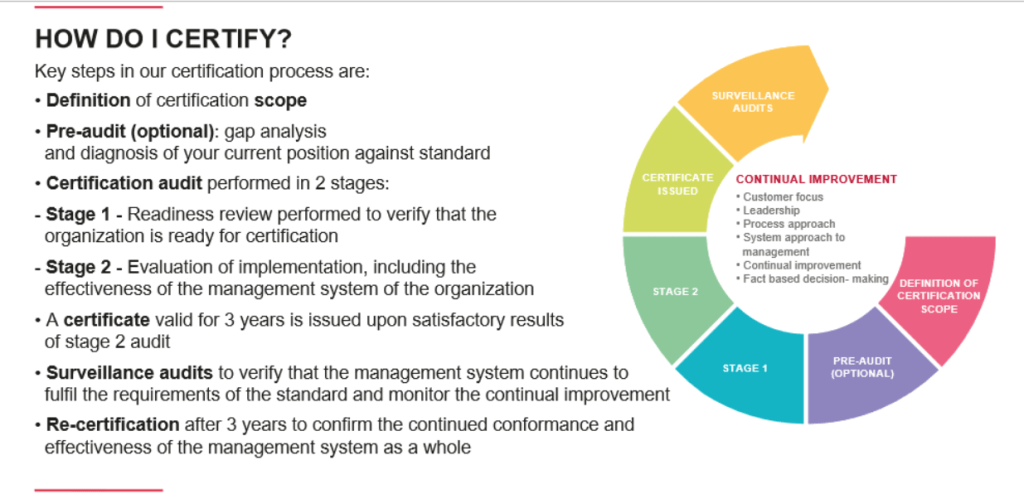
The certification process usually starts with a pre-audit or gap analysis to assess your current practices against the standards.
This is followed by a two-stage certification audit:
- Stage 1 assesses your readiness,
- Stage 2 evaluates the effectiveness of your implementation.
Once you receive certification, you’ll undergo regular surveillance audits to ensure ongoing compliance.
Yes, these certifications can enhance your reputation.
However, maintaining them requires a consistent commitment to best practices.
So, regularly reviewing and refining your maintenance processes to stay compliant and keep the certification is all the more important.
And for that, you need the third type of maintenance audit: an internal one.
Internal
Internal audits are, essentially, your facility’s self-checkup.
They should be conducted by your team to ensure that maintenance processes align with your company’s standards and policies.
These audits help you identify and address issues before they escalate.
Paul Michalicka, former sales manager for maintenance products at SKF USA, advises conducting internal audits as soon as you notice any of the following signs:
- Rising energy consumption
- Frequent equipment failures
- Rapid growth in your maintenance staff
- Breakdowns in your work order system
- A series of maintenance-related failures
- An increase in overtime (10%+ of total maintenance hours)
Any of these issues can be a sign that you either don’t plan maintenance or your maintenance planning is not as it should be.
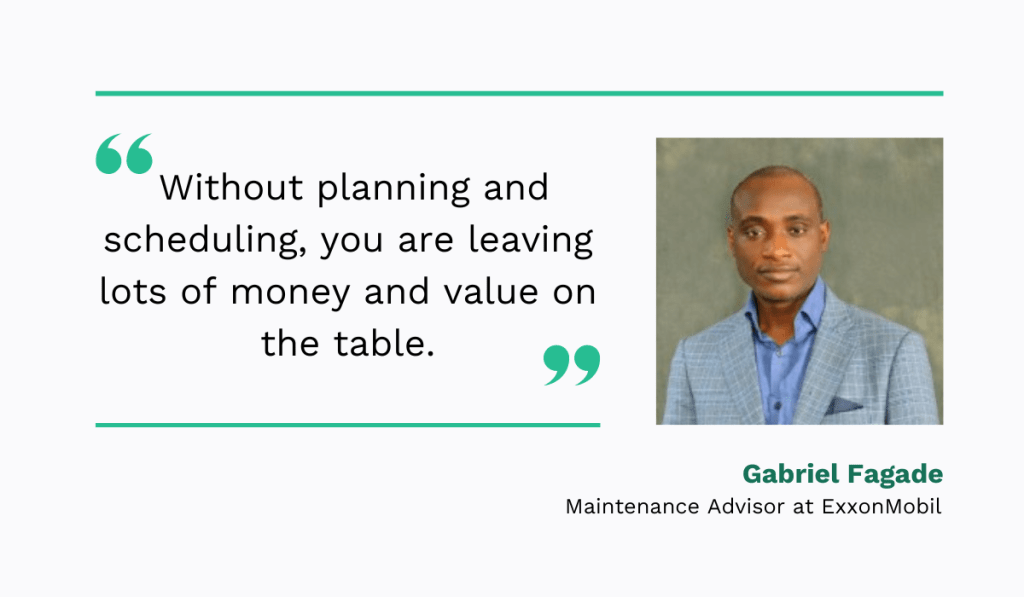
This can cost you a lot of money in the long run, as Gabriel Fagade, a maintenance advisor at ExxonMobil, rightly points out:
Conversely, internal audits can show whether your technicians follow procedures or have all the necessary tools.
Regular internal audits will pinpoint inefficiencies and help ensure that your maintenance planning, scheduling, and execution are as effective as possible.
This will ultimately prevent costly equipment breakdowns and downtime.
So, take it from the experts and make internal audits a regular part of your maintenance strategy.
What Does a Maintenance Audit Examine
Depending on your industry, the specifics of what’s examined can vary.
However, the core elements typically include safety practices, maintenance planning and scheduling, and adherence to documented procedures.
Here’s a quick overview of what maintenance audits commonly examine:
| Policies and Procedures | Are technicians adhering to your maintenance policies and procedures? |
| Planning and Scheduling | Are your maintenance activities well planned and scheduled to avoid downtime? |
| Work Order Management | Is your work order system efficient? Do work orders include all necessary information? |
| Preventive Maintenance Programs | Review preventive maintenance schedules. Are maintenance intervals based on equipment specifications? |
| Shutdown Maintenance | Review procedures for planned shutdowns and overhauls. |
| Condition Monitoring | Check the use of predictive maintenance technologies. |
| Training and Skills | Is training provided to maintenance staff good? Are their skill levels adequate? |
| Safety Practices | Are safety protocols followed? Is equipment maintained to prevent accidents? |
| Documentation | Are maintenance records accurate? Do they match the equipment’s condition? |
But these are not the only elements that audits examine.
Audits also check how you communicate with your maintenance team, how you budget and allocate resources for maintenance, and if you have emergency response plans for maintenance-related incidents.
To gather all this information, auditors observe maintenance processes, interview maintenance staff, and review all your documents or, ideally, go through your CMMS.
What’s The Role of CMMS In Maintenance Audits
A CMMS provides auditors with easy access to historical records for all maintenance activities.
This allows them to quickly verify maintenance tasks, check compliance with regulations, and review historical data without sifting through different spreadsheets.
For example, a key aspect of maintenance auditing involves reviewing past work orders.
It is a procedure done in almost every maintenance audit, and below is an example from the City of Denton’s facilities maintenance audit:

But if your work orders are scattered across several spreadsheets or printed out and put into various folders, the process becomes chaotic and inefficient.
Don’t you agree?
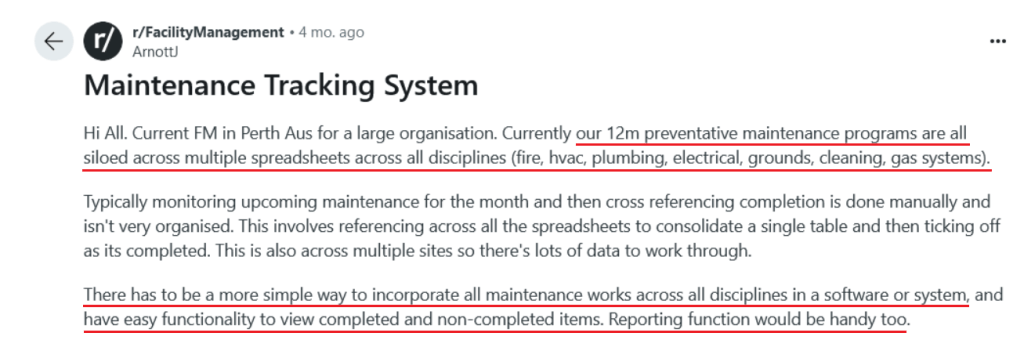
This Reddit user certainly does.
They describe struggling with siloed maintenance programs across multiple spreadsheets, making it hard and time-consuming to monitor and cross-reference tasks manually:
A CMMS, such as our WorkTrek, solves this problem by centralizing all asset and maintenance data in one place.
It features a robust work order management system that lets you assign tasks to technicians with step-by-step instructions.
Maintenance checklists are saved and linked to work orders, making it easy to see who completed each checklist and when.

Moreover, technicians can update task status and add details such as time spent and parts used. This creates a history showing what work was completed, by whom, and when.
WorkTrek also allows users to directly link OSHA rules and maintenance manuals to equipment records, ensuring that maintenance activities follow the required standards.
You can even specify which personal protective equipment (PPE) technicians should use, adding an extra layer of safety and compliance.
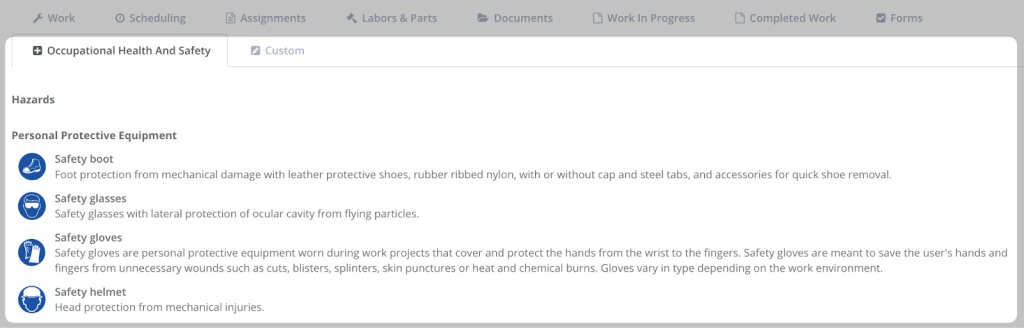
Also, WorkTrek replaces paper documentation with electronic signatures to track sign-offs, ensuring clear accountability for each task.
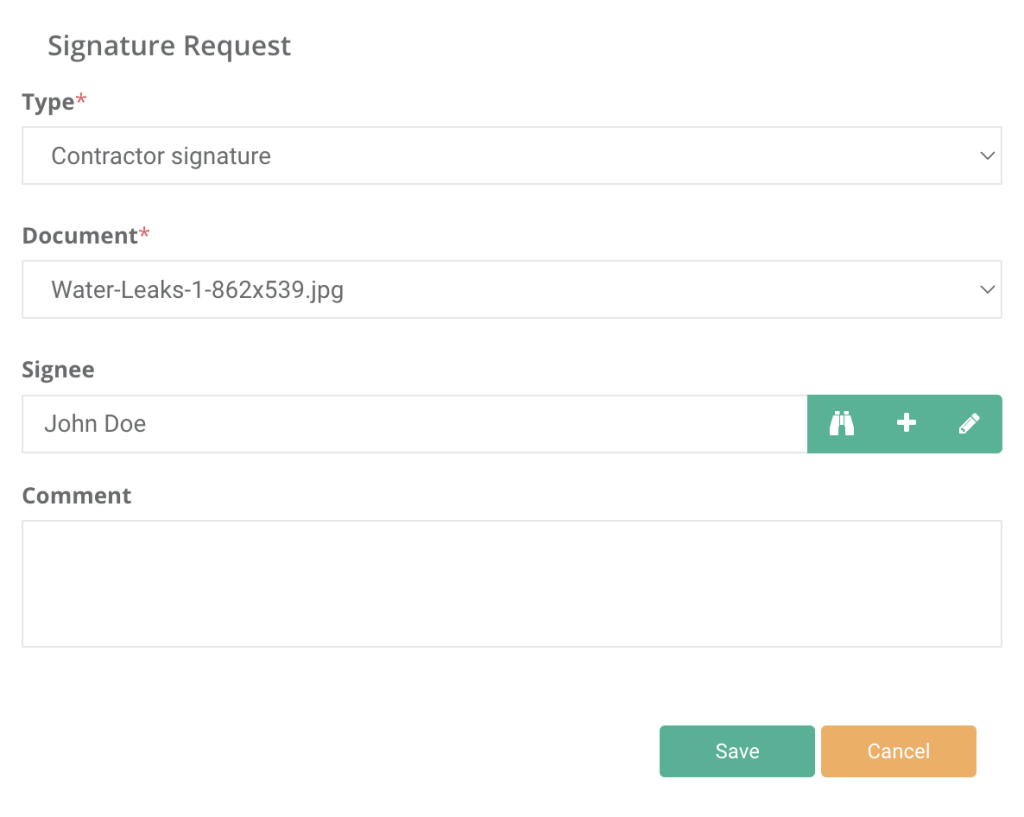
You can even enforce approval requirements before closing work orders.
Also, generating maintenance activity reports is quick and easy, so you’ll be well-prepared when auditors come knocking.
In summary, a robust CMMS like our WorkTrek simplifies maintenance audits by consolidating all your data and providing a clear, organized record of maintenance activities.
It’s a more efficient solution than managing various spreadsheets or keeping paper records, making your audit process much smoother.
Conclusion
Hopefully, we’ve clarified that maintenance audits are essential for keeping your plant or facility running smoothly and efficiently.
They help you identify areas for improvement, ensure compliance, and avoid costly downtime.
So, make sure your internal audits are regular and thorough—you have control over that.
For mandatory and external audits from regulatory bodies, you don’t need to worry if you follow the rules and use a reliable CMMS.
With all your data centralized, this tool will make your audits a breeze.