Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeManufacturing maintenance is an ever-evolving field, with new processes, technologies, and best practices always emerging.
It seems like, just when we think we know everything there is to know about this important process, a new innovation appears, reminding us there’s always more to learn and improve.
That’s why we’ve dedicated this article to exploring six trends in manufacturing maintenance that you need to be aware of right now.
By staying on top of these trends, you’ll not only be able to stay ahead of your competition but also unlock new ways to maximize the potential of your assets.
Let’s dive right in.
Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a proactive strategy focused on predicting and preventing equipment failure by collecting and analyzing data from the machines themselves.
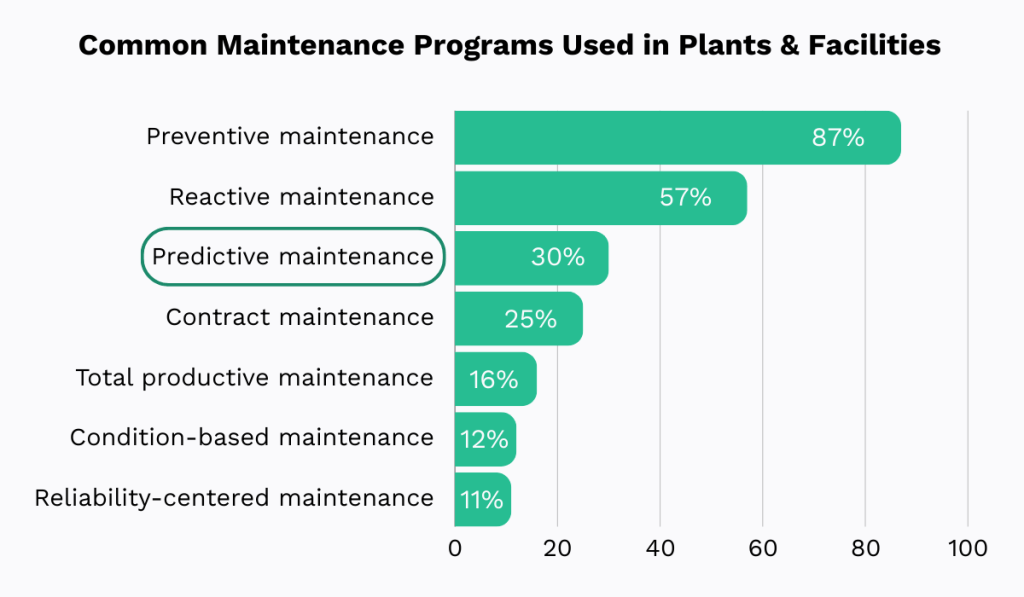
According to a 2024 MaintainX survey, it is currently the third most commonly used type of maintenance, following the traditional reactive and preventive methods.
So, how does it work exactly?
First, data is collected in real-time through various sensors installed on equipment, like the nanotechnology-powered sticker sensor produced by Feelit, as shown below.

These sensors track all sorts of metrics related to the operational condition of assets, like vibration, temperature, operating hours, and so much more.
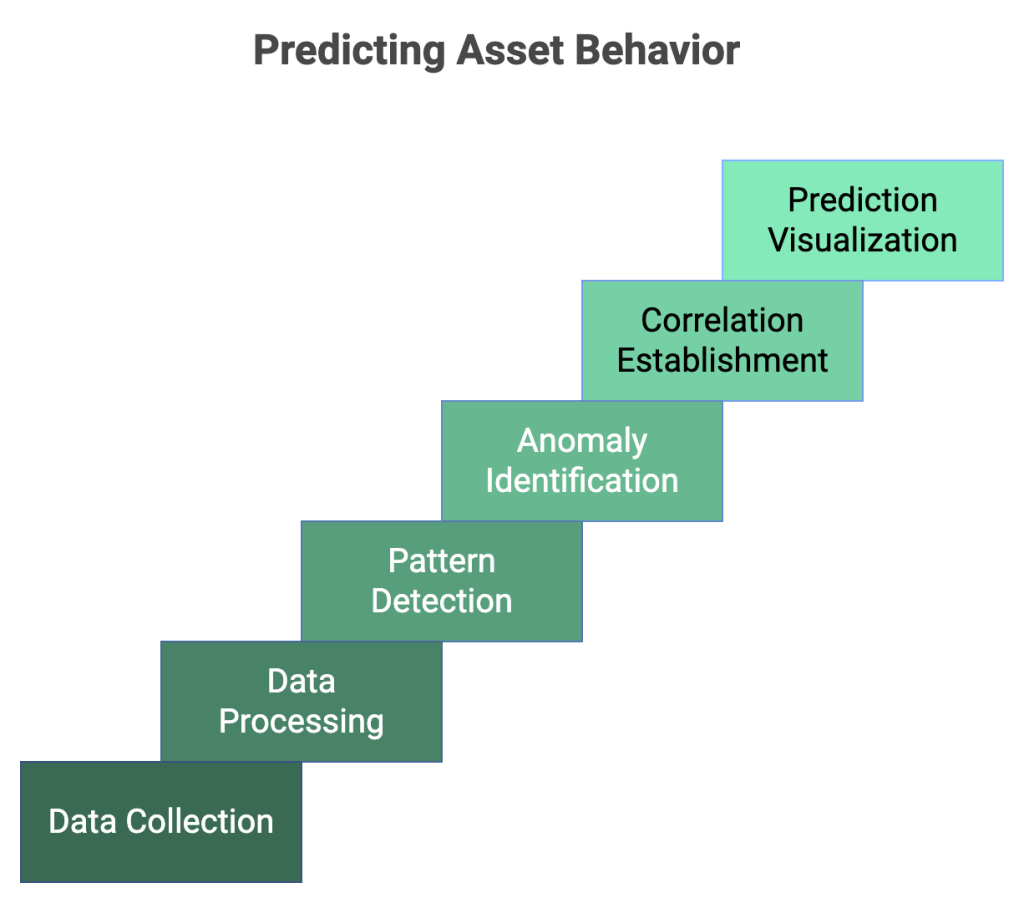
The data is then processed by machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) software to detect patterns, identify anomalies, establish correlations between parameters, and assess their impact on equipment health.
Ultimately, this enables the system to predict future asset behavior and show it to you in an easy-to-understand way.
Plus, these systems can send alerts to users when potential failures are detected, allowing repairs and checkups to be scheduled in advance.
Overall, PdM is a real game-changer, ensuring that upkeep is performed only when actually necessary, reducing the risk of both under- and over-maintenance.
This, in turn, translates to less downtime (both planned and unplanned), lower repair costs, and more reliable assets.
No wonder this type of maintenance is becoming increasingly popular in the manufacturing sector.
Take Cintas, for example, an American corporation that provides various products and services to businesses, including uniforms, mats, mops, cleaning and restroom supplies, and more.
As their Maintenance Supervisor, Woody Rogers points out; it’s precisely predictive maintenance that empowers them to achieve their high production standards:
Because we strive to operate higher than the standard, it’s critical for us to stay ahead of any issues that might impact asset performance or uptime. By monitoring and analyzing historical and real-time data that we collect on the conditions of our assets, we’ve been able to proactively identify, detect, and fix issues before they become bigger problems.
After all, in this industry, you have to be able to stay ahead of potential issues if you want to keep your operations running smoothly.
And predictive maintenance is all about staying ahead.
Maintenance-as-a-Service (MaaS)
One of the main barriers to adopting predictive maintenance is its high setup cost, which is driven by the costly, high-tech infrastructure required.
Luckily, there’s a solution to this problem on the horizon called Maintenance-as-a-Service (MaaS).
This new, subscription-based model allows companies to outsource their upkeep to third-party service providers instead of building and managing their maintenance systems and teams.
These vendors offer sophisticated predictive tech and the expertise needed to make it work so that the plants have more time to focus on their core activities.
The best part?
Manufacturing facilities pay only for the maintenance they need, on a pay-as-you-go basis—just like they would for their SaaS solutions like, say, CMMS.
MaaS itself is a broad concept, encompassing a variety of sub-services, such as:
| Fault-Detection-as-a-Service | Delivers detailed information on asset status, including predictions of failures based on parameters like End of Life (EOF) and Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) |
| Recommendations-as-a-Service | Provides suggestions on when to perform repairs for specific parts or equipment |
| Simulation-as-a-Service | Simulates future asset operation based on historical data in the cloud |
| Training-as-a-Service | Offers cloud-based training, including VR (Virtual Reality) and AR (Augmented Reality)-based services |
Thanks to MaaS and its flexibility, businesses can tailor their subscription plans based on their actual needs and budget, which enables them to use advanced technologies without breaking the bank.
Precognize is one of the providers of such services.
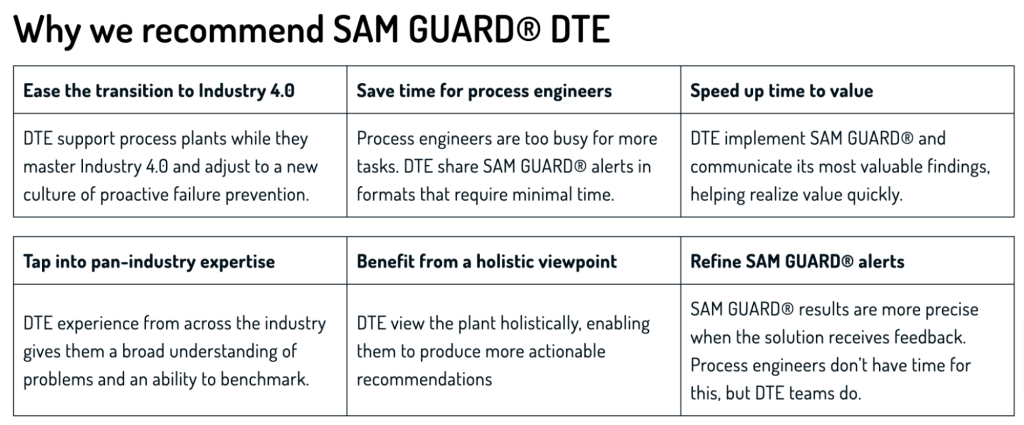
They offer SAM GUARD®, an AI-powered predictive maintenance solution that detects issues in equipment and operational processes.
In addition to this, their Digital Transformation Experts (DTE) team works closely with clients to implement this tool and help analyze the data it generates.
This expert team monitors and evaluates alerts, compiles reports and ensures companies get the most out of the system.
Here’s a more detailed description of what the team does, as found on their website:
All in all, although MaaS is still in its early stages, it holds immense potential, especially for smaller facilities.
It presents an amazing opportunity to experiment with almost anything the maintenance industry offers without compromising the organization’s profitability.
So, as it matures, expect it to become a go-to solution for businesses looking to stay ahead of the game while keeping costs under control.
3D Printed Replacement Parts
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, enables maintenance teams to create replacement parts on the spot, which eliminates all sorts of concerns related to inventory management.
Before you ask, yes, these 3D-printed parts are reliable.
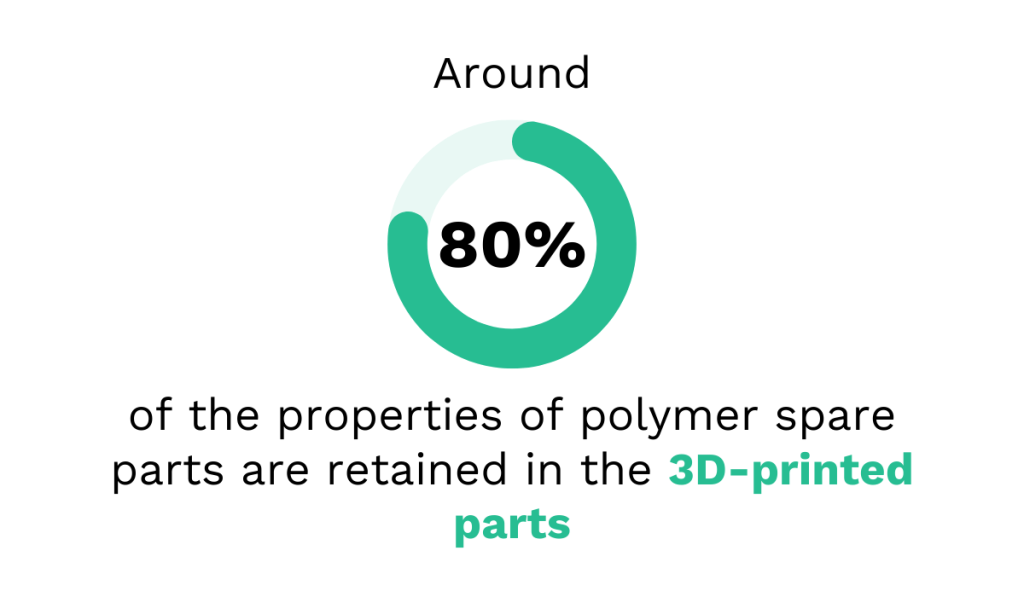
In fact, research published in MDPI examined parts produced for Stellantis, a Spanish automotive manufacturer, and found that 80% of the original properties were retained in 3D-printed components.
In other words, they perform just as well as their traditionally produced counterparts.

The research also highlights that additive manufacturing plays a key role in preventive maintenance and “will become even more important in the future.”
We agree.
With on-demand spare parts printing, lead times are significantly reduced, unlocking many benefits for manufacturing facilities.
Massimiliano Cecconi, Innovation Engineering Director at Baker Hughes, one of the world’s largest oil field services companies, elaborates:
Additive manufacturing allows us to develop parts and products more efficiently, with better performance and cost-effectively, and it accelerates the speed at which we can bring products to market: production times are drastically reduced—the finished product can be completed in weeks instead of months, significantly reducing production cycles, which ultimately benefits the customer.
Faster production, less downtime, and more efficient inventory control are all made possible by additive manufacturing.
Even when you need components no longer in production, 3D printing can help.
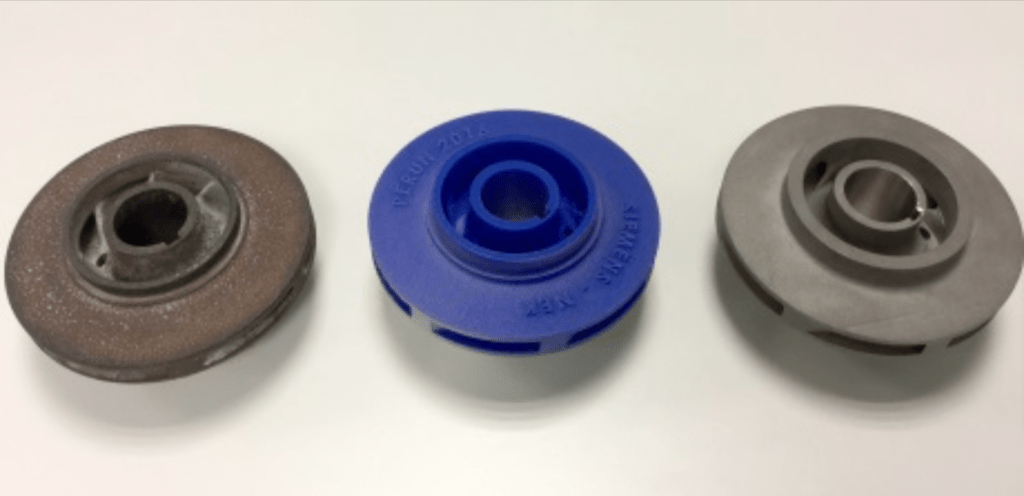
This was demonstrated in 2017, when Siemens reverse-engineered and 3D printed one such component for the Slovenian nuclear power plant, Krško.

Namely, the plant needed a new 108 mm diameter impeller for a fire protection pump that has been in operation since 1981.
The problem was that the original manufacturer had since gone out of business.
Fortunately, Siemens successfully produced the component, which marked “the first successful commercial installation and continuing safe operation” of such a part in a nuclear power plant.
You can see the result below. From left to right, the photo shows the original part, Siemens’ 3D-printed prototype, and the 3D-printed replacement installed and operating in Krško.

Vinko Planinc, Head of Maintenance at the Krško plant, praised the tech’s capability to prolong assets’ useful lives.
Ultimately, while the high costs of 3D printers mean it may take a little time for every plant to have one, the benefits are simply too powerful to ignore.
It’s only a matter of time before we see this technology become a must-have tool for factories across industries, transforming spare part management for good.
Use of Augmented Reality For Visualization and Diagnostics
Immersive technologies, once the stuff of sci-fi movies, are now becoming part of our reality, and manufacturing maintenance is not left behind.
In particular, augmented reality (AR) is gaining more and more traction in this area.
In the simplest terms, this technology allows technicians to overlay digital information onto real-world environments and equipment through AR-powered headsets, mobile devices, or wearables.
As Drew Bowers, Group Leader for Human Factors in UDRI’s Sensor and Software Systems division, notes, many of us have already seen this tech in action.

In the context of maintenance, it looks quite similar. A technician points a tablet camera at a machine, and the device displays relevant notes on the screen.
For example, it could indicate which wire or pipe is which, which drive controls which motor, or which spare parts are required for repair.
Some systems show whether these parts are available in the warehouse.
This, in turn, dramatically speeds up problem diagnosis and makes repairs more precise, with fewer mistakes.
However, AR also improves upkeep processes by enabling remote support.
In this scenario, an off-site expert shares the technician’s view in real-time, providing advice and annotating screens with instructions, data, and other helpful information.
That’s precisely the service they offer at ABB, says Stuart Thompson, the President of the Electrification Service Division.

ABB has supported customers in over 20 countries this way, reducing repair time and costs by eliminating the need to send experts to facilities.
You can see a demonstration of how it all works in this video:
It seems futuristic, doesn’t it? Yet, it’s already here.
And as AR technology keeps developing, we’ll surely be seeing a lot more of it.
Maintenance Robotics
Speaking of sci-fi-like technology, there are now all sorts of robots available that can perform various routine upkeep tasks, either alongside humans or even all on their own.
And the benefits are almost too many to count.
For one, robots can significantly increase the efficiency of your maintenance efforts.
Take, for example, Bristola’s remote-controlled submersible robots that clean and maintain liquid storage tanks.

The Bristola team installs its patented equalization chamber entry system, and the machine takes it from there, removing all the sediment and build-up within the tank.
No need to drain the tanks, plan for downtime, or send anyone inside for manual cleaning.
The process becomes much faster and more cost-effective, taking two days instead of the usual six weeks.
In addition to efficiency, robots also greatly improve safety.
Maintenance personnel at the global stainless steel manufacturer, Outokumpu, know this very well.
The company is currently piloting safety inspection robots, which are expected to reduce employee exposure to hazardous substances by over 80% and cut down dangerous repairs by 20%.
Thorsten Piniek, Outokumpu’s Vice President of Health Safety, provides some more information.

He adds that the robots can also shorten malfunction times since they can detect defects earlier through temperature and sound profile measurements.
The most fascinating thing about these maintenance robots is that they get smarter daily.
Just recently, Boston Dynamics’ robot dog, Spot, learned predictive maintenance.
Spot can now perform acoustic leak detection and vibration inspections, helping maintenance technicians identify early signs of bearing failure.
You can learn more about Spot in this video:
Given all these amazing advancements, it’ll be very interesting to see what else the future holds for the field of robotics and its role in manufacturing maintenance.
One thing is for certain, though: even more ground-breaking innovations are on the horizon.
Green Maintenance
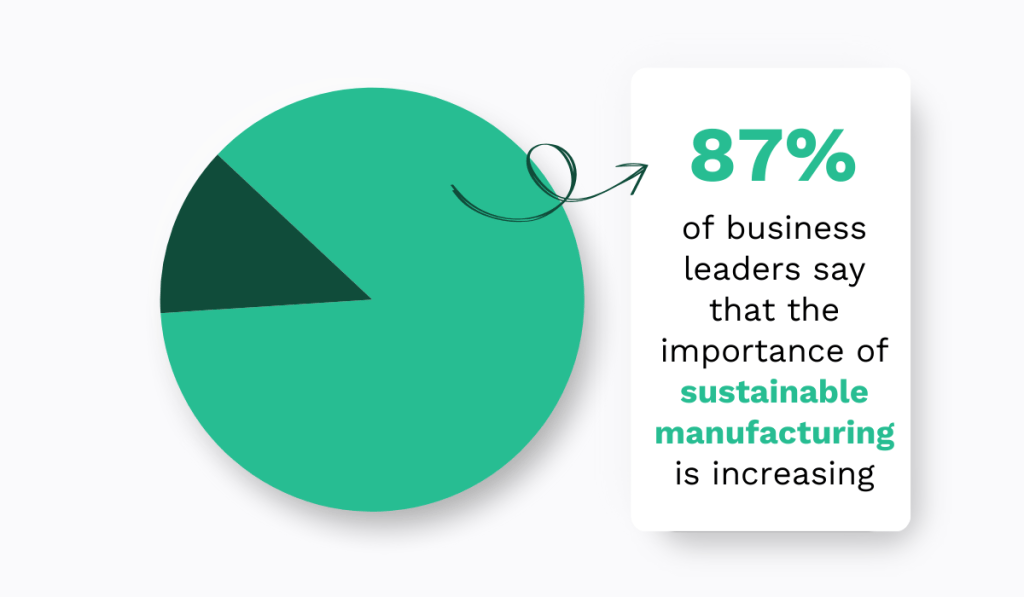
With 87% of business leaders acknowledging the growing importance of sustainable manufacturing, we see more and more factories working to reduce the environmental impact of their maintenance activities.
They are embracing innovative practices to hit those goals.
For instance, many are swapping out materials and tools used for upkeep for more eco-friendly alternatives.
The market, flooded with greener options, reflects this trend, too.
For example, take EcoChem’s Eco-Green Kleen, a water-based industrial degreaser that cuts out the need for harsh chemicals.

Many, however, go further and evolve their maintenance processes to drive sustainability.
According to Bill Zujewski, CMO at NetFoundry, a zero-trust connectivity platform, predictive maintenance is a good example of a maintenance strategy that can yield more sustainable results:
There are two use cases around predictive maintenance that jump out at me as win-wins – for the environment and manufacturers. The first one is around the service process. If you can reduce the truck rolls that have to come out to […] fix something that’s broken, you’re reducing your carbon footprint – there’s less fossil fuel burned for all those service people coming on-site for routine checkups when they’re not needed. […]
The other use case is around the parts and the machines themselves. If you can get the machines and part replacements to last longer and not replace parts prematurely, you’re saving scarce resources. You’re not sending them to the dump and creating pollution and waste.
Interestingly enough, nearly every trend we’ve discussed in this article contributes to greener maintenance in a similar way.
This is because, broadly speaking, all these innovations are developed specifically to decrease the frequency of repairs and help businesses achieve more with less in the long run.
This naturally translates to less waste, lower energy consumption, and optimized resource use.
3D printing is another case in point, as it significantly cuts down on material waste.
Adam Lea-Bischinger, Partner at Asset One LLP, a company providing Asset Management Advisory services, elaborates:
[Subtractive manufacturing] involves starting with a raw material, such as a block of metal, and cutting it down to get the shape you need, creating a lot of waste. An alternative – enabled by new technologies – is additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing. In this case, you build a product by adding material, rather than subtracting it, so there is very little waste.
The bottom line?
The environmental impact of manufacturing facilities is no longer being ignored.
Companies are finally stepping up, taking responsibility, and actively trying to reduce their negative footprint wherever possible.
And when it comes to maintenance in particular, there’s a huge opportunity to make a real difference.
Conclusion
Looking at all these amazing innovations and trends, it becomes clear that there’s never been a more exciting time to work in manufacturing maintenance.
Augmented reality, robotics, and the ability to predict future asset behavior—things we used to see only in films—are now our everyday tools, helping us make equipment more reliable, safer, and longer-lasting.
And the field is evolving rapidly, which means we’ll likely see even more advanced technologies in the near future.
In other words, this is just the beginning.
The cutting-edge breakthroughs will probably transform the industry in ways we can barely imagine.