Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeKey Takeaways
- Preventive maintenance reduces equipment downtime by up to 30% and machinery failures by up to 40%
- Companies implementing structured preventive maintenance programs experience 33% less equipment failure and see an ROI of up to 10 times their investment
- Digital maintenance management systems improve preventive maintenance scheduling by 35% and reduce planned downtime costs by 15-30%
- 88% of manufacturing companies use preventive maintenance, with 67% actively implementing it to reduce downtime
Your production line grinds to a halt at 2 AM. A critical pump has failed once again. Your maintenance team is scrambling to find replacement parts while production losses mount by the minute.
Sound familiar? You’re not alone. Nearly 70% of plants experience unexpected downtime at least once a month, rendering what should be predictable operations into an expensive and time-consuming firefighting exercise.

Following a reactive approach has trapped countless organizations in a costly cycle of emergency repairs, rushed part orders, and frustrated teams.
You are probably wondering why your maintenance budget continues to grow, yet equipment reliability continues to decline. Meanwhile, planned maintenance activities get postponed because “we can’t afford the downtime right now,” creating the very crisis you’re trying to avoid.
The solution to that problem is to employ a preventative maintenance program.
1. Prioritize Your Assets
The first step in implementing a preventive maintenance plan is to prioritize your equipment.
Not all equipment deserves equal attention in your preventive maintenance program.
Start by identifying your critical assets. This refers to the machinery and systems whose failure would have the most significant impact on production, safety, or operational costs.
Using this risk-based approach can ensure that you’re allocating necessary resources where they matter most.

You should start by conducting a comprehensive asset inventory that categorizes equipment by criticality level.
Consider factors like replacement cost, impact on production cycles, safety implications, and availability of backup systems. Assets that directly affect your production line or pose safety risks should receive the most frequent and thorough preventive maintenance attention.
For lower-priority equipment, less intensive maintenance schedules may be appropriate.
According to industry data, 68% of organizations report that preventive maintenance prolongs equipment life beyond 10 years. This, however, only works when you’re focusing on the right assets.
Use failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) to understand how and why equipment fails, and then design your preventive maintenance tasks to prevent those specific failure modes.
This structured approach prevents the common mistake of spreading maintenance resources too thin or wasting time on unnecessary maintenance for equipment that doesn’t require intensive care.
Once you’ve identified your critical equipment, you can build targeted preventive maintenance schedules that deliver maximum impact.
2. Create Data-Driven PM schedules
Developing a preventive maintenance schedule requires more than just following the manufacturer’s intended intervals.
While original equipment manufacturer (OEM) recommendations provide a solid foundation and a good starting point, the best preventive maintenance programs combine these guidelines with historical data and real-world operating conditions.
Start with manufacturer specifications as your baseline. The next step is to refine schedules based on your equipment’s actual usage patterns and performance history.
For example, a machine running three shifts daily requires more frequent maintenance than one operating eight hours per day.
The average plant loses 25 hours monthly to unplanned downtime, much of which could be prevented through properly calibrated maintenance schedules.
Another step is to implement both time-based preventive maintenance and usage-based maintenance strategies. T
Time-based approaches schedule tasks at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, annually), while usage-based methods trigger maintenance after specific operating hours, production cycles, or units produced.
Successful preventive maintenance programs use a hybrid approach. This means scheduling routine inspections on a calendar basis while planning more intensive service based on actual equipment usage.
Don’t forget to track when preventive maintenance tasks are performed and correlate this data with equipment performance.
If you use a CMMS platform like WorkTrek, a lot of these tasks can be automated.
If you continue to experience failures despite regular maintenance, your schedule may need adjustment.
The goal is to find the optimal balance that prevents breakdowns without performing excessive or unnecessary maintenance that wastes resources.
3. Create Standardized PM checklists and procedures
Consistency is the backbone of any successful preventive maintenance program.
Standardized preventive maintenance checklists ensure that every maintenance technician performs tasks the same way, every time, regardless of their experience level. This consistency dramatically improves the reliability of your preventive maintenance process.
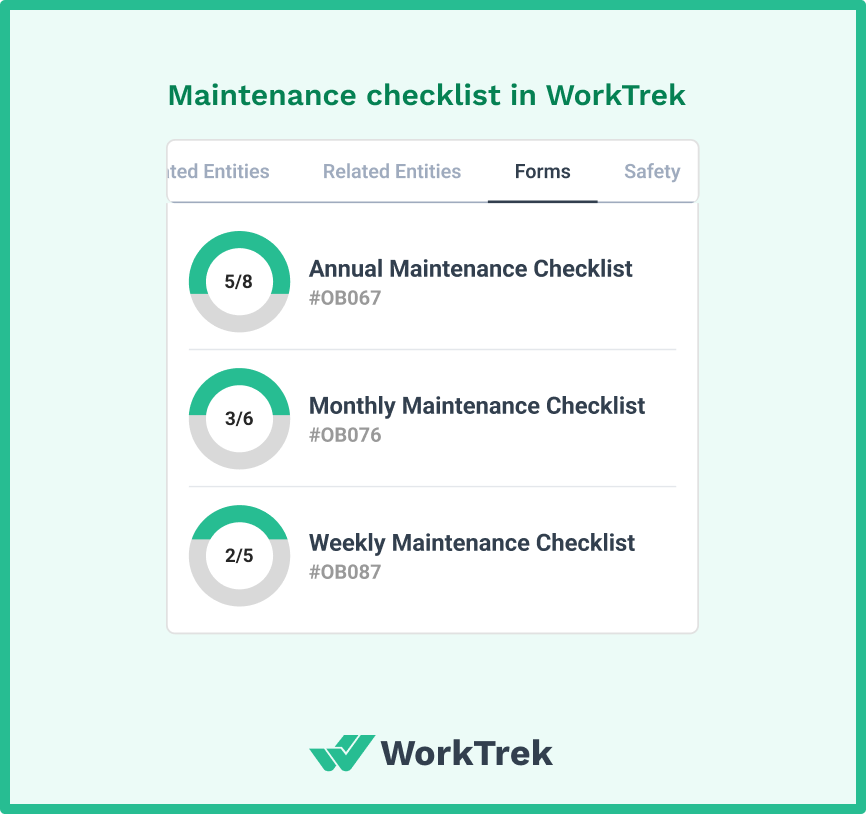
Create a detailed, step-by-step checklist for each type of preventive maintenance task.
This includes specific inspection points, measurements to take, acceptable ranges, lubrication requirements, and safety precautions.
An effective PM checklist does not just list what to do. It also includes repair instructions, necessary tools, condition state, and health and safety guidelines.
A good practice is to document these procedures as standard operating procedures (SOPs) that become part of your maintenance knowledge base.
When maintenance activities follow clear protocols, you reduce the risk of human error and ensure quality regardless of which team member performs the work. This is particularly valuable when training new technicians or dealing with staff turnover.
Companies that integrate preventive maintenance with standardized procedures experience 25% fewer safety incidents.
Well-documented checklists also create valuable maintenance history that helps you identify patterns, optimize procedures, and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Store these checklists in your CMMS where they’re easily accessible and can be updated as equipment ages or procedures improve.
4. Train Your Maintenance Team
Implementing preventive maintenance successfully requires a well-trained team.
Your preventive maintenance program is only as effective as the people executing it.
Investing in comprehensive training for your maintenance team pays major dividends through improved equipment performance, faster problem resolution, and more effective preventive maintenance implementation.
Provide both technical training on specific equipment and systems, as well as training on your preventive maintenance methodology and tools.
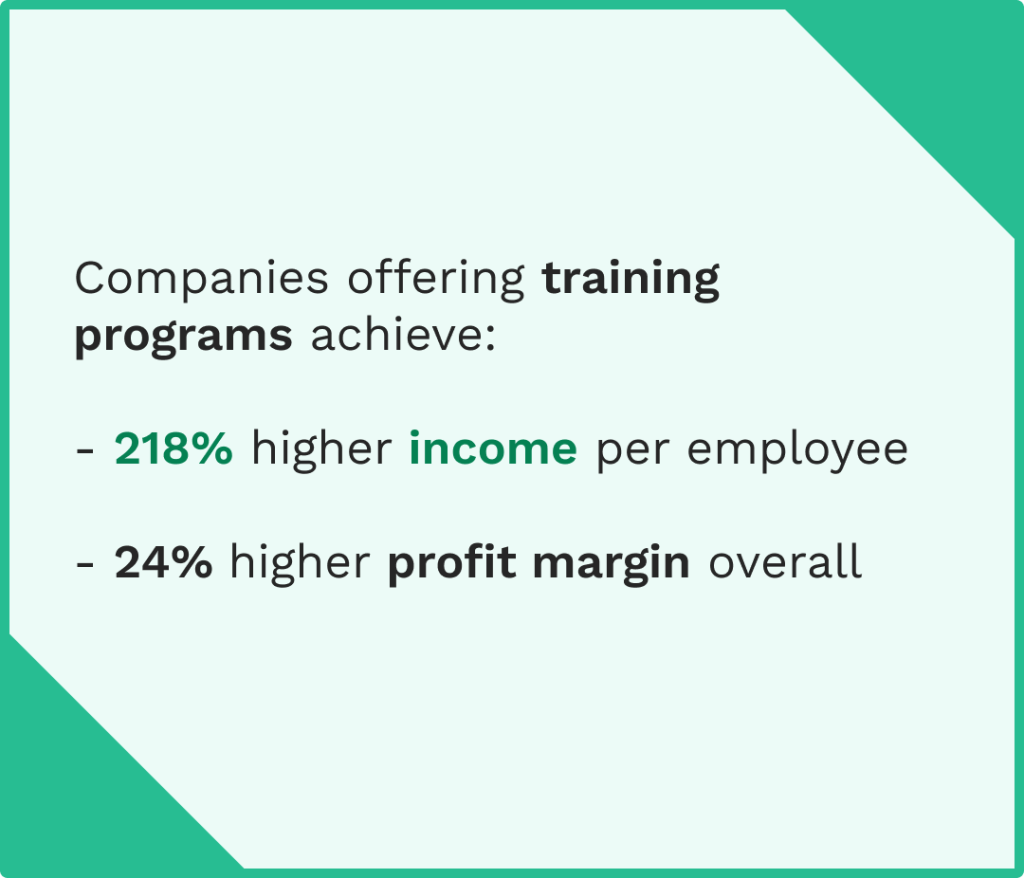
Every team member must understand not just what tasks to perform, but why those tasks matter. When maintenance technicians understand the connection between their daily activities and equipment reliability, they’re more engaged and thorough.
Cross-training team members creates flexibility and resilience in your maintenance operation. When multiple technicians can perform critical preventive maintenance tasks, you’re not vulnerable to disruptions from absences or turnover affecting your scheduled maintenance.
Encourage your team to learn from equipment service personnel during vendor visits. With this knowledge transfer, you can quickly build internal expertise over time.
Empower your maintenance team to identify and suggest improvements to preventive maintenance procedures.
Create channels for this feedback and act on valuable suggestions. Studies show that maintenance staff productivity improves by 15% with effective preventive maintenance programs.
5. Use Historical Data to Optimize Maintenance
Every work order generates valuable data that can improve your preventive maintenance program.
Part of a preventive maintenance best practice is to systematically capture, analyze, and apply this historical data to refine your maintenance strategy over time.
Start by tracking detailed information about each preventive maintenance activity:

- What was done?
- Who performed it?
- How long did it take?
- What parts were used?
- What conditions were observed?
Equally important, document all equipment failures, unplanned maintenance, and performance issues. Over time, this equipment data reveals patterns that guide smarter maintenance decisions.
Analyze this maintenance history to identify which preventive maintenance tasks actually prevent failures and which might be unnecessary.
For example, if you’re replacing a component every six months as preventive maintenance, but historical data shows it typically lasts three years, you’re wasting resources.
Conversely, if a particular component frequently fails despite scheduled maintenance, you may need more frequent service or a different maintenance approach.
Use this data to calculate key metrics like mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and equipment availability.
With these metrics, you can measure the effectiveness of your preventive maintenance program and justify investments to management.
According to McKinsey research, data-driven digital work order management can reduce planned downtime costs by 15-30%.
6. Implement Condition-Based Monitoring
Scheduled preventive maintenance follows predetermined intervals.
Condition-based maintenance, on the other hand, takes a more sophisticated approach by monitoring the actual condition of equipment and triggering service sensors to notice problems.
This hybrid strategy combines the best aspects of preventive and predictive maintenance.
Condition-based maintenance works best with IoT Sensors that help track performance indicators like vibration, temperature, pressure, oil quality, and energy consumption.
Implementing predictive maintenance helps organizations reduce unplanned machine downtime by up to 50%.
Condition monitoring is not meant to replace your preventive maintenance schedule. It is designed to complement it.
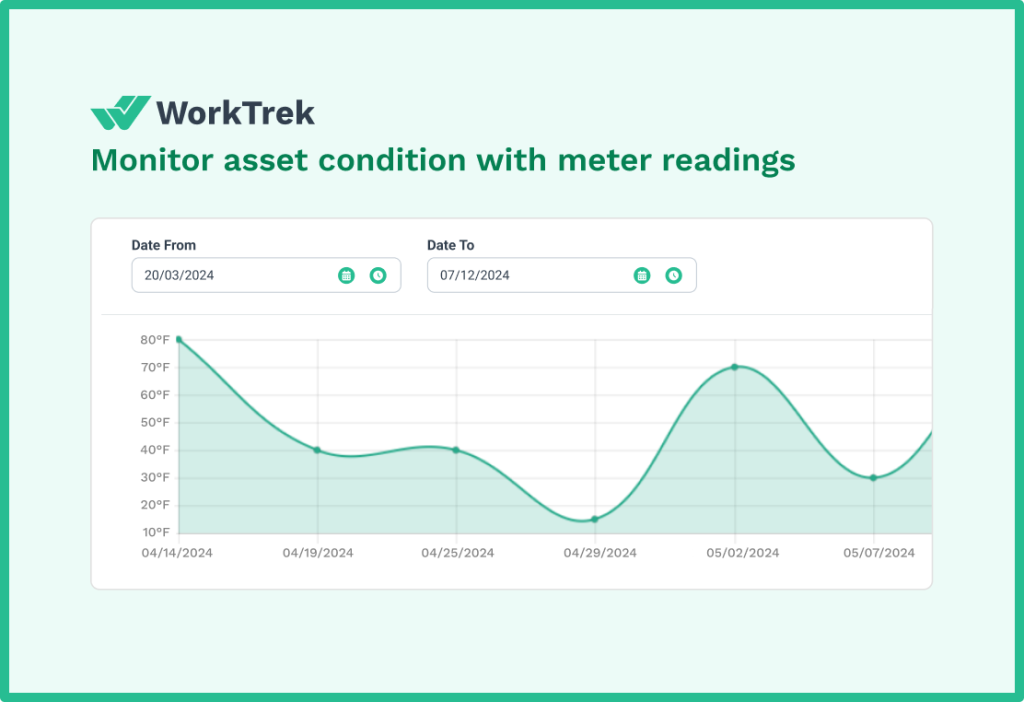
Continue performing regular inspections and routine maintenance while using condition data to identify developing issues that require attention before the next scheduled service.
The good news is that technology has made condition monitoring increasingly accessible. Even without sophisticated sensors, regular inspections that document observable conditions (unusual sounds, smells, excessive heat, or vibration) provide valuable data.
Train your team to recognize early warning signs during routine maintenance and document their observations systematically.
7. Balance Time and Usage-Based PM programs
The most successful preventive maintenance programs don’t rely exclusively on calendar-based scheduling.
Instead, they implement a strategic mix of time-based preventive maintenance and usage-based maintenance that reflects how equipment actually operates.
Time-based maintenance schedules tasks at regular calendar intervals:
- Weekly,
- Monthly,
- Quarterly
- Annually.
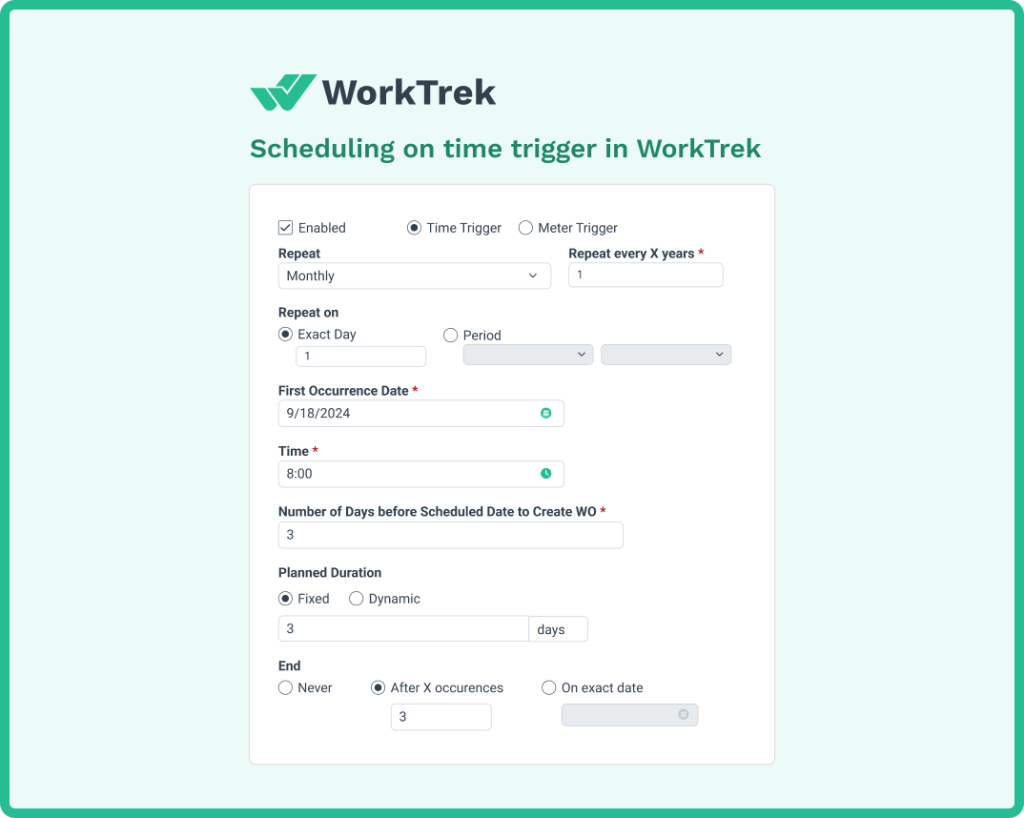
This approach works well for equipment that operates relatively consistently and for routine inspections that should occur regardless of usage.
Calendar scheduling also simplifies planning since you know in advance when maintenance will occur.
Usage-based maintenance triggers service based on actual equipment operation—hours run, units produced, cycles completed, or miles traveled. This method better reflects actual wear and tear on equipment with variable usage patterns.
For equipment that sits idle for extended periods or operates at dramatically different intensities, usage-based scheduling prevents both over-maintenance and under-maintenance.
Successful maintenance organizations find optimal results with a hybrid approach: schedule routine inspections on a time basis while planning more intensive preventive maintenance tasks based on usage metrics.
For instance, perform visual inspections monthly and schedule component replacements based on operating hours. This strategy ensures regular attention to all equipment while aligning major service with actual wear.
8. Document Everything
Maintaining comprehensive documentation can transform preventive maintenance from a series of disconnected tasks into a coherent, improvable system.
Good record keeping creates the foundation for data analysis, compliance demonstration, and continuous improvement.
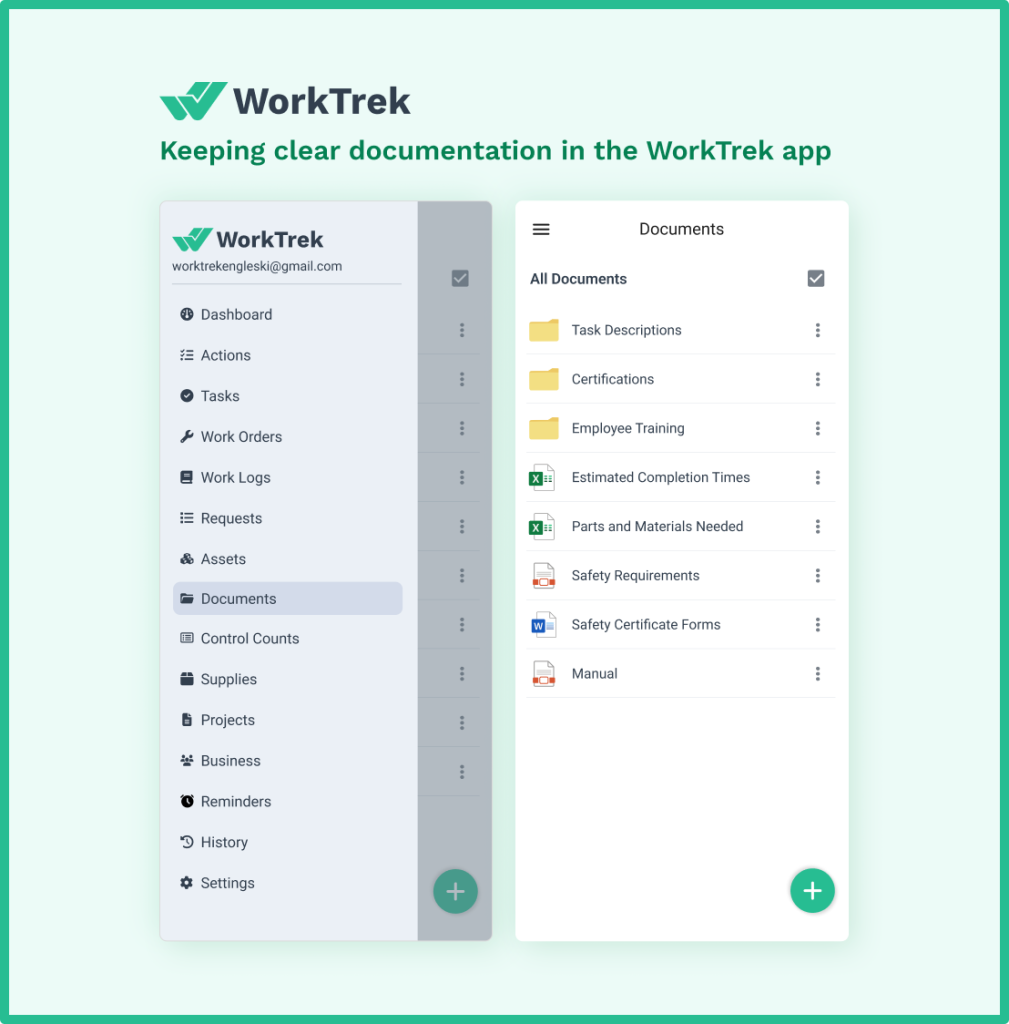
Document every preventive maintenance activity with complete details:
- Date performed
- Technician assigned
- Tasks completed
- Parts used
- Observations made, and
- Repair time invested.
This maintenance history becomes invaluable for troubleshooting when problems arise, planning future maintenance, and demonstrating due diligence to regulators or insurers.
It also helps when equipment ages. Historical maintenance records spanning years reveal long-term trends that might otherwise go unnoticed.
If you use a CMMS like WorkTrek, you can easily access WorkOrder data and history using the built-in reporting system, saving you a lot of time.
Store all equipment documentation, service manuals, warranties, technical specifications, and vendor contacts in a centralized, searchable location.
This is another task that can be automated with a CMMS like WorkTrek. You can store all of your documentation in a single repository and easily search and access this information.
When a maintenance technician needs information quickly, easy access to documentation prevents delays and ensures proper procedures are followed.
9. Create a Culture of Continuous Improvement
The best preventive maintenance programs need to evolve. The continuous improvement should be based on performance data, team feedback, new technologies, and changing operational requirements.
Building continuous improvement into your maintenance culture will keep your operation on track as circumstances change.

The way to do this is to schedule regular reviews of your preventive maintenance program’s effectiveness.
Start by analyzing key performance indicators like equipment downtime, maintenance costs as a percentage of asset value, percentage of planned versus unplanned maintenance, and maintenance backlog.
Per industry standards, if 63% of maintenance costs are related to corrective maintenance, your preventive maintenance program may need improving.
Also, conduct post-failure analyses when equipment breaks down despite scheduled preventive maintenance. A few matrices to look at include:
- What did the preventive maintenance plan miss?
- Was the failure preventable?
- Should you adjust the maintenance schedule?
By considering these questions, you can fine-tune and turn failures into learning opportunities.
Involve your team by encouraging your maintenance team to suggest improvements.
One practice is to hold regular meetings where technicians share observations, discuss challenges, and propose solutions. Some of the best preventive maintenance innovations come from the people performing the work daily.
Create a culture where suggesting improvements is valued and implemented suggestions are recognized.
10. Secure Strong Management Support
The best-designed preventive maintenance plan can fail without leadership support and sufficient resources.
Management commitment is more than just budget approval. It means prioritizing scheduled maintenance, supporting the maintenance team, and viewing maintenance as a strategic investment rather than a cost center.
Educate leadership on the ROI of preventive maintenance. Present data showing that investing in preventive maintenance yields returns up to 10 times the initial investment.
Additionally, demonstrate how proper maintenance reduces costly repairs, extends equipment lifespan by 25-30%, and can prevent unplanned equipment failures.
Part of the management buy-in includes ensuring that your maintenance team has the necessary resources such as:
- Adequate staffing,
- Proper tools and equipment,
- Training programs
- Quality replacement parts
Without adequate resources, it will be difficult for the team to implement a preventive maintenance plan.

Management must also protect scheduled maintenance from being constantly postponed for production demands.
While flexibility is sometimes necessary, regularly skipping preventive maintenance to keep production running creates a vicious cycle.
Strong leadership maintains the discipline to follow through on scheduled maintenance even when it’s inconvenient.
11. Integrate Preventive and Predictive Maintenance
While this article focuses on preventive maintenance, the most sophisticated maintenance programs integrate preventive and predictive maintenance into a comprehensive strategy.
Used together, these approaches complement each other and deliver superior results compared to either method alone.
Preventive maintenance provides the foundation for regular, scheduled tasks that maintain equipment in good condition.
Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, adds an intelligence layer, using data analytics, machine learning, and advanced monitoring to forecast when specific components will fail.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, predictive maintenance saves roughly 8-12% more than preventive maintenance alone, and up to 40% more than reactive maintenance.

The key is to start with a solid preventive maintenance program as your base, then gradually incorporate predictive elements as you build capabilities and invest in technology.
Begin by analyzing patterns in your maintenance history data to identify leading indicators of failure. As you gain experience and sophistication, add condition monitoring sensors and analytics tools that provide real-time insights.
This integrated approach helps you maintain regular service schedules while also responding to early warning signs between scheduled maintenance.
Combined predictive and preventive maintenance can extend equipment lifespan by 35-80%, significantly more than either approach alone.
The benefits of this approach cannot be underestimated. You get the reliability of scheduled maintenance plus the intelligence to intervene early when problems develop.
12. Leverage a CMMS Platform
Modern preventive maintenance programs require sophisticated organization, scheduling, documentation, and analysis that manual systems can’t provide at scale.
CMMS has become an essential tool for implementing and optimizing successful preventive maintenance programs.
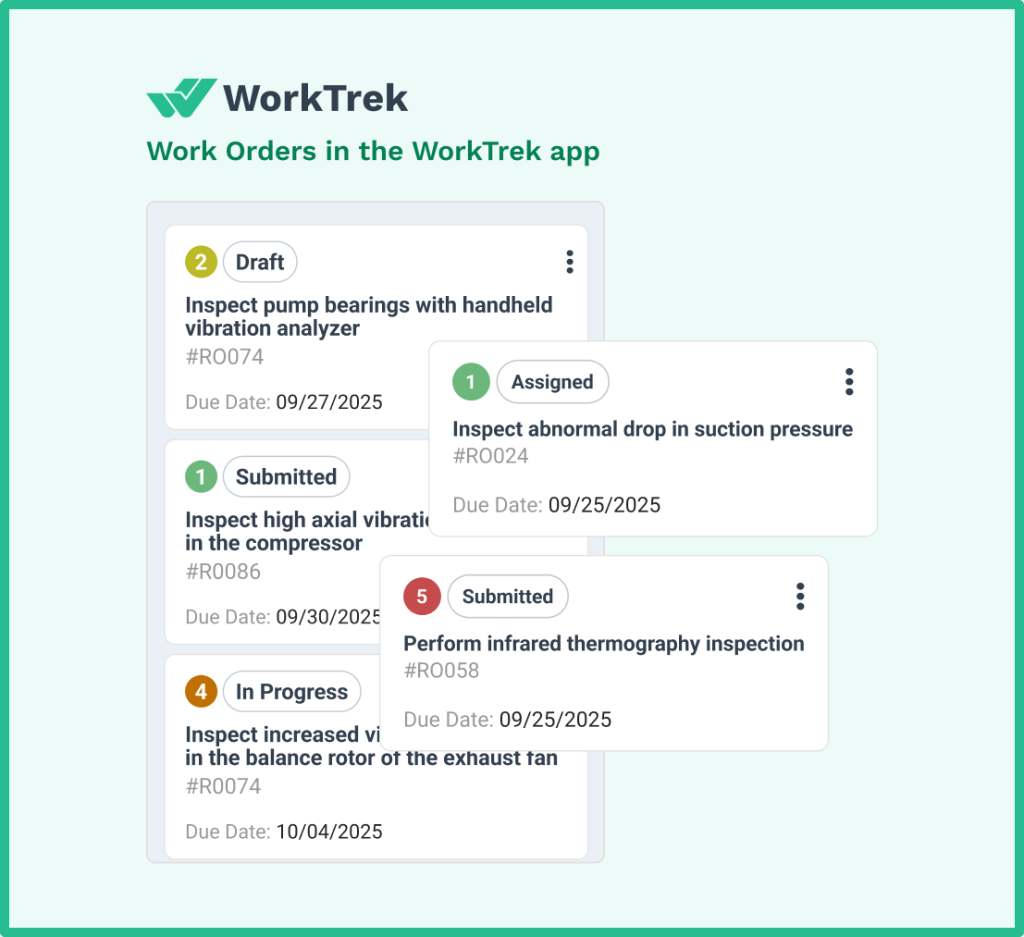
CMMS platforms can automate preventive maintenance scheduling, ensuring tasks never fall through the cracks.
They generate work orders automatically based on time or usage triggers, assign tasks to appropriate technicians, and track completion.
Integrating CMMS improves preventive maintenance scheduling by 35%, while 74% of CMMS users believe these tools improve productivity.
With CMMS you can centralize all maintenance data such as:
- Equipment records
- Service history
- Spare parts inventory
- Vendor information
- Documentation
All of this data can be stored in a single accessible location. This centralization eliminates the chaos of scattered spreadsheets, paper files, and tribal knowledge.
When a maintenance issue arises, technicians have complete equipment history at their fingertips, enabling faster, better-informed decisions.
CMMS platforms also provide the analytics capabilities needed for data-driven program optimization. You can easily generate reports on maintenance costs, equipment downtime, work order completion rates, and other key metrics instantly.
WorkTrek: Built for preventive maintenance excellence
WorkTrek provides a comprehensive, user-friendly CMMS solution specifically designed to support successful preventive maintenance programs.
The platform combines powerful capabilities with intuitive interfaces that make adoption easy for organizations of any size.
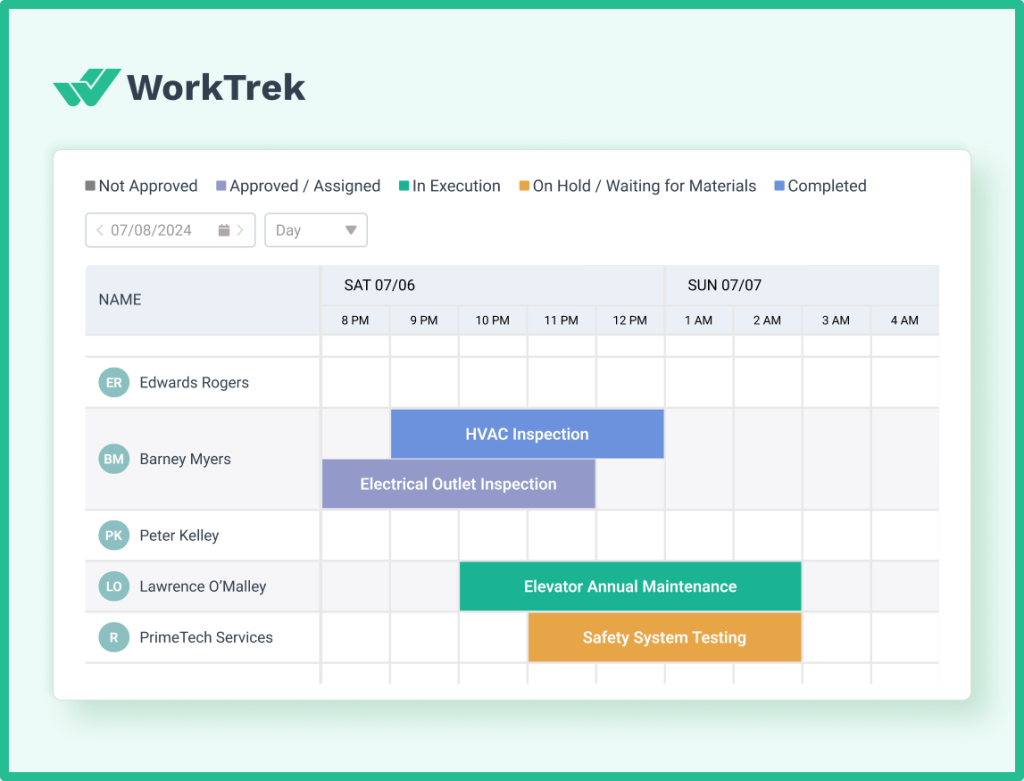
WorkTrek excels at preventive maintenance automation, allowing you to configure detailed maintenance plans for every asset with flexible scheduling options such as time-based, usage-based, or condition-based triggers.
The system automatically generates work orders, assigns them based on technician skills and availability, and sends notifications, ensuring nothing gets overlooked. This automation is complemented by customizable preventive maintenance checklists that standardize procedures and ensure quality.
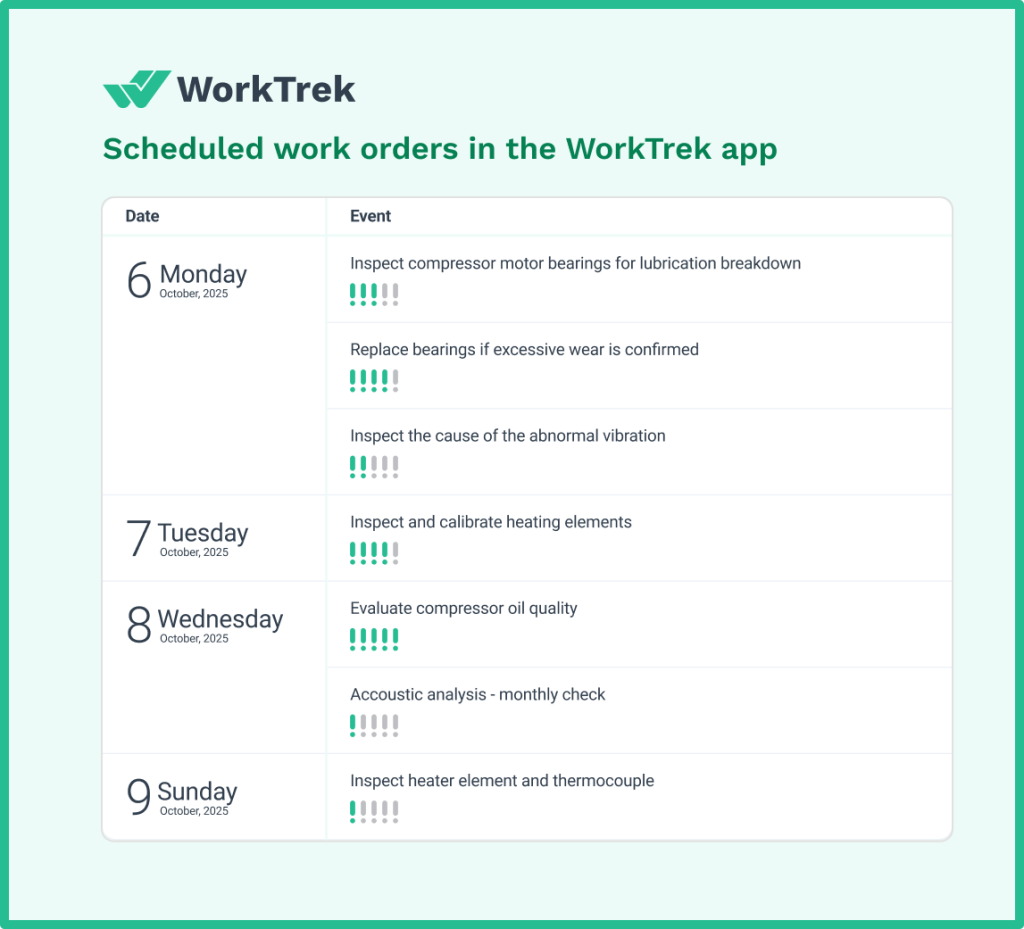
The platform’s mobile applications put complete CMMS functionality in your maintenance team’s pockets. Technicians access work orders, equipment data, and documentation from anywhere, complete tasks offline if needed, and automatically sync data when connectivity returns.
This mobile-first approach eliminates paper-based workflows and keeps your maintenance operation running smoothly.
WorkTrek’s analytics capabilities help you demonstrate program value and identify improvement opportunities.
Built-in dashboards provide real-time visibility into maintenance operations, while flexible reporting tools let you analyze data from any angle. Track maintenance costs, equipment performance, work order completion rates, and other key metrics to support data-driven decision-making.
The platform also integrates seamlessly with other business systems, ERPs, accounting software, IoT sensors, and building management systems. This creates a unified maintenance ecosystem for your organization.
Conclusion
Successfully implementing these 12 best practices transforms your maintenance operation from reactive firefighting to proactive asset management.
But remember, building a successful preventive maintenance program is a journey, not a destination. Start with the fundamentals, like identifying critical assets, establishing schedules, standardizing procedures, and training your team. Then progressively add sophistication through data analysis, condition monitoring, and technology integration.
The statistics speak for themselves. Organizations implementing structured preventive maintenance programs experience 33% less equipment failure, extend equipment lifespan by 25-30%, and see ROI of up to 545% in some industries.
Ready to transform your maintenance operation? Start with one critical asset, implement a data-driven preventive maintenance schedule, and use the results to build momentum for broader program expansion. The tools are ready, the benefits are proven, and your equipment is waiting for the attention it deserves.









