Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeWhat is a work order?
A work order is a document used to detail the details of a request for goods or services received from a customer. In some industries, the work order is created using information obtained from a sales order prepared by the salesperson working with the customer. There are also situations where the sales order and the work order are the same documents, with the terms used to identify the current status of the fulfillment of the customer’s request.
Any firm, whether it operates online or off, must have documentation as a necessary component. You will encounter numerous commercial documents throughout the course of a firm, including bills of supply, standard operating procedures (SOP), and invoices.
What is work order used for?
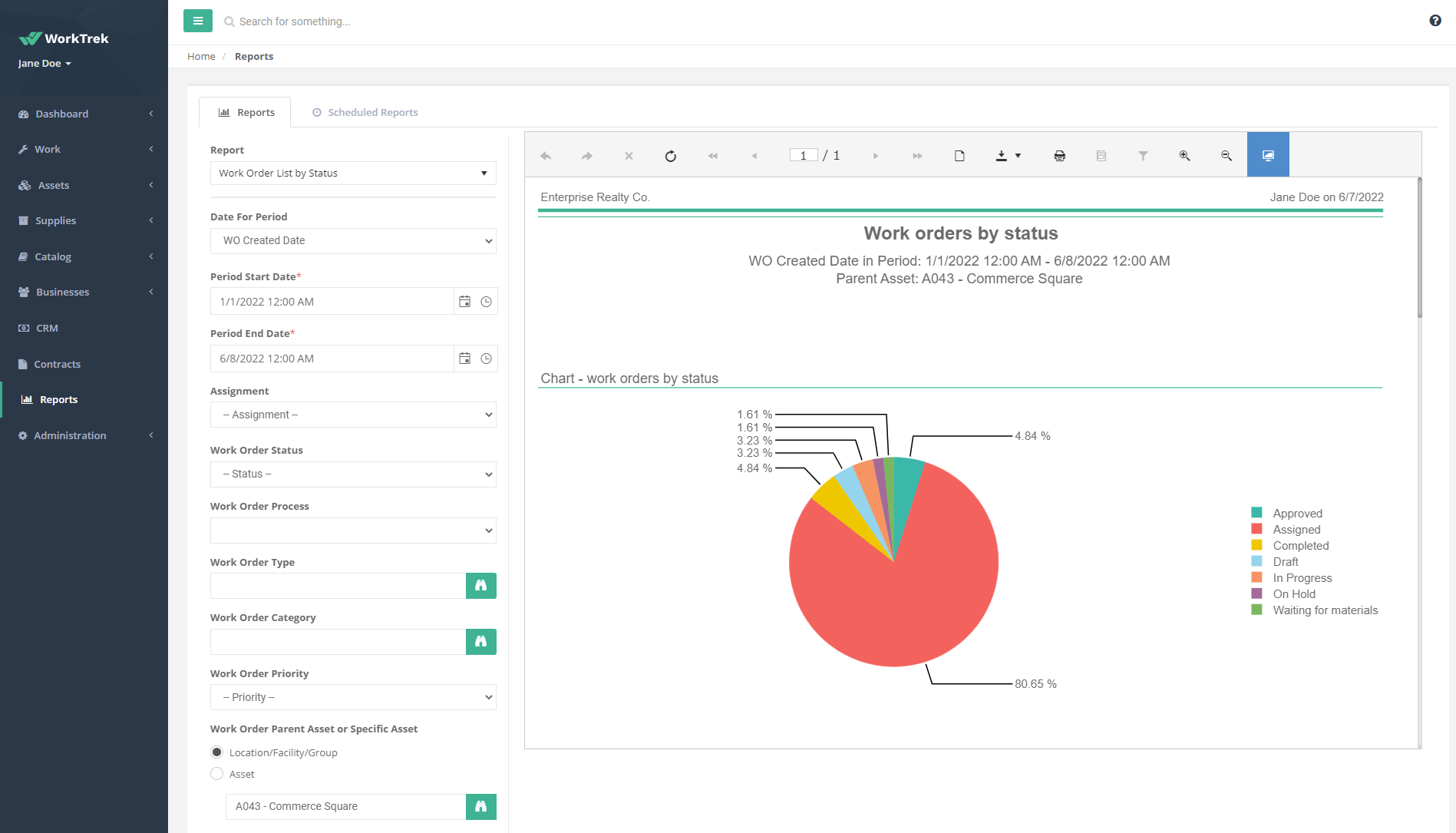
A work order is a highly regarded document that, once issued, triggers your company’s equipment to begin providing the goods or services and begin earning money once the order has been fulfilled.
If you lack experience in writing and handling such papers, job orders for internal or external business operations may be extremely difficult to understand. However, you shouldn’t worry because this article will enable you to learn enough about this aspect of the company.
The exact structure of the work order will vary depending on the type of goods or services required. For example, the landlord can open a work order in response to a tenant’s request to have a room in their apartment painted. The owner will prepare the order in a way that documents the task at hand, the materials needed to complete the job, the time needed to handle the repainting, and the expenses involved in successfully completing the task. In this application, the work order essentially functions not only as a record of the client’s request, but also as the escalation list of steps needed to complete the job, and a record of how much it will cost the owner to comply.
What Work Order includes?
The work order in a manufacturing plant is often prepared from data obtained from a customer order drafted by the sales department. Here, the order will include details of the product ordered, including size, number of units, color, and any other applicable information. The ticket will often include details of the delivery date agreed upon between the sales department and the customer. If the customer has expressed a preference regarding the method of shipping the items ordered, this information may also be included in the work order.
Regardless of the context, the purpose of the work order is to ensure that all parties involved in the fulfillment process know exactly what the customer has ordered, what it will take to fulfill that order, and when the order needs to be fulfilled. From this perspective, the order can be viewed as a necessary document that increases the potential for products to be prepared to customer specifications and delivered to the customer in a timely manner. For this reason, small and large businesses are very likely to use this type of document in one form or another.
Other phrases that business people could use in place of work orders are:

- Service ticket
- Job order
- Work ticket
- Job ticket
Download the free work order template.
The Purpose of Work Orders
Such a document is only meant to serve the single function of maintaining a record of all work authorizations, service provider information, charges, and job completion times. A service ticket can be created by both internal and external clients, such as customers and staff.
Depending on whether it is an internal or external request for work, the paper is then sent to the appropriate team. Vouchers are frequently created by businesses using computer software and circulate through numerous physical or digital desks.
Find a quick list of the following work objectives here:
- Describe the problem, the fix, and the installation or delivery of the products
- the provision of materials and tools required for the task or maintenance work
- Provide thorough instructions on the work, job, or maintenance to the technicians.
- recording formally the resources, labor, and materials used to complete the work
- Track all repair and maintenance jobs that have been performed on each authorization
- Contains monetary data like cost, taxes, levies, cess, etc.
Work Order Management Terms
Work Approver
The assignment and authorization of maintenance requests for equipment management are handled by an administrative or a member of that team. The approver function may occasionally be performed by the warehouse manager and the front desk support for customer interactions.
Work Requester
The person or group that makes the request to execute a certain task is known as the requester. In the services and goods sector, customers generate task orders through online or in-person purchases. Business-to-business requests for work may originate from commercial clients or an internal team, such as when a manager of customer service operations demands workstation maintenance.
Field Technicians
Field technicians are engineers, millwrights, repair personnel, etc. who are qualified to carry out the task specified in the work order document in maintenance job tickets.
The Components of a Work Order
Using job order records, a business can keep track of several things and related information. Here are some examples of what you need to write.

Mandatory Elements:
- Any job ticket’s main element is the asset.
- Additionally required is the name of the person requesting the work.
- Another crucial component is the scope of the work, which will decide the required expertise, equipment, and standard operating procedure (SOP).
- The description of the issue field must also be completed by the person requesting the work. It makes it easier for the service coordinator or technicians to recognize the issue promptly.
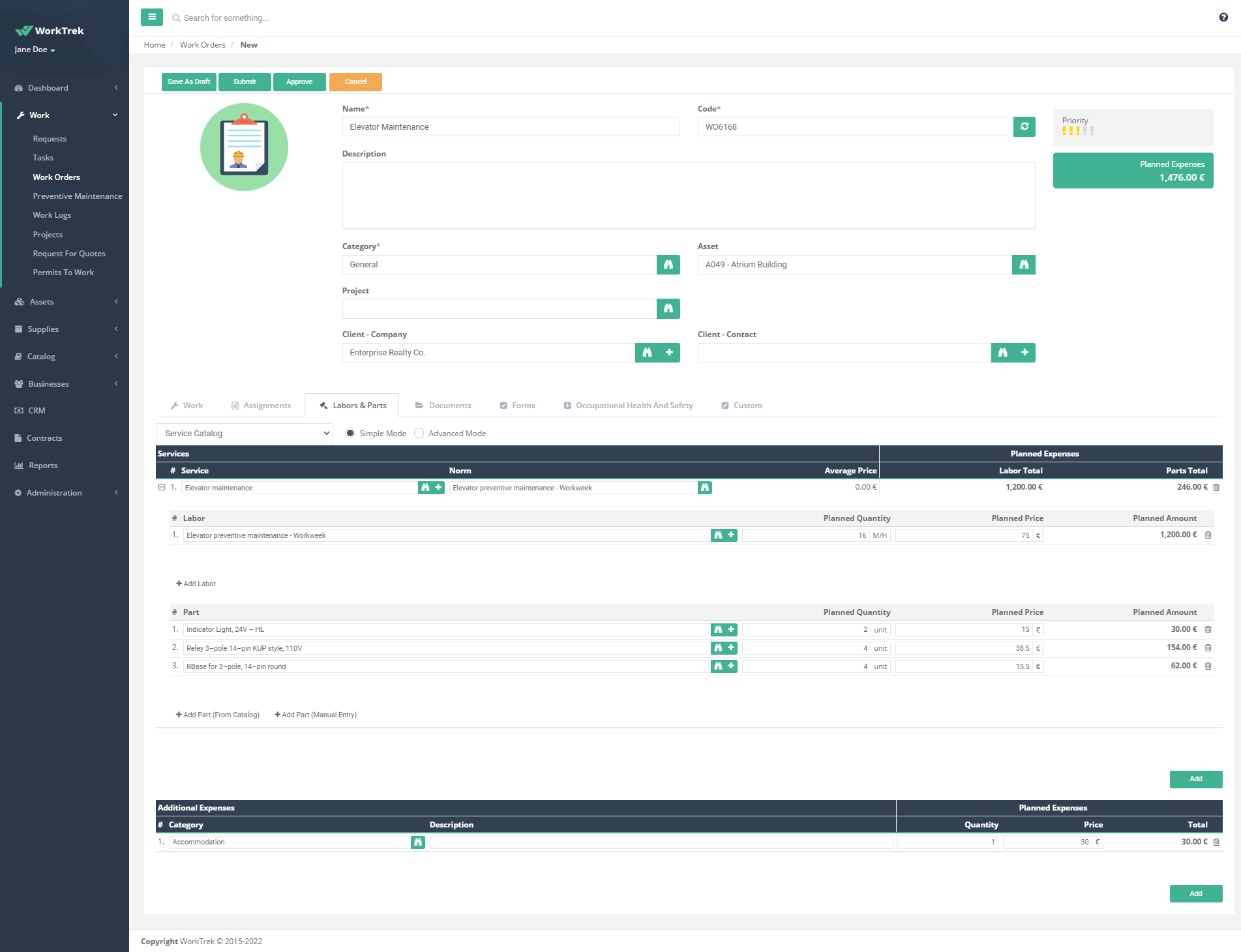
- Replacement parts for equipment or specifications for specialized tools must be included in the document.
- Every industry has some form of health risk. The work order needs to make note of it.
- Additionally, dates and timings are crucial. A start date, start time, expected end date, expected finish time, actual end date/time, etc., could all be present.
- Contact information for the requester, order manager, technician, etc. should also be included in a service order. As a result, you are able to include things like office addresses, verified email addresses, websites, FAX IDs, and mobile numbers.
Voluntary Components:
- A job ticket can contain multiple signer fields for the customer, manager, technician, accountant, etc.
- Working hours must also be scheduled for proper billing and reconciliation.
- It is useful to have a list of tasks on a service order form. It allows the work order manager, facilitator, and client to stay informed about the work done.
- Modern service ticket formats also have a special field for order importance. For example, depending on the priority level, managers plan service orders. You can also add a checklist of tools, computer applications, spare parts, consumables, etc. to check and return to inventory.
- You can provide the estimated cost of the delivered order for open-cost orders. In the case of blanket orders with predetermined prices, some companies indicate the actual costs. Finally, there should be an Order ID and Job Title, as this will help you with the work order documentation.
The Benefits of Using Work Orders
- Your company documents all work tickets with the necessary records. The accounting firm will ask for these records during any audit to validate the performance of your business.
- You make your business more transparent by including service tickets for each service. Clients like working with agencies that value documenting work, going through a client approval process, and sharing collected data.
- Quickly pay internal or external technicians by viewing the work order and keeping them satisfied.
- Help the inventory team procure all spare parts in advance so that machine maintenance does not encounter bottlenecks. Review work order notes and take appropriate action to prevent future downtime.
- Service- and product-oriented businesses can reasonably estimate annual revenue by reviewing completed and billed service order documents.
- Finally, work orders act as a communication thread between several departments. As a result, your business units can eliminate the harmful effects of working in silos.
How to write a good work order?
Step 1: The task is identified
Maintenance tasks fall into two groups, scheduled maintenance and unscheduled maintenance. Planned maintenance includes all tasks that you know in advance, such as B. Routine inspections and unscheduled maintenance includes all tasks that you cannot predict, such as B. Unexpected failure.
Step 2: The maintenance request is created
Job details are compiled and presented to the maintenance team for further processing. For example, if a machine breaks down, an operator creates a work request and submits it for maintenance. When a task is scheduled, a work order is created and triggered at the right time.
Step 3: The work order is prioritized and planned
Some jobs are more time sensitive than others. A blown light bulb does not need to be repaired immediately, unlike a broken treadmill. For this reason, you need to prioritize every work order that comes to your desk. After prioritizing, it’s time to plan. Work orders can be scheduled based on a set deadline, scheduled maintenance triggers, or dedicated time blocks. Setting a deadline makes everyone accountable and informed so that nothing falls between their heads.
Step 4: The work is assigned and completed
It’s time to put those words into action on a page. The work order is assigned to a technician, who completes the task. This could be a five-minute equipment check or it could be a complex repair job that takes several days.
Step 5: The work order is closed and documented
Once you have completed all the terms of the work order, you can close it. Managers may need to sign the work order for compliance requirements. Once closed, the work order is archived. A well-organized work order log is critical for building asset histories, reviewing past solutions, preparing for audits, and more.
Step 6: The work order is analyzed and/or reprocessed
Completed work orders contain valuable information. They can provide insights into your processes and systems with which you can refine your business operations. A work order log also allows technicians to quickly identify missed steps or workarounds if a problem reoccurs.