Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freePredictive maintenance in manufacturing leverages data to foresee and prevent equipment failures. It boosts efficiency, reduces downtime, and cuts emergency repairs. This article covers the core benefits and transformative impact of predictive maintenance in manufacturing. Implementing predictive maintenance by planning and setting up the necessary processes is crucial.
Predictive maintenance (PdM) in manufacturing leverages real-time monitoring, data analysis, and predictive analytics to maximize uptime, streamline resource utilization, and reduce emergency repairs.
Some key technologies that enable PdM include IoT sensors, machine learning algorithms, and integrated systems, which help predict potential equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
Implementing PdM requires careful planning, including criticality analysis, installation of IoT sensors, and integration with existing systems to ensure effective data management and overcome workforce skill gaps.
Introduction
The foundation of contemporary manufacturing is a focus on enhancing efficiency and reliability. At the core of this evolution is predictive maintenance, which leverages data analytics to allocate resources efficiently, increase operational uptime, and reduce unexpected repairs.
Its advantages include:
- Cost Savings
- Proactive problem-solving that targets issues once considered inevitable
- Elevated operational time with reduced instances of downtime
- Efficient management and usage: you need to rewrite it. So please do not include specific parts from my previous messages.
- A decrease in unexpected maintenance demands
These factors highlight the importance of integrating predictive maintenance into manufacturing environments.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance represents a significant transformation in maintaining operational systems, moving from a reactive stance to a proactively strategic one.
Modern industries increasingly demand maintenance strategies that surpass the outdated practice of repairing equipment only after a failure occurs.
Predictive Maintenance (PdM), which incorporates continuous monitoring and real-time data evaluation alongside predictive analytics, provides a solution by forecasting potential equipment breakdowns before they interrupt workflows.
Let’s explore what constitutes Predictive Maintenance (PdM), its workings, and the technologies enabling it to be effectively implemented.
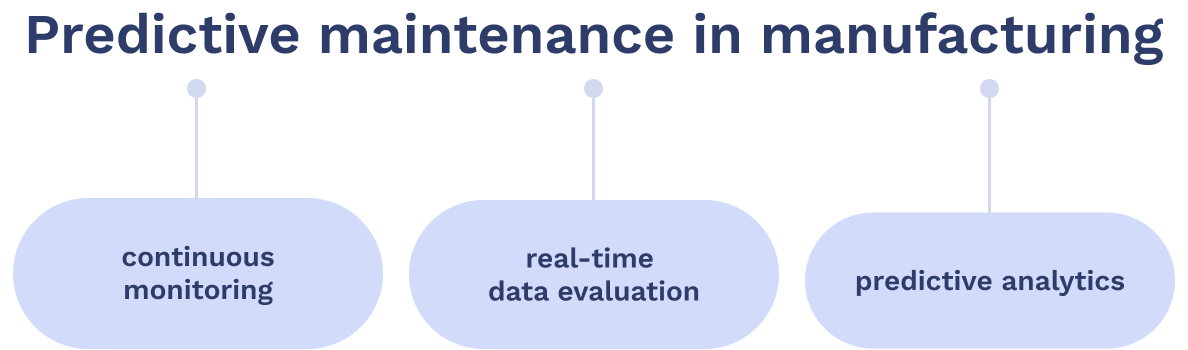
Source: WorkTrek
Definition of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance stands at the forefront of condition-based maintenance, harnessing a constant flow of data to identify and avert potential problems in equipment performance.
Predictive maintenance involves monitoring equipment performance, utilizing real-time sensor data, and creating conditional baselines for comparison. With sensors that observe assets nonstop—recording various parameters such as temperature fluctuations and vibrational shifts—predictive maintenance initiatives dispense with conjecture and avoid needless actions by determining when predictive maintenance efforts are required.
This approach is the benchmark within industrial settings, providing the insight necessary to preserve peak equipment health and functionality.
How Predictive Maintenance Works
The cornerstone of predictive maintenance is the extensive collection of data. By gathering vast amounts of historical and immediate information from IoT sensors, PdM utilizes Machine-Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI) techniques to identify irregularities that may signify impending breakdowns.
Data Scientists can use this data to build models that provide a predictive maintenance strategy for the organization.
Leveraging this cutting-edge approach helps forecast probable problems at specific times and places. It enables the maintenance team to arrange timely repairs that avert expensive operational failures, reduce maintenance costs and corrective maintenance, prolong machinery life, and minimize reliance on reactive maintenance strategies.
Key Technologies Used in Predictive Maintenance
A triumvirate of IoT devices, machine learning algorithms, and integrated platforms like computerized maintenance management systems forms the technological core of predictive maintenance. Intelligent sensors and IoT apparatus collect vital performance metrics, which are then analyzed by machine learning techniques to detect trends and forecast potential breakdowns.
These processes are unified within a comprehensive system architecture, often cloud-based, that facilitates seamless management of vast data flows and supports prompt maintenance decisions based on informed insights that can help optimize equipment performance.
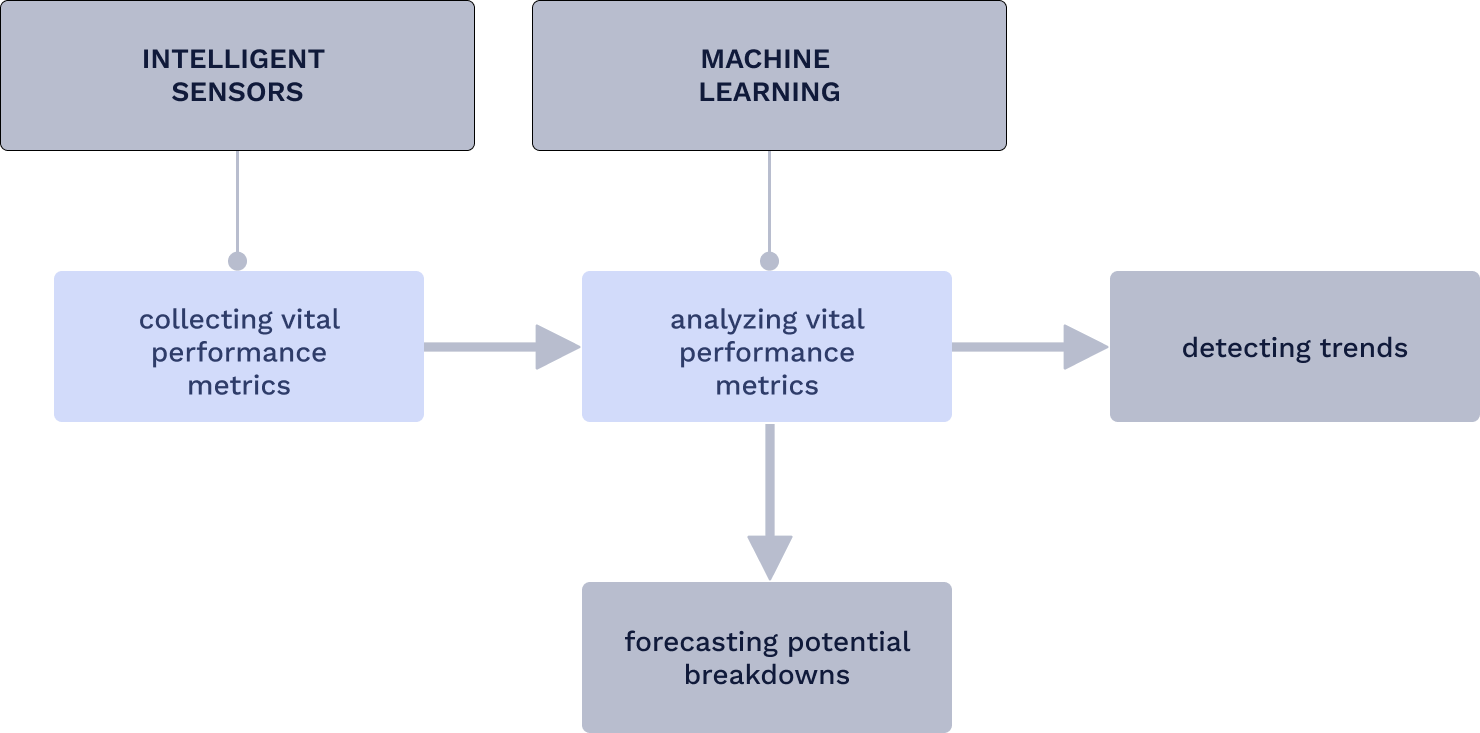
Source: WorkTrek
Core Benefits of Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Adopting predictive maintenance (PdM) in manufacturing holds significant justification. PdM identifies optimal times to carry out maintenance activities and forestalls asset failures, offering several key benefits: it curtails unforeseen downtime, slashes maintenance costs, and prolongs machinery’s durability. These factors can collectively strengthen financial performance and provide a market advantage.
Minimizing Unplanned Downtime
Predictive maintenance protects productivity from the disruptive effects of unplanned downtime. It equips maintenance crews with advanced warnings about potential equipment malfunctions, allowing for timely fixes that maintain uninterrupted workflow.
By aligning service schedules with operational usage trends, predictive maintenance extends the machinery’s life and ensures continuous production by preventing expensive and unexpected shutdowns.
Reducing Maintenance Costs
The economic benefits of predictive maintenance (PdM) are remarkably substantial. PdM can drastically reduce upkeep costs by optimizing maintenance frequency and concentrating on repairs as needed.
Extending Equipment Lifespan
Predictive maintenance goes far beyond merely saving costs. It plays a crucial role in enhancing the value derived from equipment. Its advantages include:
- Preventing minor problems from developing into significant damage through early detection
- Maximizing the useful life of each component
- Minimizing unnecessary capital investments by reducing premature replacement needs
Implementing Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing
Adopting a predictive maintenance (PdM) strategy effectively involves strategic planning, investing in appropriate technology, and integrating it smoothly with current systems. This process, from ideation to actual implementation, entails various essential steps to guarantee that PdM yields its anticipated advantages while maintaining the continuity of existing operations.
Planning Your Predictive Maintenance Program
Initiating predictive maintenance requires formulating a comprehensive strategy for predictive maintenance programs. This framework must specify explicit targets, fiscal parameters, and quantifiable objectives for the Predictive Maintenance (PdM) initiative.
Manufacturers must analyze asset criticality to identify which equipment is most appropriate for predictive maintenance and then compile historical data to feed into their predictive models.
Installing IoT Sensors and Devices
Implementing a predictive maintenance program begins with outfitting essential machinery with IoT sensors. These devices act as critical sensory components, providing live sensor data to track equipment’s performance within the predictive maintenance framework.
Thanks to Plug and Play technology, incorporating this approach into existing older machines is straightforward. This ensures that even legacy equipment can reap the advantages of predictive maintenance without necessitating their substitution.
Integrating with Existing Systems
For a predictive maintenance program to operate at its peak efficiency, PdM solutions must be fully integrated with current enterprise systems like ERP and MES.
Such integration must facilitate strong API management and allow uninterrupted data flow, ensuring seamless communication between the predictive maintenance system and other vital business platforms.
Standard Techniques in Predictive Maintenance
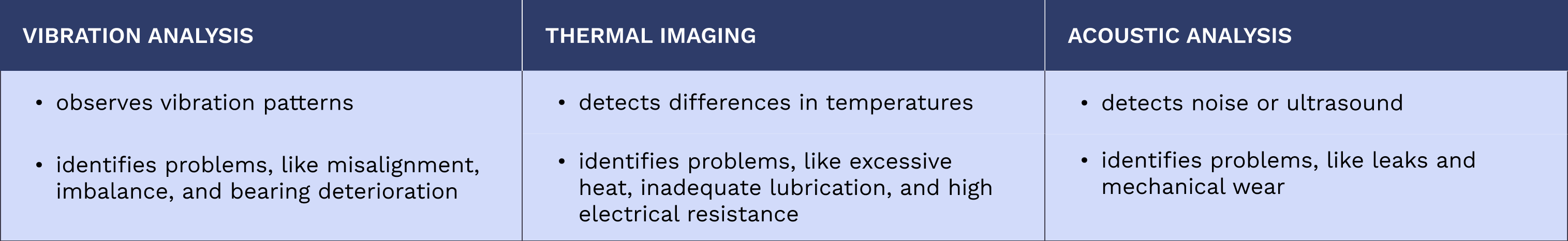
Utilizing techniques like vibration analysis and thermal imaging, predictive maintenance monitors the condition of equipment to foresee breakdowns.
These methods are vital for detecting issues early on and streamlining maintenance processes. Acoustic analysis is also frequently employed in this proactive approach to fault identification and preventive care of machinery.
Vibration Analysis
Predictive maintenance heavily relies on vibration analysis to monitor machines’ mechanical condition. By observing vibration patterns, maintenance crews can identify potential problems, like misalignment, imbalance, and bearing deterioration—typical indicators that often lead to equipment failure.
Thermal Imaging
Infrared analysis, known as thermal imaging, is essential in the preventive maintenance (PdM) toolkit. This method detects differences in temperatures and assists in pinpointing issues such as excessive heat, inadequate lubrication, and high electrical resistance. Such insights allow for early intervention to circumvent expensive equipment failures.
Acoustic Analysis
Listening to the noise or ultrasound machines produce, acoustic analysis detects deviations that may signify problems, including leaks and mechanical wear. It is especially effective for identifying issues with lubrication and aids in averting severe mechanical failures.
Source: WorkTrek
Challenges and Solutions in Predictive Maintenance
The deployment of predictive maintenance (PdM) has many benefits but poses several hurdles. These include handling extensive data quantities and confronting workers’ resistance to embracing novel technologies.
Moreover, integrating PdM into existing workflows can be challenging, requiring a significant shift in organizational culture and processes. Companies must invest in training programs to ensure their workforce is skilled in using new technologies and interpreting data analytics. Additionally, implementing PdM technologies, such as IoT sensors and machine learning software, can be substantial, necessitating a careful cost-benefit analysis to justify the investment.

Another challenge is the accuracy and reliability of predictive models. It is crucial to ensure that the data collected is of high quality and that the models are continuously updated to reflect the latest operational conditions. Without this, the effectiveness of PdM can be severely compromised, leading to potential misdiagnoses and unplanned downtimes.
Lastly, cybersecurity concerns must be addressed, as the increased connectivity of equipment and systems opens up potential vulnerabilities. Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data and maintain the integrity of the PdM system.
Successfully tackling these barriers is essential for harnessing the full advantages that PdM can provide.
Data Management Issues
Robust data governance, including validation, cleaning, and quality assurance processes, is crucial for overcoming challenges like data silos and maintaining high-quality information in predictive maintenance (PdM) programs.
Data governance ensures that data collected from various sensors and systems is accurate, reliable, and accessible. This involves implementing standardized data entry, storage, and retrieval procedures, which helps minimize errors and inconsistencies. By maintaining a centralized data repository, organizations can break down silos and foster a more collaborative environment where data-driven decisions are made seamlessly.
Moreover, investing in advanced data analytics tools and techniques can significantly enhance the quality of insights derived from PdM programs. These tools can automate the process of data validation and cleaning, ensuring that only high-quality data is used for predictive modeling. This improves the accuracy of predictions and enables more effective maintenance strategies, ultimately leading to better asset performance and reduced operational costs.
These steps are foundational to successful data management within PdM, ensuring the program’s effectiveness.
Integration Difficulties
Implementing predictive maintenance (PdM) solutions within current systems might seem challenging. However, producers can guarantee effective handling of their PdM initiatives alongside uninterrupted data flow by creating secure Internet of Things (IoT) networks and strong API integration.
Skill Gaps in the Workforce
One obstacle to predictive maintenance is the need for qualified staff to carry out maintenance duties. Several measures can be taken to overcome this issue.
- Establishing in-depth training initiatives to close any shortcomings in proficiency.
- Equipping employees with the capability to employ tools related to predictive maintenance efficiently.
- Offering continuous education and assistance to guarantee the persistent effectiveness of the initiative.
Summary
To summarize, predictive maintenance is a revolutionary strategy in manufacturing upkeep. It provides many advantages that permeate all aspects, from the production environment to fiscal reporting.
Employing data analysis, cutting-edge technology, and forward-thinking methodologies enables manufacturers to diminish downtime, cut expenditures, and prolong machinery service life.
This article has demonstrated that with proper execution and dedication to overcoming obstacles within its framework, predictive maintenance emerges as an invaluable asset for any manufacturer striving toward optimal functionality and productivity.