Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeHeavy machinery is essential for many industries but requires proper care to function safely and efficiently. Regular maintenance helps prevent costly breakdowns and extends equipment lifespan. This article covers tips for heavy machinery maintenance.
Proactive maintenance can predict when failures might occur, allowing you to fix problems before they happen.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: PTC
Heavy machinery is usually used in harsh environments, which makes maintenance critical. Let’s explore some important tips for maintaining heavy machinery effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Regular inspections and preventive care extend equipment life and reduce costly breakdowns
- A clean work environment and well-trained staff improve machinery performance and safety
- Tracking maintenance activities helps evaluate and improve overall equipment effectiveness
Understanding Machinery Maintenance Essentials
Like any critical equipment, heavy equipment’s maintenance process keeps it running smoothly and safely.
It prevents costly breakdowns and extends the life of machines.
Key Principles of Machine Health
Planned maintenance schedules are important for machine health and reduce reactive maintenance and major breakdowns.
These schedules should include daily inspections and routine service.
Equipment operators must check fluid levels, tire pressure, and controls before each use. They should look for leaks, cracks, or loose parts.
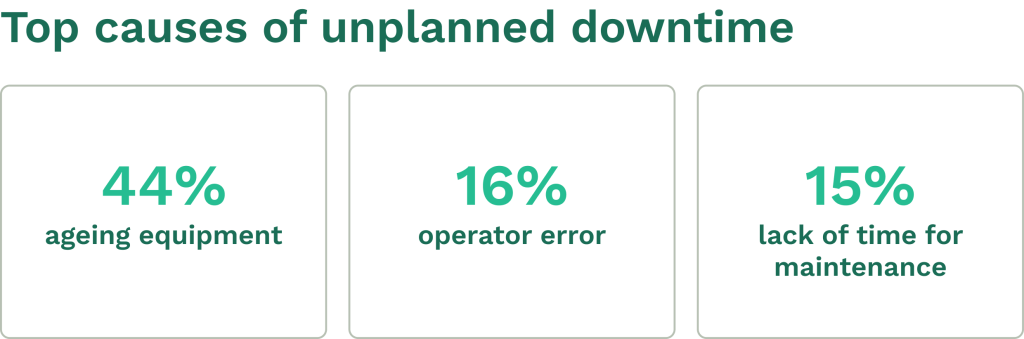
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: GoCodes
Regular oil changes and filter replacements keep engines clean and efficient. Greasing moving parts reduces wear and tear.
Keeping machines clean prevents dirt buildup that can cause damage. Washing equipment after use removes harmful debris.
Proper storage protects machines when not used—indoor storage shields construction equipment from weather damage.
The Impact of Regular Maintenance
Performing maintenance ensures that equipment lasts longer and performs better. Regular upkeep catches minor issues before they become big problems.
Maintained machines use less fuel, emit fewer emissions, and operate at peak performance, which saves money and helps the environment.
Safety improves with good maintenance. Properly working brakes, lights, and controls prevent accidents.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Micromain
Breakdowns decrease when equipment gets regular care. This means less downtime and more productivity.
The resale value stays higher for well-kept machines. Detailed maintenance records attract buyers and boost resale prices.
Maintenance costs are lower than repair costs. Fixing small problems early prevents expensive repairs later.
Understanding Heavy Equipment
Heavy equipment is important to various industries, including construction, mining, and agriculture.
These machines are designed to perform specific tasks, such as excavation, lifting, and hauling, and are often the backbone of a company’s operations.
Understanding the intricacies of heavy equipment is essential for effective maintenance and operation. This includes knowledge of the machine’s components, systems, and functions, as well as its limitations and capabilities.
Knowing how each part of the machine works and interacts with others can help operators and maintenance teams identify potential issues before they lead to equipment failures.
For instance, understanding the hydraulic system’s role in an excavator can help diagnose problems related to lifting and digging performance.
Similarly, knowing the importance of proper tire pressure in loaders can prevent premature wear and tear, ensuring the machine operates efficiently.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: FinancesOnline
Moreover, being aware of the machine’s limitations and capabilities allows operators to use the equipment within its designed parameters, reducing the risk of overloading and subsequent damage.
This knowledge is crucial for maintaining heavy equipment, optimizing its performance, and extending its lifespan.
Establishing a Maintenance Schedule
A well-planned maintenance schedule and preventive maintenance programs keep heavy machinery running smoothly and prevent costly breakdowns.
They also help catch issues early and extend equipment life.
Creating a Preventive Maintenance Plan
A good heavy equipment maintenance checklist can be part of your preventive maintenance plan. Start with the manufacturer’s recommendations to meet each machine’s needs.
Review equipment manuals for suggested service intervals and tasks.
List all maintenance tasks for each piece of machinery. Include daily checks, weekly inspections, and monthly or quarterly services.

Source: WorkTrek
Assign responsibilities to specific team members. Make sure they’re trained on proper procedures.
Use a maintenance management system to track schedules, tasks, and equipment history. This helps spot trends and adjust the plan as needed.
Set up reminders for upcoming maintenance. Consider using software that sends automatic notifications to staff.
Maintenance Frequency for Different Machinery
Maintenance needs vary depending on equipment type and usage. Heavy equipment needs more frequent care to be maintained effectively, while lesser-used equipment can follow a routine maintenance program.
Excavators and loaders often need daily hydraulic fluid checks, air filters, and greasing. Inspect tracks or tires weekly.
Bulldozers require regular undercarriage inspections and proper tire inflation. Track tension and wear should be checked every 50-100 hours of use.
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: ConEquip
Cranes need thorough inspections before each use. Conduct more detailed checks monthly or quarterly.
Adjust maintenance schedules based on real-world data. If a machine shows early wear, service frequency will increase.
Keep detailed service records. Use this info to refine your maintenance plan over time.
Conducting Thorough Inspections
Heavy equipment maintenance checklists are key to keeping heavy machinery in top shape. They help spot issues early and prevent costly breakdowns.
Let’s look at how to make effective checklists and spot common problems.
Inspection Checklist Creation
A good checklist is the backbone of any inspection. Start with the basics:
- Check oil and coolant levels
- Look at fuel levels and quality
- Inspect belts and hoses for wear
- Test lights and safety features
- Check tire pressure and tread depth
Source: WorkTrek
Customize your checklist for each piece of equipment. Include items from the maker’s manual. Update the list as you learn more about your machines.
Add spots to note dates, times, and who did the check. This will help you track issues over time and adhere to a preventive maintenance program.
Make the heavy equipment maintenance checklist easy to use with clear steps and checkboxes.
Identifying Common Wear and Tear
Knowing what to look for helps catch problems early. Here are key areas to watch:
- Metal parts: Check for cracks, bends, or rust.
- Moving parts: Listen for odd noises or vibrations.
- Hydraulic systems: Look for leaks or slow movement.
- Electrical systems: Test all switches and gauges.
Train your team to spot these issues.
They should know how parts typically look and work, which helps them notice changes quickly.
Keep detailed records of what you find.
This can help you see if problems are worsening and which parts need replacing soon.
Implementing Proactive Maintenance Techniques
Preventative maintenance helps prevent breakdowns and extends equipment life. It uses data and technology to spot issues before they cause problems.
Predictive Maintenance Strategies
Predictive maintenance uses tools to check equipment health. It spots signs of wear before parts break, cutting downtime and repair costs.
Key strategies include:
- Oil analysis to check for metal particles
- Vibration monitoring to detect loose parts
- Thermal imaging to find hot spots
- Ultrasonic testing to find cracks or leaks
- Checking battery connections
- Keeping diagnostic equipment on hand
These tests help schedule repairs at the right time. They avoid both fixing things too early and waiting until they break.
Regular inspections also play a significant role. Trained staff can often spot issues during daily checks.
Utilizing Technology for Maintenance
New tech makes proactive maintenance easier and more effective. Smart sensors and software track machine health in real time.
Some helpful tools include:
- IoT sensors that send data to central systems
- AI that predicts when parts will fail
- Mobile apps for easy equipment checks
- Digital twins to model machine performance
These technologies clearly show equipment status. They help teams plan work and order parts ahead of time.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Coast
Computerized maintenance systems track all this data, create schedules, and keep records.
This makes it easy to spot trends and improve processes over time.

Essential Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance is vital to extend the life of heavy equipment, prevent equipment failures, and ensure optimal performance. Essential maintenance tasks include:
- Daily Inspections: Operators should conduct daily inspections to identify potential issues before they become significant proheavymends to prevent contamination and wear on the machine. Clean filters ensure that the engine and other systems receive clean air and fluids, which is crucial for optimal performance.
- Lubrication: Regularly lubricate moving parts to reduce wear and tear. Proper lubrication minimizes friction between components, preventing premature wear and extending the machine’s life.
- Tire Maintenance: Check tire pressure and tread depth and look for signs of damage or wear. Proper tire maintenance ensures the machine has good traction and stability, which is essential for safe and efficient operation.
By incorporating these essential maintenance tasks into your routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of equipment failures and ensure that your heavy equipment remains in top working condition.
Fluid Management and Filter Maintenance
Fluid management and filter maintenance are critical components of heavy equipment maintenance. Fluids like engine oil, hydraulic fluid, and coolant lubricate and cool the machine’s components.
Regularly checking and maintaining fluid levels can help prevent equipment failures and extend the machine’s life.
For instance, engine oil lubricates the engine’s moving parts, reducing friction and preventing overheating. Hydraulic fluid is essential for operating hydraulic systems, providing the necessary pressure to lift and move heavy loads.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: ConEquip
Coolant helps regulate the engine’s temperature, preventing it from overheating during operation.
Filter maintenance is also essential to prevent contamination and wear on the machine. Air, fuel, and hydraulic filters should be replaced as the manufacturer recommends to ensure optimal performance and avoid damage to the machine.
Clean filters ensure that the engine and other systems receive clean air and fluids, which is crucial for optimal performance.
By prioritizing fluid management and filter maintenance, you can prevent equipment failures, reduce downtime, and extend the life of your heavy equipment.
Maintaining a Clean Work Environment
A clean work environment is crucial for heavy machinery maintenance to prevent equipment failure. It affects machine performance and prevents contamination. Proper cleaning protocols help extend equipment life and improve safety.
The Role of Cleanliness in Machine Performance
Clean machinery runs better. Dirt and debris can cause wear on moving parts, leading to breakdowns and costly repairs.
Regular cleaning helps spot small issues before they become big problems.
Clean equipment also runs cooler. Dust and grime act as insulation, trapping heat. This can cause overheating and damage to sensitive components.
Pressure washing and steam cleaning are effective for deep cleaning heavy machinery. These methods remove tough grime and built-up residues.
Regular cleaning also improves safety. It reduces fire hazards from oil and grease buildup. Clean surfaces also provide better traction, reducing slip-and-fall risks.
Contamination Prevention Protocols
Preventing contamination can improve machine health.
Set up cleaning stations near work areas and stock them with appropriate cleaning supplies and tools.
Implement a “clean as you go” policy. Train workers to wipe down equipment after each use. This prevents the buildup of dirt and grime over time.
Use sealed containers for fluids and lubricants. This prevents spills and keeps contaminants out. Label containers clearly to avoid mix-ups.
Install filtration systems on equipment. These catch particles before they can cause damage. Change filters regularly according to manufacturer guidelines.
Create designated clean zones for sensitive tasks. Use air filtration in these areas to maintain a dust-free environment.
Training and Safety Procedures
Maintain your heavy equipment with proper training and up-to-date safety procedures to keep heavy machinery maintenance safe and effective. These elements help prevent accidents and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Developing Comprehensive Training Programs
Operator training programs for heavy equipment maintenance should cover technical skills and safety protocols and be tailored to specific machinery and job roles.
Key components include hands-on practice, safety simulations, and regular refresher courses.
Don’t forget to include programs addressing emergency procedures and proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Certification tracks can help ensure all staff meet minimum competency levels. These may include specialized certifications for different types of equipment or maintenance tasks.
Regular assessments help identify areas for improvement in both individual skills and overall training effectiveness.
Emerging Safety Standards and Compliance
Safety standards for heavy machinery maintenance evolve as technology and best practices advance. Staying current with these changes is crucial for workplace safety and legal compliance.
New safety procedures often focus on lockout/tagout protocols, which prevent accidental equipment start-up during maintenance. These procedures are essential for protecting workers from serious injuries.
Digital safety management systems are becoming more common. They can help track maintenance schedules, worker certifications, and incident reports.
Regular safety audits help identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with current standards. These audits should cover equipment conditions, work practices, and documentation.
Handling Repairs and Replacement Parts
Proper repair procedures and smart parts replacement are key for keeping heavy machinery running smoothly. These practices help cut costs and extend equipment life.
Best Practices for Effective Repairs
Regular inspections are crucial for catching issues early. Check fluids, belts, and hoses often. Listen for odd noises and watch for leaks.
Train machine operators to spot problems. They use the machines daily and can notice changes quickly.
Keep detailed maintenance records. This helps track recurring issues and plan future maintenance.
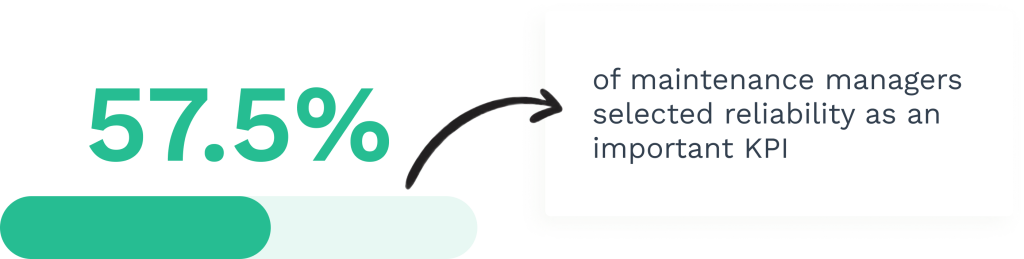
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: dynaway
Use high-quality replacement parts to ensure reliability. Cheap parts may save money upfront but can lead to more breakdowns.
Clean the work area before starting repairs. This prevents dirt from getting into systems and causing more problems.
Navigating Parts Replacement and Suppliers
Choose suppliers carefully. Look for those with a wide range of parts and good customer service.
Consider total ownership costs when buying parts. Cheaper isn’t always better if it means more frequent replacements.
Keep common wear items in stock. This reduces downtime when repairs are needed.
When possible, use original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts. They’re made to fit and work with your specific machines.
Build relationships with multiple suppliers. This ensures you can get parts quickly when needed.
Consider refurbished parts for older machines. They can be a cost-effective option for less critical components.
Outsourcing Heavy Equipment Maintenance
Outsourcing heavy equipment maintenance can be a cost-effective and efficient way to manage specific maintenance tasks. However, carefully consider the pros and cons before deciding./
Benefits of Outsourcing Maintenance
Access to Specialized Expertise:
Organizations gain immediate access to technicians with extensive experience across different types of equipment and manufacturers. These specialists often have advanced certifications and training that would be costly and time-consuming to develop in-house.
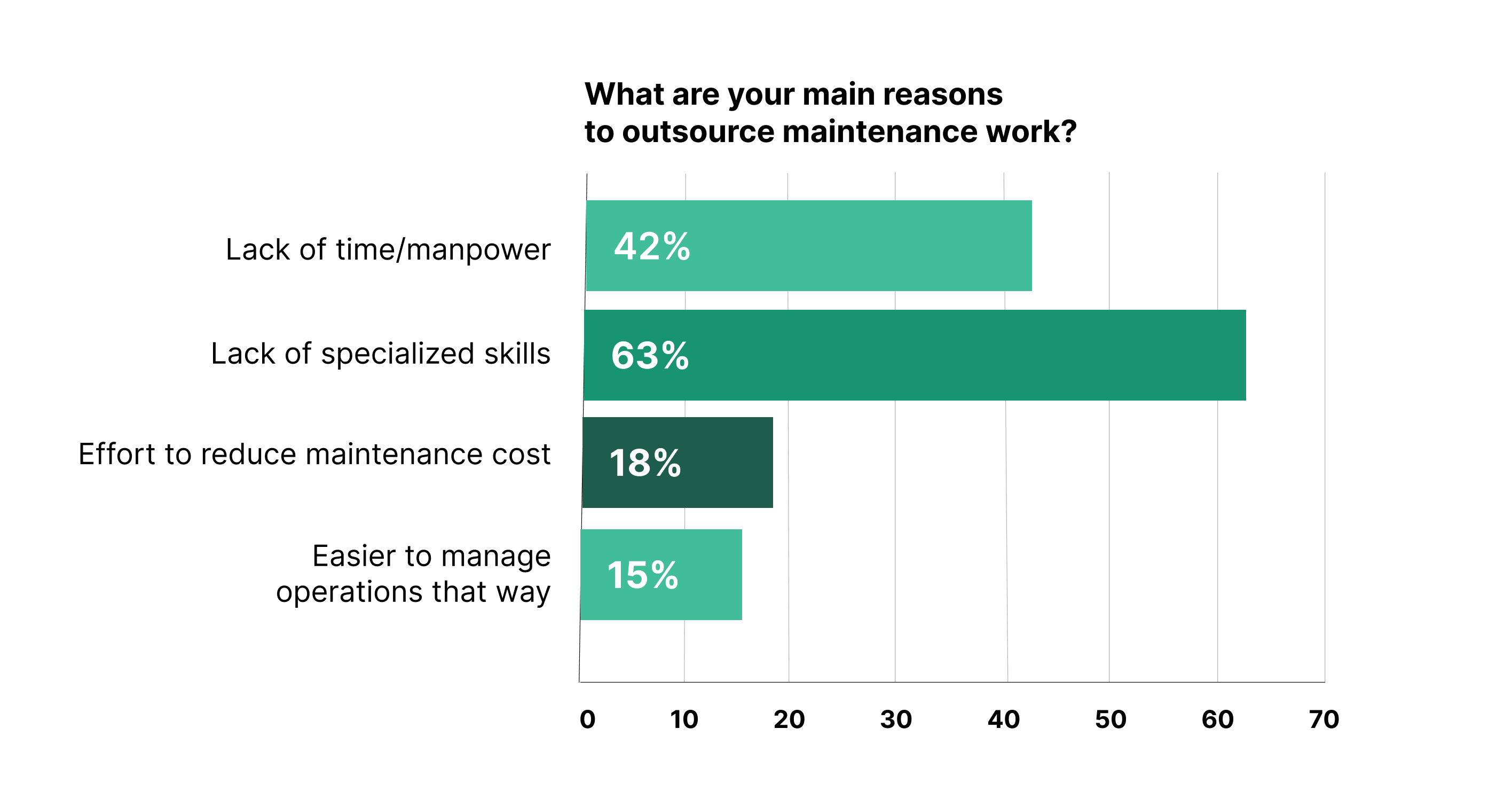
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Limble
For example, a specialized technician might have deep expertise in hydraulic systems and electronic controls across multiple equipment brands, providing comprehensive maintenance solutions requiring multiple in-house specialists.
Reduced Labor Management Burden
Outsourcing eliminates the complex challenges of recruiting, training, and managing maintenance staff. Organizations no longer need to handle scheduling, vacation coverage, certifications, ongoing training, or performance management for maintenance personnel.
This reduction in administrative overhead allows management to focus more on core business operations and strategic initiatives.
Predictable Maintenance Costs
Service contracts typically operate on fixed-fee arrangements, making it easier for organizations to budget and forecast maintenance expenses.
Companies can rely on predetermined monthly or annual costs instead of dealing with fluctuating labor costs, overtime pay, benefits, and unexpected equipment repairs. This predictability helps with financial planning and cash flow management.
Access to Advanced Tools and Technology
External maintenance providers often invest heavily in specialized diagnostic equipment, advanced maintenance tools, and cutting-edge technology that might be too expensive for individual organizations to purchase.
This access to superior equipment can lead to more accurate diagnoses, faster repairs, and improved maintenance outcomes without requiring capital investment from the organization.
Cost Savings
Outsourcing maintenance can reduce labor costs and minimize the need for in-house personnel. This can be particularly beneficial for smaller companies that may not have the resources to maintain a full-time maintenance team.
Improved Expertise
Vendors may have access to the latest technology and techniques, ensuring that maintenance is performed to the highest standards. This can result in better maintenance outcomes and longer equipment life.
Evaluating Maintenance Performance

Checking how well maintenance works is key to keeping heavy machines running smoothly. It helps find ways to improve and save money.
Measurement and Analysis of Maintenance Efforts
To evaluate maintenance, track key numbers. Look at how often machines break down and how long they stay broken. Check how much time and money go into fixing them.
Collect this data using CMMS software like WorkTrek. It will help you spot trends and issues. Then, compare your numbers to industry standards to see how you’re doing.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Reliable Plant
Look at which parts break most often. This can show where to focus your efforts. Also, check if preventive maintenance works by seeing if breakdowns happen less.
Continuous Improvement in Machinery Maintenance
Always try to improve your maintenance. Use what you learn from your measurements to make changes. Train your team on new methods and tools.
Try out new tech sensors and IoT devices that warn you before things break. This can help you fix problems before they become major ones.
Have regular meetings to talk about what’s working and what’s not. Get ideas from the people who work with the machines every day. They often know best what needs to change.
Keep up with new maintenance methods. What works for other companies might work for you, too. But always test new ideas carefully before using them on all your machines.
Summary
In conclusion, maintaining heavy machinery is essential for optimal performance and safety, as regular maintenance prevents costly breakdowns and extends equipment life.
Implementing a preventive maintenance program is crucial. It should include routine checks, fluid management, and filter replacements. Using technology for predictive maintenance can further enhance efficiency and reduce downtime.
Customized heavy equipment maintenance checklists ensure all tasks are covered. Proper training and safety protocols for equipment operators are vital for safe operation. Consider the pros and cons of outsourcing maintenance to decide what works best for your organization.
Remember, well-maintained heavy equipment is the backbone of successful operations. Stay proactive and prioritize maintenance to ensure your machines run smoothly and efficiently for years.









