Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeDo you struggle with unexpected equipment breakdowns that disrupt operations, create safety hazards, and drain financial resources as a maintenance manager?
When equipment fails without warning, production halts, deadlines are missed, and costs skyrocket as teams scramble to implement emergency repairs.
The true cost of poor maintenance extends far beyond the immediate repair expenses. Each breakdown triggers a cascade of consequences: production delays that disappoint customers, safety risks that endanger employees, compliance violations that lead to hefty fines, and excessive energy consumption that increases utility bills.
This article covers the top 7 benefits of implementing a maintenance management system in your organization.
Without effective maintenance strategies, your organization remains trapped in a reactive cycle that wastes resources and prevents you from achieving operational excellence.
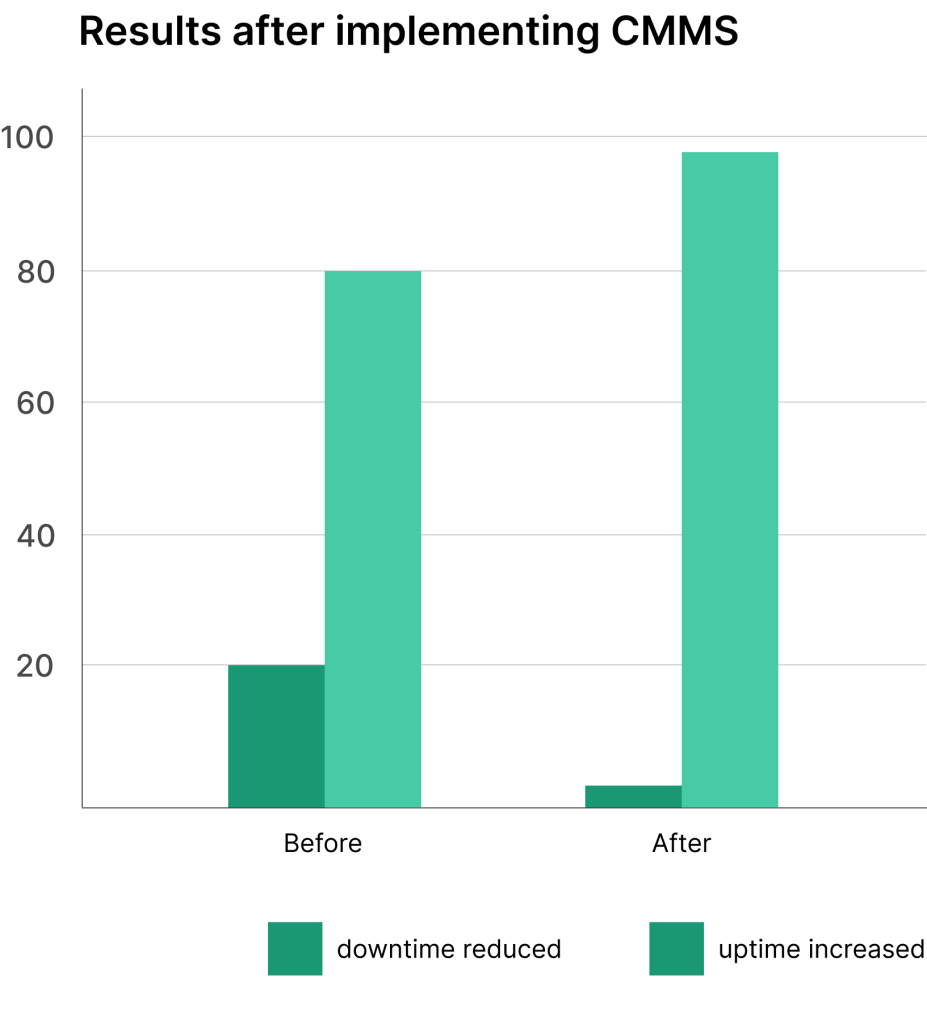
This is where maintenance management comes in. Implementing a comprehensive maintenance management system transforms how your organization handles equipment upkeep and maintenance tasks.
By shifting from reactive to proactive maintenance, you’ll prevent problems before they occur, extend asset lifespans, reduce operational costs, and dramatically improve efficiency. The following seven maintenance management benefits show how proper maintenance practices can revolutionize your operations and deliver measurable results to your bottom line.
In this article the seven benefits of maintenance management and how it can help your organization.
Key Takeaways
- Preventive maintenance strategies prolong equipment life and reduce unexpected breakdowns, saving time and money.
- Maintenance management systems provide real-time monitoring and alerts that help teams address issues before they cause major disruptions.
- Effective maintenance practices improve safety compliance while reducing maintenance costs and extending asset lifecycles.
1. Optimized Asset Utilization
Maintenance management directly improves the efficiency of your organization’s use of its assets. When equipment is well-maintained and runs optimally, businesses experience immediate performance benefits and long-term lifespan advantages.
Enhanced Equipment Performance
If you have expensive equipment, you want it to keep running without interruptions. Asset utilization is a key maintenance metric that shows how efficiently you use equipment and extract value from it.
Well-maintained equipment operates at peak capacity, reducing downtime and maintaining consistent production levels.
Like changing the oil in your car, regular maintenance prevents minor issues from developing into major failures that could halt operations completely.
This proactive approach helps organizations maintain productivity targets and meet customer demands on schedule.
One of the most significant benefits of well-maintained equipment is less energy use. For example, a well-lubricated machine requires less power to operate than one with friction issues.
This efficiency translates directly to lower operational costs.
Extended Asset Lifespan
We all want our equipment to last longer. Consistent maintenance significantly extends the useful life of equipment and infrastructure.
Components that receive regular service can remain operational far beyond their expected lifespans, leading to long-term cost savings.
Implementing clear asset management practices, such as preventive maintenance scheduling, helps organizations transition from reactive to proactive maintenance.
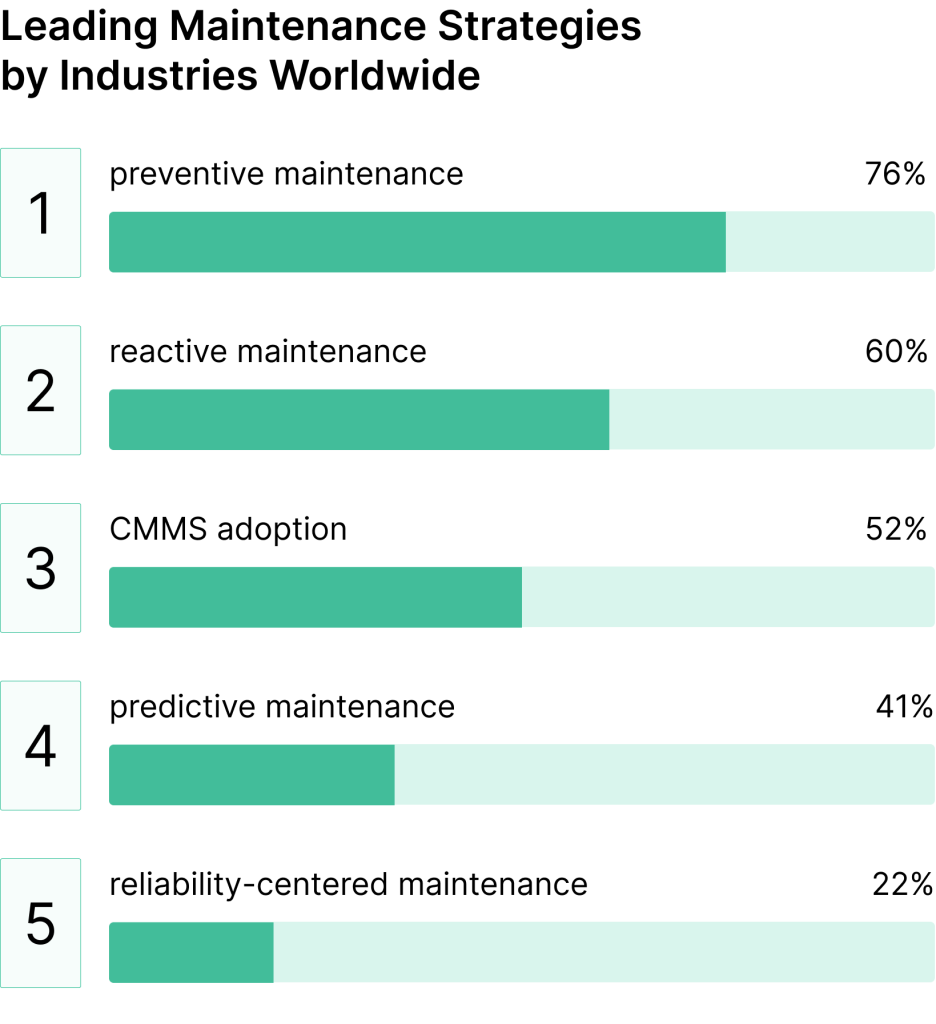
Rather than replacing equipment prematurely, businesses can strategically plan for repairs and parts replacement.
This approach creates more predictable cash flows by spreading maintenance costs over time instead of requiring large capital investments for unexpected replacements.
Extended equipment life also means organizations can delay new purchases, improving initial investment returns. This aspect of maintenance management directly impacts the bottom line through reduced capital expenditures.
2. Streamlined Maintenance Processes
Maintenance management systems revolutionize how organizations handle repairs and upkeep. These systems transform scattered, reactive approaches into methodical, data-driven processes that save time and resources.
Automated Maintenance Scheduling
A popular type of maintenance management software is Computerized maintenance management systems like WorkTrek.
CMMS can eliminate manual scheduling and reactive maintenance headaches by automatically generating work orders based on predetermined schedules.

This automation ensures critical maintenance tasks are never overlooked or delayed, improving equipment maintenance.
With mobile apps provided by CMMS systems, technicians receive timely notifications about upcoming work, complete with detailed task instructions and required parts information.
This proactive approach decreases unplanned downtime and reactive maintenance by addressing potential issues before they cause equipment failure.
The scheduling features allow for better resource allocation, enabling maintenance managers to distribute workloads evenly among team members.
This balanced approach prevents overworking maintenance workers while ensuring all assets receive proper attention.
Standardized Procedures
One of the benefits of maintenance management solutions is the enforcement of consistent protocols across all maintenance activities.
Each task follows documented procedures, ensuring repairs meet quality standards regardless of which technician performs the work.

This type of standardization creates a detailed log of each machine in the facility, tracking maintenance history and establishing best practices for specific equipment types.
Standard operating procedures can reduce new employee training time. This allows new employees to follow step-by-step instructions rather than rely on tribal knowledge.
Maintenance teams benefit from clear maintenance checklists that:
- Identify required tools and parts to perform maintenance
- Outline safety protocols and implement a safer working environment
- Specify quality checks
- Document completion criteria
- Preventative maintenance protocols
- Improved overall operational efficiency
These standardized approaches ultimately increase efficiency throughout the maintenance operation.
What does this mean to you as a maintenance manager? It ensures consistent results while minimizing errors and rework.
3. Cost Reduction and Control
Every maintenance organization wants to reduce maintenance costs without reducing equipment performance.
Effective maintenance management directly impacts a company’s financial health by reducing expenses and providing better cost control.

The effective approach to maintenance can yield significant savings in both direct repair costs and indirect downtime expenses.
Lower Repair Costs
A regular preventive maintenance plan helps catch small issues before they become major problems.
When equipment is routinely inspected and maintained, you reduce the need for expensive emergency repairs. Plus, you can avoid those late-night emergency calls to fix failing equipment.
With a well-implemented maintenance management system, companies typically experience significant cost savings in the long run. These savings come from:
- Reduced frequency of major repairs
- Lower parts replacement costs
- Decreased labor hours for maintenance staff
- Extended equipment lifespan
- Improved production process
- Happier maintenance technicians
- Reduction in unplanned maintenance
Implementing a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can help reduce costs over time.
Minimized Downtime Expenses
As a maintenance professional, you know that unplanned downtime is exceptionally costly, often far exceeding the direct repair expenses. When equipment fails unexpectedly, businesses face numerous hidden costs.
Preventive maintenance strategies decrease unplanned downtime significantly. This protection delivers several financial benefits:
- Maintained production schedules and deadlines
- Protected revenue streams
- Preserved customer satisfaction and retention
- Reduced overtime costs for emergency repairs
Buy quality parts. While they might seem more expensive initially, they can lower failure rates and prevent production slowdowns. This approach minimizes both maintenance labor costs and lost productivity expenses.
Implementing a comprehensive maintenance program helps boost operational efficiency by preventing cascading equipment failures that can halt entire production lines.
4. Improved Safety and Compliance
Effective maintenance management significantly enhances workplace safety standards while ensuring operations meet regulatory requirements. These improvements protect workers and the organization from potential hazards and legal complications.
Improved Regulatory Compliance
Most maintenance organizations we’ve worked with have to adhere to industry compliance standards.
Maintenance management systems can help organizations comply with industry regulations and standards.
Companies can easily demonstrate compliance during inspections or audits by tracking maintenance activities. This documentation creates a reliable paper trail that proves due diligence.
Regular maintenance checks identify potential compliance issues before they become violations. This proactive approach helps avoid costly fines and penalties that result from non-compliance.
CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) often include built-in compliance features that:
- Automate regulatory requirement tracking
- Schedule mandatory inspections
- Generate compliance reports
- Alert managers about upcoming deadlines

These systems can be customized to address specific industry regulations, whether OSHA, EPA, or other governing bodies. The result is consistent adherence to changing regulatory landscapes without constant manual oversight.
Enhanced Safe Working Conditions
Proper maintenance management can and will improve workplace safety by reducing accident risks.
Well-maintained equipment is less likely to malfunction in dangerous ways that could harm operators or nearby personnel.
Regular preventive maintenance identifies worn components, loose connections, and other potential safety hazards before they cause injuries.
This approach creates a safer work environment where employees can confidently perform their duties.
The safety benefits extend beyond equipment reliability. Clean, well-maintained facilities reduce slip-and-fall accidents and other common workplace injuries, and proper lighting maintenance ensures visibility in critical areas.
Maintenance teams can also:
- Identify recurring safety issues
- Implement corrective measures
- Track safety incidents and near-misses
- Provide data for safety training programs
When employees see a commitment to maintenance, they develop greater trust in their equipment and working conditions.
This promotes a stronger safety culture throughout the organization.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Maintenance management systems collect vast amounts of data that can transform organizations’ decisions.
This information enables teams to identify patterns, predict failures, and allocate resources more effectively. More importantly, a good maintenance management system will let you quickly find the needed data.
This is a much better approach than shuffling through manual paperwork orders.
Accurate Maintenance Records
Modern maintenance systems create detailed digital records of all equipment history, repairs, and performance metrics.
These systems replace error-prone paper logs and manual work orders with reliable digital documentation that maintenance teams can access instantly.
Equipment details such as installation dates, warranty information, and component lifespans become searchable and analyzable. This accessibility helps technicians quickly identify recurring issues and make informed repair decisions.
Accurate records also track maintenance costs at the asset level, revealing which equipment consumes the most resources. Maintenance managers can then determine if a machine requires replacement rather than continued repairs.
Digital records also eliminate information silos by making critical data available to all stakeholders, improving cross-departmental communication and coordination.
Performance Tracking and Analysis
Data analytics tools and detailed reports can transform raw maintenance data into actionable insights.
These tools identify patterns humans might miss, such as subtle changes in equipment performance before a major failure occurs.
Real-time monitoring and alerts allow teams to respond immediately to developing issues. Dashboard visualizations display key performance indicators (KPIs) that show maintenance effectiveness at a glance.
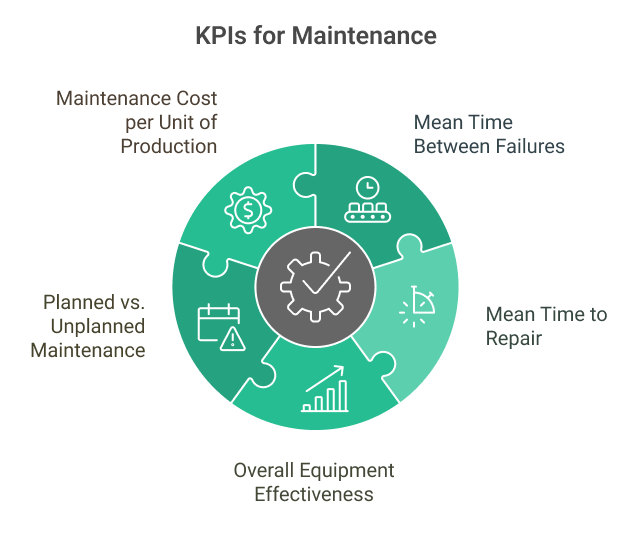
Analytics also enable maintenance teams to:
- Compare actual performance against benchmarks
- Identify bottlenecks in maintenance workflows
- Determine optimal maintenance intervals
- Forecast future resource needs
Organizations can shift from reactive to predictive maintenance strategies by leveraging data from various sources. This approach reduces downtime, extends equipment life, and optimizes maintenance spending.
6. Boosted Team Productivity
Effective maintenance management can directly impact how well teams perform their daily tasks.

Outlining and implementing proper systems and protocols enable staff to work more efficiently while ensuring resources are allocated where needed.
Empowered Maintenance Staff
Maintenance management systems provide staff clear instructions and procedures, eliminating confusion about task priorities.
Technicians can instantly access equipment histories and maintenance requirements, reducing diagnostic time and improving repair accuracy for routine maintenance.
Digital tools enable technicians to document their work comprehensively without time-consuming paperwork.
What does this mean? This means you can increase uptime, improve operations productivity, and help optimize maintenance costs.
Training becomes more targeted when management systems track performance metrics and identify skill gaps. Staff feel more confident when they have the right tools and information.

Teams with proper maintenance management report higher job satisfaction and lower turnover rates. When technicians can solve problems effectively, they develop professional pride in their work.
Efficient Resource Allocation
Smart maintenance practices help organizations distribute labor, parts, and equipment where they’ll have the greatest impact. Predictive analytics identify which assets require attention before failures occur, reducing unexpected breakdowns by up to 90%.
Inventory management features ensure necessary parts are always available without excess stock tying up capital. Teams waste less time waiting for components to arrive when systems track usage patterns accurately.
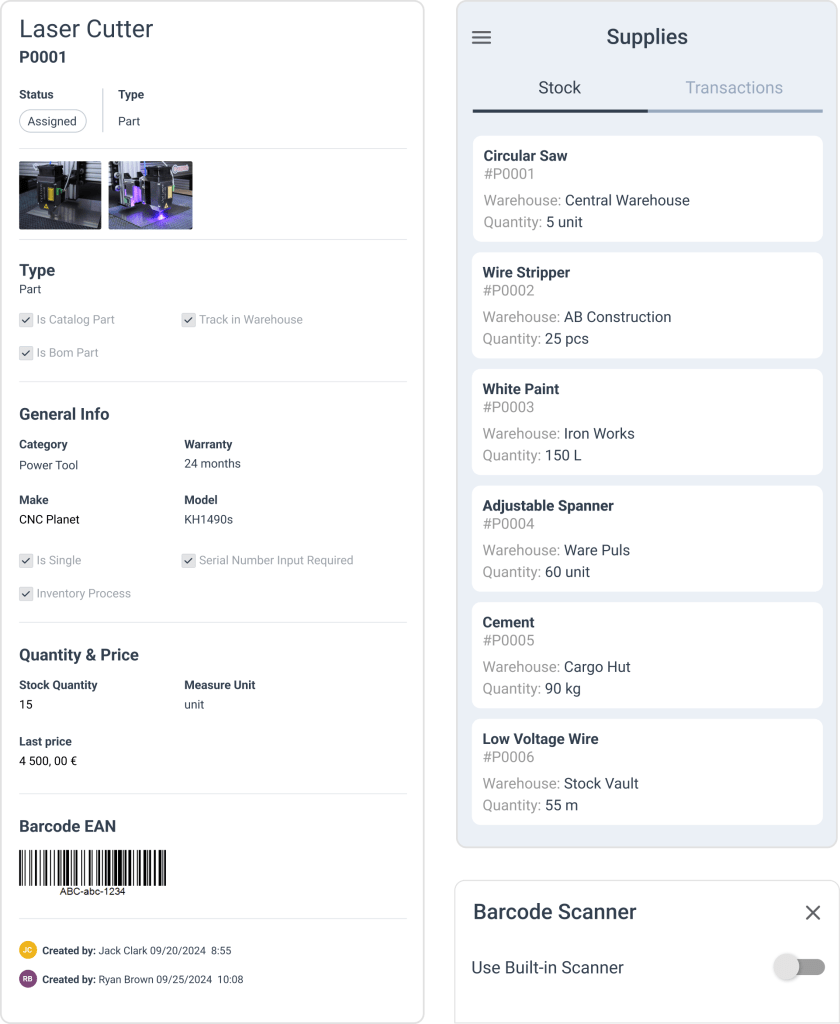
Resource scheduling tools match technician skills to appropriate tasks, maximizing expertise while minimizing downtime. This optimization leads to faster completion times and more efficient operations.
Digital maintenance systems eliminate paperwork and automate routine processes, freeing staff to focus on critical maintenance activities.
Time previously spent on administrative tasks can be redirected to preventive maintenance and timely repairs. All this can lead to fewer equipment replacements and a boost in customer satisfaction.
7. Environmental Sustainability

Modern maintenance management practices contribute significantly to environmental protection while delivering operational benefits. Effective maintenance strategies reduce facility impact through energy savings and waste reduction practices.
Reduced Energy Consumption
Well-maintained equipment operates more efficiently, using less energy to perform the same tasks. Smart maintenance systems provide real-time monitoring that identifies energy waste sources before they become costly problems.
Regular inspection schedules ensure HVAC systems, motors, and machinery function optimally. Companies typically achieve 10-15% energy savings through preventive maintenance programs focused on efficiency.
Several benefits to energy-saving maintenance practices include:
- Scheduled lubrication of moving parts
- Filter replacements before performance degradation
- Prompt repair of compressed air leaks
- Calibration of temperature controls and sensors
- Insulation maintenance for heating/cooling systems
These practices reduce utility costs and decrease operations’ carbon footprint.
Minimized Waste Generation
Effective maintenance extends equipment lifespan, significantly reducing material waste from premature replacement.
Sustainable maintenance practices balance operational efficiency with environmental responsibility.
Proper maintenance procedures include recycling or responsible disposal of replaced parts, fluids, and consumables.
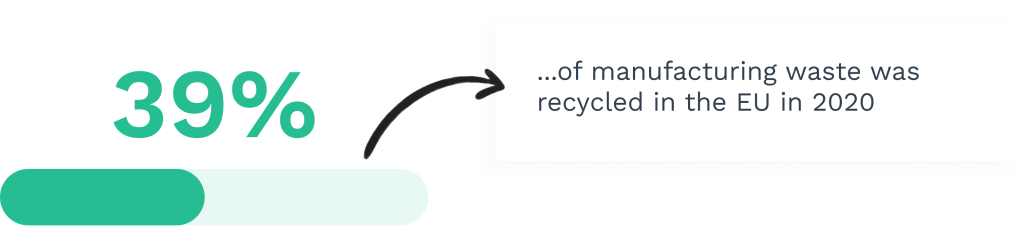
Modern maintenance management systems track material usage and waste streams, helping facilities meet environmental compliance requirements.
Predictive maintenance technologies further reduce waste by:
- Replacing only components that need service
- Minimizing emergency repairs that generate excess waste
- Using condition-based maintenance to optimize part lifespans
- Implementing CMMS software
- Reducing chemical usage through precise application
- Implementing sustainable facilities management practices
These approaches deliver environmental and financial benefits. Studies show that maintenance-driven waste reduction can lower disposal costs by 20-30% in manufacturing settings.
Conclusion
Effective maintenance management transforms reactive, costly approaches into proactive strategies that deliver measurable operational benefits.
Implementing comprehensive maintenance systems, such as CMMS software, can help organizations optimize asset utilization, streamline processes, and significantly reduce costs while enhancing safety compliance.
Data-driven decision-making empowers maintenance teams to identify potential issues before they cause disruptions while boosting team productivity and morale through clear workflows and proper resource allocation.
The transition from reactive to preventive maintenance creates a virtuous cycle of improved equipment reliability, extended asset lifespans, and enhanced operational efficiency.
For maintenance managers seeking to break free from the costly cycle of emergency repairs and unplanned downtime, implementing these seven maintenance management benefits provides a clear pathway to operational excellence and sustainable business growth.
The investment in proper maintenance management consistently delivers returns that benefit the entire organization.