What is Scheduled Maintenance?
Scheduled maintenance refers to planned maintenance tasks performed on assets at predetermined intervals to ensure continued performance and longevity.
Unlike reactive maintenance, which occurs after a breakdown, scheduled maintenance is proactive and aims to prevent failures before they happen.
By regularly servicing equipment and addressing potential issues early on, organizations can avoid costly unplanned downtime and extend the useful life of their assets.
Maintaining equipment, machinery, and infrastructure is crucial for any organization looking to maximize reliability, minimize downtime, and extend asset life.
That is where scheduled maintenance comes in. This is one of the key strategies for improving overall organization maintenance.
Key Components of Scheduled Maintenance:
Planning and Scheduling
Careful planning and scheduling are at the core of any practical scheduled maintenance tasks. Maintenance tasks should be planned based on manufacturer recommendations and industry standards.
It is also helpful to use KPIs and historical performance data to help plan maintenance.
They are generally part of a larger preventive maintenance program and can reduce reactive maintenance.
Tasks can be scheduled at regular intervals, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or annually, depending on each asset’s specific requirements.
Comprehensive Scope
Scheduled maintenance covers several tasks that are designed to keep assets in optimal condition.
The maintenance planner may include the following preventive maintenance programs:
- Inspections to identify potential problems
- Cleaning to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants
- Lubrication to reduce friction and wear
- Adjustments to ensure proper operation
- Repairs to fix any identified issues to reduce costly downtime
Scheduled maintenance can address all aspects of asset health which can keep minor issues from escalating into significant failures.
Detailed Documentation
Keeping detailed records is an important part of scheduled maintenance.
Maintenance teams document all activities, observations, and any necessary follow-up actions. This documentation serves multiple purposes:
- It provides a historical record of maintenance work for each asset
- It helps identify trends and patterns in asset performance
- It enables compliance with regulatory requirements and audits
- It facilitates knowledge sharing among maintenance team members. Detailed documentation also supports data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement efforts.
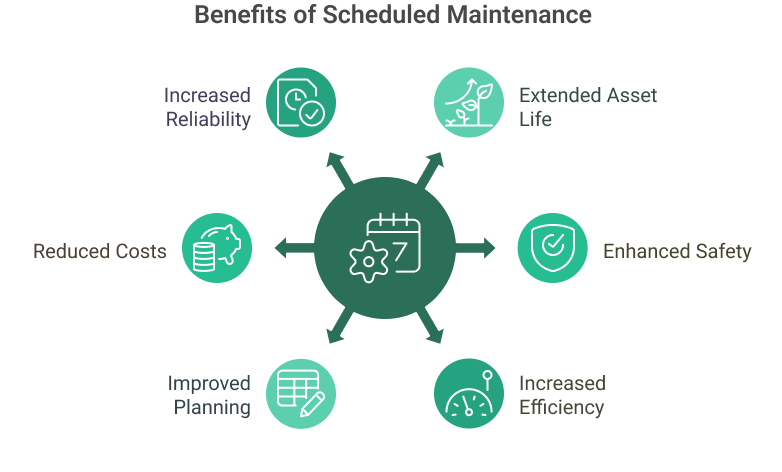
Benefits of Scheduled Maintenance for Maintenance Organizations
- Increased Reliability and Uptime: Scheduled maintenance reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns and failures by proactively maintaining assets. This increases asset maintenance and uptime, enabling organizations to meet production targets, reduce costly repairs, and consistently meet customer demands. Maintenance technicians can focus on proactive tasks, improving the reliability of critical business assets.
- Extended Asset Life: Regular maintenance and recommended maintenance schedules help assets reach or exceed their designed useful life and reduce reactive maintenance. One approach is to focus on and document factory-scheduled maintenance schedules. Maintenance teams can prevent premature asset failure by addressing wear and tear, corrosion, and other degradation mechanisms early on. This maximizes the return on investment for each asset and reduces the need for costly replacements.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: While scheduled maintenance requires an upfront investment, it can significantly reduce overall maintenance costs in the long run. By catching and addressing issues early, organizations can avoid more extensive and expensive repairs down the line. Additionally, planned maintenance allows for better resource allocation, reducing overtime costs associated with emergency repairs.
- Enhanced Safety: Scheduled maintenance plays a critical role in ensuring the safety of employees and the environment. Regular inspections and servicing help identify and address potential safety hazards, such as faulty electrical connections, worn safety guards, or leaking hydraulic systems. By maintaining assets in a safe and compliant condition, organizations can protect their workforce and minimize the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Improved Planning and Budgeting: Maintenance organizations can better plan and budget for their activities with a well-defined scheduled maintenance program. Knowing when tasks will be performed and what resources will be required enables more accurate forecasting and allocation of staff, parts, and tools. This predictability helps avoid last-minute scrambles and ensures that maintenance teams have what they need to work efficiently.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Scheduled maintenance promotes a proactive and organized approach to maintenance work. Maintenance teams can work more efficiently and productively by planning tasks and allocating resources accordingly. Regular servicing also keeps assets operating at peak performance, reducing the risk of quality issues and production delays.
- Better Compliance Many industries have strict regulations and standards governing the maintenance and operation of equipment and infrastructure. Scheduled maintenance helps organizations stay compliant by ensuring that assets are regularly inspected, serviced, and documented according to these requirements. This avoids costly penalties and demonstrates a commitment to safety, quality, and environmental responsibility.
Key Differences: Scheduled vs. Planned Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance involves designating individuals to carry out specific maintenance tasks at set times to reduce the likelihood of equipment breakdowns.
It outlines who will perform the task and when it should be completed. Planned maintenance, on the other hand, is designed to predict when equipment will require service and schedule maintenance based on that data.
Scheduled maintenance takes into account resources and assigns tasks based on availability.
This systematic approach clarifies roles and timelines for each participant, improving responsibility and operational effectiveness.
Conversely, with planned maintenance, identifying potential issues takes precedence before arranging subsequent task scheduling.
In this case, timing depends on a comprehensive assessment of working hours against priorities.
Implementing Scheduled Maintenance
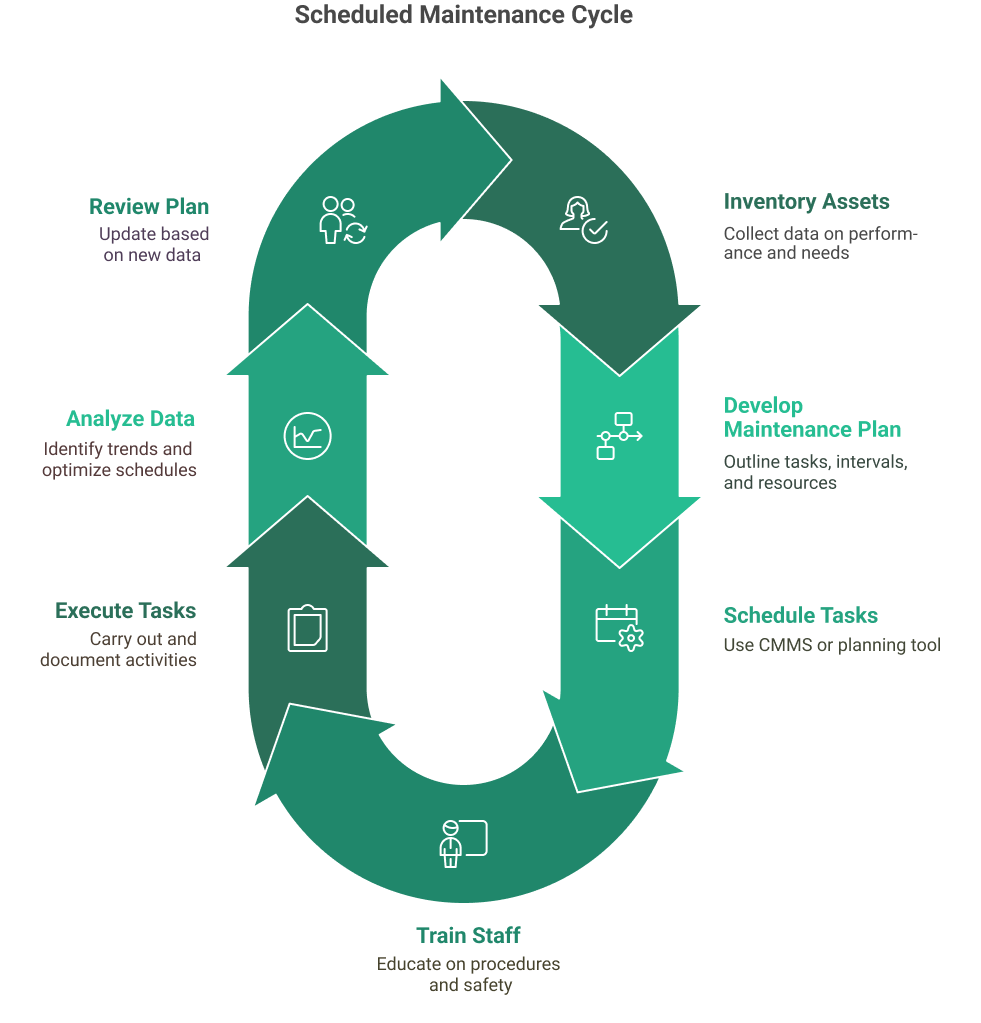
To implement an effective scheduled maintenance program, organizations should follow these steps:
- Inventory assets and gather data on their performance, criticality, and maintenance requirements
- Develop a comprehensive maintenance plan outlining tasks, intervals, and resources needed
- Schedule tasks in a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) or other planning tool
- Train maintenance staff on procedures, safety, and documentation
- Execute tasks as planned, documenting all activities and observations
- Analyze maintenance data to identify trends, optimize schedules, and drive continuous improvement
- Regularly review and update the maintenance plan based on changing needs and performance data
Scheduled maintenance is a powerful strategy for optimizing physical assets’ performance, reliability, and longevity.
By proactively planning and executing maintenance tasks, organizations can prevent failures, reduce downtime, and extend asset life.
The benefits of scheduled maintenance are far-reaching, from increased uptime and reduced costs to enhanced safety and compliance.
By investing in a robust scheduled maintenance program, maintenance organizations can drive operational excellence and achieve a competitive edge in today’s challenging business environment.
Use CMMS to optimize Scheduled Maintenance
Here are key ways a Computerized Maintenance Management System like WorkTrek can enhance scheduled maintenance:
Asset Management
A comprehensive understanding of the maintained assets is at the heart of effective scheduled maintenance. A CMMS acts as a detailed asset register, capturing vital information such as:
- Asset specifications and manuals
- Warranty information
- Maintenance history
- Spare parts inventory
With all this data in one place, maintenance teams can make informed decisions about when and how to service each asset. It’s like having a digital filing cabinet that instantly provides the information needed to plan and execute maintenance.
Planning and Scheduling
One of the biggest challenges in scheduled maintenance is planning and scheduling tasks to optimize resource utilization and minimize disruption to operations. A CMMS streamlines this process by:
- Automatically generating work orders based on predefined maintenance schedules
- Assigning tasks to available technicians based on skills and workload
- Providing visibility into upcoming maintenance for better coordination with production
- Enabling efficient scheduling of resources (tools, parts, etc.) to avoid conflicts
Think of the CMMS as a digital assistant that handles the complex logistics of maintenance scheduling, freeing up time for strategic planning and execution.
Work Order Management
Efficient management of maintenance work orders is crucial for ensuring that tasks are completed on time and to the required standard. A CMMS supports this by:
- Providing a central repository for all work orders, accessible from anywhere
- Enabling real-time tracking of work order status and technician progress
- Facilitating communication between technicians and supervisors
- Capturing data on task completion, labor hours, parts used, etc. for analysis
A CMMS helps maintenance teams stay organized, accountable, and focused on critical tasks by digitizing and automating work order workflows.
Preventive Maintenance:
Preventive maintenance is the backbone of any successful scheduled maintenance program. A CMMS makes it easy to implement and sustain a robust preventive maintenance strategy by:
- Automatically generating PM work orders based on time or usage triggers
- Tracking PM compliance and overdue tasks
- Providing a library of standard PM procedures and checklists
- Enabling continuous improvement of PM schedules based on performance data
With a CMMS, organizations can move from reactive to proactive maintenance, preventing failures before they occur and extending asset life.
Inventory Management
Effective spare parts management is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring that maintenance tasks are completed efficiently. A CMMS supports this by:
- Maintaining a real-time inventory of spare parts and consumables
- Tracking part usage and automatically generating reorder alerts
- Enabling efficient procurement and vendor management
- Providing insights into inventory costs and optimization opportunities
A CMMS helps ensure that the right parts are always available when needed by integrating inventory management with maintenance workflows.
Performance Tracking:
Continuous improvement is a hallmark of best-in-class maintenance programs. A CMMS enables this by providing a wealth of data and analytics on maintenance performance, such as:
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) like SMCP, MTTR, MTBF
- Asset reliability and failure trends
- Maintenance cost and budget tracking
- Labor utilization and productivity metrics
Scheduled Maintenance Critical Percent (SMCP)
Scheduled Maintenance Critical Percent (SMCP) is a metric used to assess the effectiveness of a scheduled maintenance program.
It helps organizations prioritize their maintenance efforts and ensure that the most important tasks are completed on time to improve asset maintenance.
Here’s a detailed explanation of SMCP, its calculation, and how it supports scheduled maintenance:
Definition:
Scheduled Maintenance Critical Percent (SMCP) represents the percentage of critical maintenance tasks completed on schedule out of the total number planned for a given period.
Critical tasks directly impact asset reliability, safety, compliance, or other key performance indicators.
How to calculate SMCP
The formula for calculating SMCP is as follows:
SMCP = (Number of critical tasks completed on schedule ÷ Total number of critical tasks scheduled) × 100
For example, if an organization plans 100 critical maintenance tasks for a month and completes 85 of them on schedule, the SMCP would be:
SMCP = (85 ÷ 100) × 100 = 85%
Importance of SMCP
Prioritization of critical tasks
SMCP focuses on critical maintenance tasks, ensuring that these high-priority items receive attention to help minimize equipment failure. By tracking SMCP, organizations can identify areas where critical tasks are being missed or delayed and take corrective action to improve performance.
Reliability and safety
Completing critical maintenance tasks on time is essential for maintaining asset reliability and safety. A high SMCP indicates that an organization effectively addresses its most important maintenance needs, reducing the risk of failures, accidents, and non-compliance.
Resource allocation
SMCP helps organizations allocate their maintenance resources effectively. By prioritizing critical tasks and tracking their completion, maintenance teams can ensure that they dedicate their time and efforts to the most impactful work.
Performance monitoring
Regularly measuring and reporting SMCP provides a clear indicator of maintenance program performance.
It allows organizations to set targets, track progress, and identify trends. It can also quickly highlight overdue maintenance tasks.
This data-driven approach supports continuous improvement efforts and helps demonstrate the value of the maintenance function to stakeholders.
How to Improve SMCP?
To improve SMCP, organizations can take the following steps:
- Clearly define and communicate what constitutes a critical task vs routine inspections.
- Ensure maintenance workers properly plan and schedule critical tasks, including recurring ones.
- Allocate sufficient resources (staff, tools, parts, etc.) to complete critical tasks on time. Also, make staff availability part of your maintenance scheduler.
- Provide training and support to maintenance staff to improve efficiency and effectiveness. This should be part of your organization’s maintenance strategy.
- Regularly review SMCP performance and identify root causes of missed or delayed tasks.
- Implement corrective actions and process improvements based on SMCP analysis.
- Celebrate successes and recognize teams and individuals who contribute to high SMCP performance.
Integration with Scheduled Maintenance
SMCP is a key metric within a broader scheduled maintenance program. By incorporating SMCP tracking and analysis into the planning and execution of scheduled maintenance, organizations can:
- Ensure that critical tasks are given the highest priority in maintenance schedules
- Adjust schedules and resources as needed to improve SMCP performance
- Use SMCP data to optimize maintenance intervals and task lists over time
- Communicate the impact of scheduled maintenance on critical task completion to stakeholders
- Drive a culture of reliability and continuous improvement through a focus on critical maintenance
Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for free



