Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIn this article, we will walk you through the maintenance workflow process, a structured approach to doing maintenance safely and efficiently. We will reduce downtime, reduce costs, extend asset life, and be cost-effective for your organization.
We’ll break down the steps in this process and show you how to refine your maintenance workflow. We’ll also look at what effective maintenance planning means, prioritizing assets, auditing regularly, and setting SMART goals to improve resource allocation and continuous improvement.
We’ll also show you how CMMS software can streamline maintenance workflows through defined steps, reduce downtime, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Maintenance Workflow
Maintenance workflow is sequenced to ensure maintenance tasks are done efficiently and safely. This standardized sequence outlines the coordinated management of resources, people, and technology to implement various work orders.
Critical industries such as manufacturing, transportation, facilities management, and public works rely heavily on these workflows to maintain operational effectiveness and safety standards.
What is at the heart of it?
Reducing downtime and extending asset life are at the heart of good maintenance management. It’s about spending less while keeping safety standards high.
Led by a knowledgeable maintenance manager, this workflow follows four stages:
- Request or need identification,
- Approval processes,
- Execution to completion.
- Reporting.
Following these stages will give you less unexpected downtime, cost savings, efficiency gains, compliance with regulations, and longer asset life.
Reduce Downtime
Not following processes can lead to equipment downtime. Breakdowns on critical machinery or infrastructure can add up to costs.
This can also shorten the life of these expensive assets and reduce productivity. So, it puts a big financial burden on operations compared to a scenario where planning is aligned with the strategy. This will give you better production rates and cost control.
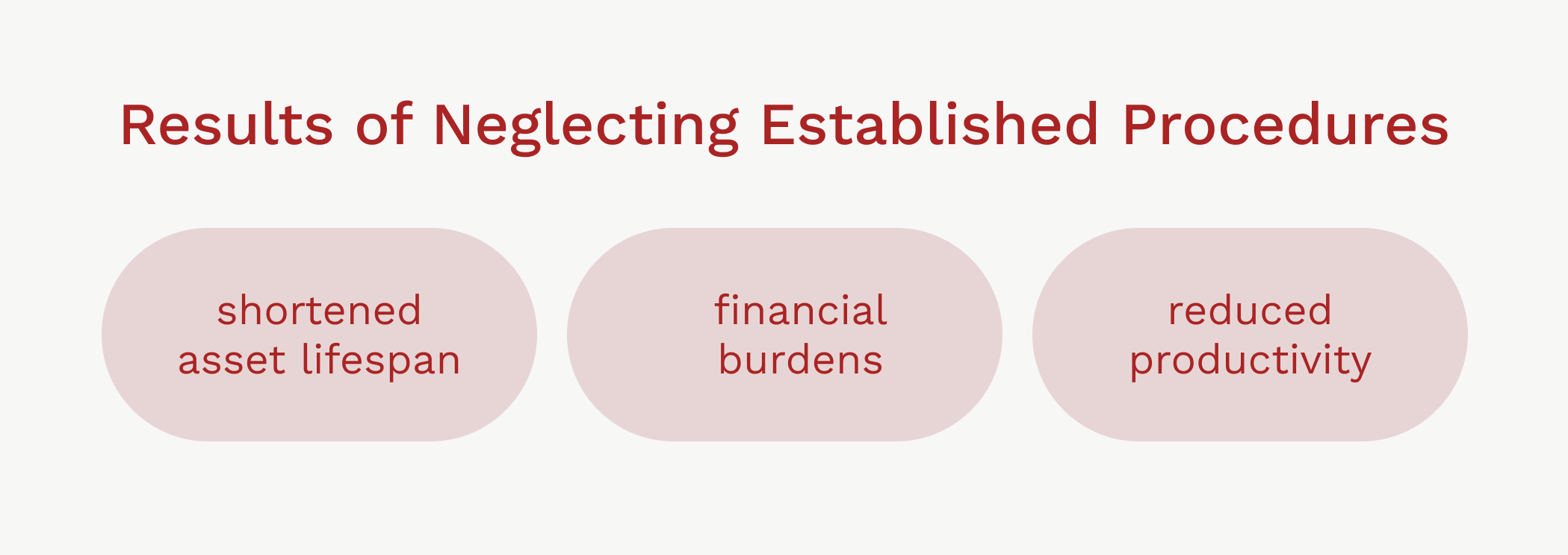
Source: WorkTrek
Industry Standards
Following industry standards, effective resource allocation, and financial forecasting will ensure smooth daily operations and reduce the risk of unexpected events that can disrupt continuous processes. By following these standards, you can create a framework that supports current operational demands and future challenges.
This proactive approach identifies and mitigates risks before they become major issues, ensuring efficient resource allocation and accurate financial forecasts.
Following industry standards also creates a culture of excellence and continuous improvement, where teams strive for better performance and innovation. This focus on quality and precision will give you a more resilient and agile organization that can confidently and quickly navigate the complexities of modern industry.
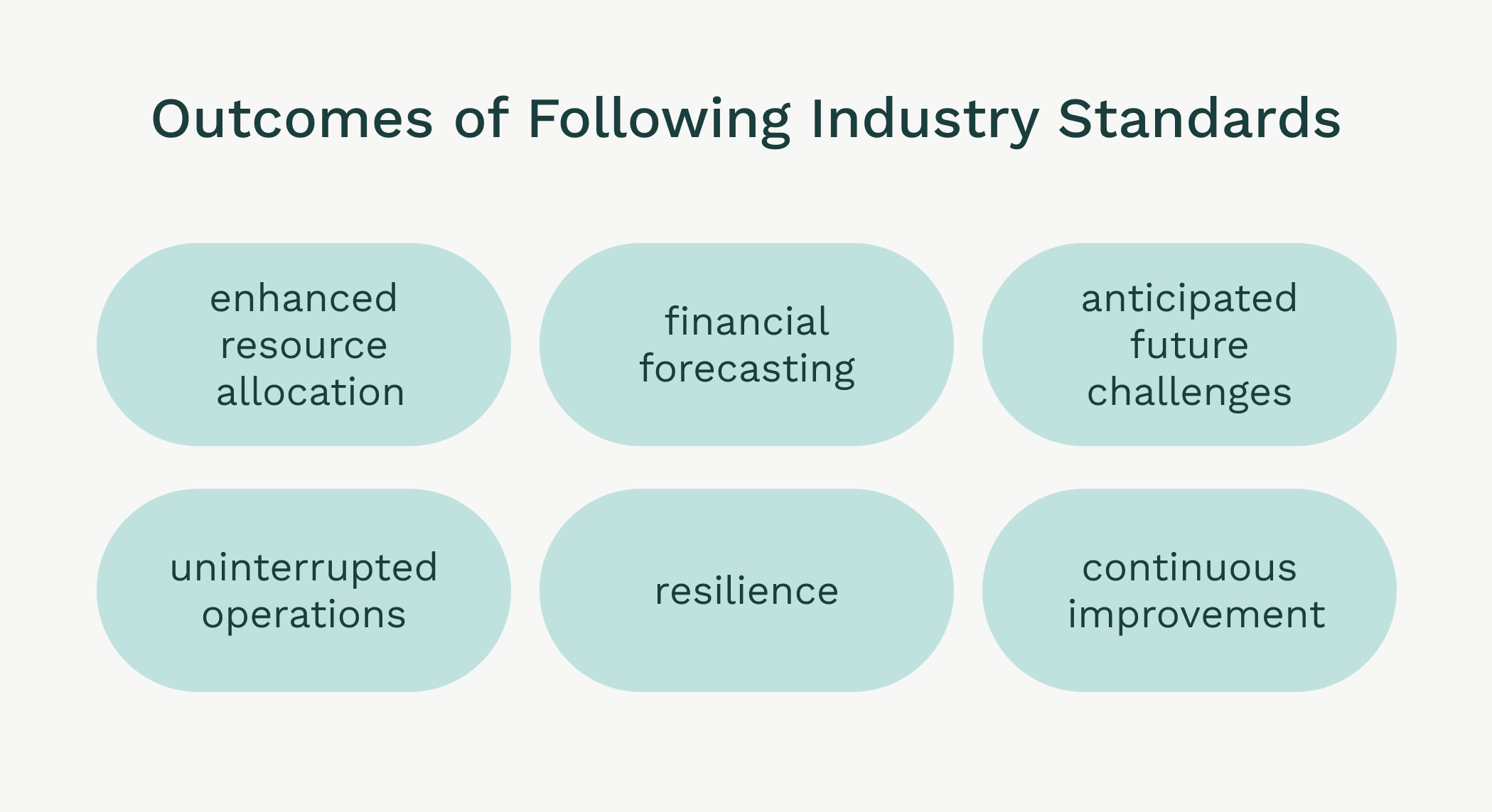
Source: WorkTrek
Maintenance Workflow Steps:
Three essential steps form maintenance workflow:
- Identify tasks for maintenance
- Schedule these activities
- Work orders for these tasks. These stages will ensure all maintenance processes run smoothly
Identifying Maintenance Tasks for Maintenance
To maintain equipment reliability and performance, you need to identify and schedule maintenance tasks. By systematically identifying and scheduling these tasks, we improve process efficiency.
This will ensure all maintenance activities are accounted for and scheduled, so you reduce the risk of unexpected failures on the equipment.
Source: WorkTrek
Scheduling Maintenance
Scheduled maintenance tasks are the key to avoiding costly operational issues and equipment failures. Proper scheduling reduces downtime, saves money, and eliminates the need for emergency repairs. By prioritizing scheduled maintenance tasks, you can ensure your critical assets are always in optimal condition.
Two ways to create a preventive maintenance schedule are fixed and floating. Fixed schedules are based on specific usage intervals or time triggers. Floating schedules are based on the timing of previous maintenance tasks and asset usage or maintenance history.
Both will help you to organize and prioritize maintenance tasks to ensure equipment runs efficiently and safely.
Work Orders
The final stage of the maintenance workflow is the work orders, which guide maintenance jobs and tasks for technicians. Completing these work orders on time is key to equipment performance and reliability.
Using CMMS software, you can streamline your process by automating work order assignments and task completion.
Source: WorkTrek
Optimized Maintenance Workflow
Optimizing maintenance workflows will give you:
- Higher operational efficiency
- Less equipment downtime
- Lower costs
- More safety measures
- Compliance with industry standards
For example, manufacturers on reactive maintenance lose between $10,000 and $250,000 per hour during outages because they miss production targets.
Companies that refine and improve their maintenance workflows are better equipped for proactive maintenance and new process development.
A good maintenance workflow will give you:
- Helps with compliance with regulations by having explicit steps and assigned tasks to prevent non-compliance.
- It clarifies procedural sequence so team members know what to do and what to act upon.
- Keeps equipment running optimally so there’s less chance of faults that can put workers or customers at risk.
- Contributes to a safer workplace by having regular checks and balances on asset health.

Source: WorkTrek
CMMS for Maintenance Workflow
Implementing CMMS software offers numerous advantages, including:
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency: Automating manual tasks reduces errors and speeds up maintenance tasks.
- Better Communication: Facilitates communication between maintenance teams so everyone is on the same page.
- Centralized Data Management: One platform for all maintenance data, so it’s easy to access and analyze.
- Predictive Maintenance: Uses data analytics to predict when equipment will likely fail, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing unexpected downtime.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure all maintenance activities comply with industry regulations and standards to reduce the risk of non-compliance penalties.
- Cost Savings: CMMS can save you a lot by optimizing maintenance schedules and reducing downtime.
- Asset Lifecycle Management: Helps you track asset lifecycle so you can make informed decisions on repairs, replacements and upgrades.
- Resource Allocation: Optimizes resource allocation so you can make informed decisions on repairs, replacements, and upgrades.
- Mobile Access: Many CMMS solutions offer mobile access, allowing maintenance teams to update and access information on the go.
- Customizable Reports: Generates detailed and customizable reports that provide insights into maintenance performance, helping in continuous improvement.
In facilities management, CMMS is used to manage maintenance tasks. 58% of these facilities use maintenance management software to simplify operations and comply with regulations.
Automating Work Orders
A CMMS allows you to manage, track, and complete work orders through its mobile features. This will automate the inclusion of:
- Maintenance and facilities information
- Checklists
- Priority levels based on urgency
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
- Asset Maintenance History
- Instruction manuals
- Visual aids like images
- Observations and notes
This will simplify and standardize the whole process.
Maintenance History Tracking
A CMMS database will track tasks from start to finish so you can have traceability and accountability. Monitoring asset performance over time in a CMMS will help you identify the required maintenance and basis for decisions.
Using historical data will improve planning for maintenance and refine the scheduling process.
Maintenance Planning Best Practices
A maintenance planner is key to a robust asset management system. They simplify maintenance by prioritizing assets, doing regular assessments, and setting SMART goals for all maintenance activities.
These industry best practices will help you organize maintenance tasks, optimize resource utilization, and improve the maintenance planning process through continuous improvement.

Source: WorkTrek
Critical Assets
A criticality analysis is required to rank assets and prioritize maintenance activities objectively. This will remove personal bias and ensure assets are prioritized based on criticality.
To calculate equipment criticality, follow these steps:
- Determine the failure frequency per year for each asset.
- Calculate the cost consequence, including the cost of lost production and repair costs.
- Multiply the failure frequency per year with the cost consequence to get the equipment criticality.
Following this process, you can prioritize maintenance activities and allocate resources where needed.
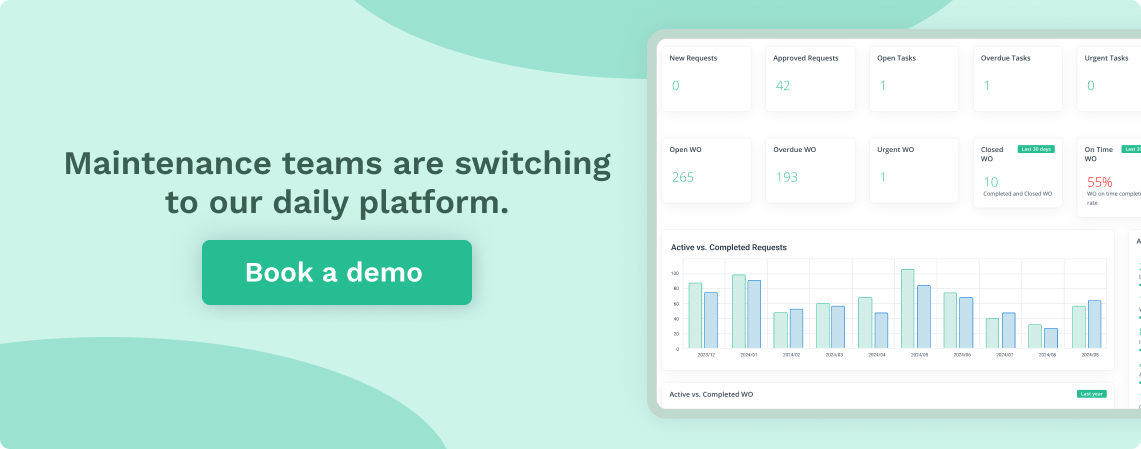
High-criticality assets may require predictive or prescriptive maintenance to prevent severe impact. Low-criticality assets with multiple redundancies may only require preventive or reactive maintenance. Using the P-F curve will help you prioritize maintenance for critical assets by showing potential failure points.
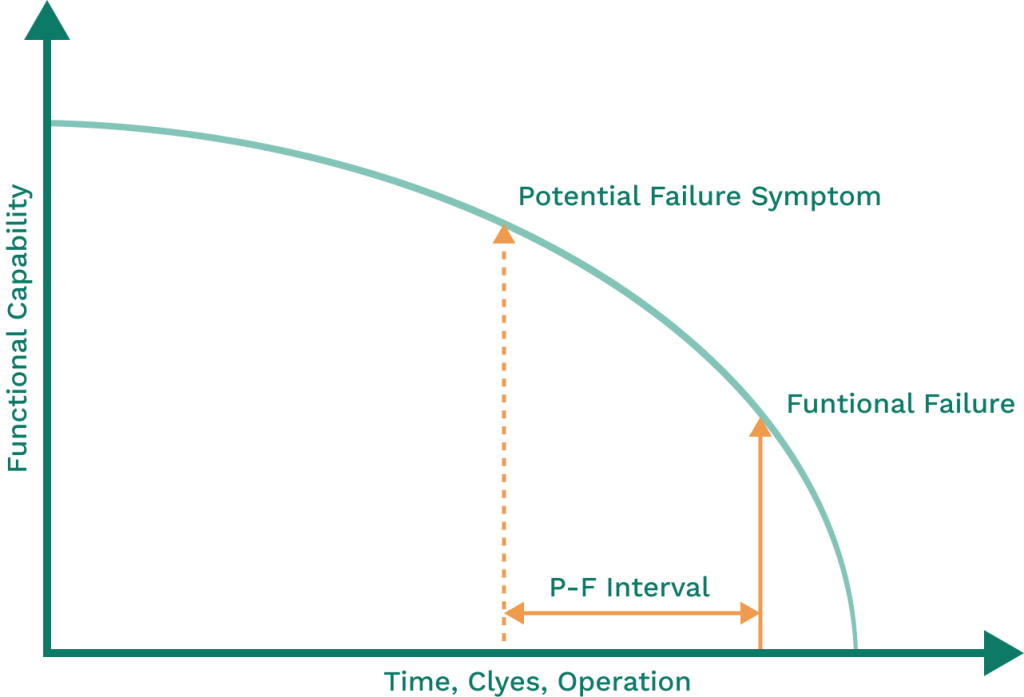
Source: WorkTrek
Regular Audits
Regular inspections are key to following maintenance protocols and the system. They can also be a tool to find areas for improvement. By breaking down the sequence of actions in maintenance workflows, you can spot inefficiencies by comparing the current process against the designed process and seeing what extra steps are there.
These audits can check the preventive maintenance schedule and checklist and highlight changes required to keep it practical.
Maintenance Workflow Improvement
Communication failures, a lack of standard processes, and insufficient resource allocation are common workflow issues in maintenance. To fix these issues, you need better communication methods, standardized processes across operations, and practical resource allocation.
A root cause analysis will help you identify inefficient areas in the maintenance system and allow you to make the necessary adjustments.
Maintenance Workflows
To improve maintenance workflows, you need to overcome cultural barriers, fully involve staff, and set clear key performance indicators (KPIs). Any changes will require buy-in from all parties, especially those in leadership positions.
Assessing changes to operations and reviewing outputs and processes regularly will help optimize resource allocation.
Education and active communication with staff is key to ensuring everyone understands and follows the updated protocols and objectives.
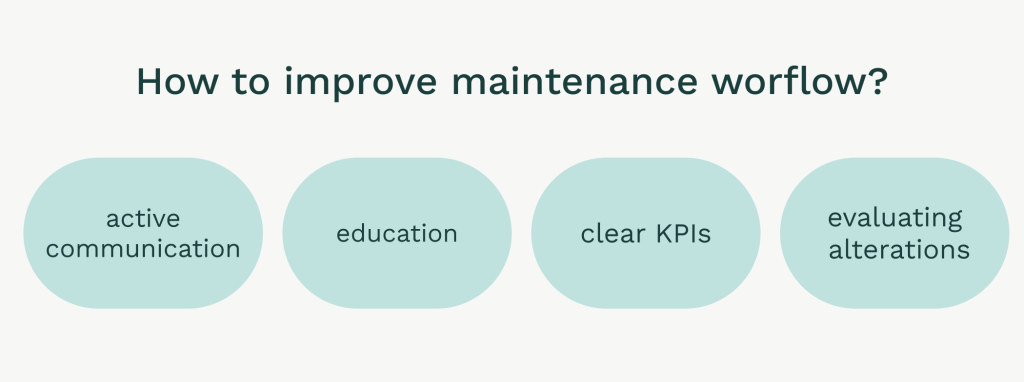
Source: WorkTrek
Unattended Work Requests
Having a centralized work request management system through CMMS will make the process more efficient with fast and accurate assessments. Categorizing these work requests will allow tasks to be prioritized based on criticality and impact on the business.
Having standard forms for work requests will help with consistency and reduce duplication of work.
Source: WorkTrek
On-Time Task Completion
Fixed or floating preventive maintenance will help monitor completed tasks more closely. The benefits of having this scheduled maintenance are:

- On-time task completion
- Verify that maintenance tasks are done as planned
- Better management of work requests throughout their life cycle
With these structured and planned maintenance methods, you can improve the efficiency of your operations.
Train Your Maintenance Team
Training your maintenance technicians will improve efficiency and productivity by enabling them to perform fast and accurate maintenance tasks. Training sessions for staff responsible for maintaining assets are key to improving communication and understanding of complex equipment.
Hands-on training for maintenance personnel will help them experience complex systems, and on-the-job training will allow them to gain practical skills applicable to their work environment.
Source: WorkTrek
Regular training sessions ensure that maintenance staff can:
-
Operate and repair new and advanced equipment safely
-
Identify areas where individuals or teams are underperforming and need to improve
-
Improve problem-solving skills so maintenance staff can handle complex issues efficiently
Training programs are key to high performance and safety of maintenance operations.
Source: WorkTrek
Monitor and Improve Maintenance Performance
Using key performance indicators (KPIs) will help you measure maintenance task efficiency and on-time performance. KPIs are used by maintenance teams to monitor routines, processes, and equipment performance.
Examples of KPIs are Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) which measures the average time between failures of repairable equipment and indicates machine reliability and Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) which indicates the average time to repair an asset, lower is better.
Other KPIs are availability, which is the ability of an asset to perform a function at a given time, and reliability, which is the probability of an investment performing its intended function under specific conditions for a certain period. Monitoring these KPIs will help maintenance teams identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to improve maintenance performance.
Source: WorkTrek
Preventive Maintenance Programs
A preventive maintenance program is a strategic approach to servicing and maintaining equipment before problems occur. Its main objective is to have assets running efficiently, reducing the risk of equipment failure and unexpected downtime.
Facilities can avoid costly emergency repairs and replace machinery prematurely by having a preventive maintenance plan.
The following are types of strategies under preventive maintenance:
- Maintenance on a fixed-time basis
- Maintenance based on usage
- Maintenance based on equipment condition
- Predictive for foreseeing potential failures to prevent breakdowns
By following these strategies, you will extend machine life and consistent maintenance and attention.
By implementing these proactive measures, facilities can reduce their maintenance costs by up to 18%.
Summary
Maintenance workflows are key to asset management, downtime reduction, safety, and compliance. Organizations can improve their maintenance process by knowing the steps of a maintenance workflow, using CMMS for optimization, and following best practices for maintenance planning.
Having preventive maintenance programs, overcoming common challenges, and training maintenance teams are important to equipment performance. By monitoring and improving maintenance performance through KPIs, organizations can keep their assets in top shape, resulting to higher efficiency, cost savings, reduced replacement costs and safer work environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key steps in a maintenance workflow?
It is crucial to develop an efficient maintenance workflow to pinpoint tasks associated with maintenance, organize scheduled activities about upkeep, and carry out work orders. This process guarantees that equipment receives appropriate maintenance, remains operational, and people involved are notified.
How does CMMS help in optimizing maintenance workflows?
A CMMS streamlines maintenance workflows by monitoring work orders, managing inventory, and recording maintenance history. It automates the issuance of work orders and offers a consolidated repository for maintaining records, enhancing accountability, and tracking within maintenance operations.
Why is preventive maintenance necessary?
Preventive maintenance is crucial for maintaining equipment. It ensures that assets remain in the best possible state, diminishes the likelihood of equipment breakdowns, and ultimately contributes to financial savings by avoiding costly unplanned emergency repairs.
What are some common challenges in maintenance workflows?
Difficulties in maintenance workflows include communication failures, the absence of uniform protocols, and insufficient resource allocation. These elements can markedly impact both the proficiency and the efficacy with which maintenance processes are conducted.
What are key performance indicators (KPIs) in maintenance?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as MTBF, MTTR, availability, reliability, and backlog are essential for assessing the effectiveness and promptness of maintenance tasks. They offer a crucial understanding of how sound maintenance is performed and are a significant resource for making informed decisions regarding maintenance tasks.










