Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIntroduction
CMMS in Remote work has become increasingly popular and widespread, particularly with advancements in technology and changes in workplace dynamics. The COVID-19 pandemic further accelerated the adoption of remote work as organizations shifted to remote operations to ensure employee safety and business continuity. As a result, remote work is now a common and viable option for many employees and organizations worldwide.
What is CMMS?
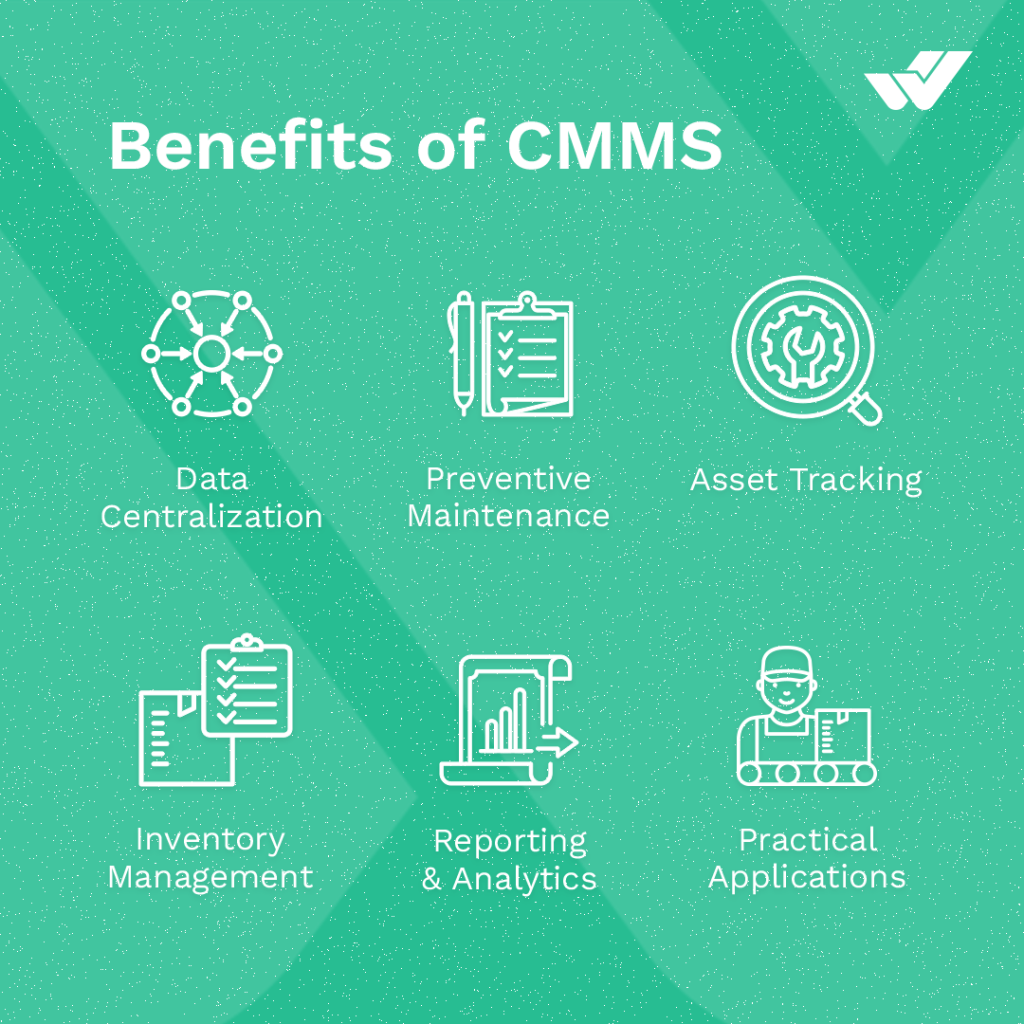
CMMS stands for Computerized Maintenance Management System. It’s a software solution used by organizations to streamline maintenance operations, manage assets, schedule and track maintenance tasks, and optimize resources. CMMS software helps businesses keep track of equipment maintenance schedules, work orders, spare parts inventory, and maintenance histories. CMMS is used in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, facilities management, transportation, and utilities to improve maintenance efficiency, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of assets.
What is Remote Work?
Remote work, also known as telecommuting or telework, refers to a work arrangement in which employees perform their job duties from a location outside of the traditional office environment. Instead of commuting to a physical office, remote workers typically work from home, a co-working space, or any other location with an internet connection.
Key characteristics of remote work include:
Flexibility: Remote work offers flexibility in terms of where and when work is performed. Employees have the freedom to choose their work environment and set their own schedules, within the parameters established by their employer.
Technology-Enabled: Remote work relies heavily on technology, such as computers, internet connectivity, collaboration tools, and communication platforms, to facilitate work-related tasks, meetings, and interactions.
Communication: Effective communication is essential for remote work success. Remote workers rely on email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and other digital communication tools to stay connected with colleagues, supervisors, and clients.
Productivity: Remote work can lead to increased productivity for some individuals, as it eliminates commuting time, reduces distractions, and allows for a more customized work environment. However, it also presents challenges related to work-life balance, isolation, and maintaining focus.
Collaboration: While remote work allows employees to work independently, collaboration remains important for team projects and initiatives. Remote teams use collaborative platforms, project management tools, and virtual meetings to collaborate effectively and achieve shared goals.
Work-Life Balance: Remote work offers the potential for better work-life balance by allowing employees to avoid long commutes, spend more time with family, and pursue personal interests. However, it can also blur the boundaries between work and personal life, leading to challenges in disconnecting from work.
Remote Management: Managers play a crucial role in supporting and managing remote teams. Effective remote management involves setting clear expectations, providing support and resources, fostering communication and collaboration, and measuring performance based on outcomes rather than hours worked.
You may also like: Boosting productivity with CMMS
The Role of CMMS in Remote Working
CMMS platforms play a key role in supporting remote working by providing tools and functionality that enable maintenance teams to effectively manage assets, track maintenance activities, and collaborate remotely. Here’s how CMMS contributes to remote work:
Remote Access: CMMS software can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing maintenance technicians, supervisors, and managers to work remotely. This allows teams to view asset information, access work orders and update maintenance records from home, a coworking space or other remote locations.
Cloud-Based Solutions: Many CMMS platforms offer cloud-based solutions that allow users to access the system through a web browser or mobile app. Cloud-based CMMS software ensures that maintenance data is stored securely and accessible from anywhere, making remote working and collaboration easier.
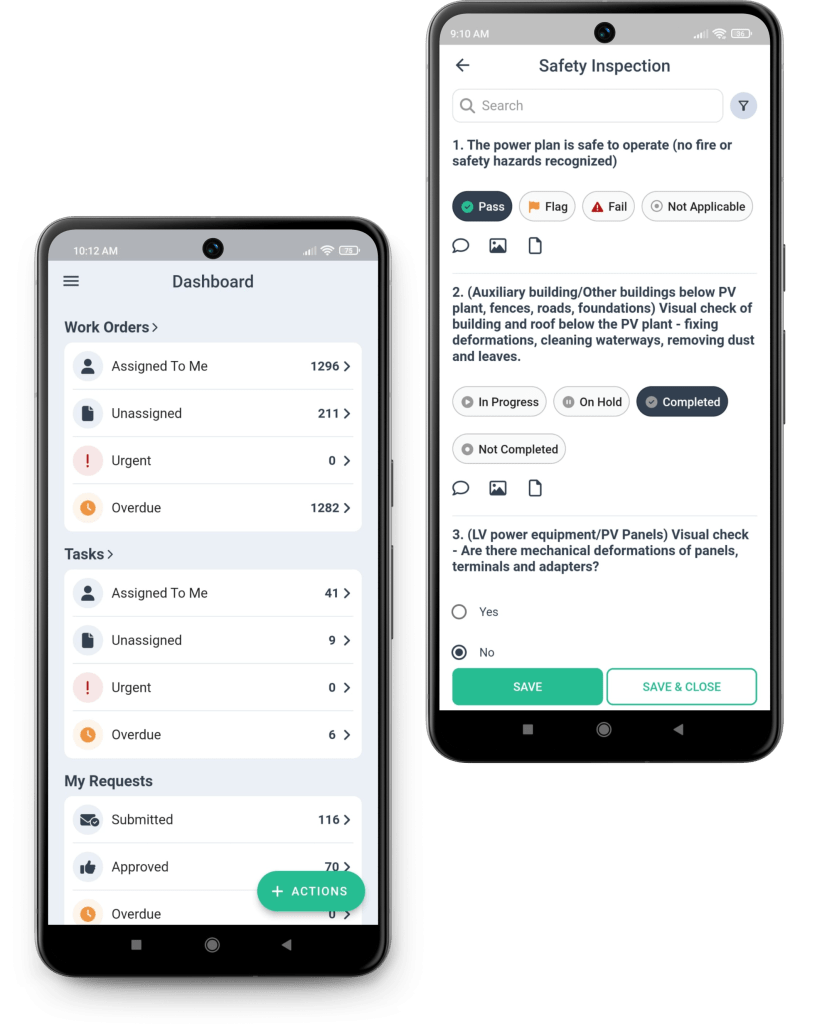
Mobile Capabilities: CMMS mobile apps allow maintenance technicians to perform tasks such as viewing work orders, updating task status and recording maintenance activities directly from their smartphone or tablet. Mobile capabilities enable remote workers to stay productive on the go without having to access a desktop computer.
Remote Monitoring and Alerting: CMMS systems can integrate with sensors, IoT devices, and other monitoring technologies to provide real-time data on equipment performance and health. Remote monitoring capabilities enable maintenance teams to identify issues, receive alerts and take proactive action from remote locations, minimizing downtime and optimizing asset reliability.
Collaboration Tools: CMMS platforms often include built-in collaboration tools such as messaging, commenting, and document sharing, allowing remote teams to communicate effectively and collaborate on maintenance projects. These tools facilitate teamwork, knowledge sharing, and decision-making even when team members are geographically dispersed.
Automated Workflows: CMMS software automates maintenance workflows and processes, streamlining tasks such as work order creation, assignment, and approval. Automated workflows ensure maintenance activities run smoothly even among remote team members, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency.
Reporting and Analysis: CMMS systems provide reporting and analysis tools to help maintenance teams analyze performance metrics, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and identify trends. With remote access to reports and analytical data, managers and supervisors can monitor maintenance operations, make data-driven decisions and optimize maintenance strategies from anywhere.

You may also like: CMMS vs Traditional Maintenance
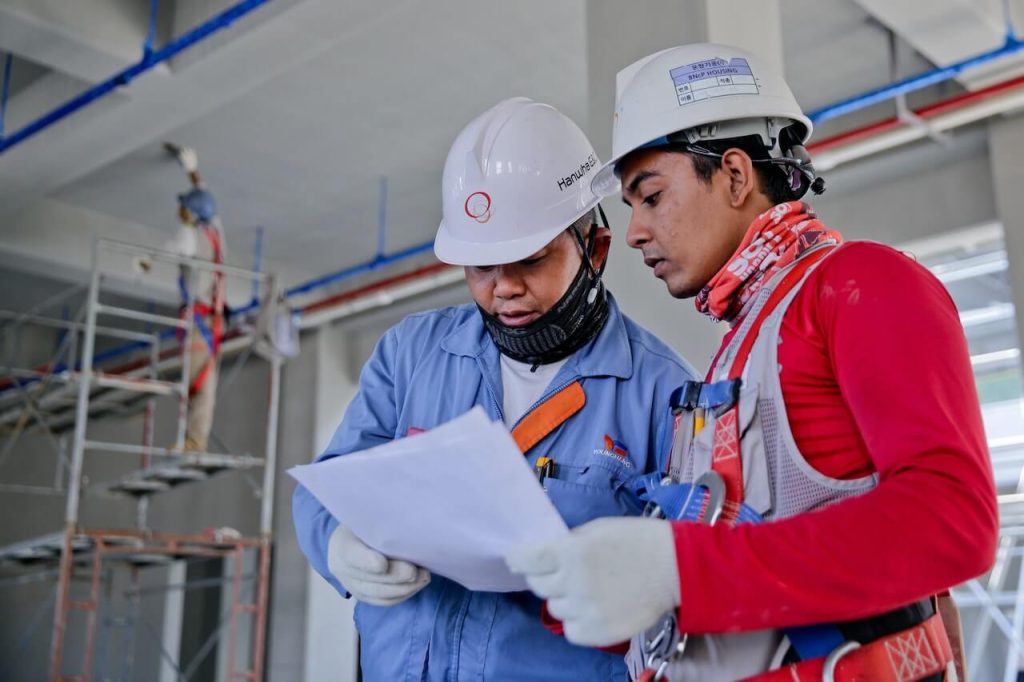

Remote Collaborative Maintenance
How to collaborate remotely with physical assets? What does it mean to fix a system together when everyone is not in the same place? What does remote maintenance actually look like?
Remote collaboration is particularly useful in manufacturing because equipment is often located in different parts of the factory or even in different parts of the world. In these situations, it may not always be possible or practical for maintenance professionals to travel to the equipment site to perform maintenance.
Maintenance teams can use a range of tools and technologies to facilitate remote collaboration. For example, video conferencing software allows maintenance professionals to communicate and share information in real time regardless of their physical location. This is particularly useful when solving problems or seeking advice from colleagues with expertise. In addition, managers can facilitate remote collaboration through remote monitoring and diagnostic tools, allowing maintenance professionals to remotely assess equipment health and identify potential issues.
You may also like: Common CMMS mistakes to avoid
Greater Mobility Among Technicians
For field technicians, CMMS mobile apps are an important tool to increase their efficiency and effectiveness. Using mobile devices, technicians can access work orders, document repairs, and update asset information in real time. Long gone are the days of carrying around cumbersome paperwork or relying on sporadic updates.
Consider a scenario where a technician is called to a remote location to perform an emergency repair. Equipped with the CMMS mobile app, they can instantly view equipment details, view historical maintenance records, and even consult remote experts through video calls to solve complex problems. Not only does this increase technician confidence, but it also ensures that the right decisions are made regardless of physical location.
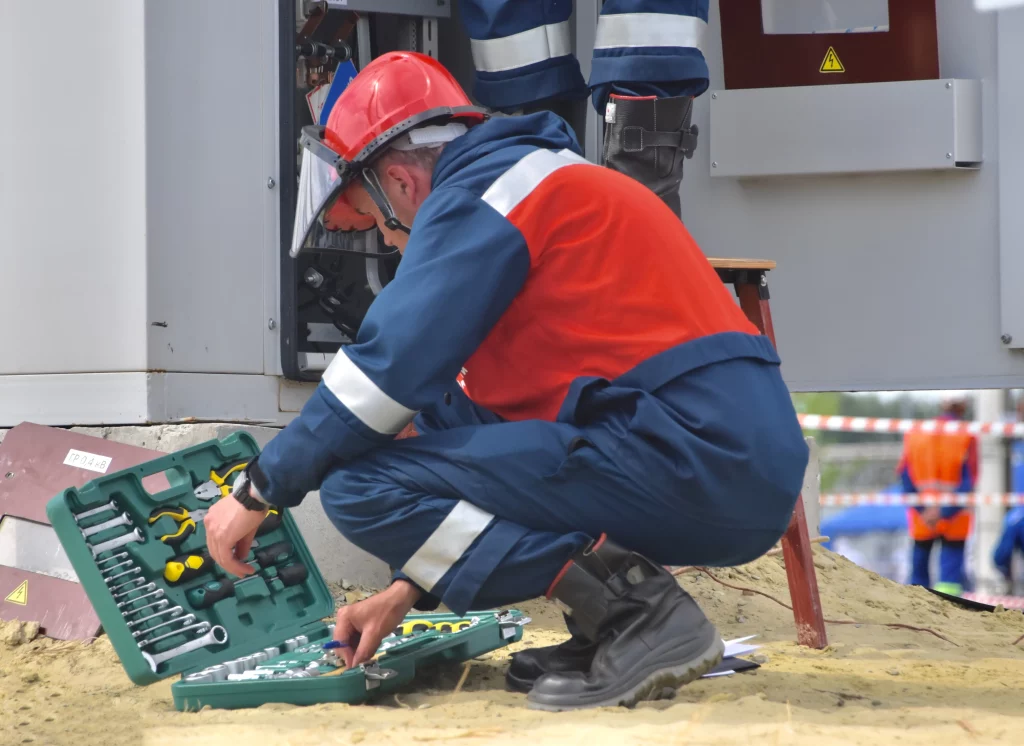

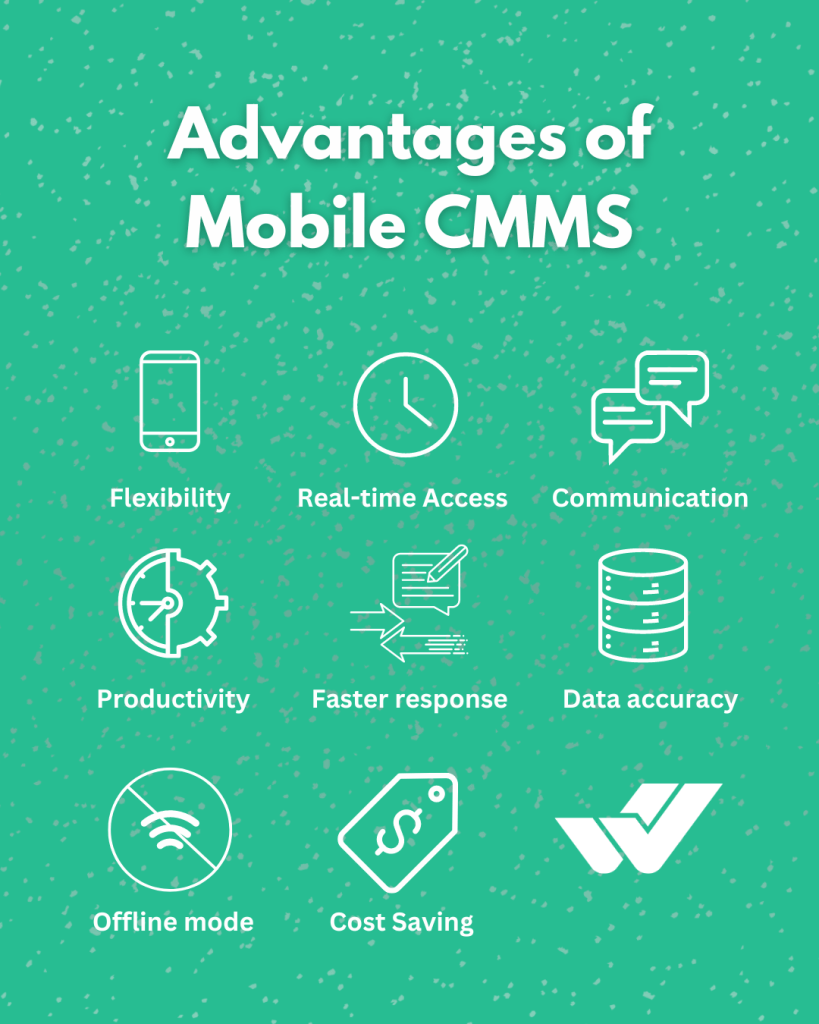
Advantages of Mobile CMMS for Remote Working
Mobile CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) offers several advantages for remote working environments:
Flexibility: A mobile CMMS provides flexibility in performing work by allowing maintenance technicians to access work orders, update task status, and record maintenance activities from anywhere. Technicians can work from home, in the field, or while traveling without being tied to a physical office.
Real-Time Access: A mobile CMMS provides real-time access to maintenance data and information, allowing technicians to view asset details, review maintenance plans and instantly access history from their smartphone or tablet. This ensures technicians have the information they need to complete their tasks efficiently, even when working remotely.
Improved Communications: Mobile CMMS facilitates communication between remote technicians, supervisors, and administrators through integrated messaging and collaboration tools. Technicians can communicate with colleagues in real time, request help and share the latest information, improving teamwork and coordination.
Increase Productivity: A mobile CMMS enables technicians to complete tasks, update records, and resolve maintenance issues remotely, maintaining productivity on the go. By eliminating the need to return to a central office to access information or perform administrative tasks, a mobile CMMS can help technicians make better use of their time and resources.
Faster Response Times: A mobile CMMS enables technicians to quickly respond to maintenance requests and emergencies, regardless of their location. Technicians can receive work orders, prioritize tasks and initiate repairs immediately via mobile devices, reducing downtime and minimizing service interruptions.
Improved Data Accuracy: A mobile CMMS allows technicians to capture and update maintenance data directly in the system while performing tasks in the field. This reduces the risk of data entry errors, ensures data accuracy and increases the reliability of maintained records.
Offline Functionality: Some CMMS mobile apps offer offline functionality, allowing technicians to continue working in areas with poor or no network connectivity. Technicians can access work orders, view asset information and log maintenance activities offline, with data automatically synchronized once connectivity is restored.
Cost Savings: Mobile CMMS helps companies save costs associated with paper-based processes, manual data entry, and travel expenses. A mobile CMMS helps save costs and increase operational efficiency by enabling remote working and increasing efficiency.
Mobile CMMS offers numerous benefits to remote work environments, including flexibility, real-time data access, improved communications, increased productivity, faster response times, improved data accuracy, offline capabilities, and cost savings. By leveraging the benefits of a mobile CMMS, companies can support remote technicians, streamline maintenance operations, and ensure business continuity even in remote or distributed work environments.
You may also like: Why your business needs a CMMS
What About CMMS Remote Training?
Remote CMMS training involves providing training and instruction on how to use CMMS software through online or virtual platforms. Remote training typically involves virtual sessions in which a trainer walks participants through CMMS software functionality and demonstrates how to enter and retrieve data, create reports, and optimize maintenance processes.
Training also covers preventive maintenance planning, work order management, inventory tracking and other functions necessary for efficient asset or equipment management. Remote CMMS training allows participants to access learning resources from different locations, thereby increasing flexibility and accessibility for different audiences. This approach allows companies to effectively train employees at their own pace without having to be physically present, making it a convenient and cost-effective solution. Let’s look at the pros and cons of remote CMMS training.
Advantages
Value for money:
- Remote training eliminates travel and accommodation costs, making it a more cost-effective option.
- Participants can attend training at their workplace or at home, reducing overall costs.
- Participants can receive training at their own pace and time.
Flexibility:
- Remote training provides scheduling flexibility and allows participants to choose a time that is convenient for them.
Training sessions can be recorded for future reference, allowing for autonomous learning. - Participants can review specific aspects of the training at their own time and pace.
- Remote training can accommodate multiple participants, whereas on-site training limits participants due to available space and facilities.
Global wide:
- Remote training can be taken regardless of where participants are located, making it suitable for companies with dispersed workforces.
- Remote training is particularly useful for shift workers.
Minimize distractions:
- Remote training minimizes disruption to daily operations because participants do not need to leave the workplace to participate.
Disadvantages
Limited practical experience:
- Participants may require additional opportunities to gain hands-on experience with the actual equipment and systems they will manage.
- Remote training has a general format and is not tailored to a specific process, equipment or industry.
Communication challenges:
- Remote training relies on virtual communication tools, which can create challenges in conveying complex concepts or providing instant clarification.
- Training does not provide opportunities for further breakdown or repetition of tasks as some users may require.
- The ability to obtain immediate or detailed feedback or support is limited.
Possible interference:
- Participants may experience distractions in a remote work environment, which may affect their focus, engagement, and motivation during training sessions.
Technical problem:
- Technical issues such as internet connectivity or software compatibility may cause interruptions in remote training.
Conclusion
Overall, CMMS system plays a key role in supporting remote working by providing remote access, cloud-based solutions, mobile capabilities, remote monitoring, collaboration tools, automated workflows, and reporting and analytics capabilities. By leveraging these capabilities, maintenance teams can effectively manage assets, track maintenance activities, and collaborate remotely to ensure continuity and efficiency of maintenance operations.