Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIn maintenance management, Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) is an important metric that is the proportion of total maintenance hours devoted to planned maintenance tasks compared to the total maintenance hours.
This metric is essential for efficient operations, reducing downtime, and optimizing maintenance costs. This article covers the various aspects of planned maintenance percentage, its calculation, and its significance in maintenance processes.

Source: Reliability Connect
Understanding Planned Maintenance
Planned maintenance is the scheduled and systematic approach to maintaining equipment and assets, which contributes to improving maintenance schedules. This proactive strategy includes preventive maintenance tasks designed to prevent equipment failure and extend the lifespan of assets.
It also gives the maintenance technician a predictable schedule, allowing organizations to control costs better.
Since planned maintenance tasks are performed during designated maintenance hours instead of reactive or unplanned maintenance tasks, which occur in response to unexpected equipment failures, labor rates are more predictable.
Calculate Planned Maintenance Percentage
Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) =
Planned Maintenance HoursTotal Maintenance Hours×100Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)=TotalMaintenance HoursPlanned Maintenance Hours×100
PMP reflects the portion of planned maintenance hours compared to the total hours worked. A high PMP reflects a well-structured maintenance strategy in which preventive measures take precedence over-reactive work.
This metric is crucial because it directly affects reduced downtime, improved asset reliability, and savings. By prioritizing planned maintenance, an organization can schedule such work during off-peak periods, allocate resources more effectively, and enhance workplace safety.
Moreover, tracking PMP helps optimize maintenance schedules and improve the efficiency of maintenance teams. An organization with a high PMP will tend to have fewer emergency repairs, which can be expensive and disruptive.
This will enable the maintenance manager to determine the maintenance workload, prepare the necessary materials and tools, and guarantee that technicians are available and competent to do the job.
High PMP reflects that a well-planned maintenance program shows proactive asset management, leading to longer asset life cycles and better alignment with business objectives.
This formula helps the maintenance manager evaluate the efficiency of his maintenance program in showing the right balance between planned and unplanned maintenance activities.

Source: WorkTrek
Importance of PMP in Maintenance Processes
- Improving Asset Reliability: A higher PMP indicates a well-maintained asset management system, reducing the likelihood of unexpected equipment failure and unplanned downtime. This leads to improved asset reliability and overall operational efficiency.
- Cost Control: Planned maintenance allows for better budgeting and resource allocation, leading to controlled maintenance costs. Unplanned maintenance is often more expensive due to emergency repairs and expedited spare parts procurement.
- Enhanced Maintenance Planning: By focusing on planned maintenance, maintenance teams can ensure proper planning and scheduling, leading to better resource utilization and reduced disruptions in production processes.
Planned and Unplanned Maintenance
Planned maintenance encompasses scheduled activities like inspections, lubrication, adjustments, and part replacements based on a predetermined schedule. On the other hand, unplanned maintenance refers to reactive maintenance tasks that arise unexpectedly, often due to equipment failure.
Improving planned maintenance workflows will reduce asset failure, improve asset reliability, and reduce maintenance time. It can enhance total productive maintenance and delivery times for the maintenance department.
Planning Maintenance Hours for Improved Processes
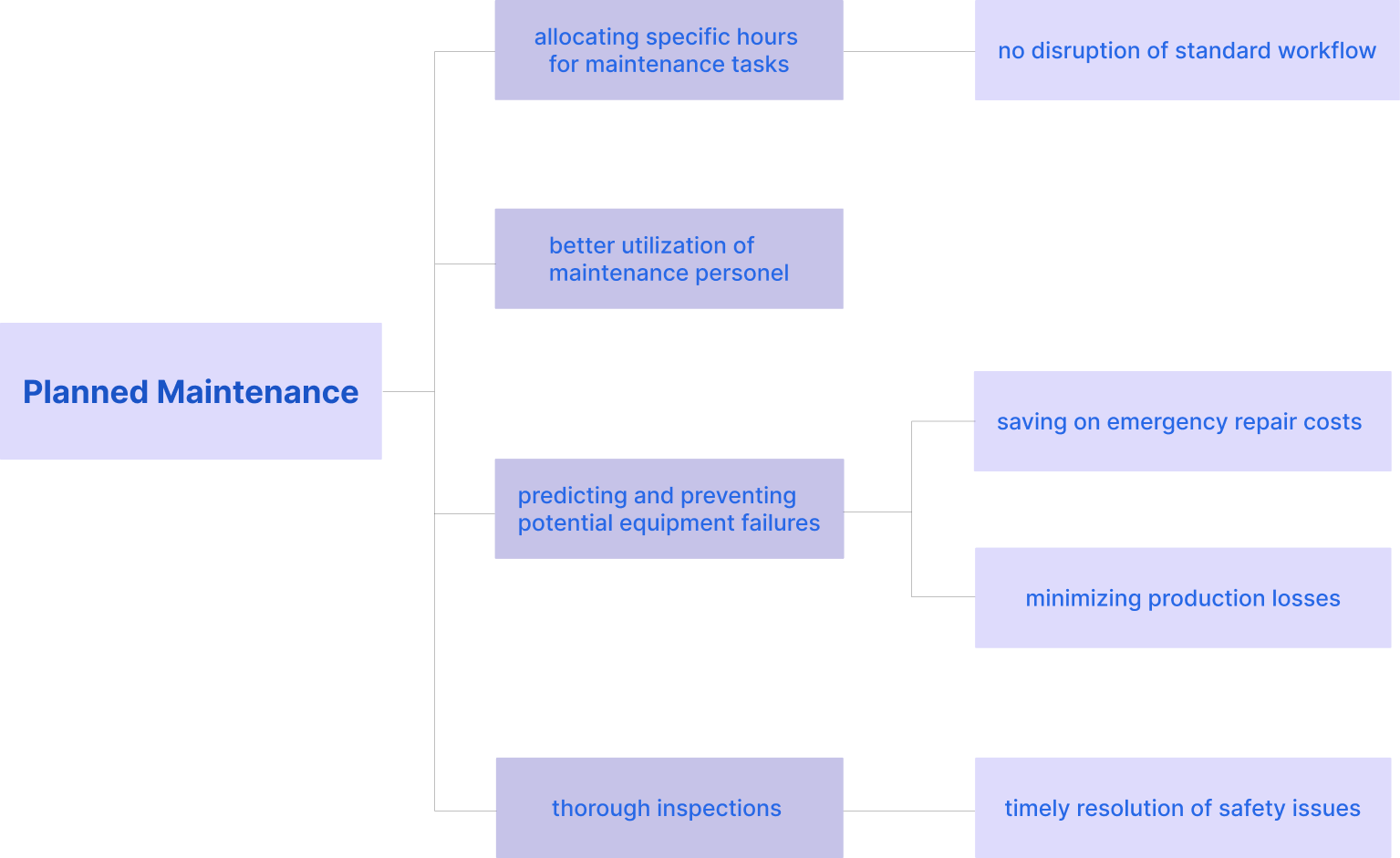
Allocating specific hours for maintenance tasks is a strategic approach that can significantly enhance maintenance. Organizations can ensure maintenance activities are conducted without disrupting the standard workflow by scheduling dedicated time slots for routine checks, repairs, and updates.
This planning also allows for better utilization of maintenance personnel, as tasks can be aligned with their expertise and availability, leading to more efficient operations and reduced downtime.
Proactive maintenance hour planning also aids in predicting and preventing potential equipment failures, thereby saving on emergency repair costs and minimizing production losses.
Furthermore, planned maintenance hours contribute to a safer working environment, allowing for thorough inspections and timely resolution of any safety issues. They also help maintain a high level of equipment reliability and performance, which is crucial for the long-term success of any operation.
By incorporating planned maintenance into their routine, organizations can streamline their maintenance processes, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately improve their bottom line through increased operational efficiency and equipment longevity.
Source: WorkTrek
Improving Planned Maintenance Percentage
- Preventive Maintenance Program: A robust preventive maintenance program improves PMP. This involves regularly scheduled maintenance activities aimed at preventing equipment failures.
- Proper Documentation: Ensuring adequate documentation of maintenance activities helps track and analyze maintenance data, which is crucial for improving PMP. Maintenance technicians should record all maintenance tasks, including planned and unplanned activities.
- CMMS Software: Utilizing a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software can significantly improve PMP by automating maintenance schedules, tracking maintenance hours, and providing data-driven insights for better decision-making.
- Training and Development: Regular training for maintenance technicians and the maintenance team ensures they have the necessary skills and knowledge to perform planned maintenance tasks efficiently.
- Continuous Improvement: Adopting a constant improvement approach allows maintenance managers to continually identify trends, analyze maintenance data, and implement necessary procedures to enhance maintenance processes.
Measuring Planned Maintenance Percentage
To measure PMP effectively, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- Time Period: Define a specific period for measuring PMP, such as weekly, monthly, or annually. This helps you track trends and make informed decisions.
- Maintenance Schedule Compliance: Ensure that maintenance schedules are adhered to and any deviations are recorded and analyzed.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources, including maintenance technicians and spare parts, efficiently to planned maintenance activities.
- Data Collection: Collect accurate data on maintenance hours, including planned and unplanned maintenance activities.
Challenges in Maintaining High PMP
- Reactive Maintenance Culture: Organizations with a reactive maintenance culture may find it challenging to shift to a more proactive approach, which can affect PMP.
- Insufficient Resources: Lack of sufficient resources, such as skilled technicians and spare parts, can hinder the execution of planned maintenance tasks.
- Unexpected Equipment Failures: Frequent failures can disrupt planned maintenance schedules, leading to a lower PMP.
Benefits of a High Planned Maintenance Percentage
- Reduced Downtime: A high PMP indicates a proactive maintenance approach, which reduces unplanned downtime and increases operational efficiency.
- Improved Asset Lifespan: Regularly planned maintenance activities help in extending the lifespan of critical equipment and assets.
- Cost Savings: A high PMP can lead to significant cost savings by reducing the need for emergency repairs and optimizing resource allocation.
- Greater Control: Maintenance managers have greater control over maintenance processes, leading to improved schedule compliance and better overall maintenance management.
Implementing Effective Maintenance Programs
- Developing Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establish clear SOPs for all maintenance activities to ensure consistency and quality in maintenance work.
- Regular Audits and Inspections: Conduct regular audits and inspections to ensure compliance with maintenance schedules and identify areas for improvement.
- Collaborative Approach: Foster collaboration between maintenance teams, production teams, and other stakeholders to ensure alignment and effective communication.
- Utilizing Diagnostic Tools: Employ diagnostic tools and technologies to monitor equipment health and predict potential failures, enabling timely planned maintenance activities.
Using CMMS Software to Improve Planned Maintenance Percentage
One of the primary benefits of Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software is its ability to enhance the planned maintenance percentage, which refers to the proportion of maintenance activities scheduled and performed before any issues arise, as opposed to reactive maintenance tasks that occur after a failure.
For example, a manufacturing plant can use CMMS to schedule regular inspections and servicing of conveyor belts, ensuring they are always in optimal condition and reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns. This proactive approach not only prevents costly downtime but also extends the lifespan of the equipment.
Moreover, CMMS software can automatically generate work orders based on predefined maintenance intervals or equipment usage thresholds. Take, for instance, a fleet management company that implements CMMS to track vehicle usage.
The software can be configured for fleets to prompt oil changes and tire rotations based on mileage, which aligns maintenance tasks more closely with vehicle wear and tear. This leads to a higher planned maintenance percentage and a more efficient allocation of maintenance resources, ultimately decreasing unplanned downtime and increasing reliability.
Source: WorkTrek
Case Study: Improving PMP in an Automotive Factory
An automotive factory implemented a series of measures to improve its PMP. By adopting a preventive maintenance program, utilizing CMMS software, and ensuring proper documentation, the factory increased its PMP from 60% to 85% within a year. This improvement reduced unplanned downtime, cost savings, and enhanced asset reliability.

Conclusion
The planned maintenance percentage is a vital metric in maintenance management, which can directly reflect the effectiveness of a facility’s maintenance program. By focusing on planned maintenance tasks, improving maintenance schedules, and utilizing modern technologies, organizations can enhance their PMP, leading to better asset management, reduced downtime, and significant cost savings.
Maintenance managers must prioritize planned maintenance activities and adopt a proactive approach to ensure their assets’ long-term success and reliability.
FAQ
Q: What is the Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)? A: Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) is a metric that represents the proportion of total maintenance hours spent on planned maintenance tasks compared to the total maintenance hours.
Q: How is Planned Maintenance Percentage calculated? A: PMP is calculated using the formula: PMP=(Planned Maintenance HoursTotal Maintenance Hours)×100PMP=(Total Maintenance HoursPlanned Maintenance Hours)×100.
Q: Why is PMP important in maintenance management? A: PMP is essential because it helps improve asset reliability, control maintenance costs, enhance maintenance planning, and reduce unplanned downtime.
Q: What are the benefits of a high Planned Maintenance Percentage? A: The benefits include reduced downtime, improved asset lifespan, cost savings, and greater control over maintenance processes.
Q: How can I improve my facility’s PMP? A: Improve PMP by implementing a preventive maintenance program, ensuring proper documentation, using CMMS software, providing regular training, and adopting continuous improvement practices.
Q: What challenges might affect achieving a high PMP? A: Challenges include a reactive maintenance culture, insufficient resources, and unexpected equipment failures.
Q: How does CMMS software help in improving PMP? A: CMMS software helps by automating maintenance schedules, tracking maintenance hours, providing data-driven insights, and ensuring proper documentation of maintenance activities.
Q: What is the difference between planned and unplanned maintenance? A: Planned maintenance involves scheduled tasks to prevent equipment failure, while unplanned maintenance refers to reactive tasks that address unexpected equipment failures.
Q: Why is proper documentation necessary in maintenance management? A: Proper documentation is vital for tracking maintenance activities, analyzing data, improving PMP, and ensuring compliance with maintenance schedules.