Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIntroduction
Root cause analysis (RCA) and detailed equipment records in a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) can help solve difficult equipment and process problems.
Many companies struggle with RCA issues on equipment and processes. Many maintenance departments are so busy fighting fires that they have little time to investigate the root cause of equipment malfunctions or process failures.
You often hear maintenance people say “That machine” or “that part” broke again, and then they go out to fix it. Usually, the problem has happened so many times that they know what to do and can usually fix it pretty quickly. Very few people take the time, or have the time, to really dig into the problem and see what’s really going on.
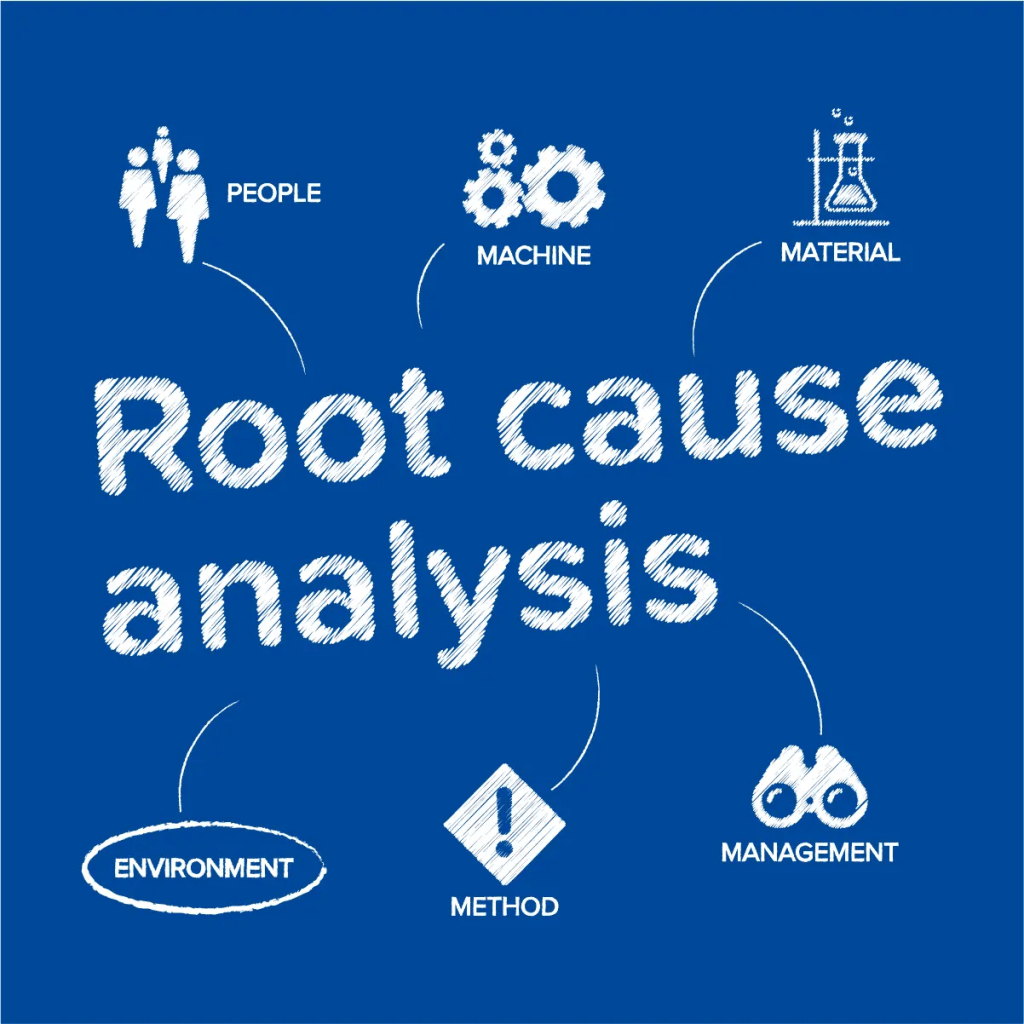
What is a Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify the underlying causes of problems or issues within a system, process, or situation. The goal of RCA is to go beyond addressing the immediate symptoms and instead focus on understanding and addressing the root causes to prevent the recurrence of problems.
The process typically involves several steps:
Problem Identification: Clearly define the problem or issue that needs to be addressed. This could be a quality problem, a safety incident, a process failure, or any other issue.
Data Collection: Gather relevant data and information about the problem. This may involve reviewing documents, conducting interviews, analyzing records, and collecting data from various sources.
Cause and Effect Analysis: Use tools such as Fishbone Diagrams (Ishikawa diagrams) or Fault Tree Analysis to map out the possible causes and their relationships. This helps in visually organizing and understanding the factors contributing to the problem.
Verify Root Causes: Validate the identified root causes through data analysis, expert input, or other means to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Implementation of Solutions: Put the recommended solutions into action. This may involve changes to processes, procedures, training programs, or other aspects of the system.
Monitor and Evaluate: Track the implementation of solutions and monitor their effectiveness over time. Evaluate the impact of the changes to ensure that the problem is indeed resolved and that there are no unintended consequences.
How does RCA Work?
RCA is based on the principle that all events are causally related.
Simply responding to the effects of adverse events is not always enough. To completely solve the problem, we must trace the events back to the original “falling dominoes.”
Simply put, root cause analysis helps you understand what happened, how it happened, and why it happened. The process is based on the “Three R’s”:
Recognize: Keep in mind that if an asset fails, you may not be able to determine the true cause of the event through simple observation. What you are observing is just a symptom. Determine the real cause of the problem to prevent it from happening again in the future.
Remedy: Once you determine the root cause of the problem, take corrective action. Then monitor the system to see if the problem recurs. If the problem reoccurs, your team may confuse part of the cause with the root cause. In this case, go back to the drawing board and do a more thorough RCA.
Repeat: Finally, replicate the working solution in other locations using similar assets. This prevents the same error from occurring in other areas of the system.
Importance of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is important for several reasons across various industries. Here are some key aspects that highlight its significance:
Preventing Recurrence: The primary goal of RCA is to identify and address the root causes of problems or issues. By doing so, organizations can implement corrective actions that not only resolve the current problem but also prevent its recurrence. This proactive approach contributes to long-term improvement and stability.
Cost Reduction: Addressing root causes helps in eliminating inefficiencies and reducing the costs associated with recurring problems. Instead of repeatedly dealing with the symptoms of an issue, organizations can invest resources in implementing long-term solutions, leading to cost savings over time.
Enhancing Quality and Reliability: Understanding the root causes of defects or failures allows organizations to improve the quality and reliability of their products or services. This is particularly crucial in industries where safety, precision, and consistency are paramount, such as healthcare, aviation, and manufacturing.
Risk Management: RCA contributes to effective risk management by identifying and mitigating potential risks before they escalate into significant problems. This proactive approach helps organizations avoid crises and enhances their overall resilience.
Customer Satisfaction: Resolving issues at their root enhances the quality and reliability of products and services, leading to increased customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend the organization to others.
In summary, Root Cause Analysis is crucial for organizations aiming to improve their processes, products, and overall performance. It provides a structured method for identifying and addressing the underlying causes of problems, leading to sustained improvements and increased organizational effectiveness.

When to Perform Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a valuable tool that can be applied in various situations to identify and address the underlying causes of problems. Here are some common scenarios in which performing RCA is particularly beneficial:
Recurring Issues: When a problem or issue continues to recur, it indicates that addressing only the symptoms is not sufficient. RCA can help in uncovering the root causes and implementing corrective actions to prevent the issue from happening again.
Significant Failures or Incidents: Following major equipment failures, accidents, or incidents, conducting an RCA is crucial. Understanding the root causes of significant events helps prevent their recurrence and enhances overall safety and reliability.
Quality Issues: If there are consistent quality problems in products or services, RCA can be employed to identify the factors leading to these issues. This is especially important in industries where product quality is a critical factor.
Safety Incidents: In situations where safety is compromised, conducting an RCA is essential. This applies to industries such as manufacturing, construction, and healthcare, where safety incidents can have severe consequences.
Process Failures: When processes are not meeting performance expectations or are consistently failing, RCA can help uncover the reasons behind these failures. This is crucial for improving efficiency and productivity.
Customer Complaints: If there is a pattern of customer complaints, performing an RCA can help identify the root causes of dissatisfaction. Addressing these causes can improve customer satisfaction and prevent future complaints.
Unexpected Variations: In manufacturing or other processes where consistency is crucial, unexpected variations or deviations may occur. RCA can help identify the reasons behind these variations and implement corrective actions.
It’s important to note that RCA is a versatile tool that can be applied in various industries and contexts. The decision to perform RCA should be based on the significance of the problem, the potential impact on operations, safety considerations, and the organization’s commitment to continuous improvement.

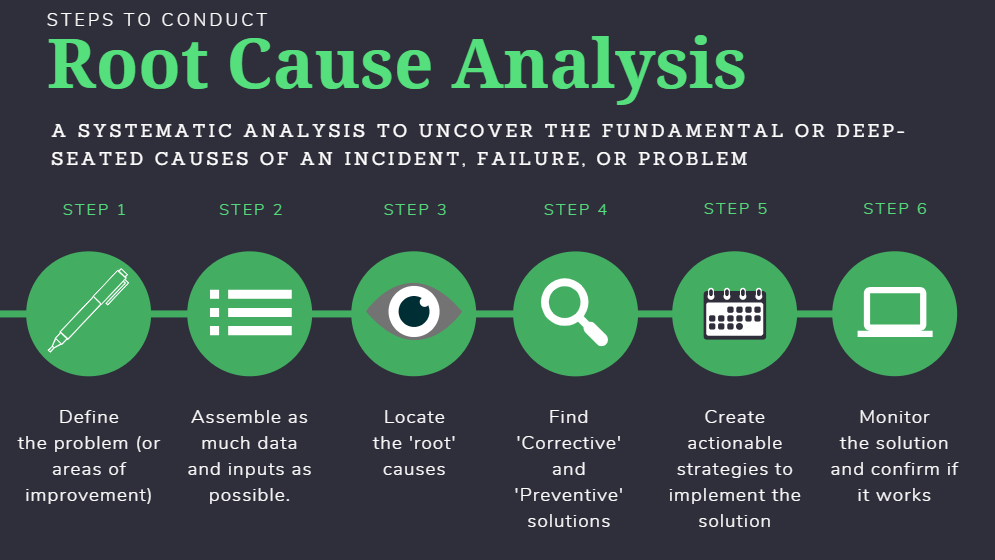
How to Conduct Root Cause Analysis in 6 Steps?
Best practices for effective root cause analysis require completing the following steps: defining the problem, collecting data, identifying additional causes, determining the root cause, prioritizing the cause, and implementing a solution.
1. Define the problem
The first step in root cause analysis is to analyze the existing situation. Here, the team identifies the factors that influenced the problem event. The result of this step is a statement that contains the specific problem. A small team is tasked with defining the problem. They can be research assistants who evaluate and analyze situations. The questions that need to be answered at this initial stage are: What is the problem? How does this issue impact customer demand? Etc.
2. Gather data about the problem
A key step in root cause analysis is collecting relevant data about an incident or problem event. Logging all the features and specifications of an event will help you answer questions like: What were the influencing factors? When did it occur? Is this a recurring event? What is the observed effect? Etc.
3. Identify possible causative factors
Creating a sequence of events is important to identify causal factors that may have caused the observed problem or event. The project team responsible for analyzing the problem should create a timeline of events and summarize as many potential causal factors as possible by asking the question “Why?” question. For example, using a cause-and-effect diagram can help visually show the connections between events and allow you to trace root causes.
4. Determine the root cause of the problem
Now is the time to find out as many reasons as possible. The analytics team can use techniques such as 5 Whys analysis, fishbone analysis, or Pareto charts to narrow down the potential causes and key contributing factors to the problem. This phase should involve stakeholders and other relevant teams.
5. Prioritize why
Once the root cause is identified, it needs to be prioritized and addressed accordingly. To determine which cause or challenge needs to be addressed first, the analytics team must assess the impact of that cause – the greater the impact, the higher the priority. Another point to consider when prioritizing root causes is the number of causal factors that arise from a particular challenge – the greater the number of causal factors, the greater the impact of the root cause and the greater the need for immediate resolution.
6. Solutions, suggestions, and implementation
Once the root causes have been identified and prioritized, the next step is to find solutions to the problem and implement them. Brainstorming is a great way to try and develop different possible solution scenarios. Another approach is to survey as many people as possible. Gathering input and implementing solutions requires everyone’s participation. On the one hand, every recommendation is important, but on the other hand, successful implementation is what makes it stick for everyone affected.

What is the Role Of CMMS in Root Cause Analysis?
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) play a significant role in facilitating Root Cause Analysis (RCA) by providing a structured framework for managing and analyzing maintenance-related data. Here are several ways in which WorkTrek CMMS contributes to the RCA process:
Data Collection and Storage: CMMS systems store vast amounts of historical maintenance data, including work orders, equipment failure reports, and maintenance activities. This data serves as a valuable resource for identifying patterns and trends related to equipment failures or performance issues.
Maintenance History Tracking: CMMS keeps a detailed record of maintenance activities, repairs, and replacements over time. This historical maintenance data is essential for RCA, allowing analysts to trace the performance of equipment and identify recurring issues.
Failure Analysis: CMMS tools often include features that help in categorizing and analyzing equipment failures. By using codes or categories, maintenance teams can quickly identify the types and frequencies of failures, which is crucial for identifying potential root causes.
Work Order Tracking: CMMS systems enable the tracking of work orders, providing information on the tasks performed, parts used, and associated costs. This information can be valuable in understanding the effectiveness of past maintenance efforts and identifying areas for improvement.
Equipment Reliability Metrics: CMMS allows organizations to generate reliability metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) related to equipment performance. Analyzing these metrics can reveal trends and patterns that may indicate underlying issues requiring further investigation through RCA.
Prioritizing Maintenance Activities: CMMS assists in prioritizing maintenance activities based on criticality and historical data. This prioritization ensures that resources are allocated efficiently to address the most significant issues first, contributing to a more effective RCA process.

How to Use CMMS for Root Cause Analysis?
Using a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) involves leveraging the system’s features and capabilities to gather, organize, and analyze maintenance data. Here are steps and considerations for using CMMS in the RCA process:
Capture Detailed Maintenance Data: Ensure that your CMMS is configured to capture comprehensive maintenance data. This includes details about work orders, equipment history, spare parts usage, and any other relevant information. The more detailed the data, the better insights you can gain during the RCA process.
Document Equipment Failures: Use the CMMS to document equipment failures and issues. Include information such as symptoms, observed problems, and any immediate corrective actions taken. This documentation serves as a starting point for RCA.
Utilize CMMS Reporting Tools: Take advantage of the reporting tools within the CMMS to generate reports and dashboards related to equipment performance, maintenance activities, and failure analysis. These reports can highlight trends and areas that require further investigation.
Analyze Failure Patterns: Use the CMMS data to analyze failure patterns and trends. Identify equipment or systems that experience repeated issues, and look for commonalities in the failure modes. This analysis helps in pinpointing potential root causes.
Review Maintenance History: Review the maintenance history stored in the CMMS to understand past maintenance activities, replacements, and repairs. Look for patterns that may indicate recurring issues or areas requiring improvement.
Collaborate Across Departments: Encourage collaboration between maintenance teams, operators, and other relevant departments. The CMMS can serve as a centralized platform for sharing information and insights, fostering a collaborative approach to RCA.
By implementing CMMS into the RCA process, organizations can benefit from a systematic and data-driven approach to identifying and addressing the root causes of maintenance issues. This not only improves equipment reliability but also contributes to overall operational excellence and continuous improvement.

Conclusion
In summary, CMMS enhances the effectiveness of Root Cause Analysis by providing a centralized platform for storing, managing, and analyzing maintenance-related data. The system contributes to a more informed and data-driven decision-making process, ultimately leading to improved equipment reliability and reduced downtime.