Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeLet’s face it—keeping machines running smoothly is like trying to juggle while riding a unicycle. As maintenance managers, we constantly balance preventive care, emergency fixes, budget constraints, and the ever-present pressure to keep production flowing.
But here’s the good news: you can master this juggling act with the right approach. This article covers 10 proven ways to improve machine maintenance.
Picture this: It’s 3 AM, and your phone rings with that dreaded emergency call. Another critical machine is down, production has ground to a halt, and the pressure is mounting by the minute. As maintenance managers, we’ve all been there.
The stress of running complex equipment smoothly while juggling limited resources, tight budgets, and ever-increasing production demands can feel overwhelming.
But many of us don’t realize that maintenance excellence isn’t just about fixing things faster or having the latest predictive tools.
It’s about building a comprehensive system that prevents those 3 AM calls from happening in the first place. Think of it like maintaining your health: You could wait until you’re sick to see a doctor or exercise regularly, eat well, and get regular check-ups.
These tips can help businesses of all sizes keep their equipment running smoothly and avoid costly surprises.
Key Takeaways
- Regular maintenance checks and repairs boost machine efficiency and safety
- Preventive and predictive techniques help avoid costly breakdowns
- Staff training and standardized procedures improve overall maintenance quality
Listen to this Article
Understanding Machine Maintenance Fundamentals
Machine maintenance is the practice of keeping equipment in good working order. It involves regular checks, repairs, and part replacements. Good machine maintenance can save money and time.
There are several types of maintenance:
- Preventive maintenance is done on a schedule to prevent breakdowns
- Corrective maintenance fixes issues after they occur
- Predictive maintenance uses data to forecast when repairs are needed
- Condition-based maintenance monitors equipment in real-time
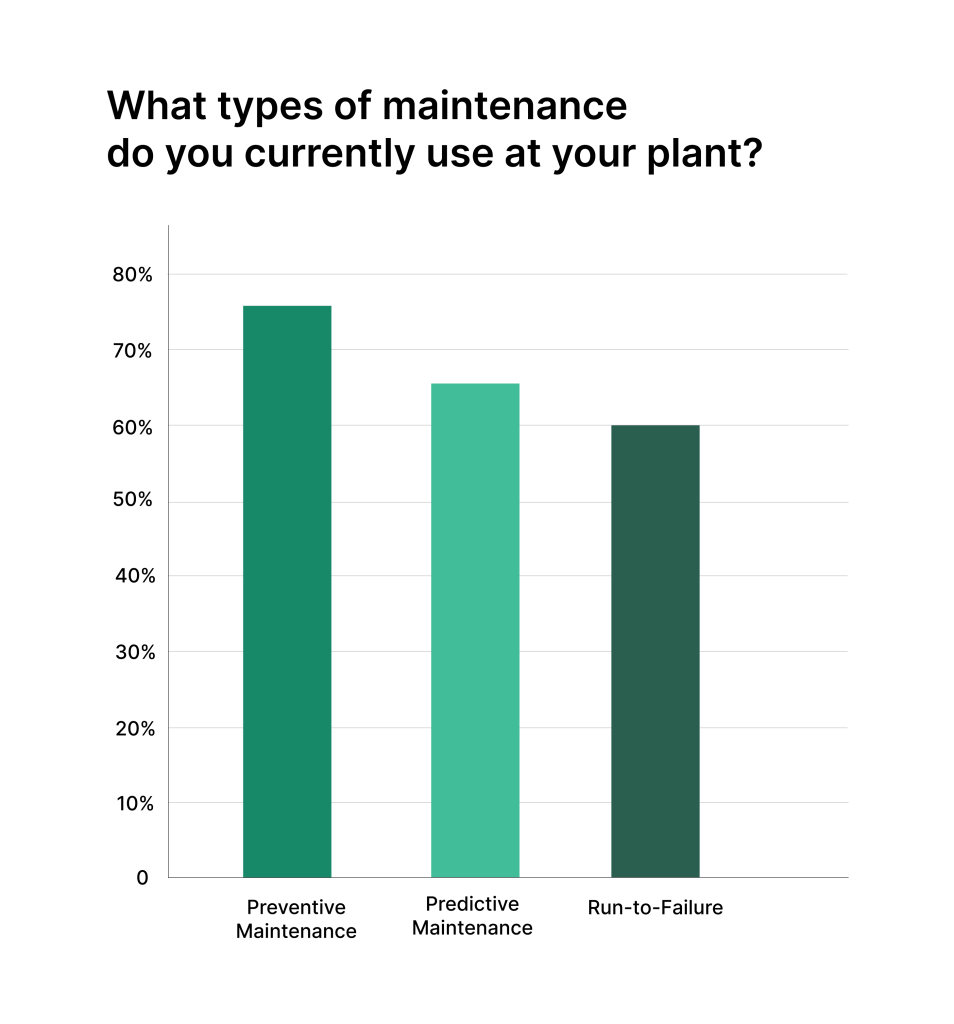
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Reliable Plant
Regular inspections are key to effective maintenance. They help spot problems early, and consistent inspections are your eyes on your machinery’s health.
Like your car’s engine, proper lubrication is crucial for machine longevity.
It reduces friction and wear on moving parts. Each machine has specific lubrication needs.
Keeping accurate maintenance records is important. These records help track repair history and plan future maintenance.
Training staff in proper machine operation and maintenance is essential. Well-trained operators can spot issues early and prevent damage.
By understanding these fundamentals, companies can keep their equipment running efficiently. This leads to increased productivity and reduced downtime.
Implementing a Preventive Maintenance Program
A successful preventive maintenance program requires careful planning and execution. Two key elements are developing a schedule and training personnel.
Developing a Maintenance Schedule
Creating an effective maintenance schedule is crucial for preventing equipment breakdowns.
Start by listing all machines and assets that need regular maintenance. Assign priority levels based on how critical each asset is to operations.
Next, determine the ideal maintenance frequency for each item. This may be based on manufacturer recommendations or historical data.
Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations until you have enough data and experience to use historical data for maintenance decisions. This approach will extend equipment life.

Source: WorkTrek
Build a calendar that spreads out maintenance tasks to avoid overloading the team and manage maintenance costs.
Use a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) like WorkTrek to track schedules and send automatic reminders. This helps ensure no tasks slip through the cracks. The system should be flexible enough to adjust for unexpected issues or changes in production schedules.
Training Maintenance Personnel
The right maintenance strategy always starts with properly trained staff. A trained staff can effectively implement preventive maintenance plans and optimize machine maintenance.
This can improve equipment reliability, improve maintenance practices, and save on costs.
Develop a formal training program that covers maintenance procedures, safety protocols, and the use of tools and equipment.
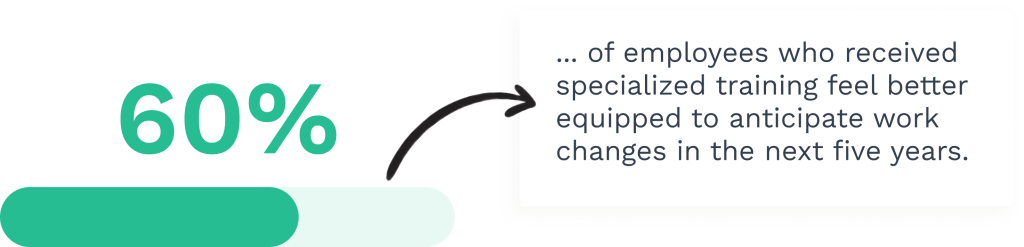
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: SC training
Training should include both classroom learning and hands-on practice. Cover topics like:
- Reading technical manuals and schematics
- Proper use of diagnostic tools
- Safe work practices
- Documenting maintenance history and activities
Regular refresher courses help keep skills sharp. Consider implementing a mentoring system where experienced technicians guide newer staff members.
Invest in ongoing education to keep the team updated on new technologies and best practices in machine maintenance. This continuous learning approach helps improve overall program effectiveness.
Adopting Predictive Maintenance Techniques
Predictive maintenance uses data and analytics to spot equipment issues before they cause breakdowns. This approach helps companies save money and avoid unplanned downtime.
Utilizing IoT for Predictive Analytics
The Internet of Things (IoT) is key in predictive maintenance.
Machine sensors collect temperature, vibration, and performance data, which is sent to a central system for analysis.
A proper maintenance approach should include IoT devices that can track machine health 24/7.
They pick up on small changes that humans might miss. For example, a slight increase in motor temperature could signal a coming failure.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: SC training
Companies use IoT data to create maintenance schedules based on actual machine conditions. This is better than fixing things on a set schedule or waiting for breakdowns.
AI-driven anomaly detection through IoT can boost machine runtime by 10-20% and cut maintenance costs by up to 10%.
Leveraging AI & Machine Learning for Prediction Accuracy
Machine learning takes predictive maintenance to the next level. It spots patterns in data that show when a machine might fail.
ML models improve over time as they learn from more data. They can predict issues weeks or months in advance, giving crews time to plan repairs during slow periods.
Some benefits of ML in maintenance include:
- Fewer surprise breakdowns
- Longer machine life
- Lower repair costs
- Less wasted inventory
Machine learning in predictive maintenance helps with tasks like safety checks, warranty claims, and plant monitoring. It’s becoming standard in manufacturing and transportation.
Ensuring Regular Cleaning and Lubrication
Clean and well-lubricated machines work better, last longer, and perform optimally. These practices reduce wear and tear, keeping equipment running smoothly.
Selecting the Right Cleaning Agents
The right cleaning agents are key for effective machine maintenance and your maintenance operation.
Choose cleaners that match your machine’s materials and dirt types. For metal parts, use degreasers or solvents. Plastic components need milder cleaners to avoid damage.
Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines before using any cleaner. Some machines need special products to protect sensitive parts.
Create a cleaning plan for each machine. Set up a schedule based on use and environment. High-traffic areas may need daily cleaning, while others can go longer between cleanings.
Remember to wear protective gear when handling cleaning agents, such as gloves, goggles, and masks. Proper safety measures protect both workers and machines.
Choosing Appropriate Lubricants
Picking the right lubricant is crucial for machine health. Different parts often need different types of lubricants. When selecting, consider factors like temperature, speed, and load.
Use lightweight oils for high-speed parts. Heavy-duty gears need thicker greases.
Always match the lubricant to the specific machine part.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: CBM Connect
Check the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubricant types and amounts. Using too much can be as harmful as using too little.
Set up a lubrication schedule based on machine use. Some parts need daily oiling, while others can go weeks or months. Keep detailed records of when each part was last lubricated.
Store lubricants properly to prevent contamination. Use clean tools for application to avoid introducing dirt into the machine.
Performing Regular Machine Inspections
Regular machine inspections are key to keeping equipment in top shape. They help catch issues early and prevent costly breakdowns. Proper training and detailed checklists are vital for effective inspections.
Creating Inspection Checklists
A good inspection checklist covers all the important parts of a machine. It should list specific items to check, like fluid levels, wear points, and safety features. Checklists need to be clear and easy to follow.
Key elements of an effective checklist:
- Machine-specific items
- Safety checks
- Fluid level checks
- Visual inspections for wear or damage
- Functional tests
Source: WorkTrek
Update checklists regularly based on machine history and manufacturer recommendations. This keeps them relevant and useful.
Digital checklists on tablets or smartphones can make the process faster and more accurate and improve machinery maintenance.
Training for Defect Identification
Proper training helps inspectors spot problems quickly and optimize maintenance. They need to know what normal looks like to catch abnormal conditions, and hands-on practice with real equipment is crucial.
Training should cover:
- Common defects for each type of machine
- How to use inspection tools correctly
- Safety procedures during inspections
- Proper documentation of findings
Use photos and videos to show examples of defects. This helps inspectors recognize issues in the field. Regular refresher courses keep skills sharp and introduce new inspection techniques.
Encourage inspectors to ask questions and share their experiences. This builds a culture of continuous learning and improvement in the maintenance team.
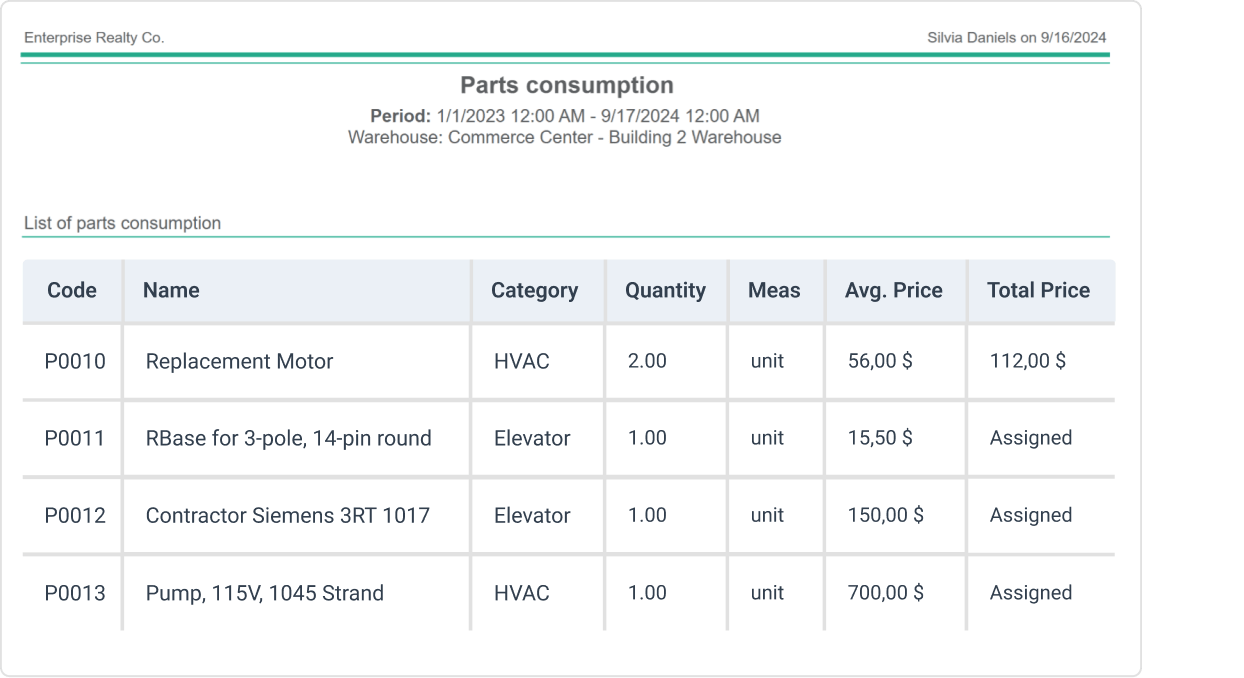
Optimizing Spare Parts Inventory Management
Keeping the right amount of spare parts is key to smooth machine maintenance. Too few parts can lead to long downtimes, and too many can waste money and space.
A good system tracks the often-used parts and knows when to order more.
Computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) like WorkTrek can help with this task.
Source: WorkTrek
Regular inventory checks are important. This helps catch errors and adjust stock levels.
It’s also smart to group similar parts for easy finding.
Some tips for better spare parts management:
- Label parts clearly
- Use barcodes for quick scanning
- Keep a clean, organized storage area
- Train staff on proper handling
Working with suppliers can also improve inventory. They might offer deals on bulk orders or faster shipping for urgent needs.
It’s helpful to set reorder points for each part. When stock drops to this level, it’s time to buy more, preventing the runout of critical items.
Tracking part life cycles is also useful.
As machines are upgraded, some parts may become obsolete. Phasing out old parts can free up space and cut costs.
By fine-tuning spare parts management, companies can save money and reduce machine downtime, leading to more efficient operations.
Standardizing Maintenance Procedures
Standardizing maintenance procedures boosts efficiency and consistency in machine upkeep. It creates clear guidelines for all maintenance tasks and helps prevent errors.
Documentation of Maintenance Workflows
Creating standard operating procedures (SOPs) is key to documenting maintenance workflows. These SOPs should cover all routine tasks and significant repairs.
Key elements of effective SOPs include:
• Step-by-step instructions
• Safety precautions
• Required tools and parts
• Estimated completion times

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Guidde’s
SOPs ensure all technicians follow the same process, reducing mistakes and improving quality. They also make training new staff easier and faster.
Continuously update your SOPs. As equipment or processes change, the documentation must reflect these updates to stay relevant and useful.
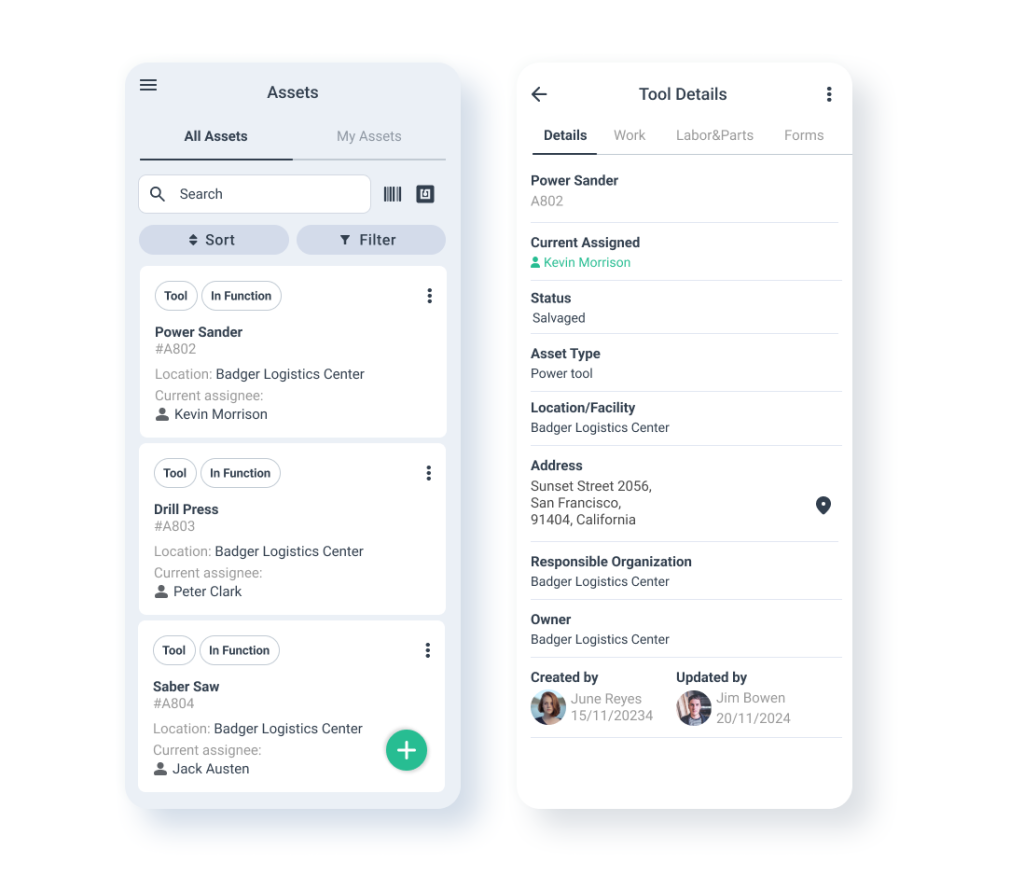
Utilization of Maintenance Management Systems
Maintenance management systems help organize and track all maintenance activities. These digital tools streamline work orders, asset tracking, and inventory management.
Benefits of using maintenance management systems:
• Real-time equipment status updates
• Automated scheduling of preventive maintenance
• Easy access to repair histories
• Improved data analysis for decision-making
Source: WorkTrek
These systems allow teams to spot patterns and improve procedures over time. They also help prioritize tasks and allocate resources more effectively.
Integration with other business systems can further enhance efficiency. This connection allows for better planning and budgeting across departments.
Emphasizing Quality Control in Machine Repair
Quality control plays a key role in effective machine repair. It ensures repairs meet high standards and machines operate reliably after maintenance.
Sourcing High-Quality Repair Materials
Using top-notch repair materials is crucial for machine longevity. Quality control in maintenance starts with selecting the right parts and components, which might not always be the cheapest.
Choose materials from trusted suppliers with proven track records. Look for parts that meet or exceed original equipment specifications. This helps maintain machine performance and safety standards.
Source: WorkTrek
Keep an up-to-date inventory of everyday repair items.
This prevents rushed purchases of subpar materials during emergencies. Regular audits of repair stock can identify any counterfeit or defective parts before use.
Train staff to spot signs of low-quality materials, such as unusual wear patterns, incorrect dimensions, or off-color components.
Reject any suspicious items immediately.
Adhering to Manufacturers’ Repair Guidelines
Following manufacturer guidelines is essential for proper repairs. These instructions are based on extensive testing and design knowledge.
Create a library of repair manuals for all machines. Keep these easily accessible to technicians. Update the library regularly as manufacturers release new information.
Train repair staff on correct procedures for each machine type. This includes proper tool usage, torque specifications, and safety precautions. Regular refresher courses help maintain high repair standards.
Use checklists based on manufacturer guidelines for each repair job. This ensures that no critical steps are missed. Document and justify any deviations from standard procedures.

Implement a review process for completed repairs. This helps catch any mistakes before machines return to service.
Upgrading to Energy-Efficient Machines
Upgrading to energy-efficient machines is a smart way to improve maintenance and cut costs. New equipment often uses less power while working better.
To start, assess which machines use too much energy. Look for old or worn-out equipment that might be wasting power.
Modern machines are built to save energy. They can do the same job with less electricity. This means lower bills and less strain on the power grid.
Some benefits of upgrading include:
- Lower energy costs
- Better performance
- Less downtime
- Fewer repairs
When choosing new machines, look for energy ratings. Pick ones with high-efficiency scores. These may cost more upfront but save money over time.
Upgrading equipment can lead to big drops in energy use. It might take longer to pay off than other changes, but the savings add up.
Don’t forget about smaller parts. Swapping old parts for more efficient ones can help, too. This can be a good step if you can’t replace whole machines.
Track how much energy you save after upgrades. This will help you demonstrate the value of the changes and plan future improvements.
Investing in Maintenance Training and Skill Development
Training and skill development are key to improving machine maintenance. These efforts boost worker competence and enhance equipment uptime.
Offering Certification Programs
Maintenance certification programs provide workers with specialized knowledge and skills. They cover topics such as preventive maintenance, troubleshooting, and safety protocols.
Certifications increase worker confidence and expertise. They also help companies meet industry standards and regulations.
Many organizations partner with technical schools or equipment manufacturers to offer certifications. This ensures workers learn up-to-date techniques on relevant equipment.
Certified technicians often command higher salaries. This incentivizes workers to pursue additional training and stay current in their field.
Incorporating On-the-Job Training Modules
On-the-job training allows maintenance workers to learn in real-world settings. This hands-on approach reinforces classroom learning and builds practical skills.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Continu
Companies can create structured training modules for different maintenance tasks. These might include equipment-specific procedures or general best practices.
Experienced technicians often serve as mentors in on-the-job training programs. They guide newer workers through complex tasks and share valuable insights.
Regular practice sessions help workers stay sharp on infrequently used skills. This preparedness is crucial for handling unexpected breakdowns efficiently.
Establishing Performance Monitoring and KPIs
Setting up a system to track machine performance is key for better maintenance. This means choosing the right metrics to measure.
Maintenance KPIs help keep costs low and avoid unplanned downtime. They give insights into how well the equipment is running.
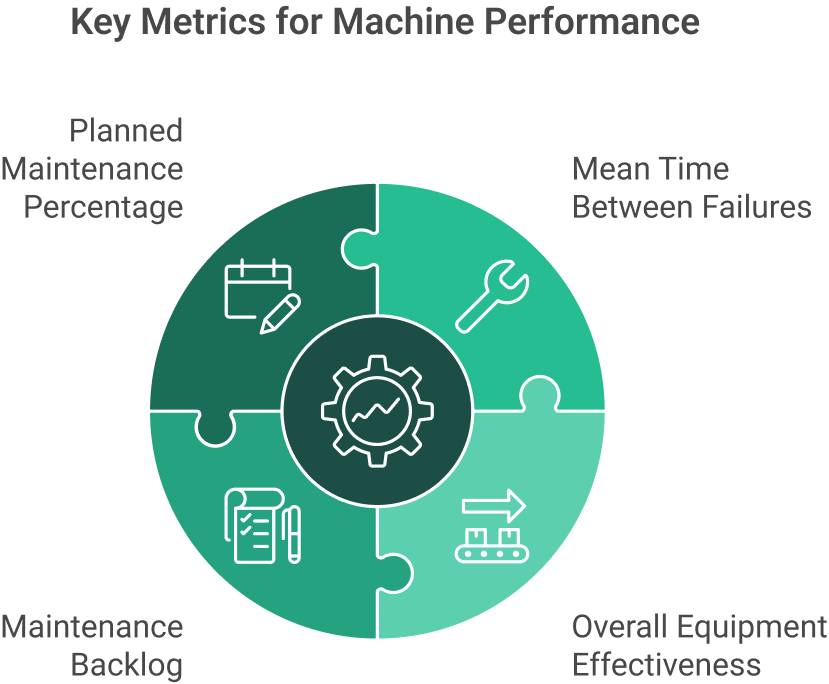
Some important KPIs to track include:
• Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
• Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
• Maintenance Backlog
• Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)
Source: WorkTrek
MTBF measures how long machines run between breakdowns. A higher MTBF means better reliability.
OEE looks at availability, performance, and quality. It gives a full picture of equipment health.
Tracking maintenance backlog shows if work is piling up. A growing backlog may mean more resources are needed.
The planned maintenance percentage tracks how much work is scheduled vs. reactive. A higher percentage often means fewer emergency repairs.
The software makes tracking these metrics easier. Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) can collect and analyze data automatically.
Regular review of KPIs helps spot trends. This allows teams to make smart choices about maintenance strategies.
Setting targets for each KPI gives clear goals to work towards. These targets should be realistic but push for improvement.
Summary
Adopting an extensive preventive maintenance program that incorporates condition-based and predictive maintenance approaches, good record-keeping for all maintenance tasks, and educating machine operators in fundamental maintenance procedures maximizes machine maintenance efficiency.
Investing in advanced CMMS software, opting for premium components, and emphasizing safety during all maintenance operations can boost equipment dependability while prolonging its operational life span and curbing overall upkeep costs.
By embracing these strategies within your company’s routine system checks, you will elevate your approach to asset maintenance.









