Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIn today’s industrial landscape, minimizing downtime and extending equipment life has never been more critical. Predictive maintenance technologies offer a revolutionary approach that helps companies detect potential failures before they occur.
Predictive maintenance systems can reduce unplanned downtime by up to 50% while extending machine life by years.
These predictive maintenance solutions rely on a sophisticated ecosystem of tools, including advanced sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity, and AI-driven analytics systems.
Integrating these elements enables machines to self-monitor, collecting real-time data on vibration, temperature, sound, and other performance indicators that can signal impending problems.
This shift from scheduled maintenance to condition-based interventions represents one of modern industry’s most significant operational improvements.
The predictive maintenance approach continues to evolve as machine learning algorithms become more sophisticated and accessible.
Companies that have embraced these technologies report substantial reductions in maintenance costs and impressive gains in productivity, equipment health, and reliability. Predictive maintenance has become part of these organizations’ standard maintenance practices and has delivered measurable returns across multiple business metrics.
Key Takeaways
- Predictive maintenance technologies combine IoT sensors, AI analytics, and machine learning to anticipate equipment failures before they occur.
- Implementation of predictive maintenance systems can significantly reduce downtime while extending asset lifespan and improving overall operational efficiency.
- The future of maintenance strategies lies in increasingly sophisticated predictive analytics that offer better accuracy, broader application, and more accessible deployment options.
Evolution of Maintenance Strategies
Maintenance strategies have transformed dramatically, from fixing equipment after failure to using data to predict when maintenance is needed.
This shift to advanced technologies has reduced downtime and saved companies significant maintenance costs.
From Reactive to Predictive
Traditional maintenance started with a reactive approach—simply fixing machines after they broke down. This method is unpredictable and leads to costly unplanned downtime and emergency repairs.
Next came preventive maintenance, which involved regular scheduled service regardless of equipment condition. While better than reactive methods, it often resulted in unnecessary work and wasted resources.

The real breakthrough came with condition-based maintenance, which monitored equipment health through inspections and tests. This approach allowed teams to perform maintenance only when specific indicators showed potential issues.
Today’s gold standard is predictive maintenance, which uses advanced sensors, data analytics, and machine learning to forecast equipment failures before they happen. This strategy has dramatically reduced maintenance costs and downtime.
Rise of PdM in Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 has accelerated predictive maintenance adoption through several key technologies to help enhance operational efficiency:
IoT Sensors—Modern equipment now contains sensors that continuously monitor temperature, vibration, and other critical parameters in real-time.

Big Data Analytics – Companies collect vast amounts of operational data that reveal patterns and anomalies in equipment behavior.
Machine Learning – AI algorithms can identify subtle changes in equipment performance that humans might miss, providing early warning of potential failures.
The food and beverage industry has been particularly successful with predictive maintenance strategies. Manufacturers use machine learning to anticipate maintenance needs, preventing costly production interruptions.
Maintenance will become even more sophisticated, with data driving every decision and remote diagnostics allowing for more efficient resource deployment.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies have transformed predictive maintenance by enabling systems to identify potential failures before they occur. These technologies process vast amounts of sensor data to recognize patterns that would be impossible for humans to detect manually.
Foundations of AI in PdM
AI-powered predictive maintenance uses complex algorithms to analyze operational data from equipment sensors. These systems establish normal operating parameters and detect subtle deviations that might indicate developing problems.
AI in predictive maintenance helps companies streamline operations and reduce costs by preventing unexpected breakdowns. The technology requires robust data collection systems that continuously monitor equipment performance metrics like temperature, vibration, and power consumption.
Modern AI systems can learn from historical failure data to improve prediction accuracy. This self-improving capability means maintenance predictions become more reliable as the system accumulates operational experience.
Advanced implementations combine multiple data sources to create comprehensive equipment health profiles.
Machine Learning Algorithms for Anomaly Detection
Machine learning algorithms analyze data to determine optimal maintenance timing, ensuring interventions happen precisely when needed. These algorithms fall into several categories:
- Supervised learning: Trained on labeled examples of normal and failure states
- Unsupervised learning: Identifies unusual patterns without prior examples
- Deep learning: Processes complex sensor data through neural networks
Anomaly detection algorithms excel at identifying subtle deviations from normal operation patterns. They can detect unusual vibration signatures or temperature fluctuations that precede equipment failure.
Predictive analytics can reduce downtime by 30-50% and extend machine life by 20-40%. The algorithms continuously refine their models based on new data, improving accuracy.
Implementing IoT in Predictive Maintenance
Integrating IoT technology into maintenance systems creates powerful predictive capabilities that dramatically reduce downtime and extend equipment life.
Combining smart sensors and advanced analytics transforms traditional maintenance approaches into data-driven decision systems.
IoT Devices and Sensor Integration
IoT predictive maintenance systems begin with strategically placed sensors that monitor critical equipment parameters.
These sensors track vibration, temperature, pressure, noise, and electrical current to detect subtle changes in machine performance.

Modern sensors take various forms, from simple temperature probes to complex vibration analyzers that detect microscopic changes in equipment behavior.
These devices continuously collect real-time operational data, which is the foundation of predictive algorithms.
Installation requires careful planning to ensure sensors capture relevant data without interfering with operations. Key considerations include:
- Sensor placement for optimal data collection
- Connectivity options (WiFi, cellular, Bluetooth)
- Power requirements (battery-powered vs. hardwired)
- Environmental factors affecting sensor durability
Processing IoT Data for Maintenance Insights
The real value of IoT maintenance comes from transforming raw sensor data into actionable insights. This requires powerful data processing systems to handle the massive information flow from connected devices.
IoT maintenance platforms typically use AI algorithms to establish standard equipment operation patterns and identify deviations that signal potential failures.
These systems become increasingly accurate as they learn from historical performance data.
Cloud-based processing solutions offer scalability for industrial implementations, while edge computing enables faster response times for critical equipment.
The data analysis approach typically follows three steps:
- Data collection and cleaning
- Pattern recognition and anomaly detection
- Failure prediction and maintenance scheduling
These systems translate complex operational data into simple maintenance recommendations that technicians can implement before equipment fails.
Best Practices for Implementing PdM
Implementing predictive maintenance requires careful planning and ongoing refinement to maximize its benefits. Organizations that follow proven methodologies achieve better equipment reliability, cost savings, and operational efficiency.
Strategic Planning for PdM Implementation
Successful PdM implementation begins with assembling a qualified support team that understands maintenance principles and data analysis. This team should include maintenance technicians, reliability engineers, and IT specialists who can collaborate effectively.
Start small and focus on critical assets first. Identify the machinery and equipment that would cause significant downtime or safety issues if they failed. This targeted approach allows teams to refine their processes before expanding.
Develop clear goals and KPIs to measure success. Effective metrics might include reducing unplanned downtime, saving on maintenance costs, or extending equipment lifespan.

Ensure connectivity to machines through appropriate sensors and monitoring tools. The right condition monitoring technologies should be selected based on failure modes and equipment criticality.
Conduct a formalized RCM (Reliability Centered Maintenance) analysis to identify where PdM technologies can best mitigate failures.
Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
PdM programs must evolve to remain effective. Regular analysis of collected data helps identify patterns and refine predictive models over time, improving the accuracy of failure predictions.
Provide comprehensive training to maintenance staff and operators on using predictive tools and interpreting results. Well-trained teams make better decisions based on the data.
Establish feedback loops between maintenance, operations, and management. Document the outcomes of maintenance actions based on PdM alerts to validate or improve the predictive model.
Obtain actionable data that can drive real decisions. This means filtering noise and focusing on meaningful indicators of equipment health.
Scale your approach gradually as success is demonstrated. Add more assets to the program and integrate additional technologies as your team’s capabilities grow.
Types of Sensors
Predictive maintenance relies heavily on various sensor technologies to monitor equipment health. These sensors collect real-time data that helps identify potential failures before they occur.
Vibration sensors are among the most widely used in predictive maintenance. They detect abnormal vibrations in rotating machinery that might indicate misalignment, imbalance, or bearing failures.
Temperature sensors monitor equipment heat levels. Unexpected temperature changes often signal friction issues, electrical problems, or component wear that requires attention.
Pressure sensors measure system pressure variations, which are significant in hydraulic systems, pipelines, and manufacturing equipment. Unusual pressure readings can indicate leaks, blockages, or pump failures.
Ultrasonic sensors detect high-frequency sound waves that humans cannot hear. These sensors excel at identifying gas or air leaks, electrical discharges, and mechanical issues before they become serious problems.
Acoustic sensors capture audible sound patterns from equipment. Changes in noise signatures often reveal developing mechanical issues, such as worn gears or bearings.
Common Predictive Maintenance Sensors:
- Vibration sensors
- Temperature sensors
- Pressure sensors
- Ultrasonic sensors
- Acoustic sensors
- Gas sensors
- Humidity sensors
- Security sensors
These sensors form the foundation of effective predictive maintenance programs by providing critical data to make informed maintenance decisions and prevent costly downtime.
Emerging Predictive Maintenance Technologies on the Horizon
Several cutting-edge technologies are poised to transform predictive maintenance in the near future:
Digital Twins with Real-Time Simulation
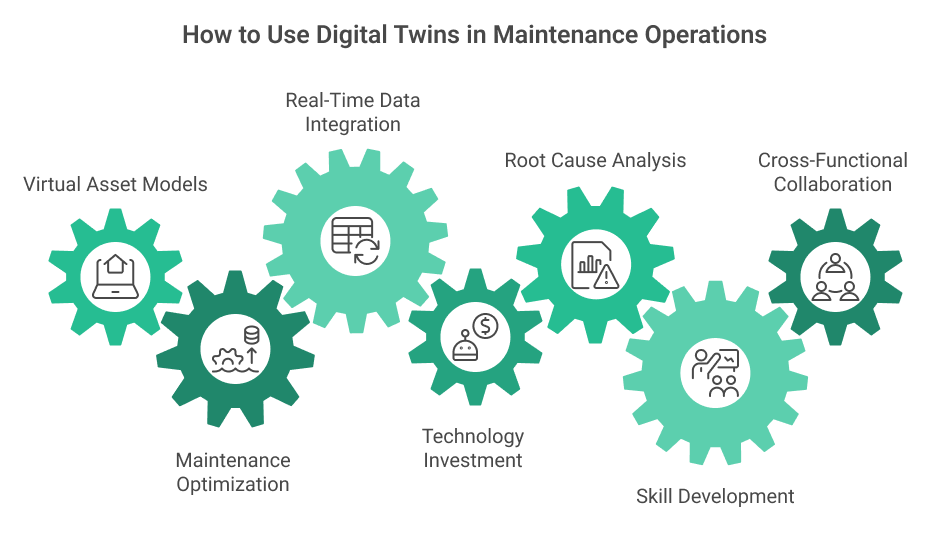
Advanced digital twin technology will soon allow maintenance teams to create virtual replicas of physical assets that update in real time. These sophisticated models will simulate component wear and degradation under various operating conditions, enabling engineers to run “what-if” scenarios before making physical adjustments. This technology will provide unprecedented insight into asset behavior and failure modes before manifesting in the physical equipment.
Edge Computing for Remote Assets
Expanding edge computing will revolutionize predictive maintenance for remote or distributed assets. These systems will enable real-time analysis even in locations with limited connectivity by processing data locally rather than sending everything to centralized servers. This advancement will be particularly valuable for utilities, transportation networks, and field operations where immediate insights can prevent critical failures.
Augmented Reality Maintenance Guidance

AR technology will soon provide maintenance technicians with real-time visual guidance overlaid on physical equipment. By integrating with CMMS systems, AR headsets will display asset histories, predictive alerts, and step-by-step repair procedures directly in the technician’s field of vision. This technology will significantly reduce repair times and errors while capturing maintenance activities automatically for future analysis.
Deep Learning for Complex Pattern Recognition
Next-generation predictive maintenance will employ deeper neural networks that identify subtle, complex patterns across multiple sensor streams.
Unlike systems that often analyze parameters in isolation, these advanced models will recognize interdependent failure signatures across dozens of variables. This capability will dramatically reduce false positives while increasing early detection rates for complex equipment.
Autonomous Maintenance Drones and Robots
Automated inspection through specialized drones and robots will become standardized for hazardous or difficult-to-access assets.
These systems will conduct regular autonomous inspections using thermal imaging, ultrasonic testing, and visual analysis, automatically feeding data into predictive maintenance algorithms. Some advanced models will even perform minor maintenance tasks autonomously based on AI-driven decisions.
These technologies represent the next frontier in predictive maintenance, promising to reduce downtime further, extend asset lifecycles, and optimize maintenance resources in ways that today’s systems are only beginning to approach.
The Role of CMMS in Optimizing Predictive Maintenance
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) like WorkTrek have revolutionized predictive maintenance by transforming reactive approaches into proactive strategies.
Centralize Data
CMMS centralizes asset data, maintenance histories, and performance metrics, enabling organizations to identify potential equipment failures before they occur.
This shift from responding to breakdowns to preventing them significantly reduces downtime, extends asset lifespans, and optimizes maintenance resource allocation.
Data Integration
The power of CMMS in predictive maintenance lies in its data integration capabilities. Modern systems collect real-time equipment data through IoT sensors, monitoring critical parameters like temperature, vibration, pressure, and energy consumption.
Data Analytics
This continuous stream of performance data, when analyzed against historical baselines, reveals subtle degradation patterns that would otherwise remain undetected until failure. The software’s algorithmic analysis can detect anomalies weeks or even months before traditional inspection methods, creating crucial lead time for maintenance planning.
AI and Machine Learning
Beyond anomaly detection, advanced CMMS platforms continuously leverage machine learning to refine predictive models. As these systems accumulate more operational data, their accuracy in forecasting maintenance needs improves, enabling increasingly precise interventions.
Streamlined Maintenance Scheduling
The software also optimizes maintenance scheduling by balancing urgency against resource availability, parts inventory, and production demands.
This holistic approach ensures that predictive maintenance occurs at the optimal intersection of necessity and operational convenience, minimizing both the risk of failure and the impact of maintenance activities on productivity.
Understanding Key Metrics and Data Points
Successful predictive maintenance relies on measuring the right metrics and interpreting data accurately. Organizations need clear performance indicators to gauge equipment health and maintenance effectiveness.
Importance of OEE in PdM
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a cornerstone of predictive maintenance strategies. This comprehensive measurement combines availability, performance, and quality to provide a score that reflects total equipment productivity.
OEE helps maintenance teams identify the root causes of equipment failures and inefficiencies. A declining OEE score often signals potential maintenance issues before they cause catastrophic failures.

For example, a gradual decrease in performance rate might indicate bearing wear that sensors have yet to detect.
Companies implementing predictive maintenance typically see OEE improvements of 10-30% compared to reactive maintenance approaches.
To calculate OEE effectively:
- Availability = Operating Time ÷ Planned Production Time
- Performance = (Total Pieces ÷ Operating Time) ÷ Ideal Run Rate
- Quality = Good Pieces ÷ Total Pieces
KPIs for PdM Success
Selecting the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) dramatically impacts the success of a predictive maintenance program. What gets measured gets improved, making KPI selection a critical decision for maintenance teams.
Essential KPIs to track include:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) – measures reliability improvements
- Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) – evaluates maintenance efficiency
- Maintenance Cost as Percentage of Asset Replacement Value – monitors economic efficiency
- Planned vs. Unplanned Maintenance Ratio – tracks program maturity
Predictive maintenance programs should monitor leading indicators (vibration levels, temperature readings) and lagging indicators (downtime, repair costs).
Leading indicators help prevent failures while lagging indicators measure program effectiveness.
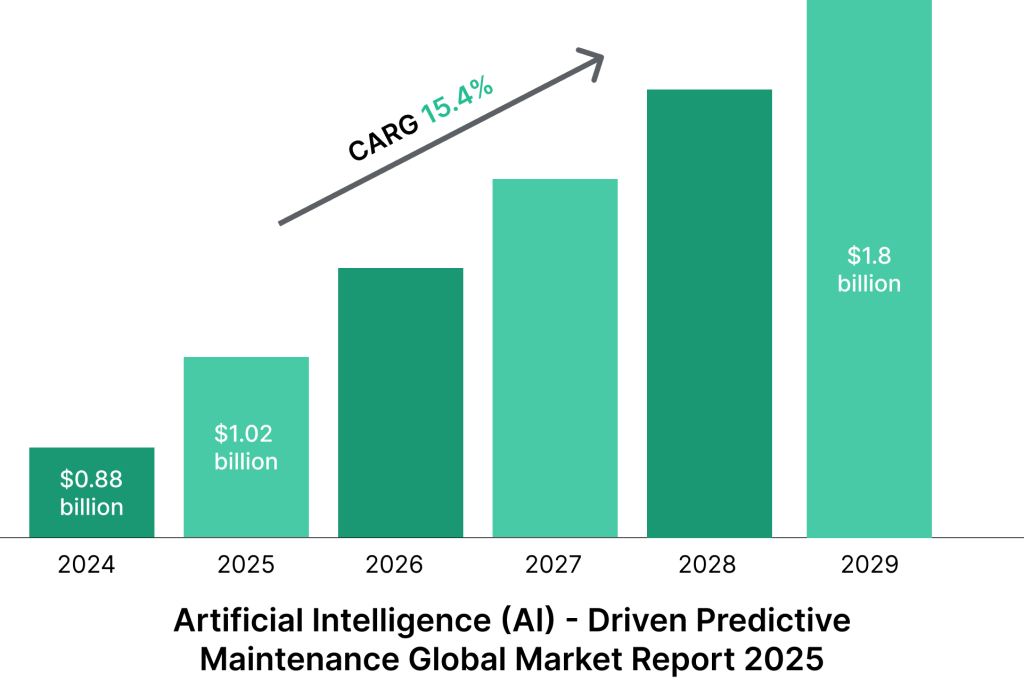
The global predictive maintenance market reached $7.85 billion in 2022, showing how organizations increasingly recognize the value of these metrics in extending equipment life and reducing costs.
Predictive Analytics for Maintenance
Predictive analytics transforms raw maintenance data into actionable insights that prevent failures and optimize operations.
This technology identifies patterns and anomalies humans might miss, enabling proactive maintenance approaches.
Leveraging Historical Data
Historical maintenance records provide the foundation for effective predictive analytics. A computerized maintenance management system could easily manage and track these records.
Maintenance personnel can identify recurring patterns preceding breakdowns and optimize maintenance tasks by analyzing equipment failures. These patterns might include unusual vibration readings, temperature spikes, or performance degradation.
Condition monitoring systems collect this valuable data through sensors that measure critical parameters like vibration, temperature, and pressure. The longer these systems run, the more robust the historical dataset becomes.
Organizations typically store this information in centralized maintenance management systems. Integration between these systems and analytics platforms enables real-time analysis and faster response times.
The most successful implementations combine different data types – maintenance records, sensor readings, and operational data – to create a comprehensive view of equipment health.
Predictive Models and Forecasting
Advanced algorithms transform historical data into predictive models that forecast when equipment is likely to fail. These models identify subtle changes in performance metrics that indicate potential problems before obvious symptoms appear.
This allows maintenance teams to fine-tune their maintenance strategies.
Machine learning algorithms improve over time as they process more data. They can detect complex relationships between operating conditions and failure modes that would be impossible to program manually.
Predictive maintenance analytics creates significant competitive advantages. Companies can schedule maintenance during planned downtime, extend equipment life, and reduce unexpected failures.
These systems’ forecasting capability helps maintenance teams prioritize their work based on actual risk rather than fixed schedules or reactive approaches. This optimization reduces unnecessary maintenance while preventing catastrophic failures.
Real-world applications include predicting motor failures in manufacturing, identifying potential transmission issues in fleet vehicles, and forecasting pump degradation in utility operations.
Economic Impact and ROI of PdM
Predictive maintenance delivers substantial financial benefits through direct cost reductions and operational improvements.
The ROI of predictive maintenance depends on several factors, including data quality, technology selection, and implementation strategy.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
Predictive maintenance significantly reduces maintenance costs by eliminating unnecessary scheduled maintenance.
Organizations typically save 8-12% over preventive maintenance approaches and up to 40% compared to reactive maintenance strategies.
The global predictive maintenance market reached $5.5 billion in 2022, growing 11% from 2021. The projected CAGR is 17% through 2028. This growth reflects the strong financial case for PdM adoption.
Key efficiency gains include:

- Reduced parts inventory (15-20% savings)
- Lower maintenance labor costs (25-30% reduction)
- Extended equipment lifespan (20-40% increase)
Energy efficiency improves as equipment operates optimally, resulting in 5-15% energy savings for most industrial operations.
Quantifying the Benefits of Reduced Downtime
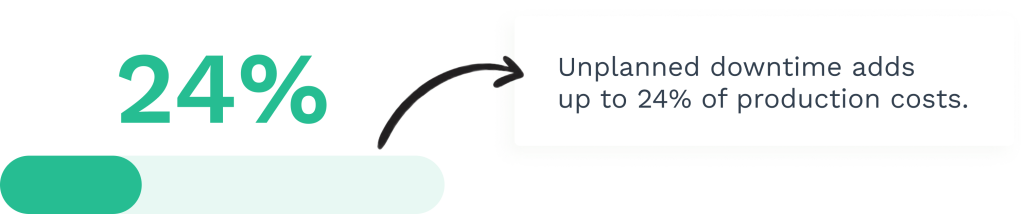
Unplanned downtime costs industrial manufacturers an estimated $50 billion annually. Predictive maintenance directly addresses this by monitoring equipment during normal operation to prevent failures.
Companies implementing PdM typically experience:
- 30-50% reduction in machine downtime
- 70-75% decrease in breakdowns
- 20-25% increase in production
When calculating PdM ROI, organizations must consider direct savings and opportunity costs from avoided downtime. For example, a production line generating $10,000/hour in revenue can save $100,000 by avoiding just 10 hours of downtime.
The most significant ROI often comes from critical equipment where failure causes extensive operational disruption. Some industries report an ROI of 10:1 or higher when PdM prevents significant outages.
Challenges and Considerations in PdM
While predictive maintenance offers significant benefits, organizations face several hurdles when implementing these systems.
Data complexity and security concerns represent major obstacles impacting successful PdM adoption.
Integration Challenges
Implementing predictive maintenance often requires compatibility between existing assets and smart sensors.
Many legacy systems were not designed with connectivity, making integration difficult and costly.
Organizations frequently struggle with workforce readiness. Staff may lack the technical skills to operate and maintain new PdM systems, requiring additional training and development programs.
The initial investment in PdM technology can be substantial. Companies must purchase sensors, analytics software, and data storage solutions to account for the high initial implementation costs.
Data quality presents another significant challenge. Inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to incorrect predictions about equipment failures, potentially missing early warning signs of catastrophic failures that could cause extensive damage and downtime.
Data Privacy and Security
PdM systems collect vast amounts of operational data, creating new security vulnerabilities. Data privacy and security become important for maintenance managers when collecting large amounts of data.
Protecting this information is crucial, especially in industries with significant privacy concerns.
While there are standardized security and privacy processes that all organizations should follow, depending on your industry, there are additional items to consider.
Healthcare
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Protects patient health information in the US
- HITECH Act: Strengthens HIPAA enforcement and breach notification requirements
- 21 CFR Part 11: FDA regulations for electronic records in pharmaceutical/medical device industries
Financial Services
- GLBA (Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act): Requires financial institutions to explain information-sharing practices and protect sensitive data
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): Security standards for organizations handling credit card information
- FFIEC (Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council): Guidelines for authentication, risk management, and cybersecurity
Technology & General Business
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Comprehensive EU data protection law affecting businesses worldwide
- CCPA/CPRA (California Consumer Privacy Act/California Privacy Rights Act): California’s privacy regulations similar to GDPR
Education
- FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act): Protects the privacy of student education records
- COPPA (Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act): Regulates data collection from children under 13
- PPRA (Protection of Pupil Rights Amendment): Additional protections regarding surveys and marketing to students
Telecommunications
- CPNI (Customer Proprietary Network Information) rules: FCC regulations protecting customer data held by telecom providers
- ePrivacy Directive (Cookie Law): EU regulations on digital tracking and electronic communications
International Regulations
- PIPL (Personal Information Protection Law): China’s data protection law
- LGPD (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados): Brazil’s general data protection law
- PIPEDA (Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act): Canada’s primary privacy law
- Privacy Act 1988: Australia’s privacy framework
Maintenance managers and facilities must safeguard proprietary production data that, if compromised, could reveal trade secrets.
Maintenance organizations must comply with industry regulations regarding data storage and transmission. This often requires additional security measures and documentation processes, adding complexity to PdM implementations.
While valuable, remote monitoring capabilities create additional attack surfaces for potential cyber threats.
Companies must implement robust security protocols to prevent unauthorized access to their PdM systems and the critical infrastructure they monitor.
Future Trends in Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is rapidly evolving, and technology advancements promise to revolutionize how industries approach equipment reliability.
These innovations create smarter, more connected maintenance systems that accurately anticipate failures.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML technologies are becoming more sophisticated in analyzing maintenance data. Modern predictive maintenance systems can now identify complex patterns humans might miss, detecting equipment anomalies before they cause failures.
Deep learning algorithms are particularly promising. They can process unstructured data, such as equipment sounds and vibrations, to identify potential failures. These systems improve over time as they analyze more data.
Industries are moving beyond simple rule-based systems to more advanced models that can adapt to changing equipment conditions. ML models now consider multiple variables simultaneously, creating a more holistic view of machine health.
Companies implementing these AI-driven strategies report up to 25% reductions in maintenance costs and 70% decreases in breakdowns. This transformation is also making predictive maintenance more accessible to smaller businesses.
The Expanding Role of IoT
IoT devices form the backbone of modern predictive maintenance by creating a constant stream of real-time equipment data.
The market for these technologies is growing rapidly, with the global predictive maintenance market reaching $5.5 billion in 2022.
Advanced sensors can now monitor:
- Temperature fluctuations
- Vibration patterns
- Sound anomalies
- Electrical consumption
- Fluid quality
These sensors are becoming smaller, more affordable, and more energy-efficient. Many can now operate on a single battery for years or harvest energy from their environment.
Edge computing enhances IoT capabilities by processing data locally before sending it to central systems. This reduces latency and allows for faster decision-making when equipment issues arise.
Sensor technology advancements are particularly transformative in industries like automotive manufacturing, where connected vehicles can now transmit performance data directly to maintenance systems.
Conclusion
The integration of predictive maintenance technologies is revolutionizing industries by enhancing equipment reliability and operational efficiency. By leveraging advanced sensors, IoT connectivity, and AI-driven analytics, companies can anticipate equipment failures before they occur, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
The shift from reactive to predictive maintenance strategies marks a pivotal improvement in maintenance practices, allowing organizations to optimize asset utilization and extend equipment lifespans.

As AI and machine learning technologies evolve, predictive maintenance systems will become increasingly sophisticated, providing more accurate and actionable insights.
The ongoing advancements in IoT and sensor technology further enhance predictive maintenance capabilities, making it more accessible and effective across various sectors.
Embracing these technologies improves equipment performance and drives significant economic benefits, positioning predictive maintenance as a critical component of modern industrial operations and a key driver of future growth.










