Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeStruggles with disorganized spare parts, stockouts, or excess inventory can disrupt maintenance schedules and increase downtime. Without a proper system, spare part management becomes chaotic, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs.
Every hour of downtime affects productivity, and untracked inventory means delayed repairs, wasted resources, and lost revenue. Over-ordering adds unnecessary costs, while stockouts leave teams scrambling to find parts.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Tractian
Maintenance organizations can streamline spare parts management with practical strategies like real-time inventory tracking, setting optimal reorder points, and utilizing a modern CMMS. This ensures the correct parts are always available, reducing downtime, lowering costs, and improving operational efficiency.
Smart spare parts management makes a big difference. It helps companies work better and save money. The rest of this post will provide a list of tips for spare parts management.
Understanding Spare Parts Management
Spare parts management can help businesses improve operations and overall inventory systems. It involves keeping the right parts on hand to minimize downtime and control costs.
Definition and Importance
Spare parts are backup components kept in stock to replace broken or worn-out parts in equipment. Effective spare parts management ensures that the right parts are available when needed. This practice is vital for:
• Reducing equipment downtime
• Maintaining production schedules
• Cutting repair costs
• Improving customer satisfaction
Good spare parts management balances having enough parts on hand without tying up too much money in inventory. It helps businesses avoid costly rush orders and production stops.
Key Principles of Spare Parts Inventory Management
Smart spare parts inventory management relies on several key ideas:
- Accurate forecasting: Predict which parts will be needed and when.
- Proper categorization: Group parts by importance, cost, and usage rate.
- Regular audits: Check inventory levels often to ensure accuracy.
- Lean inventory: Keep only what’s needed to avoid excess stock.
- Supplier relationships: Work closely with suppliers for quick deliveries.
- Technology use: Employ software to track parts and usage patterns.
These principles help businesses keep the right parts in stock without wasting resources. They support both preventive maintenance and quick repairs when breakdowns occur.
1. Inventory Control Systems
Effective inventory control systems help businesses manage spare parts efficiently. They provide accurate tracking, streamline operations, and reduce costs.
Role of Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS)
CMMS software plays an important role in spare parts management. It tracks inventory levels, part locations, and usage patterns. This system automates many tasks, saving time and reducing errors.
Source: WorkTrek
CMMS allows businesses to set up alerts for low stock levels. It also helps schedule maintenance tasks and order parts as needed. The software can generate reports on inventory turnover and costs.
With CMMS, companies can optimize their spare parts inventory. It helps identify slow-moving items and excess stock. This information guides decisions on what to keep and what to phase out.
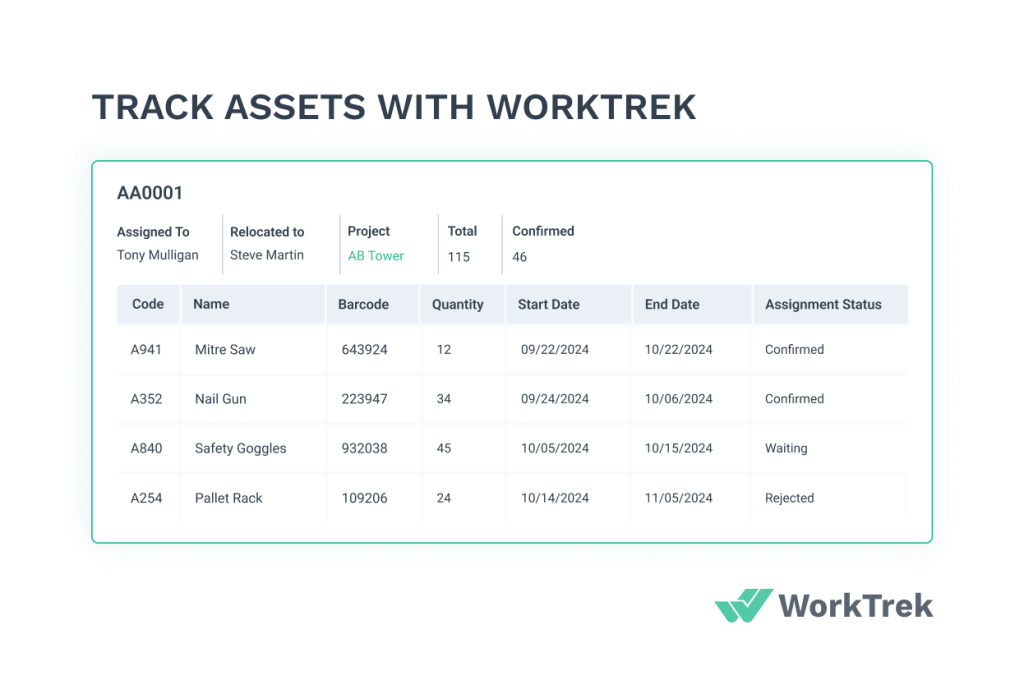
Benefits of Centralized Inventory Control
Centralized inventory control improves spare parts management. It creates a single point of access for all inventory data. This setup enhances accuracy and efficiency.
A central system allows better visibility of stock across locations. It helps prevent duplicate orders and overstocking. Businesses can quickly transfer parts between sites when needed.
Centralized control also improves security measures. It limits access to authorized personnel only, reducing the risk of theft or misuse of valuable spare parts.
The system enables better forecasting and planning. It provides a complete view of inventory trends. This data helps in making informed decisions about stock levels and purchases.
2. Strategic Spare Parts Storage and Distribution
Effective storage and distribution of spare parts are crucial for efficient operations. Proper warehousing and safety stock planning help minimize downtime and ensure parts availability when needed.
Warehousing Solutions
Centralized inventory storage improves accessibility and accuracy. Warehouses should be organized with clear labeling systems. This makes it easy for employees to locate and retrieve parts quickly.
Shelving and storage units need to be arranged logically. Similar parts should be grouped. High-use items are best placed in easily reachable areas.
Some companies use automated storage and retrieval systems. These can increase efficiency and reduce errors. Barcode scanning and inventory management software help track part locations and quantities.
Climate control is important for sensitive components. Proper lighting and ventilation create a safe work environment. Regular cleaning and maintenance keep the warehouse in good condition.
Safety Stock Considerations
Safety stock protects against stockouts and unexpected demand spikes. The right amount depends on several factors:
- Lead times from suppliers
- Demand variability
- Criticality of the part
- Storage costs
Inventory control systems help determine optimal safety stock levels. They track usage patterns and forecast future needs.
For critical parts, higher safety stock may be necessary. This prevents costly downtime if a crucial component fails. Less critical items can have lower stock levels to reduce carrying costs.
It is essential to review safety stock levels regularly. Adjustments should be made based on changing demand patterns or supplier performance.
3. Optimizing Inventory Management
Good spare parts management involves finding the right balance between having enough stock and avoiding excess. Two key strategies can help achieve this balance.
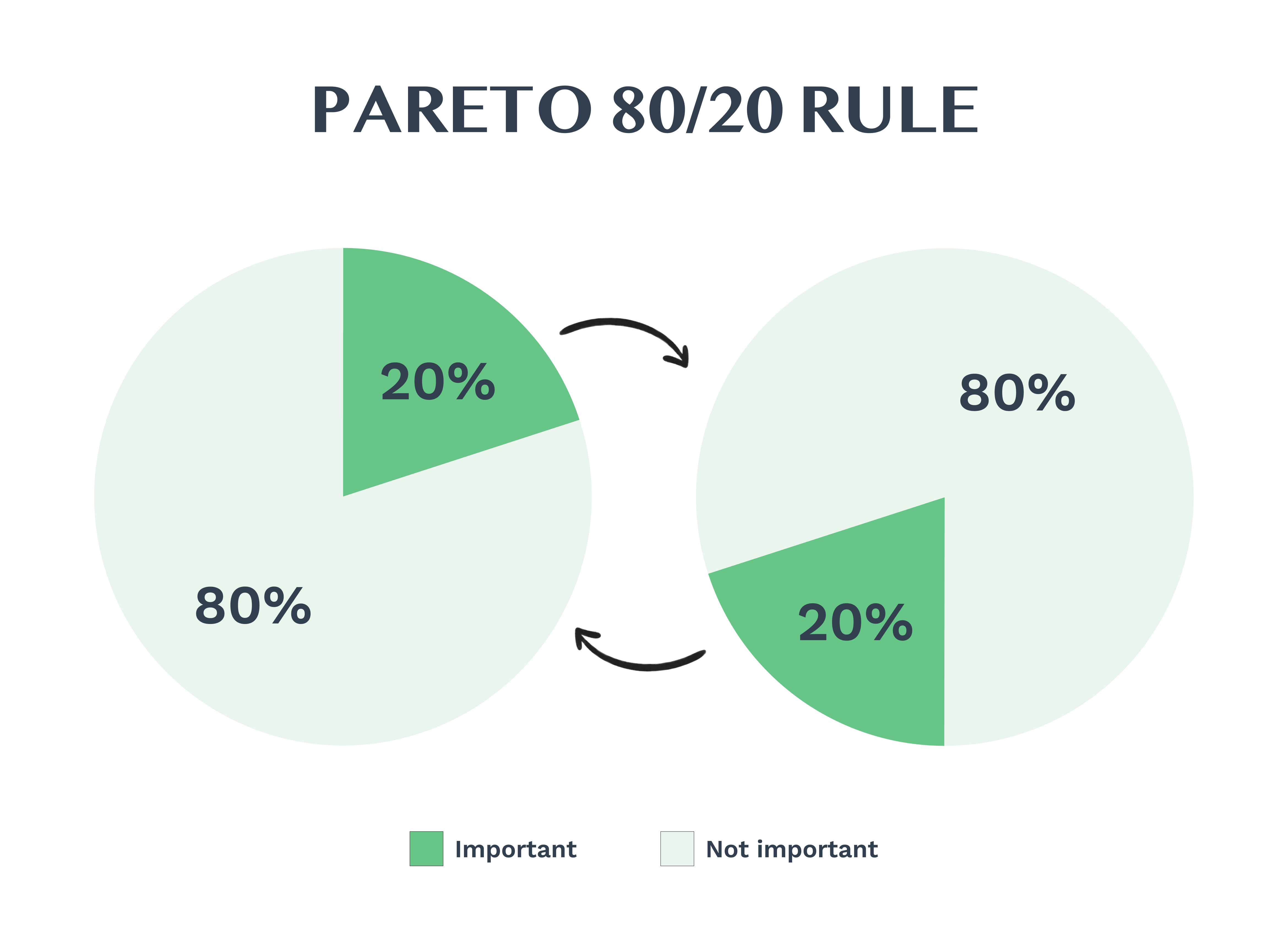
Application of the Pareto Principle
The Pareto Principle, also known as the 80/20 rule, is useful for optimizing spare parts inventory. It suggests that 80% of effects come from 20% of causes.
In inventory management, this means about 20% of parts account for 80% of usage or value. Companies can focus on these critical items to improve efficiency.
Source: WorkTrek
To apply this principle:
- Identify the top 20% of parts by usage or value
- Prioritize these items for tighter control
- Set higher safety stock levels for critical parts
- Review and adjust inventory levels more frequently
This approach helps reduce holding costs while ensuring the availability of vital components.
Implementing the Economic Order Quantity Model
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model helps determine the optimal order size to minimize total inventory costs. It balances ordering costs with holding costs.
The EOQ formula is:
EOQ = √(2DS/H)
Where:
- D = Annual demand
- S = Fixed cost per order
- H = Annual holding cost per unit
Using EOQ can lead to:
- Lower total inventory costs
- Improved inventory turnover
- Reduced stockouts
To implement EOQ:
- Gather accurate data on demand, ordering costs, and holding costs
- Calculate EOQ for each item
- Adjust order quantities based on results
- Monitor and refine over time
Optimizing inventory levels through EOQ can significantly improve spare parts management efficiency.

4. Maintenance Strategies and Work Order Management
Good maintenance practices and efficient work order systems are key to effectively managing spare parts. They help predict needs, reduce waste, and keep operations running smoothly.
Preventive vs. Predictive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance involves regular, scheduled upkeep to prevent breakdowns. It’s based on time or usage intervals, such as changing oil every 5,000 miles in a car.
 Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: EZO CMMS
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: EZO CMMS
Predictive maintenance uses data and sensors to spot issues before they cause problems. It can be more cost-effective as work is done only when needed.
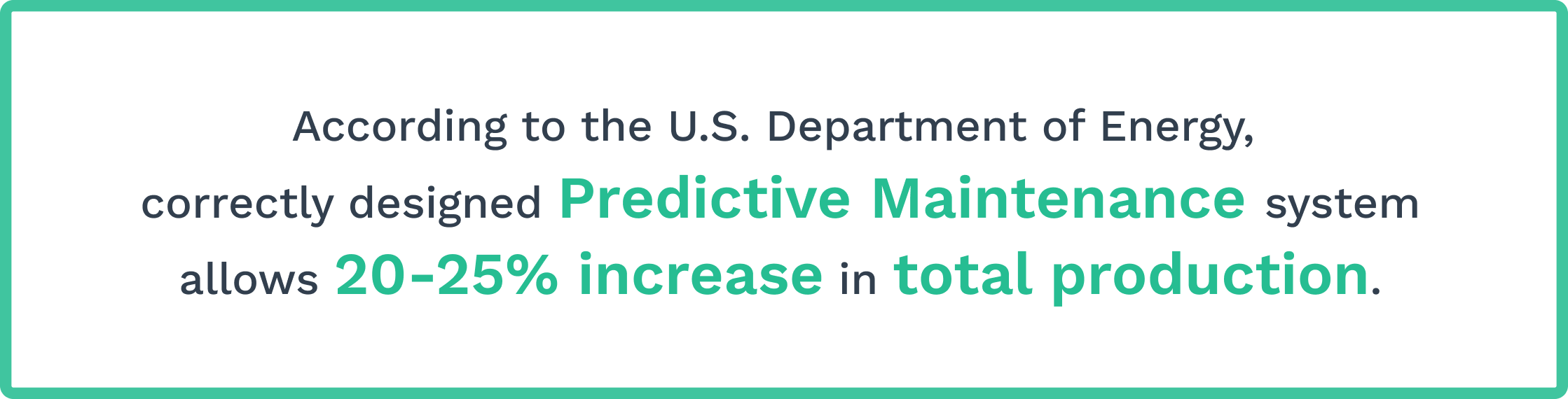
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: TheBlue
Both strategies affect spare parts needs differently:
- Preventive: Requires a steady stock of routine parts
- Predictive: Needs fewer parts on hand but demands quick access when issues arise
Companies often use a mix of both. This balanced approach helps manage inventory and reduces unexpected downtime.
Developing a Standard Work Order Process
A standard work order process ensures tasks are done consistently and efficiently. It should cover these steps:
- Request initiation
- Approval
- Planning and scheduling
- Assigning tasks
- Parts allocation
- Work completion
- Review and close-out
Clear labeling of parts is crucial. It speeds up retrieval and reduces errors. A good system also tracks parts usage, helping with inventory management.
Regular training keeps staff up-to-date on procedures. This leads to better accuracy and efficiency in parts handling.
Maintenance Scheduling and Planning
Good scheduling maximizes resource use and minimizes downtime. It involves:
- Prioritizing tasks based on urgency and impact
- Matching tasks to available skills and parts
- Coordinating with production schedules
Planning allows for better parts management. It gives time to order and receive necessary items, reducing rush orders and excess inventory.
Source: WorkTrek
Using CMMS software can greatly improve this process. It can track parts, schedule tasks, and provide data for better decision-making.
Regular reviews of completed work orders help refine the process. They can reveal patterns in parts usage and maintenance needs.
5. Reduce Unplanned Downtime
Cutting down on unplanned downtime is key to smooth operations. Proper spare parts management is also crucial to keeping equipment running.
Managing Equipment Failure Risks
Effective spare parts management helps cut costly downtimes. Companies should keep critical parts on hand for quick fixes, allowing them to make repairs quickly when things break.
A good plan groups parts by their importance. Top-priority items need higher stock levels, while less vital ones can have lower counts.
Regular checks of part quality are a must. Old or worn items should be replaced before they cause issues. This stops minor problems from turning into big shutdowns.
Training staff on proper part use is also key. When workers know the right parts and how to use them, repairs go smoother.
Leveraging CMMS for Downtime Prevention
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) helps track parts and schedule upkeep. It clearly shows what’s in stock and what needs ordering.
Source: WorkTrek
CMMS tools can predict when machines might fail. This lets teams plan fixes before breakdowns happen. They can order parts ahead of time and avoid rush fees.
These systems also log repair history. This data shows which parts often fail, allowing managers to focus on stocking these high-risk items.
Some CMMS options link to supplier systems. This setup can trigger auto-orders when stock gets low, keeping part levels steady without extra work.
6. Team Collaboration in Spare Parts Management
Working together across teams and departments is key for good spare parts management. It helps cut costs and keeps operations running smoothly.
Integrating Supply Chain Teams
Supply chain collaboration can improve spare parts management. Teams should share data on part usage, costs, and delivery times to help predict needs and avoid shortages.
Regular meetings between purchasing, inventory, and maintenance staff improve communication. They can discuss upcoming projects and plan for parts needs.
Using shared software systems allows real-time updates on stock levels. This prevents duplicate orders and reduces excess inventory.
Enhancing Collaboration Between Departments
Cross-department teamwork is crucial for spare parts management. Maintenance crews should work closely with operations to plan scheduled downtime for repairs.
IT departments can help by setting up digital systems to track parts across locations. This improves visibility and helps with reordering.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: 10xhire
Finance teams should be involved in setting budgets for spare parts. They can help balance costs with the need to avoid production delays.
Regular training sessions help staff understand the importance of proper parts management, creating a culture of collaboration across the organization.
7. Improving Service Level and Customer Satisfaction
Effective spare parts management directly impacts service quality and customer happiness. Smart inventory practices and tracking key metrics help companies meet customer needs quickly and efficiently.
Aligning Inventory to Service Goals
Companies can boost service levels by matching spare parts stock to customer demand. This means keeping enough critical parts on hand to avoid delays. Data can be used to predict which parts are needed most often.
Smart labeling systems make it easy to find parts quickly. Grouping similar items in the warehouse reduces search time when filling orders.
Some businesses use min-max levels for each part. When stock hits the minimum, they order more to reach the maximum, keeping popular items from running out.
Tracking and Enhancing Customer Service Metrics
Measuring service performance helps spot areas to improve. Key metrics include:
- Order fill rate
- On-time delivery percentage
- Average repair time
- Customer satisfaction scores
Use software to track these numbers. Look for trends over time. Are certain parts always causing delays? This info helps decide where to focus improvement efforts.
Ask customers for feedback after each service. Their input reveals issues you might miss. Act quickly on complaints to show customers you value their business.
Regular staff training keeps service skills sharp. Teach teams about new parts and repair methods. This helps them solve problems faster and please customers.
8. Leveraging Technology for Enhanced Efficiency
New tech tools can greatly improve how companies manage spare parts. These tools make tracking and organizing parts easier and faster.
The Role of Automation in Inventory Management
Automated systems have improved spare parts management. They keep track of stock levels in real-time, helping to avoid running out of parts.
When stock gets low, these systems can order more parts independently. This saves time and prevents delays in getting needed items.
Automation also creates detailed reports. These show how fast parts are used, how long orders take, and other key info. With this data, companies can make smarter choices about what to keep in stock.
Tracking Systems and Their Impact on Operational Efficiency
Modern tracking systems monitor parts using barcodes or RFID tags. This makes finding and counting items much quicker and more accurate.
These systems can tell workers exactly where to find a part in the warehouse, cutting down on search time and helping jobs get done faster.
Source: immago
Better tracking also means fewer lost or misplaced parts. When companies know what they have, they waste less money on unnecessary purchases.
Tracking data helps predict when parts will be needed. This allows for better planning and fewer urgent orders, which can be costly.
9. Implementing Effective Spare Parts Procurement
Good spare parts procurement ensures the right parts are available when needed. It balances costs with operational needs.
Understanding Lead Times and Their Impact
Lead times affect how quickly spare parts can be obtained. Long lead times require careful planning. Companies must order parts well in advance to avoid stockouts.
Short lead times allow for more flexibility. Parts can be ordered closer to when they’re needed, reducing inventory costs and storage needs.
 Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: cleverence
Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: cleverence
To manage lead times effectively:
- Track supplier performance
- Build relationships with reliable vendors
- Use historical data to predict future needs
- Consider safety stock for critical parts
Computerized systems help monitor lead times and inventory levels. They can alert managers when it’s time to reorder.
Building a Robust Bill of Materials (BOM)
A Bill of Materials lists all parts needed for a product or repair. A well-structured BOM is crucial for effective spare parts management.
Key elements of a robust BOM:
- Accurate part numbers and descriptions
- Quantity required for each part
- Alternate part options
- Supplier information
- Cost data
Inventory control systems can help maintain an up-to-date BOM. These systems track parts usage and availability.
Regular BOM reviews ensure it stays current. This helps prevent ordering obsolete parts or missing new requirements.
10. Asset Management and Parts Inventory
Good asset management and parts inventory control are key to running operations smoothly. These practices help businesses avoid costly downtime and ensure they have the right parts on hand when needed.
Tracking and Managing Asset Lifecycles
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) can track asset lifecycles. These systems help businesses monitor equipment performance and schedule maintenance.
Regular inspections and preventive maintenance extend asset life, reducing the need for emergency repairs and unplanned parts purchases.
![]()
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Innovative
Companies should keep detailed records of each asset’s:
- Purchase date
- Expected lifespan
- Maintenance history
- Repair costs
This data helps predict when parts will be needed and inform decisions about when to replace aging equipment.
Inventory Audits and Accuracy
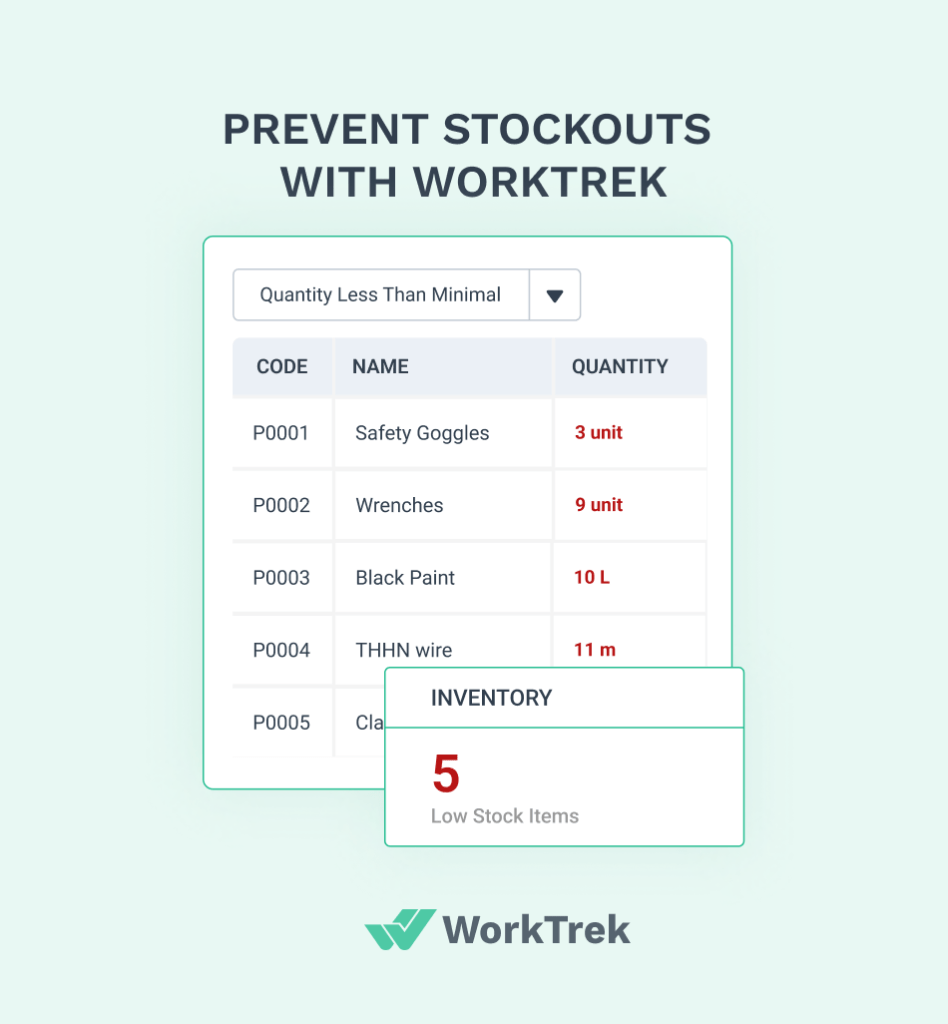
Regular inventory audits are crucial for maintaining accurate stock levels. These checks help prevent stockouts and overstocking.
Businesses should conduct physical counts of parts at least once a year. More frequent spot checks can catch discrepancies early.
Using barcodes or RFID tags makes tracking parts easier and more accurate. These technologies reduce human error in inventory management.
It’s important to set reorder points for each part. The reorder point formula is:
ROP = (Average daily usage × Lead time) + Safety stock
This ensures parts are ordered before they run out. It also prevents excess inventory from tying up cash.
Conclusion
Good spare parts management can promote smooth operations. It helps keep equipment running and avoids costly downtime.
Smart inventory practices save money. Companies can cut waste by stocking the right amounts.
Using tech makes things easier. Inventory software and barcodes help track parts accurately.
Easy access to parts is important. A central inventory lets workers find what they need quickly.
With these practices, businesses can manage spare parts effectively. This supports equipment upkeep and overall efficiency.