Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeMaintenance organizations often struggle with unexpected equipment failures and delays due to missing or insufficient parts, leading to costly downtime and operational inefficiencies.
When critical components aren’t readily available, repair timelines extend, equipment stays offline longer, and productivity suffers. The impact can ripple across the entire operation, resulting in missed deadlines, frustrated employees, and increased operational costs. 
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Verusen
Effective MRO inventory management ensures that essential parts and tools are always on hand, enabling maintenance teams to quickly respond to issues, minimize downtime, and keep operations running smoothly.
It can include tools, spare parts, safety gear, and cleaning supplies. This leads to improved operational efficiency, cost savings, and greater reliability across the organization.
Understanding MRO Inventory
MRO inventory can help your business run smoothly. It covers a wide range of items used to support daily operations and maintain equipment.
Definition of MRO
MRO stands for Maintenance, Repair, and Operations. This inventory includes supplies and materials companies need to keep their facilities and equipment in good working order.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: MRP Easy
MRO items are not part of the final product sold to customers. Instead, they support the production process and daily business activities. Examples include tools, spare parts, safety gear, and cleaning supplies.
Companies use MRO inventory to fix broken machinery, perform routine maintenance, and keep workspaces clean and safe.
Components of MRO Inventory
MRO inventory consists of several key categories:
- Maintenance supplies: Lubricants, filters, and replacement parts
- Repair tools: Wrenches, screwdrivers, and diagnostic equipment
- Safety equipment: Hard hats, gloves, and fire extinguishers
- Office supplies: Paper, pens, and printer ink
- Cleaning supplies: Mops, detergents, and trash bags
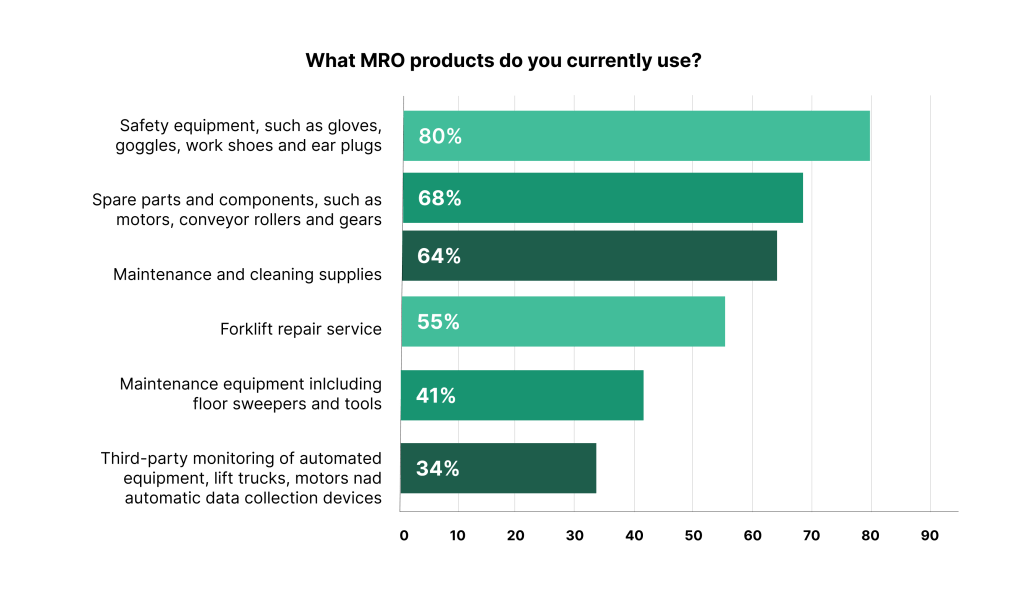
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: SupplyChain247
These items help keep operations running smoothly and safely. They prevent equipment breakdowns and ensure a clean, organized workspace.
Importance of MRO in Business Operations
MRO inventory is vital for operational efficiency. It helps companies avoid costly downtime and maintain productivity.
When machines break down, having the right repair parts can save valuable time. This reduces production delays and keeps customers satisfied.
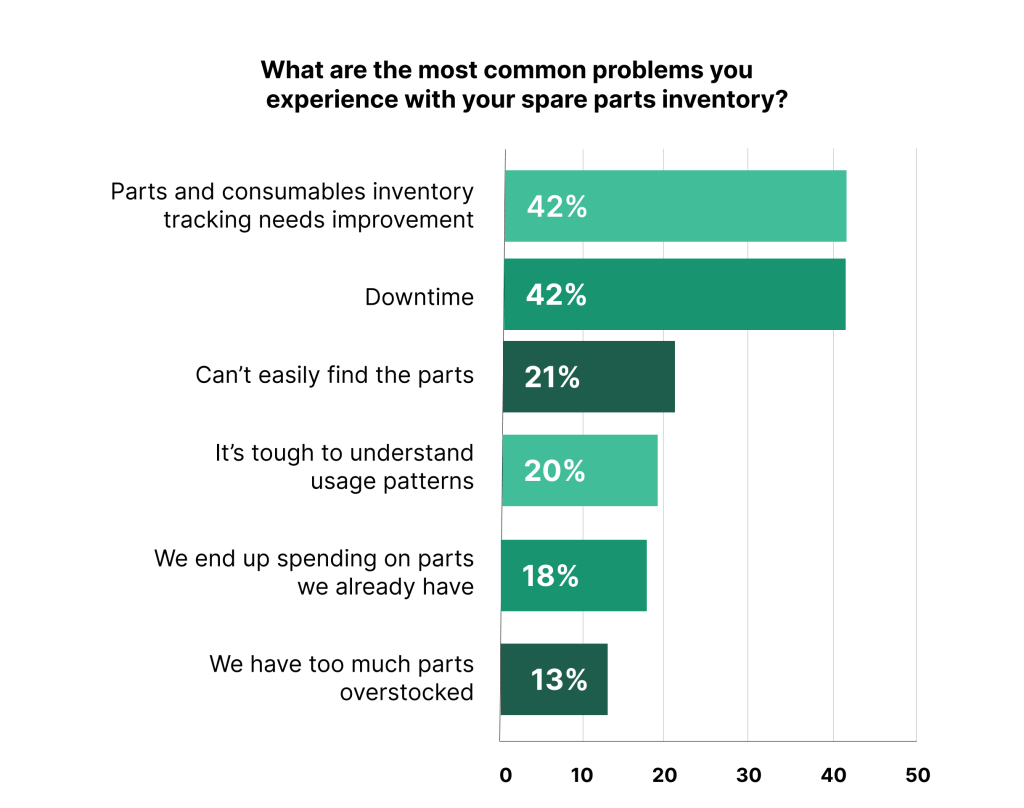
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Quality Digest
Proper MRO management also improves safety. Well-maintained equipment is less likely to malfunction and cause accidents, and safety gear protects workers from potential hazards.
MRO inventory helps control costs by preventing emergency purchases at higher prices. Regular maintenance also extends the life of equipment, saving money in the long run.
MRO Inventory Management
Managing MRO inventory effectively can reduce costs and improve operational efficiency. Proper management involves strategic approaches, control techniques, and technology leveraging.
Key Strategies for Effective Management
MRO inventory management starts with clear categorization and organization. Companies should group items by type, usage frequency, and criticality.
Implementing ABC analysis helps prioritize inventory based on value and importance. This method groups items into A (high-value), B (medium-value), and C (low-value) categories.
Regular audits ensure accuracy and identify obsolete items. Setting par levels for each item prevents stockouts and overstocking.
Standardizing parts across equipment reduces inventory variety and simplifies ordering. Establishing strong supplier relationships can lead to better pricing and faster deliveries.
MRO Inventory Control Techniques
Effective control begins with accurate tracking. Using barcodes or RFID tags improves data accuracy and speeds up processes.
Just-in-time ordering reduces carrying costs by maintaining minimal stock levels. This approach works well for non-critical, easily obtainable items.
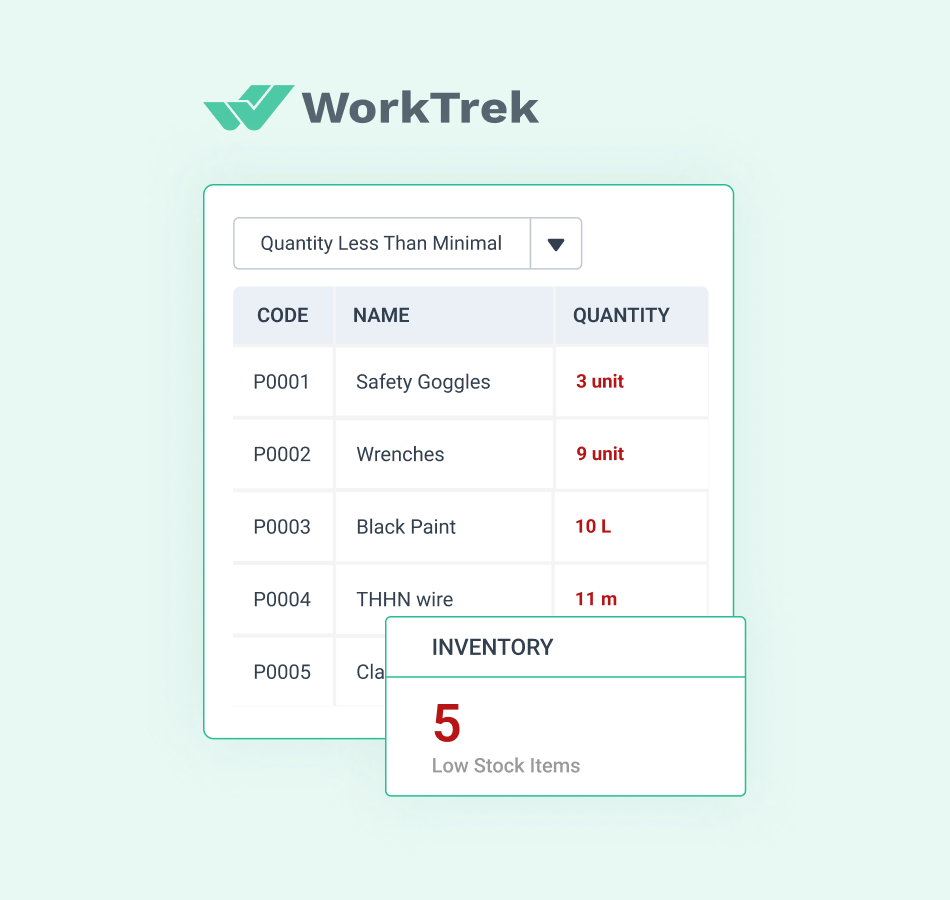
Source: WorkTrek
Consignment inventory arrangements with suppliers can lower upfront costs. The supplier owns the inventory until it’s used, reducing the financial burden.
Implementing a centralized storage system improves organization and accessibility. This setup allows better control over stock levels and usage patterns.
Technology and MRO
Inventory management software streamlines processes and provides real-time data. These systems can track stock levels, automate reordering, and generate reports.
Mobile devices and apps allow for instant updates and access to inventory data. This mobility improves efficiency in large facilities.
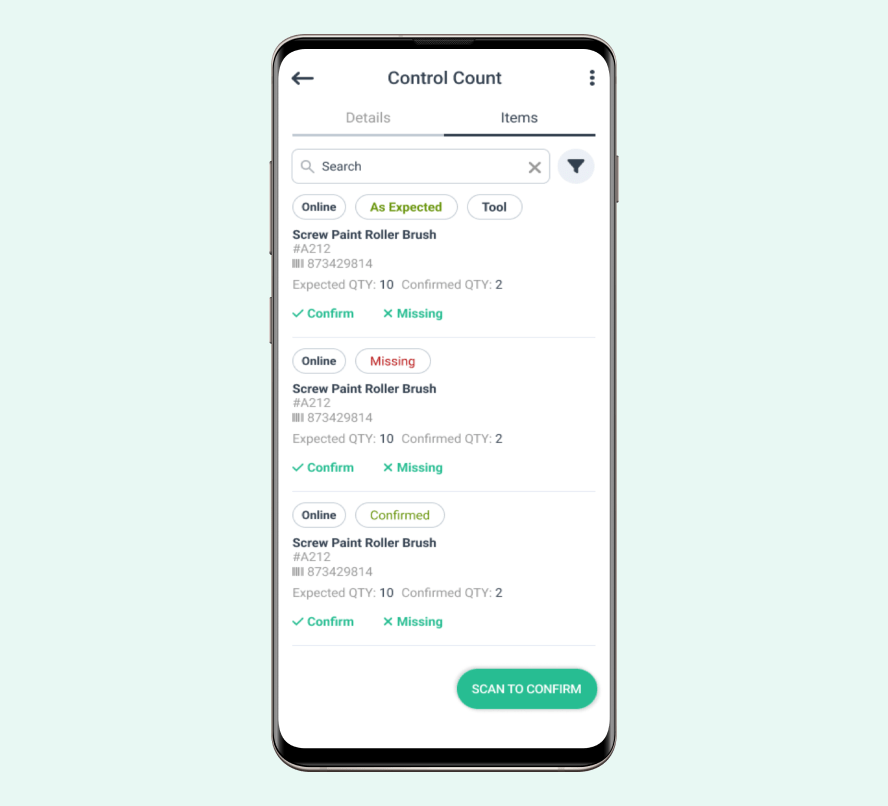
Source: WorkTrek
Data analytics helps identify trends, optimize stock levels, and forecast future needs. By analyzing historical data, companies can make informed decisions about inventory management.
Cloud-based systems offer accessibility and scalability. They allow multiple users to access data from various locations, improving collaboration and decision-making.
Inventory Optimization
Optimizing MRO inventory involves balancing stock levels, forecasting demand, and aligning with maintenance needs. These strategies help companies reduce costs while ensuring critical parts are available when needed.
Balancing Safety Stock and Overstocking
MRO inventory optimization aims to find the right balance between safety stock and overstocking. Safety stock prevents stockouts during unexpected demand spikes or supply chain disruptions.

Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Comparesoft
Too little safety stock can lead to costly downtime. Too much ties up capital and increases storage costs.
Companies use data analysis to set optimal safety stock levels. They consider factors like:
• Lead times

• Demand variability
• Criticality of parts
• Storage costs
Reorder points are set to trigger new orders before stock runs out. This helps maintain efficiency while avoiding excess inventory.
Forecasting and Demand Planning
Accurate forecasting is key to inventory optimization. It helps predict future needs and adjust stock levels.
Demand forecasting uses historical data and trends. It accounts for factors like:
• Seasonal patterns
• Equipment lifecycles
• Planned maintenance schedules
Advanced analytics and machine learning improve forecast accuracy. This leads to better inventory decisions and reduced waste.
Companies also use collaborative forecasting. They work with suppliers and maintenance teams to align predictions and plans.
Maintenance Schedules and Predictive Analysis
Aligning inventory with maintenance needs is crucial for efficiency. Predictive maintenance uses data to forecast when equipment will need service.
This approach helps:
• Reduce unexpected breakdowns
• Optimize parts ordering
• Minimize excess inventory
Companies use sensors and IoT devices to monitor equipment health. This data feeds into predictive models.
The maintenance schedules are then adjusted based on the actual equipment condition. This prevents premature part replacements and unexpected failures.
Inventory levels are synced with these schedules. This ensures parts are available when needed without overstocking.
Procurement and Supply Chain
MRO inventory management is closely tied to procurement and supply chain processes. Effective strategies can lead to cost savings, improved efficiency, and better inventory control.
Improving Supplier Relationships
Strong supplier relationships are important to effective MRO procurement. Regular communication helps ensure timely deliveries and quality products. Suppliers can offer insights on new technologies and market trends.
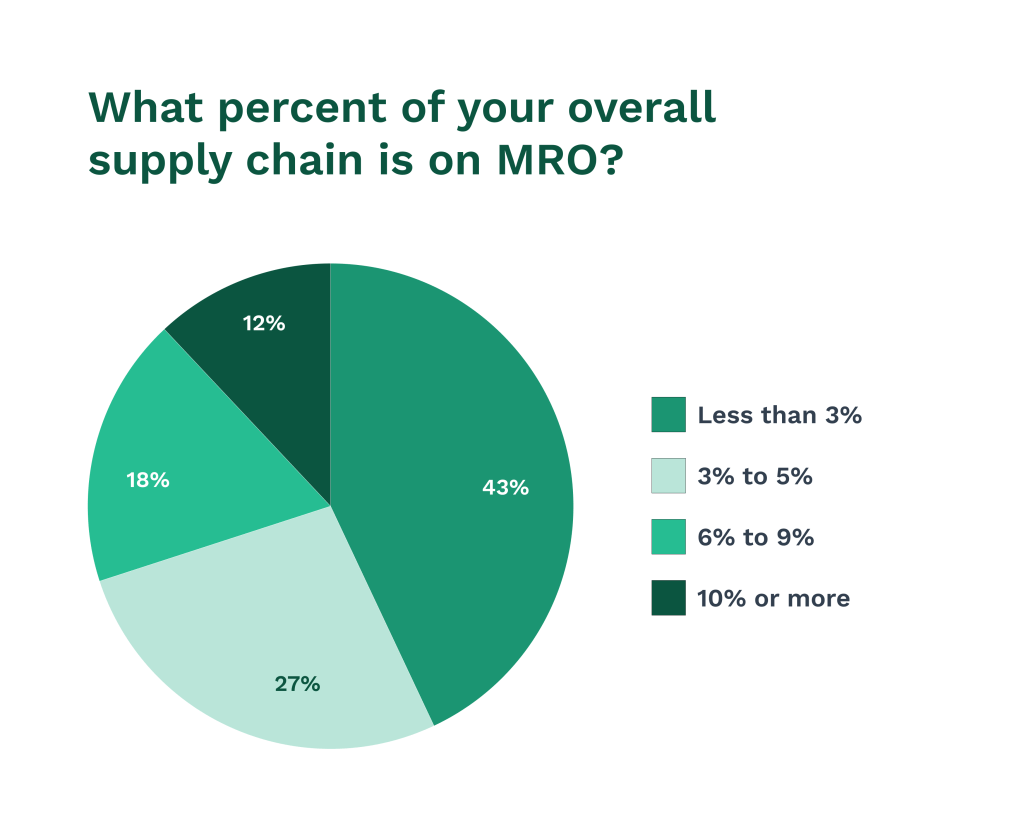
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Logistics Management
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI) is a useful approach. In this model, suppliers take responsibility for maintaining agreed-upon stock levels. This can reduce administrative burden and improve inventory accuracy.
Long-term contracts with preferred suppliers often lead to better pricing and service. However, it is important to regularly review these agreements to ensure they remain competitive.
Impact of MRO on Supply Chain Management
MRO inventory directly affects supply chain performance. Proper management helps prevent production delays and equipment downtime, leading to smoother operations and improved customer satisfaction.
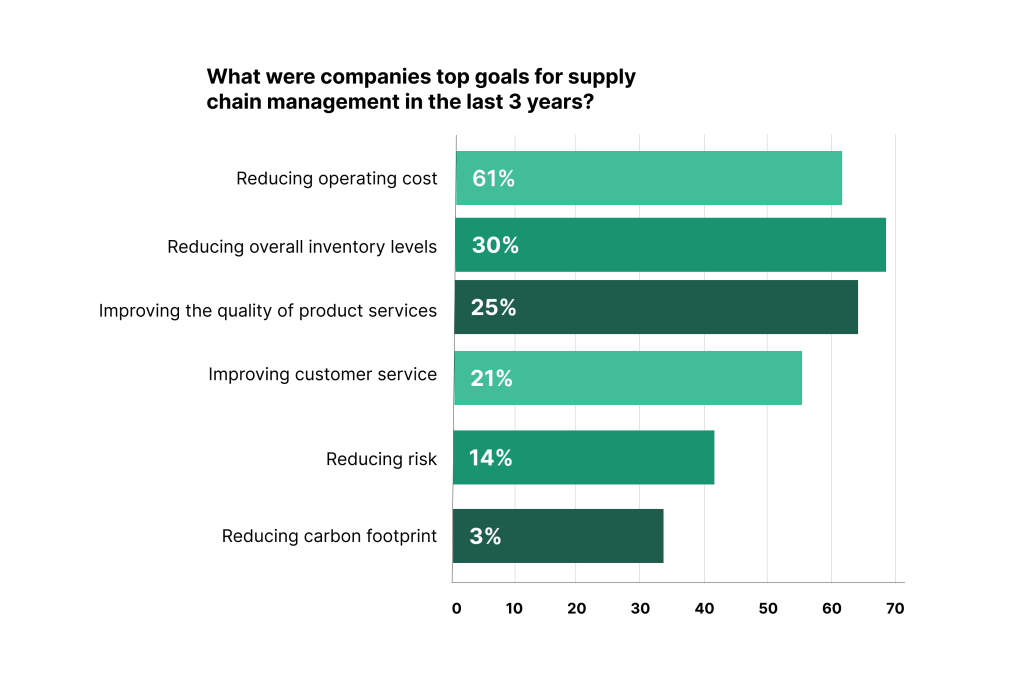
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: McKinsey&Companu
Accurate forecasting of MRO needs can help optimize stock levels and reduce the risk of stockouts or excess inventory. Advanced analytics tools can improve forecasting accuracy.
Integration of MRO processes with broader supply chain systems is beneficial. This allows for better visibility and control over inventory levels and spending.
Centralized Versus Decentralized Inventory
The choice between centralized and decentralized MRO inventory affects procurement and supply chain strategies.
Centralized inventory:
- Allows for bulk purchasing and better negotiation power
- Improves inventory visibility and control
- This may lead to longer lead times for remote locations
Decentralized inventory:
- Provides faster access to parts for individual facilities
- This can result in higher overall inventory levels
- This may lead to inconsistent practices across locations
Many organizations opt for a hybrid approach. This combines the benefits of centralized purchasing with strategically placed local inventories for critical items.
Financial Implications
MRO inventory has significant effects on a company’s bottom line. It impacts costs, profitability, and equipment performance in various ways.
Reducing Costs and Enhancing Profitability
Effective MRO inventory management can lead to significant cost savings. Companies can cut expenses by avoiding overstocking and reducing waste. Smart procurement strategies help negotiate better prices with suppliers.
Tracking usage patterns allows businesses to order only what they need. This frees up cash that would otherwise be tied up in excess inventory.
Improved inventory control also reduces downtime. When parts are available, repairs happen faster, keeping production running smoothly and boosting profits.
Analyzing MRO Expenditures
Regular analysis of MRO spending reveals areas for improvement. Companies should track costs for different categories, such as spare parts, tools, and safety gear.
Identifying high-cost items helps prioritize cost-cutting efforts. It’s also important to look at spending trends over time.
MRO inventory typically makes up 6 to 10 percent of a company’s total procurement spend. Minor improvements can have a big impact on the overall budget.
Data analytics can uncover hidden costs and inefficiencies, leading to smarter purchasing decisions and better inventory management.
Impact on Equipment Lifespan and Maintenance
Good MRO practices extend equipment life and reduce repair costs. Having the right parts on hand means faster repairs and less downtime.
Regular maintenance, made possible by proper MRO inventory, prevents small issues from becoming big problems, saving money on major repairs or replacements.

For example, timely forklift repair using stocked parts keeps the machine running longer and avoids costly rush orders for emergency repairs.
Tracking maintenance history helps predict future needs, allowing for better planning and more efficient use of MRO inventory.
MRO Inventory in Various Industries
MRO inventory can play a different role across different sectors, each with its unique challenges and requirements. Companies must adapt their MRO practices to fit their industry needs and size.
Industry-Specific MRO Challenges
Manufacturing plants face high demands for machine parts and industrial equipment. They must balance having enough spare parts on hand without tying up too much capital in inventory.
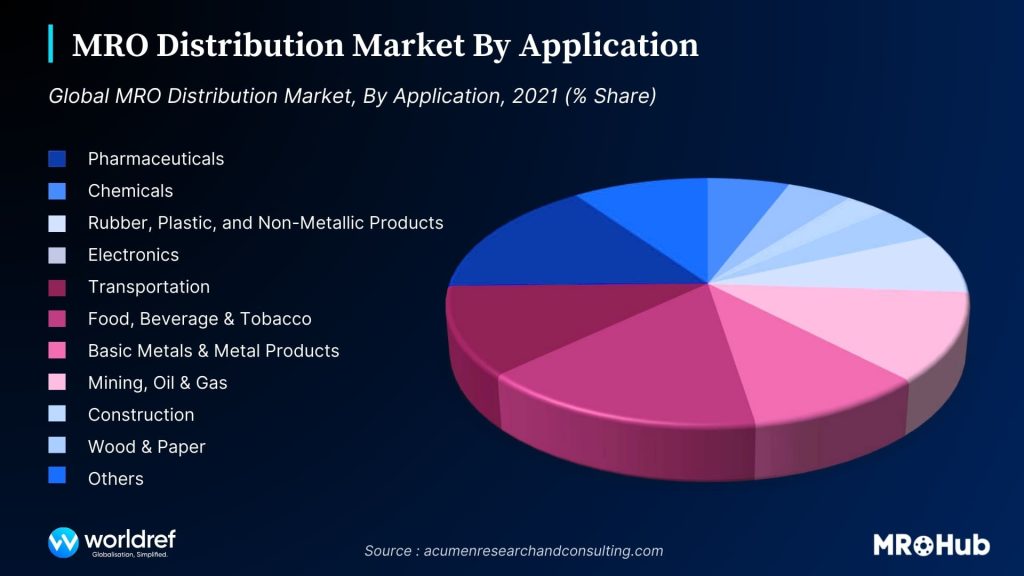
Source: Insights by worldref
Healthcare facilities require a steady supply of medical devices and laboratory equipment. Hospitals must maintain sterile environments, so janitorial supplies are critical MRO items.
Construction companies deal with tool management and equipment maintenance. They often struggle with tracking MRO items across multiple job sites.
The aviation industry has strict regulations for airplane parts. Airlines must keep detailed records of all MRO materials used in aircraft maintenance.
MRO Examples Across Sectors
In manufacturing, MRO inventory includes lubricants, safety gear, and machine components. Factories stock items like bearings, belts, and pneumatic fittings.
Hospitals maintain stocks of medical supplies, cleaning products, and repair tools. Common MRO items include syringes, disinfectants, and HVAC filters.
IT companies keep spare computer parts, networking cables, and software licenses as MRO inventory. Data centers stock backup power supplies and cooling system components.
Retail stores manage MRO goods like light bulbs, shopping carts, and price tag guns. They also stock cleaning supplies and maintenance tools for store upkeep.
Adapting MRO Practices for Small Businesses
Small businesses can also benefit from MRO best practices. They should start by identifying critical items that could cause downtime if they are not available.
A small auto repair shop might focus on stocking common replacement parts and specialized tools. This helps reduce repair delays and improves customer satisfaction.
Local restaurants can manage their MRO inventory by tracking kitchen equipment parts and cleaning supplies. This prevents unexpected stockouts that could disrupt service. 
Illustration: WorkTrek / Quote: Net Suit
Small manufacturers can use CMMS software like WorkTrek to track MRO items. This helps them avoid overstocking while ensuring they have the necessary repair components.
Key Performance Indicators for MRO
Measuring and improving MRO inventory management requires tracking specific metrics. These indicators help businesses optimize their maintenance, repair, and operations processes.
Selecting Relevant KPIs
Key performance indicators for MRO inventory focus on costs, efficiency, and demand fulfillment. Common KPIs include inventory turnover ratio, stockout rate, and carrying costs.
Inventory turnover measures how quickly MRO items are used. A higher ratio often indicates better inventory management.
Stockout rate tracks the frequency of inventory shortages. Lower rates suggest improved operational continuity.
Carrying costs reflect the expenses of holding MRO inventory. This includes storage, insurance, and depreciation.
Other useful KPIs are:
- Order accuracy rate
- Supplier lead time
- Emergency order frequency
Tracking and Improving MRO Metrics
Effective MRO supply chain management relies on robust data collection and analysis. Regular monitoring of KPIs helps identify trends and areas for improvement.
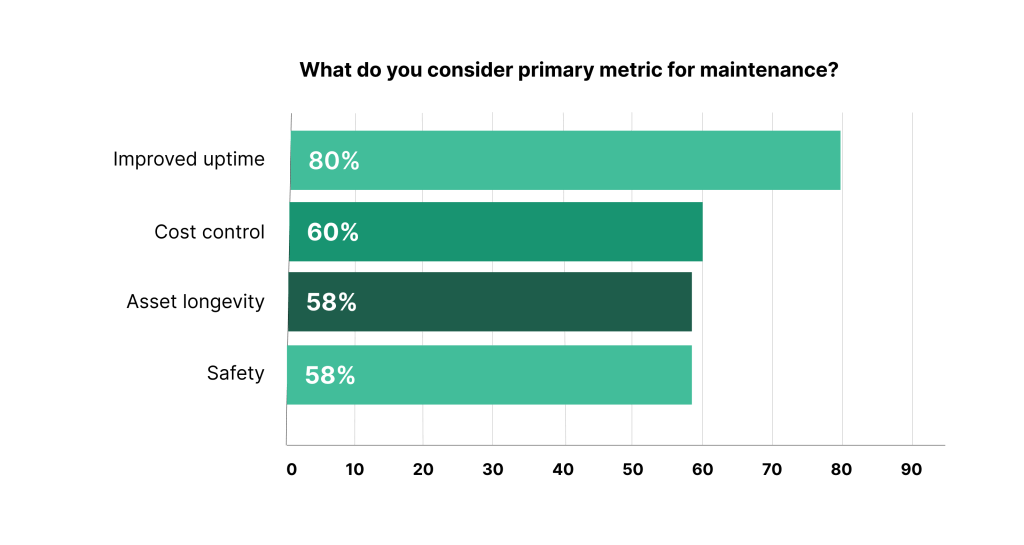
Illustration: WorkTrek / Data: Reliabilityweb
To enhance MRO inventory performance:
- Implement inventory tracking software
- Train staff on proper data entry
- Set target values for each KPI
- Review metrics regularly
Continuous improvement strategies include:
- Optimizing reorder points
- Negotiating with suppliers for better lead times
- Streamlining the procurement process
Businesses can reduce costs, minimize downtime, and improve overall operational efficiency by focusing on these metrics.
Summary
By keeping essential supplies and tools readily available, businesses can avoid costly delays, improve productivity, and enhance equipment lifespan. Effective management involves strategic categorization, forecasting, and technology to optimize stock levels and streamline processes.
Whether in manufacturing, healthcare, or small businesses, a well-managed MRO inventory contributes to smoother operations, better safety, and long-term cost savings. Investing in proper MRO practices ultimately leads to more reliable and profitable operations.









