Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
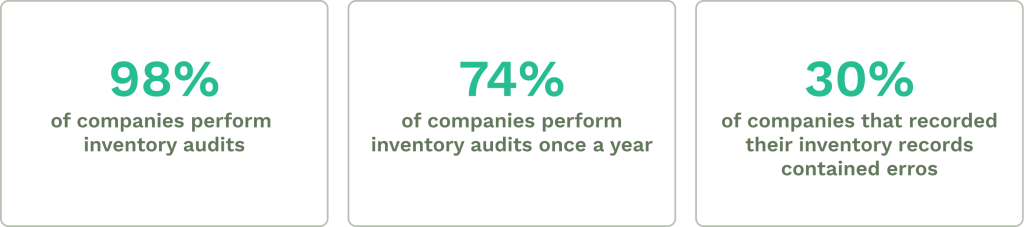
Try for freeMany maintenance managers struggle to balance day-to-day operations and compliance requirements. Important compliance details can slip through the cracks between equipment checks, repair schedules, and documentation, leading to serious consequences, including fines and workplace incidents.

The tips we’re about to share will help you build a more compliant maintenance department without adding unnecessary complexity to your workload. These practical strategies can be implemented gradually to create lasting improvements in your compliance efforts.
Key Takeaways
- A strong compliance culture reduces risks and builds trust throughout the organization.
- Well-documented procedures, preventive maintenance plans, and regular audits form the foundation of maintenance compliance.
- Technology solutions can simplify compliance tracking and reporting while improving overall maintenance efficiency.
1. Prioritize Compliance as part of Your Maintenance Plan
Make maintenance compliance part of your maintenance strategy. This approach requires following regulations, standards, and best practices that protect workers, equipment, and businesses from costly violations and hazardous conditions.
Defining Maintenance Compliance
Maintenance compliance refers to following established rules, regulations, and standards when performing maintenance activities. It involves documenting all maintenance department policies and procedures to ensure consistent organizational application.
Compliance covers several key areas:
- Equipment maintenance schedules
- Safety protocols
- Record-keeping requirements
- Training certifications
- Environmental regulations
- Fire Safety

For maintenance teams, compliance means creating systematic approaches to work. This includes developing detailed maintenance programs that specify how and when equipment should be inspected, repaired, and replaced.
Well-defined compliance frameworks help maintenance departments avoid guesswork. They provide clear guidelines for acceptable maintenance practices according to industry, government, and company standards.
The Importance of Following Standards
Following maintenance compliance standards will protect your organization from multiple risks. Depending on the severity of the violation, financial penalties for non-compliance can reach thousands or even millions of dollars.
Beyond financial concerns, proper compliance:
- Reduces workplace accidents
- Extends equipment lifespan
- Minimizes unplanned downtime
- Improves operational efficiency
- Enhances company reputation
- Reduce reactive maintenance tasks
- Improves preventive maintenance compliance rate
- Streamlines facilities management
Staying consistent when implementing compliance measures ensures that safety regulations and protocols are followed across all maintenance activities. This approach can create a safety culture to improve FM compliance and ensure peak performance.

Track and report on your preventive maintenance compliance score to reduce costly repairs.
Equipment failures due to poor maintenance compliance can lead to production losses, which often far exceed the cost of implementing proper maintenance procedures.
Regulatory Bodies and Requirements
Various regulatory agencies establish and enforce maintenance compliance requirements. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) sets workplace safety standards, including requirements for equipment maintenance.

Other significant regulatory bodies include:
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration)
- DOT (Department of Transportation)
- Industry-specific agencies
Each industry faces unique regulatory challenges. Healthcare facilities must meet strict infection control standards, while manufacturing plants might focus on machine guarding and lockout/tagout procedures.
Compliance guidelines for industrial maintenance vary by sector, but remember that they are designed to protect workers, the public, and the environment. These agencies conduct regular audits to verify compliance with established standards.
It is important for maintenance departments to stay current with changing regulations. This requires ongoing education and incident tracking to ensure continued compliance with evolving standards.
2. Develop a Compliance-Oriented Culture
Creating a strong compliance culture is essential for maintenance departments to meet regulatory requirements consistently. A well-established culture embeds compliance into daily operations rather than treating it as a separate activity.
Leadership and Management Commitment

Effective compliance begins with a visible commitment from leadership. When managers demonstrate that compliance is a priority, employees follow suit. Leaders should regularly discuss compliance in meetings and communications.
Management must allocate appropriate resources for compliance activities. This includes providing time for training and purchasing necessary equipment or software to track compliance efforts.
Leaders should develop comprehensive policies and procedures that are clear and accessible. These documents establish expectations and guide employees.
Recognition programs that reward compliance achievements help reinforce the importance of following protocols. Celebrating teams or individuals who excel at compliance motivates others to do the same.
Training and Employee Empowerment
Regular training sessions keep compliance requirements fresh in employees’ minds. Training should target specific job functions rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.

Employees need to understand not just what to do but why compliance matters. Explaining the reasoning behind regulations helps workers remember requirements and make better decisions.
Continuous documentation and evidence collection ensure controls are working properly. Training programs should teach employees how to document their compliance activities effectively.
Empowering employees to report potential issues without fear of retaliation creates a stronger compliance environment. Staff members are the organization’s eyes and ears, spotting red flags that need attention.
Communication and Documentation
Clear communication channels ensure compliance information reaches all team members. Regular updates about changing regulations help maintenance teams stay current.
Documentation systems should be simple enough that employees can easily record compliance activities. Complex systems discourage proper documentation.

Using technology tools for tracking incidents, conducting audits, and managing training programs streamlines compliance efforts. These tools provide evidence that protocols are being followed.
Visual reminders like posters, checklists, and dashboards keep compliance requirements visible. These simple tools help maintenance teams incorporate compliance into their daily routines.
Transparency about compliance successes and failures builds trust. Sharing positive outcomes and areas needing improvement demonstrates an organizational commitment to continuous improvement.
3. Optimize Maintenance Policies and Procedures
Clear documentation forms the backbone of any successful maintenance department. Well-defined policies and procedures help ensure regulatory compliance, promote workplace safety, and create consistent operations across your organization.
Creating Effective Policies to Reduce Compliance Risks
Start by documenting all maintenance department policies in clear, accessible language. These documents should outline responsibilities, compliance requirements, and safety protocols for all maintenance activities.

Effective policies should address:
- Equipment-specific guidelines for operation and maintenance
- Safety requirements including PPE usage and hazard protocols
- Compliance standards relevant to your industry
- Emergency response procedures for equipment failures
When creating policies, involve experienced maintenance staff. Their practical knowledge helps ensure policies reflect real-world conditions rather than theoretical ideals.
Review regulations from OSHA, EPA, and industry-specific bodies to ensure your policies meet all compliance requirements. Use straightforward language that all employees can understand regardless of technical background.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs translate broader policies into specific step-by-step instructions for completing maintenance tasks. Create detailed maintenance programs that outline exactly how work should be performed.
Each SOP should include:
- Purpose and scope of the procedure
- Required tools and materials
- Step-by-step instructions with safety checkpoints
- Troubleshooting guidelines for common issues
- Quality control measures to verify work
Use visual aids like diagrams, photos, and checklists to enhance comprehension. These visuals help clarify complex procedures and reduce the risk of misinterpretation.
Consider creating digital SOPs accessible via tablets or smartphones. This ensures technicians always have the most current procedures when performing maintenance tasks.
Regular Policy Reviews to Ensure Compliance
Maintenance compliance isn’t a one-time achievement but requires consistent implementation and ongoing attention. Schedule quarterly or biannual reviews of all policies and procedures.
During these reviews:
- Update documentation to reflect new equipment or processes
- Incorporate feedback from maintenance technicians
- Address any compliance gaps identified during audits
- Revise procedures based on incident reports or near-misses
Use a tracking system to manage document versions and ensure all staff work from current policies. Many maintenance management systems include document control features for this purpose.
Assign specific team members responsibility for policy updates. This accountability ensures reviews happen on schedule and necessary changes are made.
4. Improve Audit and Monitoring Systems
Regular audits and consistent monitoring serve as the backbone of maintenance compliance programs. These processes help identify gaps, prevent issues, and create a measurable pathway to improvement.
Implementing Internal Audits
Effective internal audits require clear structure and consistent scheduling.
Create a preventive maintenance task list that covers all maintenance compliance areas to ensure nothing is overlooked.
This checklist should include equipment inspections, documentation reviews, and safety protocol verification.
The audit team should include members from different departments to provide diverse perspectives. Cross-departmental involvement helps identify blind spots that specialists might miss.
Training auditors properly ensures they understand maintenance operations’ compliance requirements and technical aspects. Well-trained auditors collect more accurate data and provide more useful recommendations.
Documentation of audit findings must be standardized and accessible. Using digital tools allows for better tracking of recurring issues and improvement trends over time.
Continuous Monitoring Techniques
Daily monitoring complements formal audits by catching issues before they escalate. Implementing computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) provides real-time insights into compliance status and maintenance activities.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established for maintenance compliance:

- Equipment downtime percentage
- Preventive maintenance tasks compliance and completion rates
- Safety incident frequency
- Compliance violation occurrences
Automated sensors and IoT devices offer continuous equipment monitoring without human intervention. These technologies can alert maintenance teams to potential failures before they occur.
Regular staff feedback sessions create an additional monitoring layer where frontline workers report compliance challenges. This human intelligence often catches issues that automated systems miss.
Addressing Non-Compliance Issues
When non-compliance is discovered, a structured response protocol must be activated immediately. The first step is documenting the exact nature and scope of the issue.
Categorizing findings by severity helps prioritize corrective actions. Critical safety violations require immediate attention, while documentation issues may allow longer resolution timelines.
Root cause analysis prevents recurring problems by addressing underlying issues rather than symptoms. Teams should ask “why” multiple times to reach the fundamental cause.

Corrective action plans must include specific responsibilities, clear deadlines, and verification steps. They should also be tracked in a central system to ensure completion.
Follow-up audits verify that implemented solutions have resolved the non-compliance issues. This creates a closed-loop system where problems are identified, fixed, and confirmed.
5. Make Compliance part of your Maintenance Planning and Scheduling
Effective maintenance planning and scheduling form the backbone of a compliant maintenance department. Proper planning ensures that critical tasks are completed on time while optimizing available resources and meeting regulatory deadlines.
Prioritizing Maintenance Tasks
Maintenance departments must establish clear criteria for task prioritization. Safety-critical equipment should always receive top priority, followed by compliance-required maintenance activities.
Consider implementing a risk-based approach using a simple matrix:

Regular review of this priority system ensures maintenance is aligned with organizational goals. Document your prioritization process to demonstrate compliance during audits.
Resource Allocation and Optimization
Efficient resource allocation requires detailed knowledge of team capabilities and equipment needs—track technician certifications and skills to match the right person to each job.
Maintenance management software, such as CMMS, can help optimize workforce scheduling. These systems track:
- Technician availability and skills
- Parts inventory levels
- Equipment maintenance histories
- Regulatory requirements
Maintain adequate parts inventories for critical equipment. Stock-outs can lead to delayed repairs and potential compliance violations.
Cross-train technicians to build redundancy into your maintenance team. This practice ensures coverage during vacations, illnesses, or unexpected departures.
Compliance Deadlines and Timelines
Develop a master compliance calendar that captures all regulatory maintenance requirements. Many industries have specific timeframes for equipment inspections and maintenance activities.
Color-code your calendar by regulation type:
- Red: Safety-critical deadlines
- Yellow: Environmental compliance requirements
- Blue: Quality-related maintenance
- Green: Routine preventive maintenance
Set automated reminders for approaching deadlines. These alerts should trigger 30, 14, and 7 days before the required completion dates.
Document all maintenance activities with time stamps and technician information. This practice creates an audit trail that demonstrates your commitment to compliance.
6. Develop Risk Management Strategies
Effective risk management forms the foundation of maintenance department compliance. A proactive approach to identifying, monitoring, and addressing potential risks helps prevent costly violations and workplace incidents.
Identifying and Mitigating Risks
The first step in risk management is thoroughly identifying potential compliance issues. Maintenance departments should conduct regular risk assessments examining all operations, equipment, and procedures.
Common maintenance risk areas include:
- Equipment malfunctions
- Chemical handling procedures
- Lockout/tagout protocols
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) usage
- Documentation gaps
Once risks are identified, implement appropriate mitigation strategies. These might include risk avoidance (eliminating hazardous procedures), reduction (implementing safety measures), or transfer (insurance coverage).

Create a risk matrix that categorizes issues by likelihood and potential impact. This visual tool helps prioritize which risks need immediate attention and which can be monitored over time.
Incident Reporting and Response
A robust incident reporting system is crucial for maintaining compliance. Maintenance departments should establish clear procedures for reporting safety issues, near-misses, and incidents.
Key elements of effective incident reporting include:
- User-friendly reporting forms
- Multiple reporting channels (digital, paper, anonymous options)
- Clear escalation procedures
- Designated response teams
- Documentation requirements
Train all staff on proper reporting procedures and emphasize a no-blame culture.
Encourage reporting even minor issues, as these can reveal systemic problems before major incidents occur.
When incidents happen, follow a structured response protocol that includes immediate containment, investigation, corrective action, and follow-up verification. Document all steps taken during response for regulatory review.
Learning from Past Compliance Issues
Historical compliance data offers valuable insights for preventing future problems. Establish a system to analyze past incidents, violations, and near-misses to identify patterns and root causes.
Perform regular reviews of:
- Previous compliance violations
- Audit findings
- Safety incidents
- Customer complaints
- Equipment failure reports
Use this information to update maintenance department policies and procedures. Consider implementing a lessons-learned database that maintenance staff can access during training and planning.
Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) to track compliance improvement over time. These might include number of incidents, average response time, or percentage of completed corrective actions.
Remember that effective risk management is continuous. Schedule quarterly reviews of your risk management approach to ensure it evolves with changing regulations and operational realities.
7. Utilize and Implement Maintenance Technology
Modern technology offers powerful tools to transform how maintenance departments achieve, document, and monitor compliance. These digital solutions increase efficiency, reduce human error, and provide better tracking capabilities.
Maintenance Management Systems
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) like WorkTrek are the backbone of modern maintenance compliance.
They centralize work order management and automatically document essential maintenance activities.

A good CMMS tracks equipment history, stores maintenance procedures, and schedules preventive maintenance based on regulations. This digital approach eliminates paper-based systems, often leading to lost records or missed maintenance intervals.
Many systems now include mobile capabilities, allowing technicians to document compliance activities in real time anywhere in the facility. This immediate documentation reduces the risk of forgetting details or missing steps in compliance procedures.
CMMS solutions also store regulatory requirements, automatically flagging when compliance-related maintenance is due.
This proactive approach helps maintenance departments stay ahead of audits rather than scrambling to catch up.
Data Analysis and Reporting Tools
Data analytics tools transform raw maintenance data into actionable insights for compliance management. These tools, generally part of a good CMMS system, identify patterns and potential compliance risks before they become problems.
Automated reporting features generate compliance documentation that meets specific regulatory requirements without manual compilation. This saves time and increases reporting accuracy.
Dashboard visualization tools display key compliance metrics at a glance, helping managers quickly assess their department’s compliance status. These visual tools make it easier to spot trends and prioritize maintenance activities that impact compliance.
Predictive maintenance analytics can forecast when equipment fails or falls out of compliance parameters. This forward-looking approach allows maintenance teams to address issues before they trigger compliance violations.
Custom report templates ensure that all required compliance information is captured consistently across the maintenance department.
Emerging Technologies for Compliance
Internet of Things (IoT) sensors continuously monitor equipment conditions, providing real-time compliance data without manual inspections. These sensors can detect temperature variations, vibration changes, or other factors affecting regulatory compliance.
Artificial intelligence systems analyze maintenance patterns to suggest optimal compliance schedules that balance regulatory requirements with operational needs. This intelligent scheduling maximizes both compliance and efficiency.
Augmented reality tools guide maintenance technicians through complex compliance procedures, ensuring all required steps are completed correctly. These visual guides reduce errors in compliance-critical tasks.
Blockchain technology is beginning to see adoption for creating immutable maintenance records that prove compliance history. This technology creates tamper-proof documentation that satisfies even the strictest regulatory auditors.
Digital twins of facilities allow maintenance teams to simulate compliance scenarios and test procedures before implementing them in the actual facility.
8. Streamline Supplier and Contractor Compliance
Working with external vendors and contractors introduces complex compliance challenges for maintenance departments. Proper management of these relationships is essential for safety, quality, and regulatory adherence.
Vetting Maintenance Partners
Thorough vetting of potential maintenance partners before signing contracts helps prevent future compliance issues. Establish a standardized supplier qualification process that verifies licenses, certifications, and insurance coverage.
Always verify your partners’ compliance history and safety records. This can reveal patterns of violations that might impact your operations. Request and review their written safety programs and training protocols.
Create a scoring system to evaluate suppliers based on:
- Compliance history
- Financial stability
- Quality certifications (ISO, etc.)
- References from similar clients
- Environmental practices
Document all vetting procedures to demonstrate due diligence if questions arise later. Regular reassessment of existing vendors (annually or bi-annually) ensures continued compliance with your standards.
Ensuring Contractor Compliance
Clear contractual agreements form the foundation of contractor compliance. Explicitly outline compliance expectations and consequences for violations in all contracts.
Require contractors to participate in your site-specific safety orientations before beginning work. This ensures familiarity with your protocols and emergency procedures.
Implement these practical strategies:
- Conduct periodic compliance audits of contractor work
- Require daily safety briefings for contractor teams
- Establish communication channels for reporting concerns
Consider implementing a badge system that verifies training completion and authorization to access specific areas. To address issues proactively, hold regular compliance review meetings with contractor supervisors.
Track contractor compliance metrics and include them in performance evaluations for future contract decisions.
Managing Third-Party Risks
Third-party relationships create unique risks that require specific management strategies. Develop a comprehensive risk management framework for contractor and supplier activities that identifies potential compliance vulnerabilities.
Classify vendors by risk level based on:
- Nature of work performed
- Access to sensitive areas/information
- Environmental impact potential
- Safety-critical activities
Implement more frequent inspections and documentation reviews for high-risk third parties. Create contingency plans for responding to compliance failures by critical suppliers or contractors.
Use technology solutions to monitor contractor compliance in real-time. Digital platforms can more efficiently track certifications, training records, and inspection results than paper systems.
Establish clear escalation procedures for addressing third-party compliance violations. These procedures should include defined steps, responsible parties, and timelines for resolution.
9. Develop Environmental, Health, and Safety Standards
Compliance with environmental, health, and safety standards requires systematic approaches to minimize risks while ensuring regulatory alignment. Effective EHS programs integrate preventive measures, proper training, and sustainable practices to create safer workplaces.
Preventive Measures and Controls
Implementing standardized safety checklists helps maintenance departments identify and mitigate potential hazards before they cause incidents. These tools should be tailored to address industry-specific risks and comply with OSHA regulations.
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly to identify new or changing hazards in the maintenance environment. This proactive approach allows teams to implement controls before accidents occur.

Physical controls like machine guards, lockout/tagout systems, and proper ventilation systems are essential safeguards. These barriers prevent direct contact with hazardous equipment or substances.
Administrative controls, including work rotation schedules and limited access to dangerous areas, further reduce exposure to workplace hazards. These procedures should be documented and consistently enforced.
EHS Training and Awareness
All maintenance personnel must receive comprehensive EHS training tailored to their specific roles and responsibilities. This education should cover hazard recognition, proper use of safety equipment, and emergency response procedures.
Regular training ensures staff maintain awareness of safety protocols and regulatory updates. Training records should be meticulously maintained for compliance verification.
Safety meetings provide opportunities to discuss recent incidents, near misses, and potential improvements. These gatherings reinforce the importance of a safety culture throughout the organization.
Visual communication tools like color-coded signs and safety posters constantly remind of proper procedures. These visual cues help maintain awareness even when formal training sessions aren’t in progress.
Sustainability in Maintenance Practices
Integrating sustainable practices into maintenance operations reduces environmental impact while often improving efficiency. Energy-efficient equipment upgrades and preventive maintenance schedules minimize resource consumption.
Proper chemical management includes using less toxic alternatives and ensuring correct disposal methods. Storage and handling procedures should follow both environmental regulations and safety best practices.

Waste reduction strategies, such as recycling used parts and materials, demonstrate environmental responsibility. These practices can also generate cost savings through reduced disposal expenses.
Regular inspections and audits of maintenance processes help identify opportunities for improved sustainability. Tracking key environmental metrics provides valuable data for continuous improvement efforts.
10. Implement Continuous Improvement and Adaptation
Maintenance departments must regularly review their processes and stay updated with industry standards to remain compliant. This requires both internal assessment systems and awareness of external regulatory changes.
Benchmarking and Setting Compliance Goals
Setting clear compliance benchmarks helps maintenance teams measure progress and identify areas for improvement. Establish baseline metrics for key compliance areas such as safety incidents, regulatory violations, and maintenance response times.
Compare your performance against industry standards to identify gaps. Regularly reviewing maintenance processes and seeking optimization opportunities will encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
Create SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) for compliance improvement:
- Reduce safety incidents by 15% within six months
- Achieve 100% completion of required compliance training
- Decrease audit findings by 20% year-over-year
Schedule quarterly reviews to evaluate progress and adjust goals as needed. Recognize teams that meet or exceed targets to reinforce the importance of compliance excellence.
Adapting to Changing Regulations
Regulatory requirements evolve constantly, making adaptability essential for maintenance departments. Assign team members to monitor relevant industry regulations and standards that affect your operations.
Creating a compliance-focused maintenance plan involves conducting thorough risk assessments and continuous monitoring of equipment and processes. Update your compliance documentation promptly when regulations change.
Develop a change management protocol that includes:
- Regulatory change notification system
- Impact assessment process
- Implementation plan for required modifications
- Training updates for affected staff
Consider joining industry associations to gain early insights into upcoming regulatory changes. This proactive approach gives your team time to prepare and implement necessary adjustments before enforcement deadlines.
Test your adaptation systems periodically through mock compliance scenarios to ensure readiness for real regulatory shifts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maintaining a compliant maintenance department is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and regulatory adherence. By embedding compliance into your maintenance strategy, you can prevent costly violations and enhance equipment performance. A strong compliance culture, supported by leadership commitment and continuous employee training, fosters a safe environment and minimizes compliance risks.
Implementing effective maintenance policies, procedures, and audits ensures consistency and transparency in maintenance activities.
Utilizing advanced technologies like CMMS and IoT sensors streamlines compliance tracking and enhances data analysis capabilities. Additionally, managing supplier and contractor compliance is vital for maintaining safety standards.
Regularly reviewing and adapting to changing regulations keeps your maintenance department aligned with industry standards.
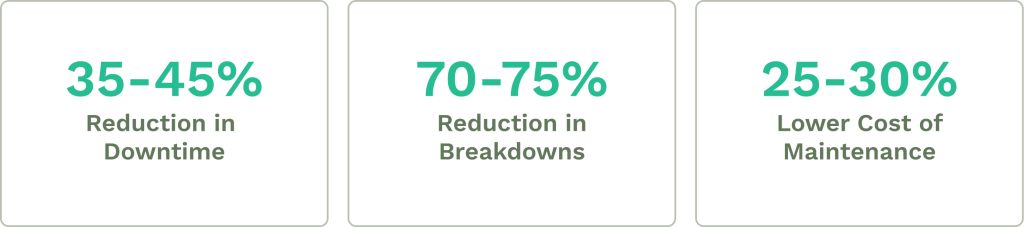
You can avoid unexpected failures and costly repairs by prioritizing preventive maintenance and risk management strategies.
Ultimately, a proactive approach to compliance protects your organization and builds trust and reliability within your team and industry.










