Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeHow can your organization improve its best practices for work order management? The correct practices are the cornerstone to efficient operations across various industries, from healthcare to hospitality, from maintenance teams in sprawling industrial plants to IT departments in bustling offices.
Understanding and implementing best practices in work order management can transform organizational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance service delivery.
This article provides a guide to the Top 10 things to consider to improve your work order management best practices.
Understanding Work Order Management
Work order management involves creating, assigning, tracking, and completing tasks related to maintenance or repair work. Effective work order management ensures that maintenance tasks are completed on time, within budget, and to the required quality standard.
These systems can also provide a single dashboard for a maintenance department to communicate with maintenance technicians, provide a digital work request, and track all work performed centrally.
This approach can also enhance efficiency, reduce labor hours and material costs, and ensure that necessary repairs are performed on schedule and adhere to maintenance workflows.
Source: WorkTrek
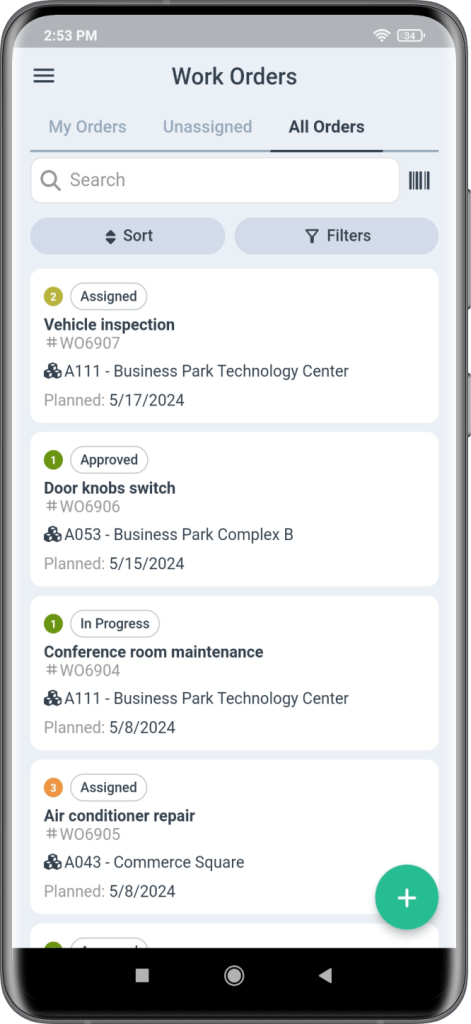
1. Implementing a Robust Work Order Management System
Adopting a robust work order management system is a game-changer for various industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, education facilities, and overall facilities management. It provides a centralized platform for managing all work orders, offering transparency and accountability in maintenance operations.
This system ensures that every task is accurately logged, assigned, and monitored, reducing the likelihood of oversight and enabling maintenance teams to respond proactively to equipment needs. A more organized workflow improves response times to maintenance requests and significantly reduces equipment downtime.
Furthermore, a robust work order management system offers powerful analytics and reporting tools that give insights into maintenance performance. Managers can track key performance indicators, such as mean time to repair (MTTR) and mean time between failures (MTBF), to evaluate the effectiveness of their maintenance strategies.
With this data, they can make informed decisions to optimize maintenance schedules, improve resource allocation, and enhance manufacturing equipment’s longevity and reliability. In the long run, this strategic approach to maintenance can lead to cost savings and an increase in production efficiency.
Key Features of an Effective System:
- Unified Platform: A centralized platform where all work orders are added to the schedule, created, stored, and tracked. This is also a centralized place to add work order priority and define the work order process.
- User-Friendly Interface: Ensures ease of use, minimizing the learning curve for staff members.
- Customizable Workflows: Allows adaptation to specific organizational needs, including outlining health and safety issues and defining standard operating procedures.
- Mobile Access: This feature facilitates on-the-go updates and tracking for maintenance technicians and departments. Maintenance technicians can easily see all their work orders and track maintenance work.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensures seamless integration with other enterprise systems like ERP, CRM, and inventory management.
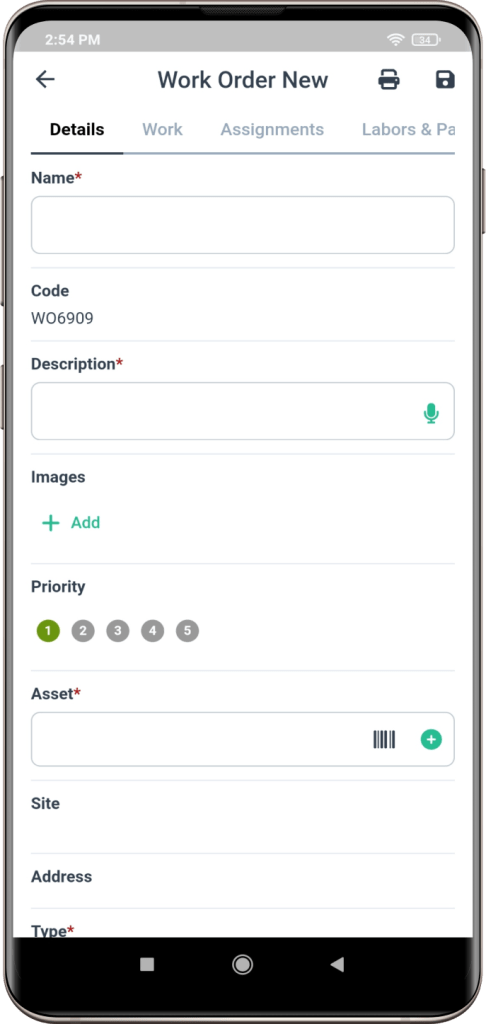
2. Standardizing Work Order Procedures
Implementing uniform procedures for managing work orders can substantially boost efficiency and uniformity in manufacturing maintenance operations. By adopting a standardized method for processing work orders, maintenance crews can swiftly recognize, sort, and carry out maintenance tasks, reducing mix-ups and aligning team efforts. This uniformity aids in the more effective tracking and evaluation of maintenance tasks, empowering managers to discern trends, refine operations, and distribute resources with greater precision.
In addition, a standardized work order system streamlines the training process for new personnel. It provides a robust foundation for initial training and ongoing professional development, ensuring each technician is well-versed in the established workflow and their specific responsibilities. This results in quicker reactions to maintenance requests, superior work quality, and more rigorous compliance with safety standards.
Best Practices for Standardization:
- Clear Work Order Templates: Define what information each work order should contain, including task identification, priority level, supplies needed, estimated time, and assigned technician.
- Consistent Terminology: Use common language across the organization to avoid confusion.
- Step-by-Step Guidelines: Provide detailed instructions on creating, processing, and completing work orders.
Source: WorkTrek

3. Prioritizing Work Orders
Efficiently managing work orders is paramount for enhancing operational performance in the manufacturing sector. Maintenance operations are optimized by evaluating the urgency, production impact, and available resources to prioritize tasks.
This method ensures prompt attention to pivotal equipment, maintaining peak functionality and minimizing potential downtime. Such strategic task management streamlines the maintenance process and mitigates the risk of workflow congestion, optimizing the deployment of maintenance personnel where their skills are most crucial.
Additionally, intelligent work order prioritization contributes to resource optimization and fiscal savings. It empowers plant managers to strategically assign maintenance crews and distribute spare parts following the factory’s overarching production objectives.
Planning routine maintenance for times when production is low reduces interference with activities. However, urgent repairs are sometimes accelerated to circumvent expensive halts in production. This approach helps maintenance technicians plan the repair process and enhance organizational efficiency.
Prioritization Strategies:
- Urgency and Impact Matrix: Classify work orders based on their urgency and potential impact on operations.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Define and adhere to SLAs to ensure timely response and resolution.
- Automated Prioritization: Use your work order management system to prioritize work orders based on predefined criteria.
4. Streamlining Communication
Effective communication is the backbone of successful work order management across various industries. Streamlining this process ensures all stakeholders, from technicians to management, access the same information in real-time, reducing misunderstandings and delays. By implementing a centralized communication system, companies can facilitate instant messaging, updates, and feedback loops between departments. This integration allows for a more cohesive workflow, where maintenance requests, status updates, and completion reports are easily accessible, enhancing overall operational efficiency and accountability.
The ability to quickly disseminate work order details and respond to changes is crucial in many industries, including manufacturing and medical facilities. Advanced software systems offer mobile accessibility, enabling field technicians to receive notifications and access work order information from anywhere.
This expedites the resolution of maintenance issues and allows for better scheduling and resource allocation. With streamlined communication, businesses can ensure that work orders are executed promptly and effectively, improving service quality and customer satisfaction.
Enhancing Communication:
- Automated Notifications: Set up automated alerts and reminders for upcoming deadlines, status changes, and required actions.
- Collaborative Platforms: Utilize digital tools that allow real-time communication and updates.
- Regular Meetings: Hold regular check-ins and debriefs to discuss ongoing and completed work orders.
5. Tracking and Reporting
Mastering the art of tracking and reporting is essential for the smooth operation of work order management systems in manufacturing. Maintenance crews can access instant task updates by observing and analyzing work orders, effectively prioritizing critical repairs.
Such comprehensive supervision helps ensure maintenance activities are performed promptly, curtailing the possibility of equipment failure and the following expensive downtime. Moreover, in-depth reporting allows an operational manager to discern patterns in equipment behavior, making informed decisions that can refine maintenance approaches and boost the plant’s overall productivity.
Beyond the operational advantages, robust tracking and reporting systems are vital in promoting accountability among maintenance staff. A transparent and responsible work environment is cultivated by keeping precise records of work orders, detailing who completed each job and the duration. This improves the quality of maintenance work and promotes a preventative mindset. Key Metrics to Track:
- Completion Time: Average time taken to complete work orders.
- Backlog: Number of pending work orders.
- First-Time Fix Rate: Percentage of work orders resolved on the first attempt.
- Maintenance Cost: Total labor hours, materials, and other resources expenditure.
Source: WorkTrek
6. Continuous Improvement through Feedback
Continuous improvement through feedback is critical in maintenance, especially regarding work order management. Companies can refine their work order processes by actively seeking and incorporating feedback from technicians, plant managers, and other stakeholders. This leads to more accurate task prioritization, efficient resource allocation of the maintenance team, and minimized downtime. This feedback loop enhances the effectiveness of maintenance work and fosters a culture of collaboration and shared responsibility for the equipment’s health.
Moreover, the iterative process of analyzing feedback helps identify recurring challenges and pain points within the maintenance workflow. Addressing these issues through targeted work order management system improvements can lead to best practices tailored to the facility’s unique demands. As a result, the organization benefits from a more agile and responsive maintenance strategy, which can adapt to changing conditions and ensure that manufacturing operations run optimally.
Collecting and Implementing Feedback:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Regularly survey maintenance technicians and other stakeholders for their input.
- Post-Completion Reviews: Conduct reviews after completing major work orders to discuss what went well and what could be improved.
- Benchmarking: Compare your performance against industry standards or competitors to identify areas for improvement.
7. Embracing Technology and Innovation
Adopting cutting-edge technology and innovation in work order management ushers in a new era of efficiency and accuracy. Utilizing mobile devices and cloud-based platforms allows maintenance teams to receive and update work orders in real-time, ensuring immediate response to critical issues and minimizing delays.
This level of connectivity allows for a seamless flow of information between on-site technicians and management, fostering a more dynamic and responsive maintenance environment. Moreover, integrating Internet of Things (IoT) devices can automate monitoring equipment status, leading to predictive maintenance that preemptively addresses issues before they escalate into costly downtime.
Innovation in work order management also extends to using sophisticated analytics and artificial intelligence to optimize task scheduling and resource allocation. By analyzing historical data and patterns, these intelligent systems can forecast workload trends, enabling maintenance managers to plan more effectively and distribute tasks to maximize productivity while minimizing operational interruptions.
Technological Enhancements:
- IoT Sensors: Use sensors to monitor equipment in real time, triggering automatic work requests when anomalies are detected.
- AI and Machine Learning: Leverage AI for preventive maintenance scheduling, anticipating failures before they occur.
- Mobile Apps and AR: Equip technicians with mobile apps and AR tools to access real-time information and virtual guidance.
 Source: item24
Source: item24
8. Training and Development
Training and development are pivotal in enhancing best practices of work order management. By equipping maintenance teams with the latest skills and knowledge, they can more effectively navigate the complexities of work order systems, leading to improved accuracy and efficiency in maintenance execution.

Regular training sessions ensure that all team members are proficient in Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS), enabling them to update and track work orders precisely. This not only streamlines the maintenance process but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, where technicians are constantly seeking ways to optimize their workflows and reduce equipment downtime.
Additionally, well-trained personnel are better positioned to identify potential problems before they escalate, allowing for a more proactive maintenance approach. This proactive stance not only saves time and resources but also contributes to extending the lifespan of equipment, ultimately enhancing the organization’s bottom line.
Training Strategies:
- Regular Workshops: Conduct training sessions on new tools, technologies, and best practices.
- Certifications: Encourage maintenance technicians to obtain relevant certifications.
- Mentorship Programs: Pair experienced employees with newer ones to facilitate knowledge transfer.
9. Maintaining Inventory and Resources
Proper inventory and resource management is a cornerstone of effective work order management. By maintaining a well-organized inventory of parts and resources, maintenance teams can significantly reduce the time spent sourcing materials for each job, leading to quicker work order completion and less equipment downtime.
An accurate inventory system ensures that necessary parts are always on hand when needed, preventing delays that can occur when parts are out of stock or hard to find. This level of preparedness streamlines the maintenance process and enhances the ability to respond to emergency repairs swiftly, thereby minimizing the impact on operations.
When considering a CMMS or Work Order Management system, evaluate its parts management features closely to ensure it can handle low stock alerts and provide a clear view of all products in stock.
Inventory Best Practices:
- Inventory Management System: Implement a system to track inventory levels, predict usage, and automate reordering.
- Just-In-Time Inventory: Maintain optimal stock levels to avoid overstocking and understocking.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources based on the priority and urgency of work orders.
10. Ensuring Compliance and Safety
Compliance and safety are integral to work order management best practices, ensuring that maintenance activities adhere to industry regulations and protect personnel from harm. A robust work order management system incorporates safety protocols directly into the maintenance workflow, requiring technicians to complete safety checklists and acknowledge hazard assessments before commencing any task.
This process helps prevent accidents and ensures all operations align with occupational safety standards and environmental regulations. Furthermore, by maintaining comprehensive records of all maintenance activities, including safety measures taken, organizations can demonstrate compliance during audits and reduce the risk of legal liabilities associated with non-compliance.
Compliance Strategies:
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Compliance Tracking: Use your work order management system to track compliance-related tasks and deadlines.
- Safety Protocols: Integrate safety checklists and protocols into work orders.
Case Study: Transforming Work Order Management in Healthcare
Consider a real-world example from the healthcare sector, where effective work order management is critical to ensuring patient safety and operational efficiency.
The Challenge
A large hospital faced significant challenges with its manual work order management process. Maintenance requests were often lost or delayed, leading to equipment downtime and operational disruptions. The lack of a centralized system also made tracking and prioritizing work orders difficult.
The Solution
The hospital implemented comprehensive CMMS software customized to meet its specific needs. The new system featured a centralized database, mobile access for on-the-go updates, and automated notifications. The hospital also standardized its work order procedures and trained maintenance technicians on the new system.
The Results
- Improved Efficiency: The average completion time for work orders decreased by 40%.
- Enhanced Communication: Automated notifications and mobile access improved communication between staff members and technicians.
- Better Resource Management: The hospital optimized inventory levels and reduced costs.
- Increased Compliance: The new system ensured all maintenance activities adhered to regulatory standards.
Final Thoughts
Effective work order management is a multifaceted process that requires the right combination of technology, standardization, communication, and continuous improvement. By adopting best practices and humanizing the process, many organizations can achieve significant gains in efficiency, cost savings, and employee satisfaction. Whether in healthcare, manufacturing, IT, or any other sector, the principles outlined in this article can help you optimize your work order management processes and drive operational excellence.