Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeTaking control of maintenance operations requires a systematic approach to tracking and managing assets. Effective maintenance tracking combines data-driven decision-making with standardized procedures to reduce equipment downtime, extend asset life, and cut operational costs.
Modern maintenance tracking goes beyond simple paper logs or spreadsheets. Organizations now use cloud-based systems that enable real-time monitoring, automated scheduling, and detailed performance analysis.
These digital tools help maintenance teams stay ahead of problems and make smarter decisions about resource allocation.
Proper maintenance tracking creates a foundation for continuous improvement. Teams can spot patterns, predict failures, and take action before small issues become major problems.
This proactive approach keeps operations running smoothly while protecting valuable assets.
Key Takeaways
- Digital maintenance tracking systems reduce downtime and extend equipment life
- Standardized procedures and data collection improve maintenance efficiency
- Regular monitoring and analysis enable predictive maintenance strategies
Basics of Maintenance Tracking
Efficient maintenance management and tracking require detailed records of equipment repairs, scheduled upkeep, and asset performance metrics.
This historical data can help you define processes based on historical data to help manage your equipment effectively.
Defining Maintenance Tracking
Maintenance tracking systems, such as a Computerized Maintenance Management System like WorkTrek, create organized records of all equipment repairs, inspections, and preventive care tasks.
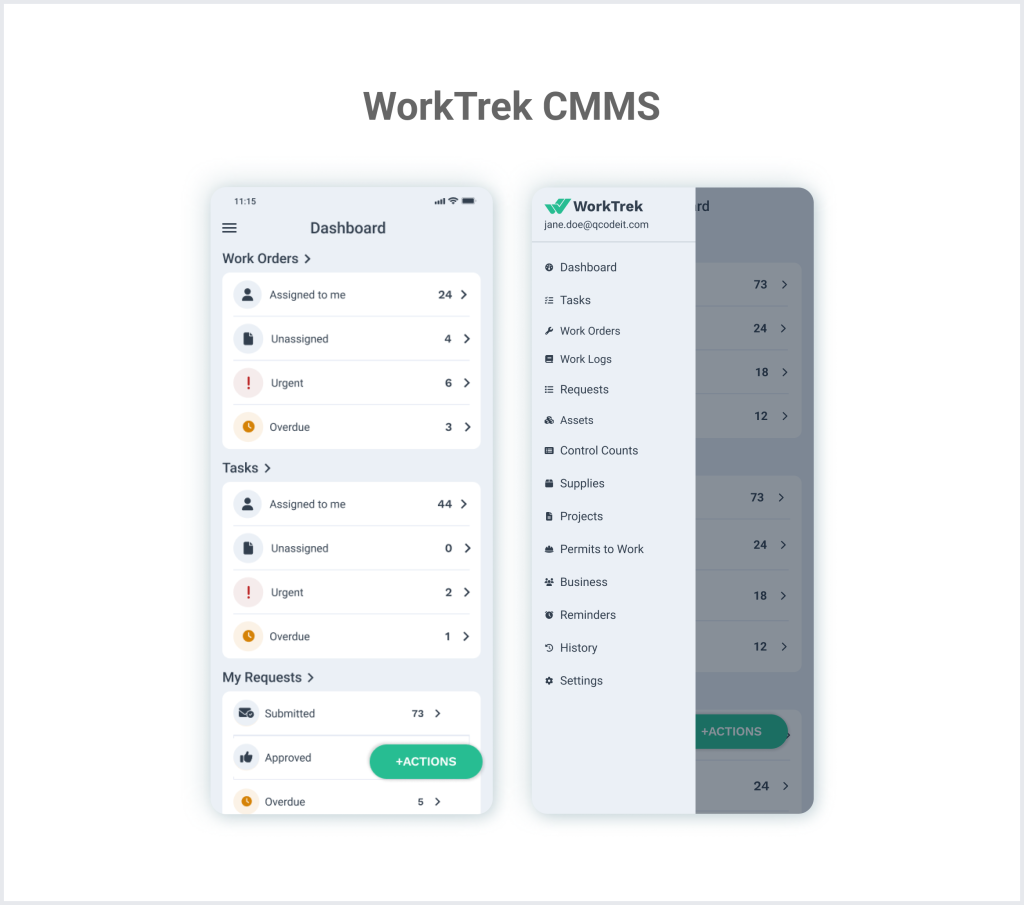
These systems are your operation’s central nervous system. They can help you monitor asset health and improve future maintenance planning. They also give maintenance technicians all of the information at their fingertips.
To help optimize the process, you need to assign each asset a unique identifier or tag to optimize asset tracking. This could be a simple barcode or more elaborate sensors like RFID tags.
Key tracking elements include:
- Maintenance dates and frequencies
- Work order details
- Parts and labor costs
- Asset condition reports
- Maintenance technician notes
- Spare parts availability
Importance of Accurate Maintenance Records
Good maintenance records help teams make smart decisions about equipment care and replacement, reducing emergency breakdowns.
Data-driven maintenance planning reduces unexpected breakdowns, extends asset life, and improves maintenance processes.
Accurate records provide these benefits:
- Early problem detection
- Better budget planning
- Reduced repair costs
- Equipment lifetime maximization
- Compliance with regulations
- Reduce equipment downtime
- Improved asset maintenance
One of the most important reasons to keep accurate maintenance records is that you can use them to spot patterns and potentially predict when equipment might need repair.
By using a CMMS, you can create customizable key performance indicators that can help guide your maintenance tasks and improve equipment maintenance. This can increase asset performance and reduce equipment breakdowns.
Having these records and regularly updating them ensures maintenance teams have current information when making repair decisions. Missing or incorrect data can lead to costly mistakes.
Setting Up a Maintenance Tracking System
A well-designed maintenance tracking system helps organizations streamline workflows, reduce equipment downtime, and cut maintenance costs.
The right implementation approach combines appropriate software selection, smooth integration with current tools, and proper access controls to ensure optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Software
Centralized maintenance management systems like WorkTrek form the backbone of effective tracking. Look for software that offers:
- Real-time asset monitoring
- Work order management
- Preventive maintenance scheduling
- Mobile Accessibility
- Custom reporting capabilities
- Asset Management
The software should match your organization’s size and complexity. Small teams might only need basic asset tracking, while large facilities require advanced features like predictive maintenance and inventory management.
Integrating with Existing Systems
Successful implementation requires a seamless connection with other business tools. Start by mapping out data flows between systems:
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
- Inventory management
- Purchasing systems
- Time tracking tools
Test integrations thoroughly before full deployment. Create clear procedures for data synchronization and backup protocols.
Role-Based Access Control
Define clear ownership and accountability through proper access management. Set up distinct user roles:
Maintenance Staff
- View work orders
- Update task status
- Log completed work
Supervisors
- Assign tasks
- Review performance
- Generate reports
Administrators
- Configure system settings
- Manage user permissions
- Set up automation rules
Each role should have the minimum access needed to perform its duties effectively.
Data Entry and Management
Good data entry and management practices form the foundation of effective maintenance tracking systems. Clear standards, proper training, and regular checks help teams keep accurate records.
Standardizing Data Input
A clear data entry plan ensures that every team member follows the same process when recording maintenance information. This includes using consistent naming conventions, units of measurement, and data formats.
Teams need specific rules for entering:
- Equipment names and IDs
- Maintenance dates and times
- Work order descriptions
- Parts and inventory numbers
- Other relevant data
Implementing mobile app software, like those with CMMS systems, can help manage the process, reduce errors, and save time.
Training for Consistency
Each team member must learn the proper ways to record maintenance data. Regular training sessions keep everyone up to date on the latest procedures and tools.
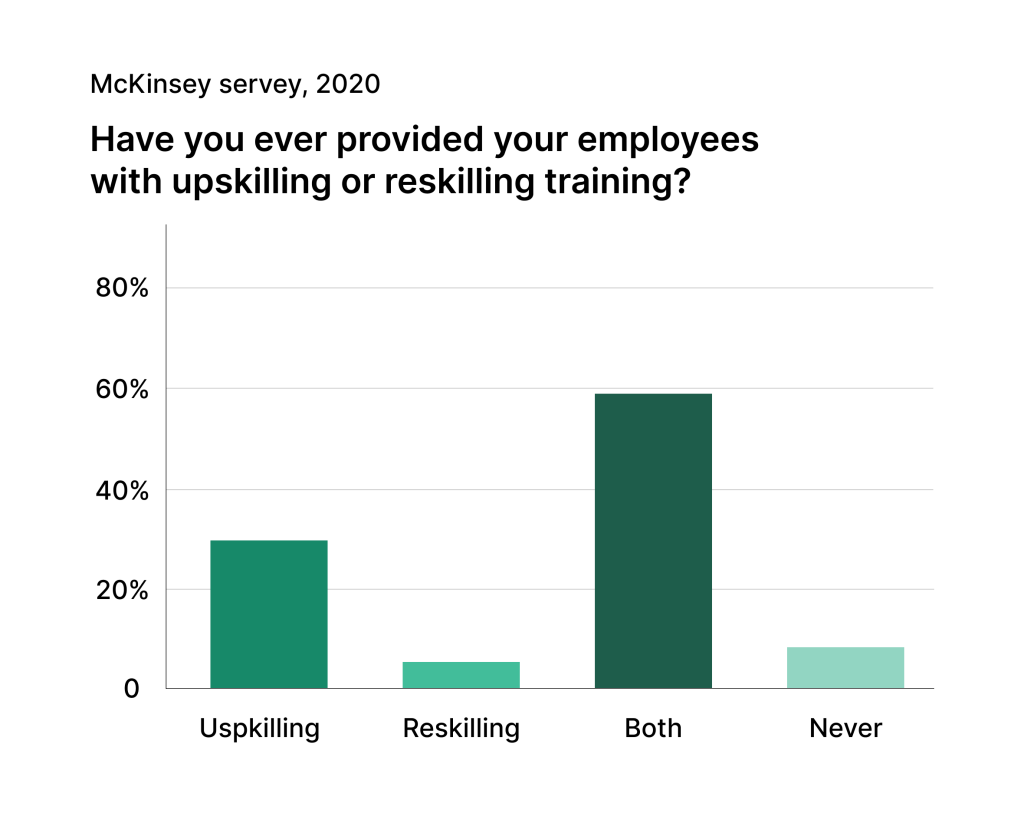
Key training topics include:
- Data entry protocols
- System navigation
- Error correction procedures
- Quality control checks
Comprehensive CMMS training helps staff understand why accurate data matters. When everyone follows the same processes, teams work more efficiently.
Regular Data Audits
Regular reviews maintain data accuracy and reveal areas that need improvement. Weekly or monthly checks catch errors early and prevent them from affecting maintenance decisions.
Data audits should examine:
- Missing information
- Duplicate entries
- Incorrect formats
- Unusual patterns
Teams can use automated tools to flag potential issues. Quick corrections keep the database clean and reliable.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
Effective maintenance scheduling reduces equipment downtime and extends asset life through systematic planning and execution. A well-structured schedule helps teams stay organized and ensures critical tasks are completed on time.
Creating Routine Schedules
Start by creating a master list of all equipment that needs regular maintenance. Each asset should have clear maintenance intervals based on usage patterns or periods.
Computerized maintenance management system software helps automate scheduling and sends alerts when maintenance is due.
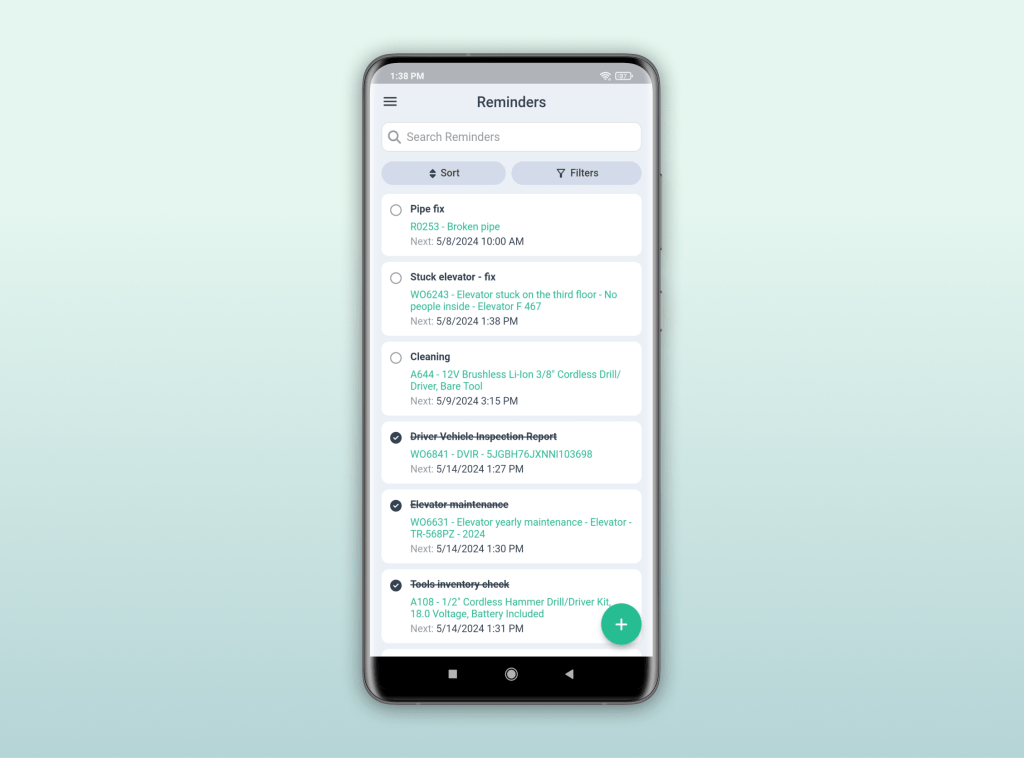
Source: WorkTrek
Compared to manual tracking methods, companies that use CMMS see up to 23% less unplanned downtime.
Break maintenance tasks into daily, weekly, monthly, and annual categories. This helps distribute workload evenly and prevents maintenance backlogs.
Key Schedule Components:
- Equipment ID and location
- Task description and duration
- Required tools and parts
- Assigned technician
- Safety requirements
Predictive Maintenance Techniques
Modern maintenance programs use data analysis to predict when equipment needs service. Sensors monitor machine performance and alert teams before problems occur.

Common monitoring methods include:
- Vibration analysis
- Oil analysis
- Thermal imaging
- Sound level testing
Teams should track task completion and asset performance to spot patterns and adjust schedules.
Aligning Schedules with Manufacturers’ Recommendations
Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance intervals and procedures. These specifications help prevent warranty issues and ensure optimal equipment performance.
Create a digital library of equipment manuals and maintenance procedures. This gives technicians quick access to proper service methods.
Keep detailed service records to prove compliance with manufacturer requirements. Include:
- Service dates
- Work performed
- Parts replaced
- Technician notes
Regular training keeps maintenance teams updated on proper procedures and new equipment specifications.
Work Order Management
Work order management software helps businesses reduce equipment downtime and material costs by up to 20%. A streamlined work order system ensures maintenance tasks are completed efficiently and on schedule.
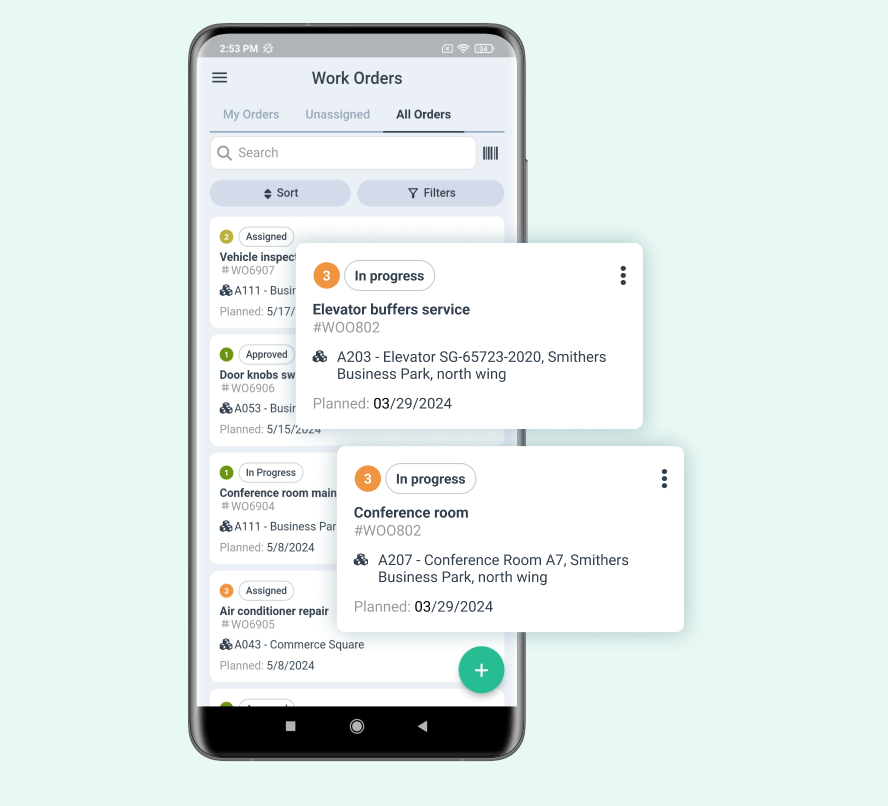
Source: WorkTrek
Designing Efficient Workflows
Every maintenance task needs a clear path from start to finish. Digital standard operating procedures make it easy to create consistent workflows.
Key workflow elements include:
- Clear task descriptions
- Required tools and materials
- Safety procedures
- Safety protocols
- Time estimates
- Priority levels
Teams should establish standardized templates for common maintenance tasks. This reduces confusion and speeds up work order creation.
Regular reviews help identify bottlenecks and optimization opportunities in the workflow design.
Tracking Work Order Progress
Work order tracking software provides real-time visibility into maintenance activities.
Essential tracking features:
- Status updates
- Time tracking
- Resource allocation
- Parts usage
- Labor costs
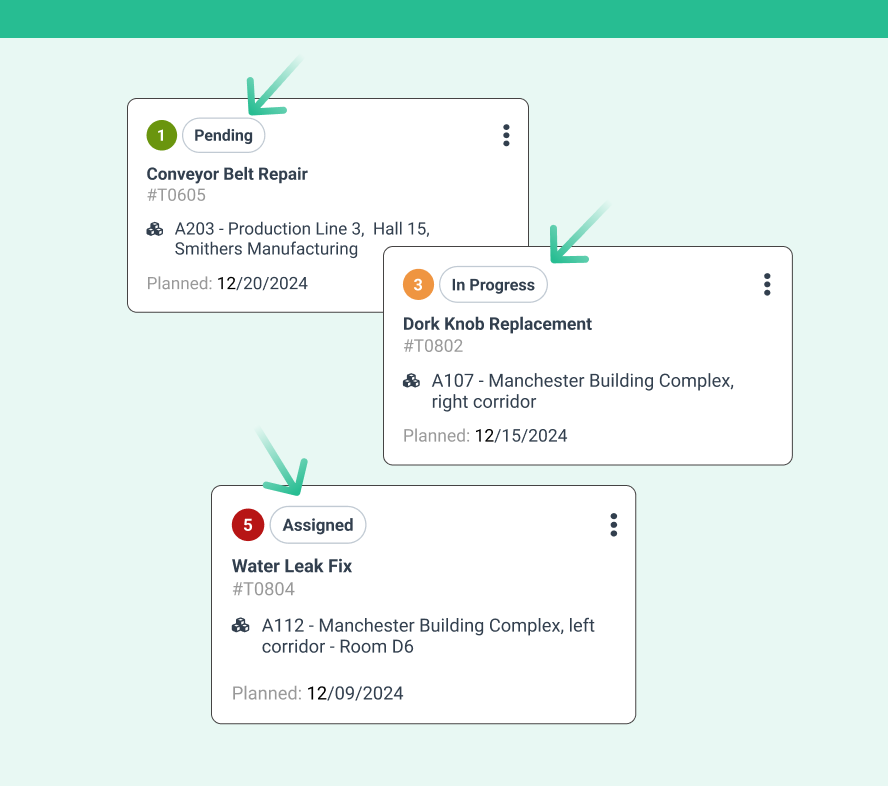
Mobile access allows technicians to update work orders from any location. This improves communication and reduces delays.
Automated notifications keep stakeholders informed of progress and completion.
Analyzing Work Order Data
Data analysis reveals patterns in maintenance operations and equipment performance.
Key metrics to monitor:
- Average completion time
- First-time fix rate
- Equipment downtime
- Labor utilization
- Cost per work order
Regular data review helps identify recurring issues and improvement opportunities.
Maintenance management systems generate reports that show trends and highlight areas needing attention. Teams can use these insights to make data-driven maintenance strategies and resource allocation decisions.
Inventory Management for Maintenance
Proper maintenance inventory management ensures facilities have the right parts available at the right time while keeping costs low. Good inventory control reduces equipment downtime and prevents both stockouts and excess inventory.
Source: WorkTrek
Automating Inventory Control
Modern inventory management systems track parts automatically using barcodes and RFID tags. They record stock levels, locations, and movements in real time.
Digital inventory tracking sends alerts when parts reach minimum levels. This prevents stockouts that could delay critical repairs.
Key automation features:
- Automatic reorder points
- Real-time stock level monitoring
- Parts location tracking
- Usage history logging
- Barcode/RFID scanning
Tracking Parts Usage
Maintenance teams must record which parts get used for each repair. This data helps predict future needs and identify patterns.
Equipment-specific parts lists (bill of materials) make it easy to track what components each asset requires.
For maintenance managers, these are some important metrics to track:
- Parts consumption rate
- Cost per repair
- Common failure items
- Seasonal usage patterns
Optimizing Inventory Levels
Setting the right minimum and maximum stock levels prevents stockouts and excess inventory. These levels depend on lead times, usage rates, and criticality.
Fast-moving parts need higher stock levels than rarely-used components. Critical spares require safety stock even if used infrequently.
Regular inventory audits help:
- Remove obsolete parts
- Adjust stock levels
- Identify slow-moving items
- Reduce carrying costs
Compliance and Safety Standards
Maintenance managers are also focused on maintenance compliance to help protect workers’ safety and prevent fines. Regular safety checks and detailed documentation help facilities meet industry regulations.
Maintaining Regulatory Compliance
Safety compliance policies should be part of your normal maintenance planning. Maintenance managers need to define clear policies and document all maintenance activities. Companies must keep detailed records to show they follow the required standards.
A CMMS system will help streamline the operation for managing safety policies and LOTO processes.

Regular staff training ensures everyone knows the current rules. Updates to procedures need quick implementation when regulations change.
Regulatory compliance prevents legal issues and helps avoid expensive penalties.
Incorporating Safety Checklists
Safety checklists prevent critical oversights in maintenance tasks. They guide workers through each step of equipment inspection and repair.
Key Elements of Safety Checklists:
- Equipment-specific inspection points
- Required safety gear and procedures
- Step-by-step maintenance tasks
- Sign-off requirements
- Date and time tracking
Regular checklist updates keep safety procedures current with industry standards. Maintenance teams should review and update checklists every quarter.
Monitoring and Reporting
Maintenance tracking requires systematic data collection and analysis to optimize asset performance. Regular monitoring and clear reporting help maintenance teams make data-driven decisions and improve operational efficiency.
Generating Maintenance Reports
A computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) makes report generation quick and accurate. Teams should create daily, weekly, and monthly reports to track maintenance activities.
Key report types include:
- Work order completion rates
- Equipment downtime tracking
- Maintenance costs and budget analysis
- Parts inventory status
- Labor hours and productivity metrics
Reports must be easily read and include visual elements like charts and graphs to highlight important trends.
Using KPIs to Measure Success
Tracking key performance indicators helps maintenance teams evaluate their effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Essential maintenance KPIs:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR)
- Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)
- Equipment Availability Rate
- Work Order Completion Rate
Teams should review KPIs monthly and adjust maintenance strategies based on the data.
Continuous Improvement Process
Condition monitoring provides real-time data to support ongoing maintenance improvements. Teams should establish regular review meetings to analyze performance data.
Improvement steps include:
- Identify problem areas through data analysis
- Develop action plans to address issues
- Implement changes systematically
- Monitor results and adjust as needed
Regular training helps maintenance staff stay current with best practices and new technologies.
Vendor and Contractor Oversight
Effective vendor oversight requires systematic selection processes, clear performance standards, and regular evaluations. Success depends on having documented criteria and using data-driven methods to track results.
Selecting Reliable Vendors
Vendor management systems help maintenance teams find and screen potential service providers through a structured process.
Create a detailed vendor profile template to gather key information about capabilities, certifications, and experience.
Check references and past performance history for each potential vendor. Request proof of insurance, licenses, and any required certifications upfront.
Use a scoring rubric with weighted criteria like:
- Technical expertise (30%)
- Cost competitiveness (25%)
- Safety record (25%)
- Response time guarantees (20%)
Managing Service Level Agreements
Contract administration best practices start with detailed Service Level Agreements (SLAs). These agreements define specific metrics for response times, completion rates, and quality standards.
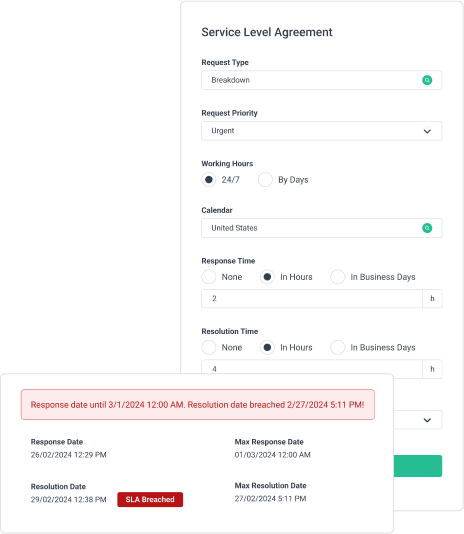
Key SLA components to include:
- Emergency response requirements
- Regular maintenance schedules
- Quality inspection protocols
- Cost structures and billing terms
- Communication procedures
Document all maintenance work performed through standardized work orders and service reports. Keep detailed records of parts used, labor hours, and completion times.
Evaluating Vendor Performance
Track vendor performance against defined KPIs using automated systems when possible. Monitor metrics like response times, first-time fix rates, and customer satisfaction scores.
Set up regular performance review meetings:
- Monthly for critical vendors
- Quarterly for standard service providers
- Annually for occasional contractors
Create vendor scorecards measuring:
- Work Quality
- Schedule adherence
- Safety compliance
- Cost control
- Communication effectiveness
Address performance issues promptly through documented improvement plans. Maintain records of all vendor interactions, inspections, and corrective actions taken.
Technology and Innovations in Maintenance Tracking
Modern maintenance tracking relies heavily on digital tools and emerging technologies that create smarter, more efficient systems. Advanced technologies have transformed how organizations monitor equipment health and manage maintenance tasks.
Leveraging IoT for Real-Time Tracking
IoT sensors provide instant data about equipment performance and conditions. These devices monitor crucial real-time metrics like temperature, vibration, and pressure.
Connected sensors revolutionize maintenance operations by detecting potential issues before they cause breakdowns. The data flows directly into maintenance management software systems.
Key benefits of IoT tracking:
- Continuous equipment monitoring
- Early warning of potential failures
- Reduced unexpected downtime
- More accurate maintenance scheduling
Emerging AI Tools
Artificial intelligence enhances maintenance tracking through pattern recognition and predictive analytics. AI systems analyze equipment data to forecast maintenance needs.
Machine learning algorithms identify trends in equipment performance and maintenance history. This helps teams spot recurring issues and optimize repair schedules.
AI tools can:
- Predict equipment failures by analyzing data
- Generate automated work orders
- Optimize maintenance intervals
- Analyze repair costs and patterns
The Role of Mobile Technologies
Mobile apps and devices give maintenance teams instant access to critical information from anywhere. Digital tools streamline work order management and documentation.
Technicians use mobile devices to:
- Access repair manuals and procedures
- Document completed work
- Scan equipment QR codes
- Submit maintenance reports
- Track parts inventory
Mobile solutions improve response times and work completion rates. Teams can quickly update task status and share information in real time.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Maintenance teams face several key obstacles that impact their daily operations. Smart solutions and modern approaches can transform these challenges into opportunities for improvement.
Handling Human Error
Manual tracking systems often lead to mistakes in data entry and task scheduling. Digital maintenance systems with built-in validation help catch errors before they cause problems.
Teams need clear protocols for data input and maintenance procedures. Simple checklists and standardized forms reduce confusion and increase accuracy.
Key error prevention strategies:
- Double-check critical maintenance data
- Use barcode scanning for asset identification
- Implement automated data validation
- Train staff regularly on proper documentation
Adapting to Changing Environments
Centralized scheduling systems help maintenance teams stay flexible when priorities shift. Digital tools enable quick updates to maintenance schedules as conditions change.
Real-time communication channels keep all team members informed about urgent maintenance needs. Mobile apps give technicians instant access to updated work orders and asset information.
Adaptation tools:
- Mobile maintenance apps
- Real-time notification systems
- Dynamic scheduling software
- Cloud-based documentation
Legacy System Upgrades
Old maintenance systems often struggle to handle modern tracking needs. CMMS solutions offer seamless integration with existing equipment while adding new capabilities.
Data migration requires careful planning and execution. Teams should transfer historical maintenance records in phases to minimize disruption.
Upgrade considerations:
- Compatibility with existing equipment
- Staff training requirements
- Data migration timeline
- System testing periods
Modern analytics tools help measure the success of system upgrades through improved maintenance metrics.
Conclusion
Good maintenance tracking brings many benefits to organizations. Regular tracking leads to fewer breakdowns, longer equipment life, and lower repair costs.
Digital tracking systems like WorkTrek CMMS, easily store maintenance history and plan future work. Teams can access records from anywhere and make better repair choices.
A strong tracking program needs both good tools and trained staff. Work order systems help teams stay organized and respond quickly to maintenance needs.
Regular data collection and review help spot trends early, allowing teams to fix small issues before they become big problems.
The right tracking methods lead to smoother operations and less downtime. Organizations save money through better planning and fewer emergency repairs.
Successful maintenance tracking requires commitment from the whole team. With proper systems and practices, equipment runs better and lasts longer.