Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeIf you manage workplaces, such as physical office spaces or physical spaces that are used, implementing effective workplace management can improve efficiency. One of the best tactics is to manage the workplace using a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS). If utilized effectively, these powerful tools can significantly improve the management of the work environment.
This category of software solutions can help you reduce operational costs, increase operational efficiency, and ensure that the workplace runs smoothly.
This article explores the various aspects of utilizing CMMS to manage a workplace effectively, from implementation strategies to leveraging its data for strategic decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Effective CMMS implementation for workplaces requires careful assessment of organizational needs, selection of appropriate software, and comprehensive user training.
- CMMS enhances workflow and promotes productivity by automating maintenance tasks, providing real-time monitoring, and facilitating better team collaboration.
- Data-driven insights from CMMS can guide strategic decision-making, helping predict maintenance needs and plan future asset management.
- Regular evaluation of CMMS impact on business outcomes, including ROI analysis and compliance management, ensures continuous improvement and alignment with business goals.
Understanding CMMS and Its Core Functions
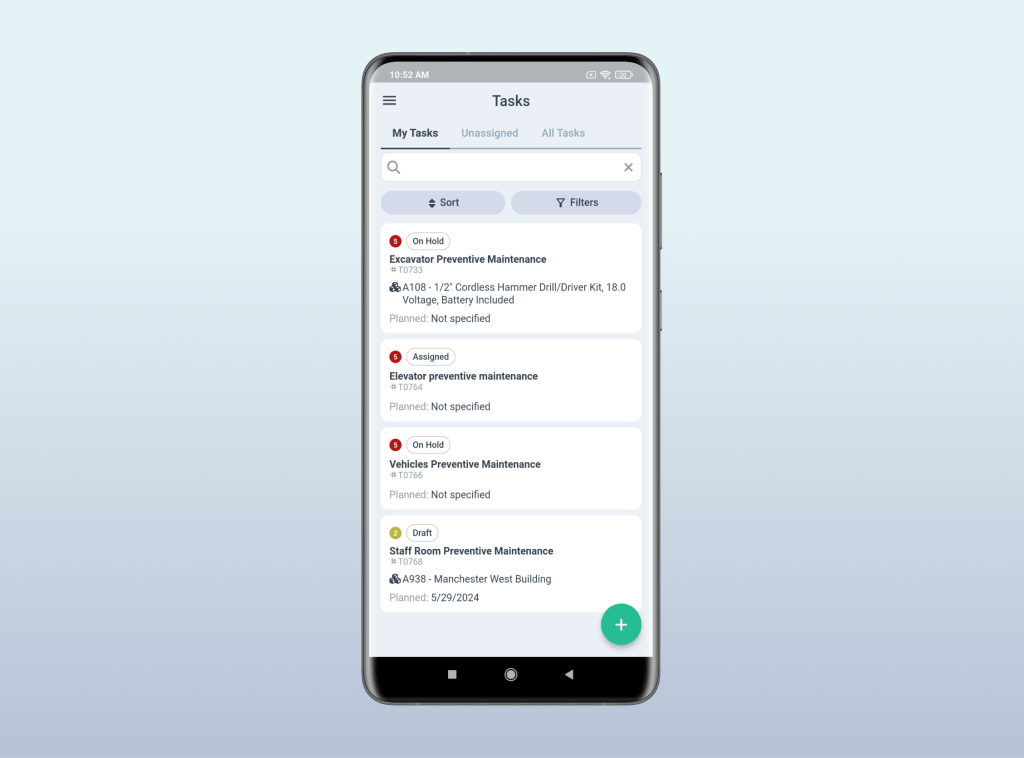
Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is the technological backbone of a preventive maintenance program. It is a database-driven software solution that automates the management of maintenance tasks, ensuring that all equipment and assets receive timely attention.
The core functions of a CMMS include work order management, which streamlines the creation, assignment, tracking, and completion of maintenance tasks. It also encompasses preventive maintenance scheduling, allowing for the systematic planning of routine inspections and servicing based on time or usage triggers.
Inventory management is another critical feature, providing real-time insights into spare parts availability and usage, which aids in minimizing stockouts and overstocking. Moreover, a CMMS offers detailed reporting and analytics tools that help maintenance managers make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and forecast future maintenance needs.
By centralizing maintenance-related information, a CMMS enhances team communication, improves operational efficiency, and ultimately increases asset lifespan while reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Source: WorkTrek
Definition and Purpose of CMMS
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is essential for centralizing maintenance information and automating operations. It enhances efficiency, employee productivity, engagement, and safety while reducing costs for asset management and maintenance operations.
I can also boost productivity, reduce overhead costs, improve customer satisfaction, and create a positive and productive work environment. I can also help facility managers make data-driven decisions regarding space management.
Some benefits of using CMMS software for Workplace management strategy include:
- Effective workplace management
- Simplify workplace management
- Seamless resource management
- Improved inventory management of spare parts
- Improve cost savings and effectiveness
- Reduce operating costs
- Enable data-driven decision-making
- Improve overall workplace management
CMMS is pivotal in modern maintenance strategies, ensuring all activities are planned, tracked, and executed efficiently.
Key Components of CMMS
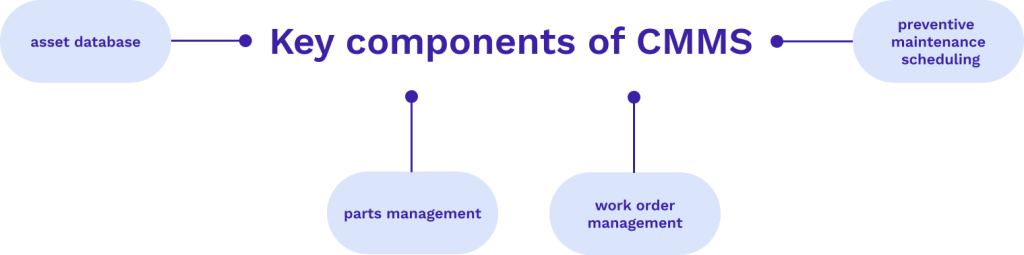
A Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is essential in implementing preventive maintenance strategies. Its key components include an asset database, parts management, work order management, and preventive maintenance scheduling.
The asset database is the cornerstone of any CMMS. It provides detailed records of all equipment and assets within an organization. It typically includes asset specifications, maintenance history, warranty details, and associated documentation.
Work order management is another vital component of CMMS and streamlining, creating, assigning, and tracking maintenance tasks. It allows maintenance managers to prioritize work orders, assign tasks to appropriate personnel, and ensure the timely completion of maintenance activities.
This module often includes features for tracking the progress of work orders in real-time and documenting any actions taken, which is invaluable for maintaining accountability and efficiency.
Preventive maintenance scheduling within a CMMS is designed to automate the planning and execution of routine maintenance tasks and create efficient workplace management. By setting up schedules based on time intervals or equipment usage, the system ensures that preventive maintenance is carried out consistently and on time.
This proactive approach helps to minimize equipment downtime, reduce the likelihood of breakdowns, and extend the lifespan of assets. Additionally, CMMS can generate reminders and alerts to inform maintenance teams of upcoming tasks, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
Source: WorkTrek
Integration with Other Business Systems
Integrating CMMS with other business systems, such as Integrated Workplace Management Systems (IWMS), enhances its functionality and scope.
This integration allows for a more holistic approach to facility management, combining maintenance with other aspects like real estate and project management.
The synergy between CMMS and other systems ensures data flows smoothly across departments, improving decision-making and operational transparency.
Workplace Management Software and the Role of CMMS
Workplace management software is designed to streamline a business’s daily operations by managing resources, space, and communication. It encompasses many applications that facilitate everything from room and desk bookings to asset tracking and employee collaboration.
These tools provide valuable insights into space utilization, help reduce operational costs, and improve workplace efficiency. By leveraging such software, organizations can optimize their physical workspace, align it with their workforce needs, and thus create an environment that fosters productivity and employee satisfaction.
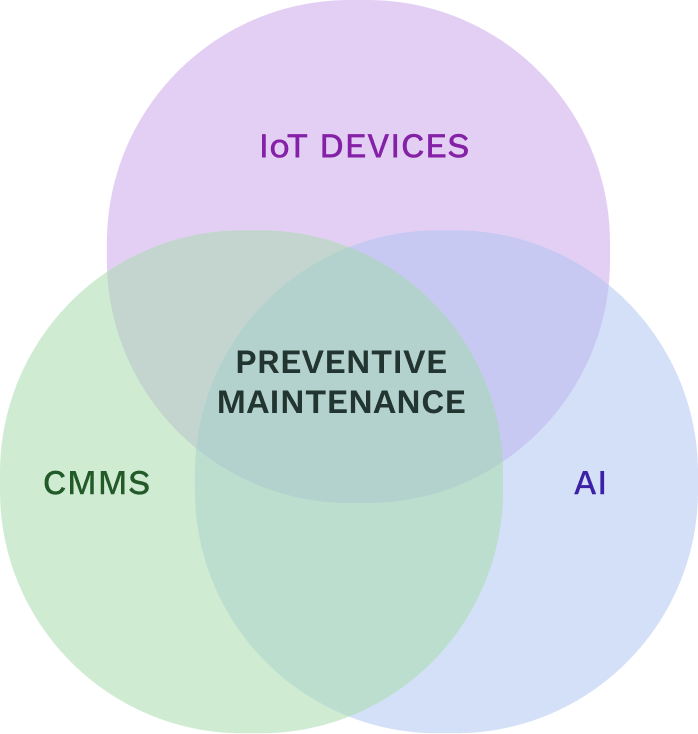
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) are often considered a subset of workplace management software focusing on operations maintenance. However, modern CMMS solutions have become more comprehensive, offering features beyond equipment and asset maintenance.
They can now assist in managing workplaces by scheduling room and equipment usage, tracking inventory levels, and ensuring safety and health regulations compliance.
By integrating IoT devices and utilizing AI, CMMS can provide a more holistic approach to workplace management, ensuring that facilities are maintained efficiently and utilized effectively.
Source: WorkTrek
Assessing Organizational NeedsAI
Before selecting a CMMS, it’s crucial to thoroughly assess your organization’s specific needs. This involves understanding the current maintenance challenges, the scale of operations, and future growth expectations. Identifying these needs will guide you in choosing a CMMS that fits perfectly with your organizational goals.
Training and Support for Users
Effective training and continuous support are essential for maximizing the benefits of your CMMS. Ensure that the provider offers comprehensive training and has a responsive support team. This will help smooth the transition for your team and maintain high operational efficiency.
Optimizing Asset Management with CMMS
Optimizing asset management is a critical component of any preventive maintenance program, and a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is at the forefront of this process. By centralizing data and automating many of the maintenance management tasks, a CMMS enhances an organization’s ability to monitor the health and performance of its assets.
This system streamlines the scheduling of maintenance activities, tracks the history of equipment repairs, and manages inventory levels for spare parts. With a CMMS, maintenance managers can also predict future maintenance needs and budget accordingly, ensuring that assets are maintained efficiently and downtime is minimized.
CMMS supports data-driven decisions, improving the overall lifecycle management of assets and contributing to a substantial return on investment.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
Effective asset management begins with a robust preventive maintenance schedule. Leveraging CMMS can automate the scheduling process, ensuring that all equipment receives timely maintenance. This not only extends the lifespan of the assets but also reduces the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
Asset Lifecycle Analysis in Workplace Management
Understanding each asset’s lifecycle is crucial. To analyze usage patterns and performance metrics with CMMS to determine the optimal replacement or upgrade timings. This strategic approach helps maximize the utility and efficiency of assets throughout their lifecycle.
Asset lifecycle analysis is an indispensable component in facilities management. It provides a comprehensive overview of an asset’s journey from acquisition to disposal. This analysis offers insights into the total cost of ownership, including acquisition, operation, maintenance, and disposal fees, which are crucial for informed decision-making.
By understanding each phase of an asset’s lifecycle, facilities managers can develop strategies that optimize asset use, improve performance, and extend lifespan. This proactive approach ensures that assets remain functional and efficient, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and the associated costs of downtime and repairs.
The importance of asset lifecycle analysis in facilities management cannot be overstressed. It enables managers to anticipate future costs and plan for replacements or upgrades, ensuring equipment failure does not disrupt the facility’s operations.
Moreover, lifecycle analysis supports sustainable practices by identifying opportunities to reduce energy consumption and waste, contributing to an organization’s environmental responsibility. Through effective asset lifecycle management, facilities can maintain a competitive edge by minimizing costs, maximizing asset performance, and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards.
Inventory Control and Management and Workplace Management
Managing inventory efficiently is key to smooth operations. CMMS allows me to maintain real-time inventory levels and set automatic reorder points to prevent stockouts. Additionally, I can track inventory usage and costs, which aids in budgeting and forecasting.
By integrating these strategies, I ensure that asset management is not just a routine task but a strategic component of overall business efficiency.
Enhancing Workflow and Productivity
Automating Maintenance Tasks
In my experience, the ability to automate management of workplace management tasks using CMMS is transformative. By setting up automated workflows, I ensure maintenance tasks are scheduled and executed without delay, enhancing overall productivity. This automation is a cornerstone of smart workplace management.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Integrating real-time monitoring systems within a CMMS allows companies to monitor all operations. Alerts notify me immediately of any anomalies or urgent maintenance needs, ensuring I can react swiftly to prevent downtime or damage.
Improving Team Collaboration
Effective collaboration in a workplace is crucial. Workplace Management software can help teams communicate and coordinate significantly better.
A CMMS’s centralized platform means that everyone—from technicians to management—has access to the same up-to-date information, which is essential for making informed decisions and maintaining a high level of operational efficiency.
Leveraging CMMS Data for Strategic Decision-Making

Source: Robin
Data Collection and Analysis
Robust data collection and analysis are the foundation of strategic decision-making in a CMMS environment. To ensure comprehensive insights, it is important to systematically gather data from every interaction and operation within the maintenance management system.
This data often includes machine uptime, failure rates, maintenance costs, and other crucial information for informed decision-making.
Generating Actionable Insights
A proficient CMMS can generate actionable insights from the data collected. Transforming raw data into understandable metrics is important to guide operational improvements. This involves using advanced data analytics tools to interpret patterns and trends that inform strategic actions.
Predictive Maintenance and Future Planning
Predictive maintenance is a strategic approach that utilizes the data to predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive method not only saves costs but also enhances machine longevity. Planning for the future with predictive analytics allows for a smoother operation and less downtime, ensuring that maintenance schedules are optimized and resources are efficiently allocated.
Maintaining Compliance and Safety Standards

Source: EQS
Regulatory Compliance Management
Managing regulatory compliance effectively is crucial for any organization. A CMMS is pivotal in documenting maintenance activities, inspections, and audits.
This documentation ensures adherence to regulatory requirements, essential for avoiding legal issues and fines. The system can automatically update to new regulations, making compliance seamless.
Safety Protocols and Procedures
Safety cannot be compromised, and a CMMS ensures it isn’t. The system helps implement and monitor safety protocols, ensuring that all procedures are followed meticulously. This includes regular safety audits and the ability to disseminate safety updates across the organization quickly.
Audit Trails and Documentation
Audit trails in Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) software play a pivotal role in equipment and facility management. They provide a comprehensive record of all maintenance activities, including when they were performed, who executed them, and the details of the tasks.
This historical data is invaluable for regulatory compliance, as it offers clear evidence of adherence to maintenance protocols and safety standards. Moreover, audit trails enable facility managers to track the effectiveness of their maintenance strategies, identify recurring issues, and make informed decisions based on trends and patterns observed over time.
Another significant benefit of audit trails within CMMS is enhancing accountability among maintenance staff. By documenting every action taken, staff members are more likely to follow procedures meticulously, knowing that their work is subject to review.
This improves the quality of maintenance work and fosters a culture of responsibility and transparency. For organizations, this means reduced errors, improved asset reliability, and decreased downtime, collectively contributing to a more efficient and cost-effective operation of equipment and facilities.
Evaluating the Impact of CMMS on Business Outcomes

Source: WorkTrek
ROI Analysis of CMMS Implementation
Conducting a Return on Investment (ROI) analysis is crucial to understanding the financial benefits of CMMS or any workplace management solution. It can quantify its value by comparing the costs of CMMS implementation to the savings from increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
For instance, a typical analysis might show a 20% reduction in maintenance costs and a 15% increase in asset uptime.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Enhancing operational efficiency with CMMS involves streamlining maintenance processes and reducing equipment failures. This leads to significant improvements in production uptime and overall operational performance. Key metrics like maintenance effectiveness and asset reliability are crucial indicators of success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effectively managing a workplace using a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) can significantly enhance operational efficiency and productivity.
Integrating CMMS into your daily operations allows you to streamline maintenance processes, optimize asset management, and improve workplace safety.
Managers must leverage CMMS’ full capabilities to maintain equipment efficiently and maximize the potential of their workforce and resources.
Staying ahead with a robust CMMS strategy will be key to sustaining competitive advantage and achieving long-term success as industries evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a CMMS, and what are its core functions?
A CMMS, or Computerized Maintenance Management System, is a software tool that helps organizations manage their maintenance operations more efficiently. Its core functions include asset management, work order management, preventive maintenance scheduling, and inventory control.
How does integrating a CMMS with other business systems benefit an organization?
Integrating a CMMS with other business systems, such as ERP or HR software, enhances data accuracy and provides a holistic view of operations. This integration helps in better resource allocation, streamlined processes, and improved decision-making.
What are the key considerations when selecting a CMMS software?
Key considerations include your organization’s specific needs, the software’s compatibility with existing systems, scalability, user-friendliness, and the vendor’s level of customer support.
How can CMMS improve asset lifecycle management?
CMMS helps track and analyze asset performance and maintenance history, facilitating better lifecycle management. This leads to extended asset life, reduced downtime, and lower replacement costs.
What role does CMMS play in maintaining compliance and safety in the workplace?
CMMS assists in ensuring that all maintenance activities are performed according to regulatory standards, helps document procedures, and maintains detailed records for audits. This promotes a safer working environment and compliance with legal requirements.
How can organizations measure the impact of implementing a CMMS?
Organizations can measure the impact by analyzing improvements in maintenance response times, reductions in equipment downtime, cost savings on repairs and operations, and overall enhancement in asset performance and productivity.









