Get a Free WorkTrek Demo
Let's show you how WorkTrek can help you optimize your maintenance operation.
Try for freeA preventive maintenance checklist is essential for any proactive maintenance strategy to minimize unscheduled downtime and equipment failure. This article details how to create and implement this checklist effectively, ensuring longevity for your assets and overall operational efficiency.
This article outlines practical advice on everything from asset identification to task prioritization and technology integration that will keep your operations running smoothly.
Key Takeaways
- Preventive maintenance checklists are essential for minimizing equipment breakdown and downtime, improving safety, and saving costs by scheduling maintenance tasks at more convenient times and preventing high expenses associated with unplanned maintenance.
- A practical preventive maintenance checklist should be well-structured, logically organized, and contain detailed, clear instructions with visual aids for tasks. It should be based on asset identification and historical performance data, and tasks should be prioritized according to their impact on operational efficiency and safety.
- Technological integration, notably Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and mobile apps, is vital in streamlining the execution and monitoring of preventive maintenance tasks, enabling real-time updates, and facilitating continuous improvement based on maintenance data analysis.
Understanding the Importance of Preventive Maintenance Checklists

Source: WorkTrek
Preventive maintenance checklists serve as the guide for maintenance management, substantially reducing the likelihood of equipment failure.
Following the effect PM checklist, you can potentially reduce 90% of mechanical failures. These checklists also enable you to schedule crucial maintenance tasks at optimal times, thus curtailing unexpected downtime.
To upgrade your maintenance strategy, even Craft preventative maintenance checklists that cater specifically to the nuances of your operations while drawing on established preventive maintenance plans and schedules as benchmarks. This practice paves the way for developing an ultimate preventive checklist.
To their role in reducing malfunctions, preventive maintenance checklists are foundational in cultivating safe work conditions—a fact underscored by their importance within lean manufacturing paradigms and Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) methodologies.
These meticulous lists contribute significantly to improvements in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), bolstering availability, performance levels, and output quality through systematic adherence to scheduled tasks and strategies.
Some examples of items to include on a PM checklist include:
- Safety instructions
- Network and data systems
- Standardize routine tasks
- Maintenance activity
- Step-by-step checklists of activities
- Pass or fail checklists
Cost Savings
The economic advantages of implementing preventive maintenance are pretty evident, as the data clearly shows.
Organizations can achieve substantial savings by adopting a preventive maintenance regimen and avoiding the steep costs of reactive or unplanned maintenance activities, which may be 3 to 9 times more expensive than their planned counterparts.
Preventive maintenance has an ongoing financial impact. The approach helps extend asset lifespan and consequently decreases the frequency of repairs and replacements and the associated expenses, yielding considerable cost benefits over time.
Safety Improvements
The relationship between preventive maintenance and safety is tightly interwoven. Consistently executing tasks related to safety protocols within the context of preventive maintenance strengthens health and safety measures across facilities. By embedding safety checklists and procedures into work orders through software solutions, compliance with regulations and overall facility safety are enhanced.
Routine safety evaluations are a critical component of preventive maintenance checklists. Such checks ensure conformity to health and security standards set by authoritative bodies like OSHA (Occupational Safety & Health Administration) and EPA (Environmental Protection Agency), reducing the likelihood of mishaps. To elevate levels of protection, it’s important that these maintenance checklists specifically review fire prevention systems and security installations following sector-specific regulatory requirements.
Enhanced Efficiency
Utilizing the correct instruments can significantly boost the effectiveness of a preventive maintenance program. One indispensable tool is a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), which augments maintenance efficiency by streamlining procedures, automating work orders, and refining the schedule for maintenance tasks.
The advantages offered by utilizing CMMS extend beyond essential organization. This system facilitates the timely scheduling of maintenance activities and early detection of problems, thus minimizing equipment idle time. This forward-thinking strategy results in improved equipment availability and enhanced quality of production outputs – all serving as evidence to underscore the efficacy inherent in a preventive maintenance approach.
Critical Components of an Effective Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Developing a preventive maintenance checklist requires careful consideration. To be effective, the checklist must:
- Have a coherent organization
- Incorporate details regarding preparations needed before starting
- Encompass safety guidelines to ensure secure operations
- Supply visual aids as required for better comprehension
- Present explicit and comprehensive instructions that allow novice technicians to proceed with minimal oversight
- Record specific equipment information, including model, serial number, and previous maintenance records, to facilitate well-informed maintenance strategies.
- Provide a guide to facility infrastructure.
Asset Identification
Initiating a comprehensive preventive maintenance checklist necessitates recognizing and classifying essential assets and equipment that need maintenance. This process serves to construct a solid base for a tower. The more durable your groundwork, the stronger your structure will be.
Determining which assets merit incorporation hinges on pivotal information streams for crafting an effective preventive maintenance strategy. These include meticulous asset inventories, manufacturer guidelines, and empirical performance histories of said assets. By anchoring your checklist in well-informed judgments, you ensure its longevity and resilience.
Source: WorkTrek
Task Prioritization
After recognizing the various assets that require attention, assigning importance to each preventive maintenance task is critical. The rationale behind this is straightforward: not every maintenance task holds the same weight regarding its effect on safety and operational efficiency. Consequently, specific tasks must be elevated in priority.

Prioritizing high-impact items within your preventive maintenance checklists ensures that resources and efforts are optimally allocated for maximum improvement in operation and safeguarding measures. This strategic prioritization amplifies the benefits reaped from your comprehensive preventive maintenance program.
Clear Instructions
Having pinpointed the assets and prioritized the routine tasks, you should now supply explicit, well-defined directives. Maintenance technicians must receive preventive maintenance checklists that display tasks sequentially with designated areas for recording outcomes.
These instructions should be specific to the type of equipment, such as HVAC systems, electrical connections, hydraulic systems, air filters, or anything related to building maintenance.
The delivery of clear-cut instructions is vital to guarantee the correct execution of maintenance steps, which is particularly essential when instructing new technicians. Incorporating visual aids such as schematics and photographs can greatly facilitate comprehension. These aids must be scrutinized by a skilled technician who has an in-depth knowledge of machinery and facility details, including the manufacturer’s advice in preventive maintenance.
Integrating Technology into Your Preventive Maintenance Program
As companies have embraced digital transformation, technology has become a cornerstone of preventive maintenance. Leveraging tools like CMMS and mobile applications enables the optimization and monitoring of preventive maintenance plans, enhancing the efficiency of general maintenance activities.
CMMS Advantages
Implementing a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) revolutionizes preventive maintenance. This system streamlines the process, enabling enhanced organization and optimization of preventive maintenance routines by leveraging insights from collected data such as equipment history and work order archives.
CMMS is integral to expediting repairs and assessments to optimize preventive maintenance schedules. It achieves this by providing on-the-go access to critical details, including asset records, schematics, and the whereabouts of replacement components.
Consistent examination of the information from CMMS-produced reports allows for perpetual refinement of preventive maintenance checklists. This ensures that they evolve continuously for maximum effectiveness in maintaining equipment health.
Mobile App Solutions
Utilizing mobile technology can significantly boost the effectiveness of preventive maintenance. Maintenance personnel can effortlessly access formalized preventive maintenance checklists via mobile apps, ensuring these vital resources are always at their fingertips for immediate reference.
Maintenance staff benefit from real-time information about machinery conditions and required maintenance tasks delivered through these applications. Instant alerts on pending or delayed maintenance activities keep them well-informed through their mobile devices, guaranteeing that necessary upkeep is timely and competently executed.
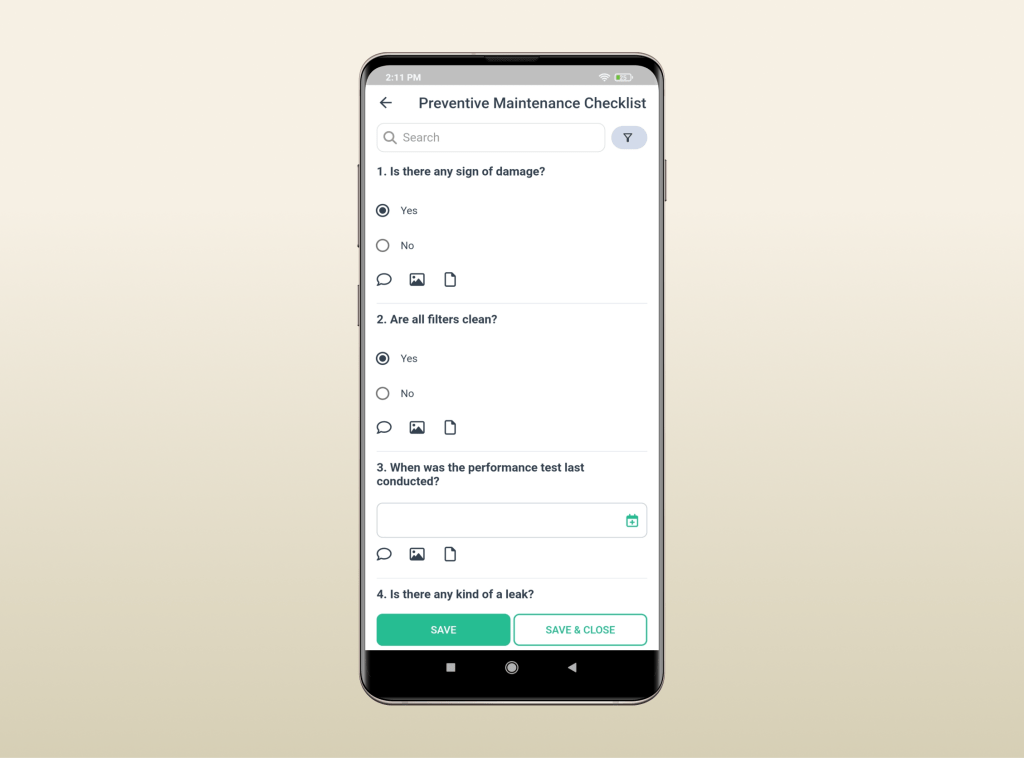
Customizing Your Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Source: WorkTrek
As every business differs, so do their maintenance requirements. To ensure continuous compliance and optimal performance, it’s essential to tailor preventive maintenance checklists according to regulations specific to the industry and the distinctive operational demands of each enterprise.
Industry Regulations and Preventive Maintenance Checklists
Industry regulations profoundly influence preventive maintenance checklists, as these rules often dictate the specific maintenance activities that must be carried out to ensure compliance. For instance, regulations in the healthcare industry may require that all medical equipment undergo rigorous sterilization and calibration processes to meet health and safety standards.
Similarly, in the aviation sector, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) mandates regular checks and maintenance of aircraft components, such as engine inspections and avionics testing, to guarantee passenger safety.
Manufacturing plants might be subject to OSHA regulations requiring the routine examination of machinery guards and emergency stop mechanisms to prevent workplace injuries.
These examples illustrate how industry-specific rules shape the structure and content of preventive maintenance checklists, ensuring that they facilitate smooth operations and adhere to legal and safety requirements.
Industry-Specific Considerations
In every sector, the potential for equipment breakdown is a common challenge that must be tackled with tailored solutions. To mitigate these risks, preventive maintenance checklists must be explicitly adapted for different classes of assets like material handling equipment and the overall infrastructure of a facility. The design of each asset demands particular attention to develop a practical formal preventive maintenance checklist that addresses all critical areas.
A deep understanding of each industry’s unique needs offers insights into essential maintenance tasks necessary for preserving each piece of equipment’s integrity and functionality. It’s also imperative to align these preventative measures with relevant regulations and standards, ensuring that such maintenance checklists are thorough and adhere strictly to health and safety norms while complying with federal and state mandates.
Adapting to Changing Needs
Just as a river’s course may change over time, so do a business’s maintenance needs. Continually revising the preventive maintenance checklist is essential to ensure its adequacy and pertinence to the ever-changing operational needs.
Continual updates to include new machinery, refresh maintenance intervals, and compliance with contemporary industry protocols are pivotal in refining the efficacy of a preventive maintenance program. Opportune evaluation periods—such as high staff turnover prior to scaling up production or in response to recurring equipment problems—are vital for making pertinent revisions to the preventative maintenance checklist.
Involvement from those who comprise the company’s mainstay—their skilled workforce—is indispensable. Maintenance team members should actively evaluate and enhance this list through practical trial runs and insightful commentary on its overall user-friendliness while confirming it encompasses all vital tasks necessary for successful prevention-focused upkeep measures within their work environments.
Training and Implementation Strategies
Even the most outstanding preventive maintenance checklists will be of little benefit unless your maintenance personnel are properly trained in their application. Hence, it is vital to implement robust training methods and track advancements meticulously to seamlessly integrate and refine these protocols.
Training Techniques
Implementing preventive maintenance checklists necessitates comprehensive training for maintenance personnel. It is imperative that they:
- Understand the components and use of preventive maintenance checklists
- Strengthen implementation strategies
- Boost effectiveness levels
- Increase safety measures
- Maintain consistency in executing maintenance processes.
Employing a variety of training techniques, such as practical demonstrations, educational workshops, and providing online materials, can ensure staff are well-prepared to apply these critical maintenance checklists effectively.
Monitoring Progress
Continuously assess the efficacy of your preventive maintenance checklists. This is crucial for effectively minimizing downtime and related costs.
Utilizing key performance indicators (KPIs) such as equipment uptime, mean time between failures (MTBF), and mean time to repair (MTTR) can serve as metrics to gauge the success of your preventive maintenance tasks. Commitment to ongoing enhancement is essential in maintaining the robustness of any maintenance program. To pursue continual improvement, consider these actions:
- Routinely analyze machine performance data to pinpoint potential enhancements.
- Keep up-to-date with advancements in technological tools and best practices for maintenance.
- Gather insights from technicians who are engaged in executing preventive maintenance tasks.
- Leverage this input by refining existing checklists and protocols accordingly.
Employing these methods will help ensure that preventative maintenance activities sustain and progressively enhance operational efficiency over time.

Source: WorkTrek
Summary
To sum up, maintenance checklists for preventive measures serve as an important resource for companies, helping them decrease the likelihood of equipment failure, extend asset longevity, reduce periods of inactivity, and promote a secure and productive working environment. Recognizing their significance, designing them with precision, leveraging technological advancements, tailoring these lists to meet particular requirements, and deploying impactful training strategies enable organizations to exploit the advantages of preventive maintenance checklists fully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of preventive maintenance checklists?
Preventive maintenance checklists are crucial in reducing equipment failure, prolonging the service life of machinery, decreasing unexpected downtime, and upholding a secure workplace setting.
How should tasks be prioritized in a preventive maintenance checklist?
Arrange the tasks on a preventive maintenance checklist by highlighting their significance to safety and operational efficiency.
How can technology enhance preventive maintenance?
Integrating technology such as a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) and mobile apps can streamline preventive maintenance schedules, enhancing overall maintenance efficiency.
How should preventive maintenance checklists be customized?
Tailor preventive maintenance checklists to align with sector-specific standards and the unique demands of operations, ensuring continual adherence to regulations and enhanced performance.
How can the effectiveness of preventive maintenance checklists be evaluated?
Regular assessment using Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), including equipment uptime, Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), and Mean Time To Repair (MTTR), can serve to gauge the success of preventive maintenance checklists in enhancing the efficiency of maintenance activities.










